What does P0422 mean?
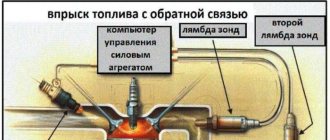
Trouble P0422 is a general trouble code that indicates that the primary catalytic converter (bank 1) efficiency is below acceptable levels. Catalyst efficiency is determined by the transmission control module (PCM), which uses exhaust gas and temperature data from oxygen sensors located upstream and downstream of the catalytic converter to determine efficiency. If the readings from both sensors match or are almost identical, this indicates that the catalyst efficiency is most likely below acceptable levels. In this case, error P0422 .
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0422 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi
- Chevrolet
- Chrysler
- Dodge (Dodge Caravan)
- Ford
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Elantra)
- Kia (Kia Spectra, Sportage)
- Mercedes
- Mitsubishi
- Peugeot (Peugeot 206)
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Beatle, Jetta)
- Volvo
- VAZ 2104, 2105, 2107, 2110, 2111, 2112, 2113, 2114, 2115
- Volga Chrysler, 31105
- Gazelle Business, Next
- Lada Vesta, Granta, Kalina, Niva, Priora
- UAZ
With fault code P0422, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common are the following: P0304, P0326, P0420, P0441, P0455.
2 years ago AutoTime 0
Trouble code P0422 is a standard OBD-II trouble code. Code P0422 indicates that the efficiency of the main catalyst is below acceptable levels. Catalyst efficiency is determined by the engine control module, which uses exhaust gas and temperature data from both the upstream and downstream oxygen sensors to determine catalyst efficiency. If the sensor readings at the input and output are too similar, then the efficiency of the catalyst will most likely be below the acceptable level and the control unit will record error P0422.
Causes of error P0422
The most common cause of P0422 is a faulty catalytic converter. Other reasons are:
- Oxygen sensor malfunction
- Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunction
- Fuel pressure regulator malfunction
- Manifold air pressure sensor malfunction
- Air flow sensor malfunction
- Engine oil contamination
- Engine leak before catalytic converter
- Misfires in engine cylinders
- Damage to wires and connectors
How is self-diagnosis performed?
We have sorted out the main errors on the Priora, now it’s worth finding out how self-diagnosis is performed. The VAZ 2170 with 16 valves has a special controller with which diagnostics are performed. If you have an on-board computer installed, then diagnostics are performed on it. There is also special equipment that allows for a more in-depth check of Priora 16 class systems.
Since most Priora 16 cars already have an on-board computer, we will consider the option without the use of special devices. Diagnostics begins with activation of the test mode. The work proceeds according to the following scheme:
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0422 code?
Error P0422 can be diagnosed using a standard OBD-II scanner. The mechanic uses a scanner to view data and gather information about the code, as well as check for other error codes that may be present. The mechanic will then clear the error codes from the PCM memory and retest the system to see if P0422 again. If the code disappears, it may indicate an intermittent error or that the code appeared in error.
If the P0422 appears again, have a mechanic inspect the wires and connectors near the catalytic converter. He will repair or replace any damaged items. The mechanic will then inspect the catalytic converter and also perform a thorough check of the exhaust system for leaks.
If the catalytic converter is the problem, the mechanic will examine other vehicle components to determine the cause of the catalytic converter damage.
How to Troubleshoot or Reset Trouble Code P0422
Some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P0422:
Diagnosis and problem solving
If error 1602 appears on the on-board computer of the Lada Priora 16 valves, this means that the on-board voltage in the controller has dropped. As the experience of VAZ 2170 owners shows, error 1602 does not affect the operation of the car; if you remove the terminal from the battery, then 1602 will disappear, but after a while it will appear again. There may be several reasons for 1602:
Common errors when diagnosing code P0422
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0422 is failure to follow the diagnostic protocol, which leads to hasty replacement of the catalytic converter. Before replacing the catalyst, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of its damage, and also consider other error codes present.
It is also a mistake to hastily replace oxygen sensors. Before replacing them, it is necessary to perform a thorough diagnosis, since usually sensor failure is not the only cause of error P0422 .
p0504
Also, many owners of a Lada Priora with 16 valves have questions about the appearance of error p0504. She tells the owner that there is a malfunction in the brake pedal sensor. To find out the exact reason for the appearance of p0504, you need to remove the sensor and disassemble it. Pay attention to its springs, one of them could burst - replace the damaged part.
see also
This error usually occurs on cars with a 127 engine. It is associated with the throttle valve, the quality of which in this power plant leaves much to be desired. P1558 does not interfere with normal engine operation, but you can still try to fix it. Some people solve the problem by flashing it, but we offer a simpler method.
Remove the throttle valve, and then remove the cover - this can be done using a hexagon. We find a plastic gear inside - this is the working part. Lubricate the gear thoroughly and reassemble in reverse order. Most likely, error p1558 will disappear after these manipulations.
How serious is the P0422 code?
The severity of the P0422 depends on the cause of its occurrence. If the problem is a bad catalytic converter, the engine may stall frequently or be difficult to start. In this case, problems with the vehicle's handling may occur. However, if everything is in order with the catalyst, there should not be any serious problems. In any case, if this code is detected, it is recommended that you contact a qualified technician as soon as possible to diagnose and repair the error to avoid serious damage to the catalytic converter.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0422 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light) illumination. It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in the ECM memory as a malfunction).
- The engine stalls or has trouble starting.
- Decrease in engine power.
- Increased emissions of harmful substances from the exhaust pipe.
Error 0422 Priora how to fix
Hello!
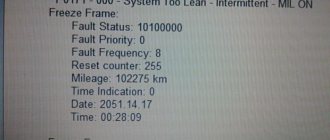
In general, the essence of the problem is that the “engine malfunction” light comes on. Priora '11, bought from scratch, passed 103,000. I connect it to the computer and see errors: P0133—Slow response to enrichment or depletion of oxygen sensor No. 1 to the converter. P0422—The efficiency of the neutralizer is below the permissible threshold. After resetting, it lasts for 700-800 km. Moreover, if you look at the computer after driving 50 km, there is only error P0422 and the check light does not light up. It only lights up when P0133 appears. If you look at the computer dk1, there is a sinusoid. more than 0.55 at idle. Dk 2 flat line 0.35. And what could it be? The cat is clogged, although it’s become stupid, I wouldn’t say it comes off in the same way. Or change the sensor? I just wouldn’t want to just throw away money by exchanging a working one for a working one...
Someone also told me that if you put an insert under 2 sensors, the check will not light up, right? I look here at the drive in the onboard ones, and by searching, I couldn’t find any croquet answers or similar examples.
Comments 23
In general, I solved the problem! I machined out a spacer (fake) for the catalyst, there is a drawing on the Internet. + on DC 2 in the wire cut there is a 1 mOhm resistor and in parallel a 1 µF capacitor. 2000 passed all the rules!
Same problem. But I have to replace the catalyst and re-flash it to Euro 2. But the check still lights up
I had the same problem. A week ago I went to the service center, they installed a 4-1 spider (there was no 4-2-1 in the nearby spare parts store) with 1 oxygen sensor, they flashed the car with some Paulus firmware (they said the most optimal firmware) and that’s it... They also said that they filled it with crappy gasoline somewhere.
p0422 catcollector is dead, install a spider and reflash and the problem will be solved, but p0133 no idea
Such a problem! Today I saw a diagnostician and he advised me to change the oxygen system and there won’t be any problems. alteration 700 rub. and the sensor is 1000r. choose! I installed a new sensor before arriving at his place. It lights up from time to time, even though it’s new. I should have immediately changed it with the old sensor - if only I had known))) -
Error 0422 – Neutralizer efficiency below threshold The error is entered under the following conditions: 1. there are no errors 0102, 0112, 0113, 0116, 0117, 0118, 0122, 0123, 0130, 0132, 0134, 0136, 0137, 0138, 0140, 0171, 0172 , 0300, 03**, 0441, 0444, 0445, 0562, 0563. 2. The ECU controls the fuel supply in a closed loop Parameter (B_LR= “YES”). 3. The conditions for the ECU to carry out the catalyst diagnostic cycle have been met. 4. The ECU has determined that the oxygen content after the neutralizer is above the threshold. The error is entered into the ECU memory on the third drive cycle. The efficiency of the neutralizer can be assessed using the ANKAT parameter (neutralizer efficiency factor). If the ANKAT value tends to zero, the neutralizer is working effectively. The larger the ANKAT value, the more the neutralizer degrades. Check procedure: 1. Turn off the ignition, connect the diagnostic tool, turn on the ignition, check for errors. If there are other errors in the ECU memory, we eliminate them first. 2. If there is an error, inspect the catalytic collector for damage, check the condition of the “filling”. 3. If malfunctions are found, replace the catalytic collector; if there are no comments, check the exhaust system between the neutralizer and the main muffler for leaks, incompleteness, or damage. Make sure that there is no damage to the DDC and that the wiring harness is not damaged. If no faults are found, replace the neutralizer. 4. If faults are found, fix them. Start the engine, warm it up to a coolant temperature of 70 degrees. Set the rotation speed of the HF to 2000 - 3000 rpm for at least 4 minutes. The load on the engine should have a stable value of 15 - 50%. If the error does not appear, the malfunction has been eliminated; if the error appears again, replace the neutralizer.
Decoding errors
Each code consists of five characters: P 1 4. Let's say right away about the fourth and fifth characters - they indicate the serial number of the error. Now it’s worth taking a closer look at what the codes consist of
The first character may vary depending on the vehicle system:
- P – malfunctions in the operation of the power plant; the symbol also indicates defects in the automatic transmission.
- U – you need to look for a fault in the interaction node between the system units.
- B – defects in the operation of body systems, which include electric lifts, airbags, etc.
- C – chassis sensors have detected a malfunction in the chassis system.
Let's move on to the second character:
- 3 – reserve.
- 2 and 1 – codes set by the manufacturer.
- – common code for on-board diagnostics (OBD-II).
The third symbol indicates to the motorist the type of breakdown:
- 1 and 2 - indicate defects in the operation of the fuel unit or the appearance of malfunctions during the air supply.
- 3 – breakdowns in the ignition unit.
- 4 – indicates auxiliary control.
- 5 – in idle mode, some components do not work correctly.
- 6 – electronic unit or its circuits.
- 7 and 8 – defects in the operation of the gearbox.
What does Bank 1, Bank 2 mean?
The designation Bank 1 and Bank 2 is usually used if the vehicle has more than four cylinders. But it is also used on four-cylinder engines.
This means that you probably have two exhaust pipes or that the engine cylinders are split into multiple O2 sensors. “Bank” indicates which side or exhaust pipe the sensor is located on.
Bank 1 is always installed on cylinders 1-3-5-7-9, etc. Bank 2 sensor monitors cylinders 2-4-6-8-10.
You can disable one oxygen sensor and read errors with the OBD2 scanner. This will allow you to find out where the sensor is installed - in Bank 1 or Bank 2.
Catalytic converter - what is it for?
Car designers are increasingly paying attention to reducing harmful emissions.
To achieve this, the power supply systems of power plants are being modernized in order to achieve the lowest possible fuel consumption, without affecting power performance.
Also, more and more cars are equipped with catalytic converters installed in the exhaust system.
The essence of the catalyst's work comes down to the breakdown of harmful elements into harmless ones through chemical reactions.
The catalytic converter consists of a housing, inside of which active catalysts, the so-called bobbins, are placed.
Nowadays these bobbins are often made of ceramic, but some are also made of metal.
The reel contains a large number of honeycombs through which the exhaust gases pass.
But ceramics do not enter into a chemical reaction; for this purpose, the surface of the honeycomb is covered with a layer of noble metals - platinum, iridium. Thanks to these metals, a reaction occurs, which reduces the harmfulness of car emissions.
The operating efficiency of this device depends on the temperature - the optimal temperature is considered to be from 300 degrees, so there is also a heat-insulating layer inside the housing, and the element itself is placed as close as possible to the exhaust manifold.
You can read more about the design features of the catalytic converter, as well as the principle of its operation, here.
One of the main disadvantages of the catalytic converter is its relatively short service life. On average, it is designed for 100-120 thousand km, after which it becomes inoperative.
How is self-diagnosis performed?
We have sorted out the main errors on the Priora, now it’s worth finding out how self-diagnosis is performed. The VAZ 2170 with 16 valves has a special controller with which diagnostics are performed. If you have an on-board computer installed, then diagnostics are performed on it. There is also special equipment that allows for a more in-depth check of Priora 16 class systems.
Since most Priora 16 cars already have an on-board computer, we will consider the option without the use of special devices. Diagnostics begins with activation of the test mode. The work proceeds according to the following scheme: