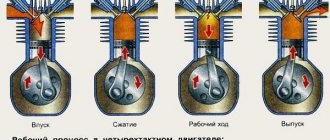
What determines the numbering of engine cylinders?
However, it is important to know that whatever the engine layout and cylinder arrangement, cylinder No. 1 - the main cylinder, always contains spark plug No. 1.
Naturally, this is the order in which the cylinders of any engine are numbered. What determines the location and numbering of engine cylinders:
- drive type: front or rear;
- engine type: in-line or V-shaped;
- engine installation method: transverse or longitudinal;
- direction of motor rotation: clockwise or counterclockwise.
The arrangement of cylinders in multi-cylinder engines is as follows:
- vertically - that is, in one row, without angular deviations;
- obliquely – at an angle of 20°;
- V-shaped - in two rows. The angles between rows can be 90 or 75 degrees;
- opposite (horizontal) – the angle between the cylinders is 180°. This arrangement of cylinders is used in bus engines, which allows the engine to be placed under the floor of the passenger compartment, freeing up usable space.
How are the cylinders located in engines?
There are different engine models - these include vintage one- and two-cylinder internal combustion engines, traditional in-line four- and six-cylinder models.
The straight-six, which was very popular in Europe in the 80s and 90s, has now become an endangered species.
It’s not worth talking about eight-cylinder models - they said goodbye to this arrangement long ago back in the 30s.
Why? As the volumes increased, the blocks also grew larger. This created a lot of problems for designers and engineers during layout.
For example, it was possible to squeeze an inline eight into a front-wheel drive car in only two cases - the Austin Maxi 2200, which was produced in the 60s, and the Volvo S80.
In two rows
How to make a large inline internal combustion engine shorter and more compact?
Article on the topic: How to calculate the heat balance of an internal combustion engine
The engine can be “cut” in half, set the two parts side by side and have the pistons rotate one crankshaft. These motors are shaped like the letter “V”.
Here the combustion chambers are arranged in two rows at an angle to each other. This configuration is very popular among manufacturers and is second only to the in-line “four”.
And the one who developed and launched the traditional boxer engine familiar to everyone is Ferdinand Porsche. The first batch of Zhuk cars was equipped with these internal combustion engines in 1937.
A similar design was used on Ford A, C, F. In 1920, the Bavarian automobile concert proposed its own design of a boxer engine.
Motors W
In these power units, a number of combustion chambers are connected to a VR arrangement. In each row, the cylinders are placed at an angle of 15 degrees.
Both rows are at an angle of 72 degrees. In the case of an eight-cylinder engine, the block consists of two V-shaped blocks that are at an angle of 72 degrees.
Numbering of cylinders on different types of engines
As such, there is no strict international system for the location and numbering of engine cylinders. And that's bad. Therefore, before you begin any type of repair of the engine or ignition system, immerse yourself in the Operating and Repair Instructions for your particular car.
Rear-wheel drive 4- and 6-row engines in the USA have a master cylinder number 1 from the radiator, the remaining cylinders are numbered towards the passenger compartment. But there is also reverse numbering, when the master cylinder is considered to be the one closest to the passenger compartment.
For French engines, cylinder numbering occurs on the gearbox side. And the numbering of the cylinders of V-shaped engines comes from the right side, i.e. on the torque side.
Front-wheel drive cars typically have a transversely mounted engine. Here the cylinders are numbered on one side, and cylinder No. 1 is located on the passenger side.
V-twin multi-cylinder engines have the driver's side master cylinder in the bank closest to the passenger compartment. Then there are the odd-numbered engine cylinders, and on the opposite side (closer to the radiator) there are the even-numbered ones.
Therefore, in order to ensure that you are not completely confused due to the lack of a unified international standard for the location and numbering of engine cylinders, use the manufacturer’s Operating Manual.
Good luck learning the numbering and arrangement of engine cylinders.
VAZ 2107 was produced from 1982 until 2012. During this time, he managed to become a truly people's car. And no wonder. Cheapness, good reliability of components and assemblies, as well as the ability to repair a car almost “on the knee”. As you know, the “heart” of a car is the engine. And in this article the VAZ 2107 engine will be discussed in detail.
Memo to the driver of VAZ 2107
This is a reminder for drivers of the VAZ 2107 (also relevant for other classics), I decided to create it because minor technical questions often arise, and it takes a lot of time to find the answer. And here everything is in one place. Save this reminder in your bookmarks or on your page on a social network, and use the social network buttons under the article for your health.
So, VAZ 2107 technical characteristics, dimensions, parameters.
VAZ 2107 was produced from March 1982 to April 2012. It has been produced in Egypt since 2006 to this day.
It has a 5-seater sedan-type body, in-line 4-cylinder gasoline engines, paired with a 4 or 5-speed manual transmission. It is included in the class of subcompact cars, according to the European classification - class “B”. And not C, as they say on the forums. C class is Ford Focus, KIA Ceed, etc. Wheel formula 4x2, rear wheel drive. The ancestor is the Italian Fiat 124.
Numbering of cylinders in different types of internal combustion engines
As for the standards for numbering combustion chambers, there are none. The way they are numbered in the internal combustion engine is influenced by the following factors:
- Type of drive;
- ICE type, block layout;
- Transverse or longitudinal arrangement of the unit under the hood;
- Side of rotation.
On standard front-wheel drive cars with a transversely mounted engine, the numbering begins on the timing side. So, near the timing belt there is the first cylinder and then all the others. The latter is located near the checkpoint.
Article on the topic: How to check a car for arrest, bail
Examples
In multi-cylinder V-twin engines, the first cylinder is located in the bank on the driver's side.
Suspension and wheels of VAZ 2107
Front suspension: independent, double wishbone, with anti-roll bar and hydraulic shock absorbers. Rear suspension: dependent, with a rigid rear axle beam and 5 reaction rods, on hydraulic shock absorbers.
Standard VAZ 2107 wheels: 5Jxl3H2 with an offset of 29 mm, mounted on 4 bolts with a hole diameter of 98 mm, hole diameter for the hub - 58.5 mm) Tires: tubed or tubeless 175/70R13 or 165/70R13
Recommended tire pressure: - front wheels - 1.7 kg/cm2 - rear wheels - 2.0 kg/cm2
For a softer and more comfortable ride, you can reduce it by 0.1 kg/cm2
What engine can be installed on this car?
Initially, 2 types of engines were installed on the VAZ 2107 model, these are:
There were also 1.3 L and 1.2 L engines, but they are very few in number and practically never found.
It is also possible to install an engine from a VAZ with front-wheel drive, but it is too labor-intensive and unjustified.
This is interesting! Sometimes the English letter “i” is added before the name of the car. This means that the VAZ 2107 engine is an injector.
Injector – fuel sprayer. Nozzle. The principle of operation of injection gasoline engines is very similar to diesel engines.
Specifications
Before we begin to describe the malfunctions, it is worth considering the engine options that were installed on the VAZ 2107 carburetor. The characteristics and design of the engine are quite simple. The engine has an in-line longitudinal arrangement of cylinders.
So, for the VAZ 2107 with carburetor versions of power units, engines marked 2103 and 2106 were installed.
VAZ 2103
VAZ 2106
The engines were equipped with gearboxes manufactured by VAZ - 4-speed manual transmission and 5-speed manual transmission. Unlike new models, all power units have a timing chain instead of a belt. Unlike the “fives”, the seventh model of the Zhiguli has higher engine power and displacement.
Maintenance of the VAZ 2107 engine is quite simple. So, the engine requires scheduled maintenance every 10,000 km. Many motorists are wondering what kind of oil to pour into the engine? Considering the design of the engine, the most suitable option is “semi-synthetic”.
Many car enthusiasts claim that it is better to pour mineral water or even synthetic water. Of course, an engine with high-quality oil will run longer, but in the case of the “seven” even the manufacturer recommends using “semi-synthetic”. But for power units equipped with an injector rather than a carburetor, it is already recommended to use a higher criterion motor oil - “synthetic”.
Where is the engine number of the VAZ 2107
The VAZ 2107 car is equipped with a number of engines. Initially, a 1.3-liter carburetor engine from a VAZ-2103 was installed on the car. Later, they began to install carburetor power units of 1.3 liters from the VAZ-2105 (VAZ-21072), 1.6 liters from the VAZ-2106 (VAZ-21074). 1.7-liter engines with injection (VAZ-21073) were exported. Regardless of the power plant, the placement of the engine marker for the VAZ-2107 is the same.
Scheme for locating the motor marker:
The motor identifier is printed using the impact method and is geographically located on the platform of the engine frame. The process is automatic, the platform is located above the oil filter element. The marking is applied by a German device “Otto Borries”, the font is provided by the same company.
Location of identification information:
As for the VAZ 2107 identifier, it is applied using the impact method; you can look at it by looking into the engine compartment, on the lower shelf of the air supply box.
VAZ 2107 body
All-metal, load-bearing, with 4 doors. Body rigidity - 7200 Nm/deg.
The width of the VAZ 2107 interior , and all classics in general (from the rear door trims at the seat level) is 1250 mm. Between the central pillars of the cabin, at a level of 80 cm from the floor - 1234 mm.
The length of the front door opening of the VAZ 2107 (and all classics) is 889 mm, the rear door is 819 mm.
Dimensions of the trunk of the VAZ 2107:
Engine VAZ 2103
Specifications
The main characteristics of the engine are presented in the table below:
| OPTIONS | MEANING |
| Year of production of engines of this type | 1972 – our time |
| Supply system | Injector/carburetor |
| engine's type | Row |
| Number of pistons | 4 |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Cylinder head material | aluminum |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 |
| Piston stroke | 80 mm |
| Cylinder diameter | 76 mm |
| Engine capacity | 1452 cm 3 |
| Power | 71 l. With. at 5600 rpm. |
| Maximum torque | 104 Nm at 3600 rpm. |
| Compression ratio | 8.5 units |
| Oil volume in crankcase | 3.74 l |
This engine uses AI-93 fuel. In practice, motorists can fill in completely different fuels. The most common deviations from the norm are the flooding of AI-92 and AI-95. You can read more about this below.
- According to available data, fuel consumption in urban conditions is 9.4 liters per 100 km.
- On a flat road at cruising speed it will already be 6.9 liters per 100 km.
- In mixed mode, consumption will be from 8 to 9 liters per 100 km. Such figures do not allow us to call this engine economical, but in this case a lot depends on the driver himself.
- Another parameter that depends on the driver is oil consumption per 100 km. For the average driver of a car with this engine, it is 700 g per 100 km. This, of course, is not small, but with careful driving you can reduce this consumption down to 450-500 g/100 km.
- The weight of the 2103 engine when fully assembled is 121 kg.
General parameters of the VAZ 2107
Length - 4145 mm Width - 1620 mm Height - 1446 mm Base - 2424 mm Front wheel track - 1365 mm Rear wheel track - 1321 mm Ground clearance - to the front suspension cross member - 159 mm, to the rear axle beam - 154, up to muffler housing - 120 mm. Not bad, for example in the Opel Zafira, only 150 mm to the highest point. Load capacity - 400 kg Trunk volume - 385 liters Curb weight - 1060 kg Gross weight - 1460 kg Towed trailer weight, without brakes - 300 kg, with brakes - 600 kg.
Cylinder numbering in the most common types of vehicles
Unfortunately, there are no generally accepted rules for numbering cylinders in automobile engines - each automaker uses its own system, which often differs even for different engines of the same automaker. Therefore, the most authoritative source for you in this matter should be the repair and operation manual for your specific car, or, in the absence of one, the knowledge of car repair professionals.
In inline 4 and 6 cylinder American engines, which are installed in rear-wheel drive vehicles and are located longitudinally, the first cylinder is usually located at the radiator, and the rest are numbered in order from the radiator to the vehicle interior. However, there are exceptions to this rule.
In transversely mounted V-twin engines in American cars, the main (first) cylinder is usually located in the bank closest to the passenger compartment, on the end closest to the driver. Behind it, in the row closest to the passenger compartment, there are odd-numbered cylinders, and in the row closest to the radiator, there are even cylinders. That is, in the row closest to the passenger compartment, counting from the driver, there are cylinders 1-3-5-7, and in the row closest to the radiator, counting from the driver, there are cylinders 2-4-6-8. This type of cylinder numbering can be found, for example, on the Jeep Cherokee.
On transversely mounted in-line 4-cylinder engines of French front-wheel drive cars, the cylinders are usually numbered from the flywheel, i.e. from the driver's side. In the case of V-shaped 6-cylinder engines (for example, on the Peugeot 607), the cylinders are numbered as follows - in the row closest to the radiator, from the driver to the passenger - 1-2-3, in the row closest to the passenger compartment, from the driver to the passenger - 4-5-6.
You don’t know anything about adjusting the ignition!
Welcome VAZ car enthusiasts to my blog RtiIvaz.ru.
You don’t know anything about ignition adjustment, which is why you need to read the auto article further. Stable engine operation, its efficiency, throttle response, and power depend on the correct installation of the ignition. The ignition adjustment itself is necessary in order to ignite the fuel-air mixture in a strictly defined sequence, depending on the order of operation of the cylinders.
For self-service, owners of these models need to remember that on VAZ 2105, 2106-07 cars the cylinder operating order is 1-3-4-2.
The operation of adjusting the ignition on VAZ 2105 and VAZ 2106-07 cars may be required in several cases. This must be done after a medium or major overhaul of the engine, replacing the block gasket, valve burnout, replacing the timing chain or belt, replacing the camshaft and other similar cases associated with partial disassembly of the engine.
To set the top dead center and adjust the ignition, there are special marks on the engine in its upper and lower front parts that must be aligned. Location of marks on VAZ 2106 and VAZ 2105 engines for adjusting the ignition system.
Features of operation and maintenance
It was said earlier that many drivers cannot decide on the type of fuel used for their engine on the VAZ 2107. And if with AI-92 everything is simple, since its composition is very similar to AI-93, then with AI-95 everything is not so smooth.
Increasing the octane number leads to an increased risk of valve burnout, but gives a small increase in power. The engine begins to run smoother and more stable.
But the designers still took into account the possibility of using AI-95 gasoline. You just need to correctly set the ignition timing on your car (if you have a conventional carburetor engine) or reflash the engine control unit (if your VAZ 2107 engine is fuel-injected). But usually even this is not required. Engines of this brand are very durable and not picky about the type of fuel (within reasonable measures).
Changing the oil on any engine must be approached with the utmost seriousness. Poor quality oil can lead to not very pleasant consequences, such as accelerated wear of main components and assemblies.
The ability to select oil is a real skill. Taking well-known brands is not always safe, since you are very likely to come across a counterfeit from dishonest companies. At best, you will not receive the positive qualities that this company has. At worst, you will have to carry out major repairs.
You shouldn't buy unknown brands either. In this case, you are buying a pig in a poke. You can buy oil that is of a quality that is not inferior to expensive analogues, or you can end up with expensive repairs. It is best to buy oil in specialized stores, where you can get at least some explanation and compensation.
Another important parameter is the oil class according to the international nomenclature. True, everything is simpler here. You just need to take the oil that the manufacturer himself recommends.
The manufacturer (AvtoVAZ) for VAZ 2107 engines and other models with this type of engine recommends:
You need to take about 4 liters of oil. When changing 3.5 liters of oil is usually enough. It’s better to carry the rest with you in the trunk, since oil consumption in this engine leaves much to be desired.
- Changing the oil in the VAZ 2107 engine
The procedure itself is quite simple and should not raise any questions. It is better to change the oil on a VAZ 2107 in the warm season.
- First you need to start the car and warm it up to operating temperature. Then turn it off and let the oil fall back into the crankcase. This will take about half an hour. During this time, we prepare a receiving container with a volume of 4-5 liters, as well as new oil, a watering can and a hose.
- Use a special wrench to unscrew the plug on the crankcase and wait for the old oil to drain out.
- If you change the type of oil or brand, you must also take flushing oil, which will clean the engine of the remnants of the old one. We pour it in the same way.
- Then we tighten the crankcase cover and fill in new oil through the neck on the cylinder head. We measure the level with a dipstick. It should be somewhere between the MIN and MAX marks. Please note that oil is not water and it cannot quickly sink into the crankcase, and therefore after a short stop the oil level in the crankcase will rise a little more.
Usually, along with changing the oil, the oil filter is also changed. It's even simpler here:
- We unscrew the old one using a special tool (you can also use an ordinary rope), lubricate the o-ring of the new filter with oil and screw it in place of the old one.
- Adjustment of valves
Adjusting valves is a rather complicated process and requires certain skills and tools. Actually, it is advisable to entrust the valve adjustment itself to competent specialists, but if you want to do everything yourself, then this video is for you:
Major repairs and maintenance
If valve adjustment can be done at home, then major engine repairs should only be entrusted to specialists.
During a major overhaul, all components and assemblies of the VAZ 2107 engine are checked for serviceability. They will check for you:
- Valve condition, adjustment;
- Chain, chain tension;
- Condition of oil seals, valve stem seals;
- Geometry of the cylinder block;
- Condition of the pistons, crankshaft, pins, connecting rods;
- Wear of compression rings;
- Condition of the oil pump and coolant pump.
If damaged, the part will be replaced. The cylinder block will be bored out, which will increase the combustion chamber and working volume. After this procedure, the car will be run-in for several thousand kilometers.
Typically, running-in lasts 5-10 thousand km. At this time, it is not advisable to give the engine heavy loads. After completing this procedure, your engine will make you happy.
VAZ 2106 – timing chain
Upper marks: one mark in the form of a hole is applied to the camshaft sprocket from the inside, the second mark is a boss in the form of a protrusion at the end of the camshaft bed. To perform this operation, the valve cover must be removed.
Bottom marks: three marks are cast on the front engine cover - one long and two short, and on the crankshaft pulley there is a molded boss on the inside (you can easily feel it with your hand) and a mark on the end of the pulley. The long mark corresponds to the top dead center, and the two short marks are the ignition timing marks.
The first short mark (the middle of the three) corresponds to an ignition advance of 7.5 degrees, this is actually the factory tolerance for installing the ignition when using AI 92-95 gasoline. The second short mark corresponds to an ignition advance of 10 degrees.
When assembling the engine during a major overhaul, the crankshaft is oriented along the internal marks. This is a mark on the sprocket (risk) of the crankshaft and a boss on the cylinder block, which are combined.
Then the timing chain is installed and the marks on the camshaft sprocket and its bed are aligned. The crankshaft is turned two turns and the alignment of the marks is checked again. If all marks match, then install the front engine cover, crankshaft pulley and valve cover.
When installing the distributor (ignition distributor), the above-mentioned valve timing marks are set, and the distributor slider, after installing it, should point with the spacer plate at the 4 cylinder wire socket in the distributor cover.
VAZ 2105 – timing belt
Upper marks: one mark “E” is located on the cover of the first journal of the camshaft, and the second “F” is applied to the camshaft pulley. In order to “get” to the marks, you need to remove the timing belt protective cover. The lower marks are similar to the VAZ 2106-07 (the designation of the marks “C” on the pulley and “D” on the cover, while three long and two short marks are marked on the protective cover of the timing belt).
Video of adjusting the ignition of VAZs for any purpose
After assembling the engine and installing the distributor, you need to set the ignition. This operation can be performed using a strobe light following the attached instructions. Also, setting the ignition timing (for a contact ignition system) can be done with an ohmmeter (present in a multimeter) or using a test lamp (you can use a car carrier).
To check and adjust the ignition using an ohmmeter, do the following:
- Remove the negative terminal from the battery
- Set neutral gear
- Remove the distributor cover
- Turn the crankshaft clockwise until the distributor slider reaches about 30 degrees to the contact in the cover numbered “1”
- Next, one ohmmeter probe is connected to the distributor bolt (where the wire from the ignition coil is connected), and the second ohmmeter lead is connected to ground. In this case, the resistance on the ohmmeter scale should be zero.
- Then the crankshaft is slowly turned until the lower marks align. If, when the marks coincide, the resistance shows infinity, then the ignition is set correctly. If the resistance begins to increase until the marks coincide, or remains at zero, then you need to adjust the ignition timing by loosening the distributor and turning it in one direction or another
- The crankshaft is turned using an X38 mm wrench. As a last resort, in its absence, you can turn on speed 3 or 4 and slowly (with an assistant) move the car, which is really not very convenient when adjusting
A similar ignition adjustment can be performed using a control lamp, but care must be taken since this operation is performed with the ignition on. One wire from the lamp is connected to ground, and the second wire is connected to the distributor bolt, as is the case with an ohmmeter.
Engine VAZ 2106
The design of the VAZ 2106 engine is almost completely identical to the VAZ 2103 engine, with the exception of some nuances, such as engine displacement.
| Year of production of engines of this type | 1976 – our time |
| Supply system | Injector/carburetor |
| engine's type | Row |
| Number of pistons | 4 |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Cylinder head material | aluminum |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 |
| Piston stroke | 80 mm |
| Cylinder diameter | 79 mm |
| Engine capacity | 1569 cm 3 |
| Power | 75 l. With. at 5400 rpm. |
| Maximum torque | 116 Nm at 3000 rpm. |
| Fuel consumption (100 km): | 10.3 l |
| city | 7.4 l |
| track | 10 l |
| mixed |
Dimensions and Weight are identical (see paragraph Characteristics of the VAZ 2103 engine).
Features of operation
Completely identical to the VAZ 2103 engine (see similar VAZ 2103 engine design). The oil volume in the crankcase is also the same and is 3.75 liters.
Engine tuning
Also identical to the VAZ 2103 engine. See the section Engine tuning (VAZ 2103). The features of boring will be described below.
- Increase in working volume
Electrical equipment VAZ 2107
Wiring type: single-wire, negative on the car body (ground).
Battery: 6ST-55, capacity 55 Ah. Batteries with a capacity of 60 and 65 Amperes are also suitable, but you need to check the dimensions. Typically it is 242mm x 175mm x 192mm.
Operating voltage in the network: 13.6 -14.6 volts. The generator (G221) must deliver a current of no more than 1/10 of the battery capacity, i.e. approximately 2 to 5.5 Amps.
Ignition coil - B117 or B117-A (for carburetor engines) Starter - ST221
Lamp type:
— low and high beam lamp: H4 or AKP2-60+55 (in Russian) — side marker lamp and side turn signals: T4W or A12-4-1 — turn signal lamp in the headlight, fog lights, reverse and brake lights: P21W or A12-21-3 - license plate and interior lighting lamp: C5W or AC12-5-1