Error p0443 indicates a malfunction of the gasoline evaporative system valve circuit (in English referred to as Evaporative System Purge Control Valve Circuit Malfunction). Most often, error code p0443 occurs on cars with considerable mileage (age), and is caused by clogged pipes or the valve itself (its filter). The error itself is not critical, and if it occurs, the car can be used, but still, at the slightest opportunity, it is better to get rid of it, especially since this is not at all difficult to do. In most cases, you will only need to clean the elements of the gasoline vapor recovery system.
What is EVAP system
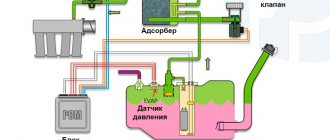
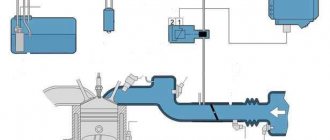
Before moving on to the description of error p0443, it makes sense to briefly describe the operation of the gasoline vapor recovery system (or in English - Evaporative Emission Control, EVAP). Its main task is to prevent the leakage of gasoline vapors into the atmosphere. These same vapors are formed in the fuel tank at high ambient temperatures, or in more rare cases, when atmospheric pressure decreases. In this case, gasoline vapors accumulate in the system, and when the engine starts, they are discharged into the intake manifold and burned in the engine along with the air-fuel mixture. EVAP is used in almost all engines of modern cars.
The gasoline vapor recovery system includes an adsorber (filled with coal granules, and, in fact, designed to accumulate gasoline vapors), an adsorber purge solenoid valve, and connecting tubes. Error code P0443 specifically indicates a malfunction of the mentioned solenoid valve, which is why it is sometimes called a fuel vapor valve error.
In engines with a turbocharger, the system is complemented by a two-way valve, which is designed to direct fuel vapors when purging the adsorber into the intake manifold (if there is no boost pressure) or to the compressor inlet (if there is boost pressure). A two-way valve is needed in the system, since in turbocharged engines a vacuum is not created in the intake manifold.
A special feature of the gasoline vapor recovery system is the fact that it has a built-in self-diagnosis module. This means that when the engine starts, this system is checked automatically for operability, in particular, for tightness and correct operation of its individual elements. This is done in order to minimize the likelihood of gasoline vapors entering the atmosphere, that is, for environmental reasons. In turn, this is dictated by the strict legislation in force in this regard in the countries of the European Union and some others, including the USA.
External symptoms of error P0443
EVAP valve
In most cases, there are no external signs of the P0443 code, with the exception of an activated Check Engine light on the dashboard. In more rare cases, the smell of gasoline may appear in the cabin, caused by the fact that a significant amount of gasoline vapor has escaped from the vehicle's fuel system into the atmosphere or its ventilation system.
Also, occasionally, unstable engine operation at idle, “floating” speed, and even a complete stop of the engine are possible. While driving, a decrease in the dynamic characteristics of the car may be observed; it accelerates poorly and does not “pull”. However, such symptoms can indicate various other malfunctions, so additional diagnostics are necessary to identify the cause.
Occasionally, there are cases when error p0443 occurs when the air conditioner or climate control system is turned on. The fact is that when these systems are activated, the engine begins to consume more fuel, and accordingly, there is more gasoline evaporation in the system. And if their value exceeds the permissible norm, then this leads to conditions for the formation of an error, provided that the system purge solenoid valve is in an emergency condition.
How to check the adsorber
Many car owners may be interested in the question of how to check the adsorber and its purge valve when the diagnostics showed it to be faulty (an absorber error popped up). It is quite possible to make such a diagnosis in a garage, however, for this it will be necessary to dismantle either the entire adsorber or just its valve. And to carry out such a test, you will need metalworking tools, a multifunctional multimeter (to measure the insulation value and the “continuity” of the wires), a pump, and a 12 V power source (or a similar battery).
Formation conditions
Error code P0443 is generated when the ignition key is turned to the ON position, that is, the ignition is on, but the engine is not running, and the ECU diagnoses an open or short circuit in the electrical winding of the evaporative emission control valve. At the same time, the “check” signal light is also activated.
Also, some vehicles have additional requirements for generating the error code p0443. For example, for the popular Chevrolet Captiva, these conditions are the ignition on, as well as the voltage on the battery and in the vehicle’s electrical system in general ranging from 11 to 18 Volts DC. In addition, the ECU diagnoses an error after 6 seconds of meeting the mentioned conditions. Other machines may have different values, but the logic remains the same.
Possible causes of error code p0443
There are a number of typical reasons due to which the so-called absorber error occurs, as error p0443 is sometimes called. Among them:
Valve circuit open
- Complete or partial failure of the electro-pneumatic valve of the gasoline vapor recovery system.
- A break or short circuit (to “+” or “ground”) of the wire connecting the terminals of the electro-pneumatic valve and the electronic engine control unit (ECU).
- A break (or damage to the insulation) of the wire between the control unit and the ground, which is responsible for transmitting the signal to the solenoid valve.
- Broken (or damaged insulation) wire between the main relay and the terminal on the evaporative emission system solenoid valve.
- Mechanical damage to the purge valve. For example, it is stuck in the fully open or fully closed position.
- Damage to the connectors, the so-called “chips”. They will be different for each car model; it is necessary to check those contacts that are responsible for controlling both the gasoline vapor recovery system in general and for controlling its solenoid valve in particular.
- Incorrect operation of the ECU. This is a fairly rare reason, however, there have been cases where, after its flashing or mechanical damage (for example, damage to the electronic track), so-called “glitches” occurred. However, in this case, as a rule, not one, but several errors occur, often unrelated to each other.
However, most often errors associated with incorrect operation of the fuel evaporation recovery system (including 0443) occur due to clogging of the filter and tubes or other elements that make up the specified system. For example, a common reason is that the foam in the adsorber rots and crumbles over time, causing coal to enter the system, clogging it. The valve also becomes clogged, as a result of which it stops working correctly, causing corresponding errors. Rotting occurs for banal reasons - old age, constant wetting from condensation, temperature changes, and so on. Often, if the EVAP system valve is clogged and the front windows are open, you can smell a distinct smell of gasoline in the cabin. This is especially true for the warm season.
There are cases where the reason for the formation of error P0443 is the absence of a fuse in the control circuit of the valve of the fuel vapor recovery system. Another option is to use a fuse with a lower trip current rating than required. For example, on the popular Chevrolet Aveo car, it was observed when installing a corresponding 10 Ampere fuse instead of the required 15 Ampere. Replacing it solved the problem.
Also, the cause of error code P0443 may be depressurization of the fuel tank cap (or hose system). For example, the rubber seal on its lid has worn out over time and does not hold the vacuum. To check this, just listen for a hissing sound when the car owner unscrews the gas tank cap. If there is sound, then most likely the system is sealed. If there is no such sound, there is a risk that it is letting air in, and this may be the direct reason for the formation of error code p0443 in the ECU.
Troubleshooting p0443
Methods for eliminating error p0443 depend on the reasons that caused it. First of all, you need to check whether the formation of error P0443 is not a so-called “glitch”. To do this, it is necessary to programmatically or mechanically delete error information from the ECU memory. There are ways to do this. The first, more “civilized” one, is to delete the mentioned information using a computer and appropriate software. However, to do this you need to have a computer or smartphone and software.
The other method is simpler. To implement it, you just need to disconnect the negative terminal from the battery for 5...10 seconds, and then return it to its place. After this, the electronic control unit will restart and diagnose all vehicle systems again. If there was a false positive, then the error information will not be repeated. If the formation conditions exist, then further diagnostics need to be performed.
To do this, you need to do one or more of the following:
EVAP valve replacement
- Check the condition of the adsorber . To do this, you need to dismantle the EVAP system solenoid valve and see if there is carbon in its body. If this is the case, then the adsorber foam separator needs to be replaced. If its body is very rusty and/or damaged, then you need to consider completely replacing the adsorber.
- Check the operation of the vacuum purge valve from the carbon adsorber. There are two ways to do this. The first is using a special diagnostic device, so it is more suitable for car service workers. To do this, you need to disconnect the vacuum hose of the purge valve from the canister, start the engine (after setting the speed to neutral and applying the parking brake) and connect the electronic diagnostic tool. Next, depending on the software used on it, look at the performance characteristics of the solenoid valve. It is much easier to check it manually. To do this, you just need to put your finger on the disconnected hose and check whether air is sucked into it or not. In working condition, it should be absorbed; if this does not happen, then most likely the solenoid valve has failed and additional diagnostics are required. When the valve is turned off, air is also not sucked in.
- If, as a result of the check, it was determined that the valve itself is in working condition, then it is necessary to inspect its wiring . To do this, you first need to disconnect the valve connector (VSV). Next, you need to use a multifunctional multimeter to measure the voltage supplied to the solenoid valve when the ignition is on. This value should be in the range of 11...14 Volts for standard passenger cars, which are designed for an electrical system voltage of 12 Volts.
- To check the integrity of the wire connecting the computer and the solenoid valve , it is necessary to disconnect them on both sides, that is, disconnect the connectors. Next, using the same multimeter (but switched to the “continuity” mode or to the resistance value measurement mode), check the integrity of the wire. The normal insulation resistance value should be between 1 ohm and 10 kohm. If the measured resistance value is outside these limits, it means there is a wire break or insulation damage. In any case, you need to understand in more detail and visually check the condition of the wire. If this fails, simply replace the wire or the entire harness with a new one.
- Check the condition of the wire between the solenoid valve and the integrated relay or fuse (this step may vary depending on the machine model, since this circuit may be implemented differently). The actions are similar to the previous paragraph. It is necessary to disconnect the wire at both ends and measure its insulation resistance value. The range here will be similar - from 1 Ohm to 10 kOhm. If the value is greater or less, it means the wire is damaged.
Automotive service technicians can check the evaporative emission system purge valve using the mentioned diagnostic tool and software. So, with the ignition on and the engine off, it is necessary to connect the device to the computer and, using software, send commands to the mentioned valve. In this case, clicks characteristic of its operation should be clearly audible. In particular, you need to give a command to open it by 50%. As this value increases, the cyclic speed of the valve should increase, and as the value decreases, it should decrease. When the value reaches 0%, the valve should stop clicking.
If the problem is mechanical damage to the valve, then you can try to “reanimate” it. The standard design of this valve implies the presence of an electromagnetic coil and a needle with a spring, which open/close this valve. Over time, the spring may “age” and not produce the required force. Or there will be an interturn short circuit in the coil. In both cases the valve will not work correctly. You can try replacing the spring and/or cleaning the mechanical valve actuator. However, in most cases, with this violation of operation, the technicians (car owners) simply replace the adsorber valve with a new one.
How to Troubleshoot or Reset Trouble Code P0444
Some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P0444:
- Repair of damaged EVAP lines.
- Repair the open or shorted voltage supply to the purge solenoid.
- Correction of the circuit going to the PCM.
- Replace the purge solenoid valve.
- Correct or repair a restriction in the EVAP line.
- Repair or clean the connector.
- Replace PCM.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Use a scan tool to command the purge valve to activate. Listen for a clicking sound coming from the purge solenoid. It should click once, and on some models it may click again.
If a click does not occur when the scan tool is activated, disconnect the connector and check the solenoid and connector for damage. Then check the battery voltage at the lead wire with the key on.
If voltage is present, manually ground the contact using a jumper and see if the valve clicks. If so, then the solenoid is working correctly, but there is a problem with the control circuit. If it does not click when manually grounded, replace the purge solenoid.
To check for a control circuit problem, reconnect the solenoid and disconnect the ground wire from the connector. With the ground wire disconnected from the controller, turn on the key and manually ground the purge valve control wire.
The solenoid should click, meaning there is no problem with the control wire to the solenoid, and there is a problem with the purge valve actuator circuit from the ECM. If it does not click, there is an open in the wiring between the ECM and the solenoid.
When troubleshooting P0444, you must clearly understand what you are doing. Otherwise, seek help from a specialist.
Additional errors
Often, an adsorber error is accompanied by other, parallel errors, which indicate problems with adjacent elements of the system. So, frequent “companions” of this problem are errors with codes:
P0444 . This error indicates that there is a short to power supply or an open circuit in the control circuit of the canister purge valve. Also, to generate an error with code p0444, the following prerequisites must be met (they may differ for different car models; the popular Hyundai Solaris is taken as an example):
- intact (not broken or damaged) electrical wiring, in particular from the ECU to the EVAP system solenoid valve;
- the value of the constant voltage on the battery and in general in the electrical system of the machine is in the range from 10.7 to 16 Volts;
- long diagnostic time;
- The Check Engine light on the instrument panel is activated after three driving cycles.
In the mentioned Hyundai Solaris car, the resistance value of the EVAP system valve winding is exactly 16 Ohms at a temperature of +20°C.
P0447 . The error code indicates that the evaporative control valve control circuit is open (broken). As a rule, the reason for the formation of this error is the “rotting” of the control wiring going to the solenoid valve. This problem often occurs on cars in which the valve is located in the rear of the body, for example, near one of the rear wheels. In this case, the wiring is affected by moisture, dirt, and reagents from the road surface. All this over time can damage the protective insulation of the wiring and, as a result, cause an error with the mentioned code. As a repair, we can only recommend replacing the wiring, and maybe the entire valve.
Conclusion
Error code p0443 is not critical, and when it occurs, you can use the car without worrying too much about its technical condition. However, the malfunctions that caused it still have a negative impact on the environment, and in critical cases can lead to poisoning of the driver or passengers with gasoline fumes. Also, in an enclosed area, large amounts of evaporated gasoline can lead to an increased risk of explosion and/or fire. Therefore, at the slightest opportunity, it is still better to get rid of error p0443 by correcting the faults that caused the conditions for its formation.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0444 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi
- BMW (BMW X5, E39, E46, E53, E60, 330i, 530i)
- Chery (Chery Amulet, Handicap)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Lacetti)
- Chrysler
- Citroen (Citroen C4)
- Daewoo (Daewoo Matiz, Nexia)
- Ford (Ford Focus)
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Genesis, Creta, Santa Fe, Solaris, Elantra)
- Infiniti
- Kia (Kia Optima, Rio, Sorento)
- Mercedes
- Nissan (Nissan Altima, Qashqai, Tiida, X-Trail, 350Z)
- Opel (Opel Corsa)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 207, 307, 308, Partner)
- Skoda (Skoda Octavia, Rapid, Fabia)
- Subaru
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Passat, Polo Sedan, Tiguan)
- VAZ 2107, 2114, 2115
- Gazelle
- Lada Vesta, Granta, Kalina, Largus, Niva, Priora
- TagAZ Accent
With fault code P0444, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common ones are: P0010, P0031, P0033, P0036, P0037, P0056, P0102, P0243, P0245, P0300, P0440, P0441, P0442, P0443, P0445, P0446, P0447, P0448, P0449, P045 2, P0453, P0455, P0456 , P0500, P0505, P0700, P0722, P1403, P2008.