Clutch is a mechanism for transmitting torque from the engine to the gearbox. The clutch also allows for a break in the power flow to change gears.
In general, the clutch mechanism is quite reliable; its service life during active use is about 80-120 thousand km. At the same time, high loads, as well as natural wear of the clutch, lead to problems associated with the clutch and clutch drive.
The list of main problems includes the following clutch malfunctions:
- the driven disc linings are worn or damaged;
- the driven disk is deformed;
- The driven disc linings become oily;
- Driven disc splines are worn
- Damper springs are broken or worn;
- the diaphragm spring is broken or weakened;
- the clutch release bearing is worn out or destroyed;
- the flywheel surface is damaged or worn;
- the surface of the pressure plate has defects;
- the clutch release fork gets stuck, etc.
At the same time, it is important to pay attention to signs of problems with the clutch, which allows you to replace only individual elements, and not the entire expensive mechanism assembly. Read more in our article.
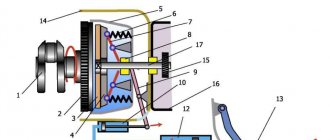
ABOUT THE CLUTCH DEVICE
Its design on this car is similar to mechanisms 2113 and 2115. It is made of a dry, single-disc mechanism. It is produced with a device that dampens torsional vibrations, and also has a pressure spring. The VAZ 2114 clutch device is shown in the figure.
Clutch components
The VAZ 2114 clutch consists of (see picture):
- Cable with a casing;
- Cable tip (lower);
- Adjusting nut;
- Housing for attaching the shell to the gearbox;
- Separating washers;
- Nut for adjustments;
- Rubber protective shell;
- Cable lead;
- Shutdown plug;
- Basket;
- Bolts securing the basket to the flywheel;
- Pressure disk;
- Flywheel;
- Driven disk;
- Gearbox input shaft;
- Shield;
- casing;
- Spring (pressure);
- "Squeeze";
- Pad;
- Release housing;
- Cable end;
- Cable thrust washer;
- Cable fastening unit;
- Pedal axle;
- Release spring;
- Off pedal.
As can be seen from the mechanism diagram, there are two working units, one of them will be the master, and the second will be the slave. The second includes a disk with linings riveted on both sides and damper springs installed. It is installed and moves along the splines that are present on all gearbox input shafts. When the pedal is pressed, the driven disk is pressed against the flywheel by the pressure disk.
The drive unit includes a pressure disc with a clutch housing, which is attached to the flywheel with six bolts. To center it, there are pins on the flywheel and guide holes in the housing. The clutch has a backlash-free design and is operated by a cable.
To turn it off, a clutch drive is installed, which operates by pressing the pedal. The cable is hingedly attached to it with its upper tip. The lower end of the cable also has a hinged connection with the shutdown fork. With its movement, the “cable” turns it, and it moves the “releaser”.
How does a clutch release bearing work?
The bearings that we will discuss further are of two types: hydraulic (the force is created by a hydraulic system) and roller (working using rigid connections between rods). Despite the fact that they have different principles of operation, they perform the same functions - turning the clutch on and off, and also helps disengage the disc from engagement with the basket.
Passenger car clutch
Tips: Wheel alignment, what is it?
Thanks to the clutch, the engine is smoothly disconnected from the transmission when gears are changed. This clutch operation has a beneficial effect on the mechanisms and elements of the transmission - it protects them from overload and dampens vibrations. This mechanism works according to the following scheme. By means of a pressure plate attached to the housing, the driven disk is pressed against the flywheel, and its hub can move along the input shaft to which it is connected. Smooth gear shifting and damping of vibrations occurs thanks to damper springs located in the hub.
The interaction of the diaphragm spring, which is made in the form of petals, with the pressure disk is aimed at providing the necessary force. It is these petals that fall under the influence of the release bearing, which is functionally designed to ensure interaction of the clutch with the drive. The clutch fork, in turn, ensures the movement of the bearing with the release clutch.
Possible causes and symptoms of bearing wear?
When the clutch is depressed, the bearing moves backward and pulls the driven disk behind it. Due to the impact of torque, it is not recommended to hold the clutch with the gear engaged at the same time, since the part is subjected to uneven loads and, accordingly, wears out faster. Of course, if you use the clutch correctly, you will not have problems with the operation of the mechanism for a long time.
The role of the clutch release bearing in the processes described above is quite large. One of the main signs that you may need to replace the release bearing in the near future is the characteristic sound that appears when you depress the clutch. If you suspect that something is not working correctly, try to determine whether the bearing is the cause of the possible problem. You can do this in the following way:
- When you start the car engine, you should listen carefully to the noise;
- Next, you need to squeeze the clutch all the way;
- If the noise does not disappear or, on the contrary, intensifies, we can safely talk about the bearing as the cause of the problem.
Old and new release bearing
Tips: The handbrake is frozen - what to do?
If the noise disappears when you press the clutch, then the cause of such noise is problems in the operation of the gearbox. If extraneous sounds (knocking) appear in the winter season, with a high degree of probability, your worries will be in vain. The fact is that in the manufacture of the clutch release bearing, high-strength steel was used, with a rather small coefficient of linear expansion, which cannot be said with just a glass that serves as a “container” for bearing parts.
Signs of a bad clutch
As you know, the clutch serves to transmit torque from the power unit of the car to its transmission. This unit, due to its load and constant use when driving, can fail quite often. Although during normal operation its resource is significant.
Clutch failure can lead to serious consequences. It's unsafe to say the least
Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the signals that the clutch usually “sends” to the driver before complete failure. What are the signs of a clutch failure?
Signs of a bad clutch
So, when the engine is not running, the clutch pedal should be pressed smoothly without any resistance. There should be no grinding or other extraneous noise. The pedal stroke should be moderate. If one of the above symptoms occurs, then most likely the clutch is experiencing problems.
After starting the engine, you must release the clutch pedal. If in this case extraneous sounds appear (noise, cutting, etc.) that disappear when you press the pedal, then this also indicates a breakdown of this unit.
One of the signs of a clutch malfunction is a characteristic crunching noise when engaging reverse gear. After starting the engine, try engaging reverse gear. The presence of a crunching or other sharp sound indicates that the pressure or driven disk has failed. Naturally, the inability to engage reverse gear indicates a breakdown that needs to be repaired urgently.
For what reasons does the clutch fail prematurely?
The operating life of this unit is approximately 150-300 thousand km, which is quite a lot. Also, life activity depends on the car itself and its operation. What factors lead to its reduction? So:
- Dangerous driving style: the driver throws the pedal, presses it sharply, which leads to faster wear of the lining.
- The vehicle moves constantly under load. This often applies to commercial vehicles
- If you are towing another vehicle that weighs much more than your vehicle, the clutch may burn out. If you feel burning, you should stop moving immediately.
- Do not hold the pedal halfway down. Only if necessary.
Replacement
The procedure is not so simple, therefore, if you lack experience, it is not recommended to do it yourself. If you have enough skills and abilities, get to work.
- Disconnect the clamps and remove the release bearing along with the clutch.
- Remove the input shaft from the bearing.
- After fully releasing the clamps, remove the damaged bearing from the coupling.
- Install a new part, but first make sure of its quality. If the bearing moves freely, there is no need to worry, it works well.
- Lubricate the clutch and the release tool itself. This device loves high-quality lubrication. Then install it on a release sleeve that has been pre-treated with machine oil.
- Using special clamps, place the new element in its rightful place.
- The final stage will be reassembling and installing the gearbox in its original position.
The work can be considered completed. It is quite possible to do it yourself, but just do not forget about the accuracy and consistency of your actions.
A high-quality squeezer lasts a long time, so you won’t have to perform such operations regularly. Of course, provided that you have correctly replaced the old bearing and your clutch is functioning efficiently.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=d1bb0mbPPsA
Purpose, design and typical malfunctions of the clutch bearing
It cannot be said that this is a “weak link” in the clutch of the VAZ 2110, however, this nuisance can and does remind you of itself with enviable consistency. Well, it “whistles”, even if it continues to “whistle”, it doesn’t affect the speed. Sometimes car owners think this way. For the time being.
The release bearing, or rather its clutch, is intended to directly act on the diaphragm (leaf) spring of the clutch basket, as a result of which the driven disk is disconnected from the flywheel and the pressure plate of the basket. We can say that this is the last link that disengages the clutch.
A malfunction of the release bearing is fraught with more serious and unjustifiable repairs, in which replacement of one bearing is no longer sufficient. This may be damage to the clutch fork, guide bushing, or breakage (bending, fracture) of the clutch basket diaphragm spring petals. The stingy one pays twice, and the lazy one in this case probably pays three times.
Of course, the noise or rustling of the release lever is not a direct command to replace it with the inability to continue driving the car, but you should not delay the repair. The need to replace the bearing manifests itself in the form of a characteristic sound (whistle, squeak, squeal - whatever you like). Sometimes it can occur after starting the engine, while all the components and assemblies of the car are still “cold”, and disappear when they warm up, or constantly remind themselves during operation of the power unit when the car’s clutch is disengaged.
In another, more serious case, when the release bearing fails, it can “grind” against the diaphragm spring, which can cause rapid wear on the clutch basket petals. In this case, the count will go on in kilometers and the sooner the bearing is replaced, the better and safer. It cannot be repaired, only replaced with a new one. Fortunately, the price of the bearing is low.
Retaining ring and diaphragm spring
Signs
We started the engine, the transmission is in neutral, but a squeak or metallic sound is heard from the gearbox. These symptoms are similar to a malfunction of the release bearing, but the clutch pedal is not pressed, which means this is not the case.
The diaphragm spring's attachment to the retaining ring may have become loose. In this case, it is not rigidly fixed and can rotate at an arbitrary speed different from the speed of the basket. As a result of this, it rubs against the hooks of the spring and makes such a sound.
How to avoid
No way. This manifests itself as the basket elements wear out over high mileage or the quality of spare parts is poor. The solution is to replace the mechanism. The video below demonstrates a similar defect in the clutch basket, the symptoms of which were initially perceived as bearing failure.
Source
Main clutch malfunctions
Clutch malfunctions should be divided into two categories - malfunctions of the clutch itself and malfunctions of the clutch drive. So, the problems of the clutch itself include:
- wear and damage to the driven disk linings;
- deformation of the driven disk;
- oiling of the driven disk linings;
- wear of the splines of the driven disk;
- wear or breakage of damper springs;
- broken or weakened diaphragm spring;
- wear or breakage of the clutch release bearing;
- flywheel surface wear;
- wear of the pressure plate surface;
- jamming of the clutch release fork.
Diagnosis of problems
The clutch does not disengage (“drive”)
When the discs do not move completely apart when you press the pedal, they say the clutch is “driving.” That is, the disks remain in some contact, and it does not turn off completely. Experienced drivers know how to check the clutch for incomplete disengagement. Diagnosis is simple. If at low speeds with the pedal pressed all the way, first gear is engaged easily and without extraneous noise, the shutdown occurs completely. If switching occurs with difficulty and is accompanied by gear noise, it “drives.”
The reasons for this may be:
- the driven disk linings are broken or the rivets on them are loose;
- decrease in full pedal travel (tight clutch);
- the driven disk is warped and its end runout exceeds 0.5 mm;
- the pressure plate is warped or warped;
- the hub of the driven disk jams on the splines of the input shaft in the gearbox;
- the rivets securing the pressure spring are loose;
- irregularities have formed on the surface of the friction linings of the driven disk.
b) associated with hydraulic drive
- fluid leakage from the hydraulic system;
- air has entered the system.
Elimination of mechanical causes involves adjusting the drive, cleaning and lubricating the splines, straightening or replacing the driven disk and, most often, replacing the friction linings. Every clutch has to be replaced at some point. Problems in the hydraulic system require bleeding to remove trapped air, checking the tightness of connections and the integrity of the pipeline. If necessary, you will have to replace failed parts, such as the main and working cylinders if fluid leaks from them.
Does not turn on (“slips”)
When, while driving, you begin to smell a burning smell, and on a climb your car noticeably slows down and generally begins to accelerate worse, you don’t even need diagnostics: the clutch is slipping. This means that the driven and driven discs do not close tightly enough when the clutch is engaged. There is an easy way to check the clutch. To do this, put the car on the parking brake and start the engine. Squeeze the clutch and engage the gear. Smoothly press the gas pedal and just as smoothly release the clutch. The engine should stall. If it continues to work, it means the clutch is slipping.
Reasons for incomplete inclusion:
- there is no free play of the pedal;
- the friction linings of the driven disk are burnt or worn out;
- oil has got or continues to get on the friction linings, on the surface of the pressure plate and flywheel.
These reasons can also be eliminated by adjusting the drive and replacing the linings. Oil that gets on the rubbing surfaces, which results in a slipping clutch, must be removed by thoroughly washing the contaminated areas with white alcohol. Of course, it is necessary to find out and eliminate the reason for its appearance.
Checking clutch wear
It’s quite easy to check the degree of wear of the driven disc and understand that the clutch needs to be changed. In particular, you need:
- Start the engine and engage first gear.
- Without accelerating, try to move off and check the condition of the clutch disc.
- if the clutch “grabs” at the very beginning, it means that the disc and clutch as a whole are in excellent condition;
- if “seizing” occurs somewhere in the middle, the disc is worn out by 40...50% or the clutch requires additional adjustment;
- if the clutch is sufficient only at the end of the pedal stroke, it means that the disc is critically worn out and requires replacement. Or you simply need to adjust the clutch using the appropriate adjusting nuts.
Examination
To make sure that the clutch really needs to be replaced with a clutch releaser on a VAZ 2114, it is first recommended to check it thoroughly for malfunctions. This will allow you to determine whether this device is really the cause of the problem.
The bearing allows the disc to disengage from the basket, plus it additionally ensures that the clutch is engaged and disengaged.
There are two types of squeezers:
- Roller. They work on the basis of a rigid bunch of rods.
- Hydraulic. The hydraulic system ensures power transmission.
Even an inexperienced car owner can detect a faulty release bearing. The failure of this element manifests itself as follows:
- When moving, extraneous sounds and noises arise;
- Gear shifting is difficult;
- When overtaking, the clutch may completely disappear;
- Slippage occurs during acceleration, etc.
If the squeezer turns out to be truly faulty, it is the responsibility of every car owner to replace it immediately. This can be done with the help of service station technicians, or with your own hands.
Basket
All parts of the clutch basket are durable and have a long service life. But if one element of the mechanism is damaged, the entire system may fail. For example, if the driven disk is worn sufficiently, the drive and pressure disk may be damaged as a result of complete abrasion of the friction linings and friction of the rivets against the surface of the rubbing parts.
If the release bearing is faulty, it may jam. At high rotation speeds that the basket has, it is capable of breaking the petals of the membrane spring.
How to avoid this? – Correct use of the gas and clutch pedals on a manual transmission is a panacea for premature failure of any part of this mechanism and its long service life.
Basic clutch malfunctions
So that we understand what we are talking about. Clutch actuators include:
- clutch basket – clutch pressure disc;
- release bearing - clutch release clutch combined with a bearing.
Replacement and repair of the clutch basket, as well as replacement of the clutch release bearing, are simplified by the fact that the clutch parts come from the manufacturer as a set, and there is no point in changing them separately. Yes, and car maintenance technology recommends such a complete replacement.
The first signs of a clutch malfunction: the car does not gain full power, when you press the clutch pedal you hear a noise, the car jerks and slips while moving away, and so on.
arise due to natural wear and tear of parts, but. As a rule, novice motorists do not get to this point. Most often, we ourselves are to blame for clutch malfunctions: the driving mode is chosen illiterately, sometimes emotions let us down (especially when trying to prove who starts faster from a traffic light, etc.)
So, the main clutch malfunctions:
- The friction material on the clutch disc is worn. This is due to loads or oil getting on the linings from the engine or gearbox. As a result, the necessary connection between the clutch basket and the flywheel does not occur. Conclusion: clutch basket repair.
- The clutch release bearing has broken. As a result, the clutch basket petals break. The cause of the characteristic noise when squeezing the clutch.
- The sensor springs of the clutch disc fail, as a rule, due to your attempts (voluntary or involuntary) to start with reckless slipping.
When starting to repair or replace the clutch basket or clutch, consider purchasing an engine main oil seal and an input shaft oil seal. This will be needed so that, after repairing the clutch, you do not have to dismantle the gearbox again due to their leakage.
Replacement and repair of clutch basket
Removing the clutch basket
Replacing the clutch basket is an operation that skilled drivers carry out in the garage, using a jack and support blocks. If it is possible to use a lift, then you should use it.
The work of replacing the basket and repairing the clutch is not an easy task for the uninitiated person. The technological features of removing the gearbox and disconnecting the clutch are different for different models, so we describe the principle and sequence of the operation for replacing the basket.
First, you need a manual, namely, a repair manual for your car. Necessarily
Namely, the method of repair and maintenance. The second thing you need is to get a catalog of parts (something may be superfluous, something may be missing). It is important that when disconnecting the gearbox, before removing the clutch, you need to mark the position of all rotating parts so that during reassembly (if installed incorrectly), vibrations do not occur. Disconnect the gear shift lever in the cabin. We get to the gearbox and disconnect it. Unscrew the bolts securing the basket to the flywheel. If the flywheel turns, then hold it with a mounting tool. Remove the clutch basket and driven disc. The clutch release clutch is dismantled along with the bearing
As the repair progresses, evaluate the condition of the clutch fork, and other parts, the bushing, and so on. The release bearing will need to be pressed out of the clutch. This is a labor-intensive operation. After pressing out, the clutch bearing is changed. For lubrication, use only those lubricants recommended by the manufacturer.
Before assembling the clutch, thoroughly wash all parts in kerosene and at the same time troubleshoot them. Never reinstall damaged clutch parts.
We assemble the clutch after cleaning the parts from old lubricant and applying new one. Naturally, we install the clutch and gearbox strictly in the reverse order.
Important! Pay attention to the tightening of the bolts. It is necessary to clarify the tightening torque parameters of the basket bolts to the flywheel, etc.
Good luck with replacing and repairing clutch parts.
Proven self-diagnosis methods
You can and should check your car clutch yourself. Experienced drivers do this. They rarely contact a service station, only when they need professional diagnostics and identification of a specific problematic mechanism.
There are several testing methods available.
- The first involves diagnostics with the engine turned off. You need to listen carefully to the operation of the pedal, pressing it several times. Various extraneous sounds - clicks, creaks, knocks - will indicate a malfunction of the unit. Additionally, it is also necessary to measure the pedal stroke at the moment of inactivity and pressing. The smaller value must be subtracted from the larger value. The norm is about 14.6 cm (depending on the car model).
- Another type of test is carried out with the unit turned on. The gearshift lever should be switched to neutral mode. Then push the clutch as far as it will go and engage reverse gear. If an extraneous, characteristic crunch is heard or vibrations appear, the driven disk or basket needs a detailed inspection. And if the rear cannot be engaged at all, this indicates serious damage to the clutch.
- Another method is carried out in motion. You need to sequentially switch gears up to third, then sharply press the accelerator. If the car does not accelerate, but the engine speed increases, this is a sign of a malfunction. You can look at the tachometer to see how much the revs are rising. The smell of burnt rubber will also be a sign of problems.
Clutch Specifications
Technical requirements for brakes
- The clutch lining must be firmly glued with VS-YUT glue. Peeling of the overlays is not allowed.
- The thickness of the new clutch lining is (5±0.1) mm. The permissible thickness of a worn lining is 3 mm.
- Driven disk. 1. When replacing friction sectors, select them with a thickness variation of no more than 0.1 mm.
- The non-flatness of the friction surfaces of the driven disk is allowed no more than 0.3 mm under a uniformly distributed load of 150 N (15 kgf). Disc straightening is allowed.
- The thickness of the new driven disk with linings is (13.5±0.47) mm. The permissible thickness of a worn disc is 10 mm.
Technical requirements for pressure plate flange
- The difference in the weight of the levers is allowed no more than 0.01 kg.
- Fluctuations in the load of the coupling springs are allowed no more than 20 N (2 kgf).
- The width of the groove for the roller is 6±0.18 mm. The permissible gap between the roller and the wall of the support groove is no more than 0.7 mm. The permissible gap between the lever fork and the flange support is no more than 1 mm. The permissible gap between the pin and the hole for it in the flange support is no more than 0.3 mm.
- Non-flatness of the friction surface of the pressure plate is allowed no more than 0.15 mm.
Technical requirements for the drive disk
- Non-flatness of friction surfaces is allowed no more than 0.15 mm.
- The thickness of the new drive disk is (23±0.105) mm. The permissible disc thickness is 22.4 mm.
Technical requirements for the engagement clutch
- The internal diameter of the flange coupling slider is 72±0.074 mm. The diameter of the flange for the slider is 72±0.174 mm. The gap between the slide and the flange is 0.1...0.248 mm. The permissible gap between the slide and the flange is 0.61 mm. The maximum gap is 1 mm. The outer diameter of the slider for the bearing is 90±0.025 mm. The permissible gap in connection with the bearing is no more than 0.005 mm.
- The inner diameter of the bushing for the lever pin is 17±0.07 mm. Finger diameter 17±0.15mm. The permissible gap between the bushing and the lever pin is no more than 0.5 mm. The maximum gap is 0.7 mm.
- The thickness of the bearing housing cover flange is (9±0.1) mm. The permissible flange thickness is 6 mm.
- The gap at the joint of the sealing rings should be no more than 1.5 mm.