Why does the gearbox crunch?
As you know, a manual transmission is highly reliable and unpretentious. With proper use and timely maintenance, the “mechanics” do not often fool the driver. However, over time, this transmission may also develop malfunctions. One of the most common problems is a squeaking sound when shifting gears. What causes it and how to fix the problem will be discussed in this article.
Most often, an unpleasant crunching or grinding noise appears when switching to only one gear (for example, to second) and when switching the lever to the neutral position. If you hear a crackling, grinding or crunching sound when upshifting or downshifting, it is important to find the cause of the problem and fix it as soon as possible.
Malfunction of differential elements
Another example is a grinding noise in an automatic transmission at the location of the differential. Here, wear of the drive or driven gear of the differential or its bearing is possible, along with an increase in the axial clearance in it. No less likely is the pin of the pinion gears in the differential getting stuck and causing play. Here, you also cannot do without disassembling the automatic transmission, since you need to check the condition of the differential and, if necessary, replace it, although it would be better if the matter ends only with replacing the worn bearings.
How to recognize the presence of a malfunction?
To check the serviceability of a particular vehicle unit, the driver must turn off the radio before starting the trip. With the radio turned off, you can easily determine whether there are any extraneous noises and knocks when the mechanisms are operating. The following factors may indicate problems with the gearbox:
- A characteristic crunching sound when engaging a gear (and it can only appear in one of the gears);
- Crackling noise when returning the lever to neutral.
If at least one of the above symptoms appears, the driver needs to identify and eliminate the malfunction as quickly as possible. Otherwise, if you ignore this problem, more serious problems may arise.
Knocking sound when changing gear
No less common is a knocking sound when switching the automatic transmission, accompanied by a jerk when the car is removed from parking mode. The reasons for this reaction include the peculiarity of the box for a particular brand of car to behave in this way. There are cases when a slight knock and jerk of the “machine” was not a malfunction, but the natural behavior of the unit. However, if this is discovered after several years of operation of the car, then, of course, a breakdown exists and it can, alternatively, be expressed in a clogged internal automatic transmission filter.
What to do if there is a hum or crackling sound coming from the box?
The gearbox is the main mechanism of the vehicle. Any problems that arise with it must be corrected in a timely manner. If the gearbox is humming, then you should trust the diagnosis and repair of this unit to trusted services.
There are a number of reasons that cause noise:
- wear of the shaft, gears, bearings, synchronizers has occurred;
- if the gearbox howls at only one speed, it is worth checking the integrity of the teeth;
- insufficient amount of transmission oil;
- The box is noisy even if the oil has thickened;
- used oil (the liquid contains metal particles or water);
- There are problems with the “fork” box, which can cause the transmission to “knock out.”
If the release bearing wears out, gearbox noise may be heard when the pedal is released. Also, there is an inaccuracy in switching on speed modes. In this case, it is worth sending the car for diagnostics. If problems are detected, the gearbox must be removed from its original location, after which it needs to be rebuilt to replace worn components.
A hum in the gearbox (mechanical) is one of the most common signs of problems with the gearbox. If there is insufficient lubrication, the manual transmission howls in higher gears (5th, 6th). In some cases, the hum is a technological feature of the gearbox or spare parts were installed that are not suitable for the gearbox.
If you notice a rattling sound in the gearbox when changing gears, this is a cause for concern. Mechanical faults can result in a crunching sound in the gearbox. In rare cases, the problem is due to a manufacturing defect.
What's the result?
The appearance of a crunching sound in a manual transmission may be the first signal of a serious breakdown of this unit. Therefore, if symptoms such as crunching, grinding or crackling appear when switching the gearbox lever from high to low speed or vice versa, it is necessary to conduct a full diagnosis and identify the cause of the malfunction.
Timely elimination of the problem will help the car owner avoid more expensive manual transmission repairs, since driving with a faulty gearbox that crunches when shifting can lead to more serious malfunctions, and after a relatively short period of time.
Sources
- https://supersto.by/hrustit-korobka-peredach-pri-pereklyuchenii/
- https://okeydrive.ru/xrustit-korobka-peredach-pri-pereklyuchenii/
- https://akpphelp.ru/stuk_v_akpp_pochemu.html
- https://vtauto.ru/stuk-v-korobke-peredach-diagnostika-i-remont.html
- https://avtoelektrik-info.ru/sovety/pochemu-mozhet-hrustet-mehanicheskaya-korobka-peredach
- https://KrutiMotor.ru/stuk-v-akpp-prichiny/
- https://KrutiMotor.ru/hrust-pri-pereklyucheni-peredach-kpp-prichiny/
How does a crunching sound manifest in a gearbox?
There is an unspoken rule among drivers - to start driving a car with the radio turned off. This is necessary to immediately check whether there are any extraneous knocks, noises or other sounds that may indicate a malfunction of a particular unit. The following sounds will indicate problems with the gearbox:
- A crunching sound when engaging a gear, and often it can only appear in one of the gears, for example, in reverse;
- Crackling noise when returning the gearshift lever to neutral.
If you notice one or both of the symptoms in the operation of your box, you should determine and eliminate the cause as soon as possible.
Crunching sound when changing gears on a new car
Unfortunately, new cars also have problems with the gearbox, namely a crunching noise when changing gears.
Why is there a knocking noise in the automatic transmission?
People who repair cars can name many possible reasons for a knocking noise in an automatic transmission. If you ask them the question: “Where does the automatic transmission knock come from?”, you can hear:
- due to the oil level not being set in the gearbox;
- due to incorrectly adjusted distances between brakes and clutch packs;
- due to sagging of a certain valve in the automatic transmission valve body, or in its mechatronics;
- due to a non-working solenoid;
- due to an unadjusted pressure regulator;
- due to the need to replace the old wiring harness;
- due to a faulty electronic unit,
- due to engine mounts that were very worn out
and so on…
Familiar picture, right? But if you look at the very essence of the problem, you can deduce the main sign of a breakdown, which in one interpretation or another sounds like “a knock in the automatic transmission.” And this despite the fact that there are a huge number of reasons for the problem...
Where do the legs come from, or why does the automatic transmission knock?
Let's try to explore this issue as deeply as possible. To begin with, let’s think about the following statement: in a classic automatic transmission (when the switching procedure itself is performed), knocks or knocks appear. Where are they from?
- How to determine the cause of automatic transmission jerking?
When gears are changed in an automatic transmission, the angular acceleration of the outgoing roller (transmitting, as you understand, torque to the drive axle) is constant. Due to this, the gears replace each other, and the angular speed of the pump wheel, as well as the turbine wheel of the hydraulic transformer, changes. The crankshaft also changes its rotation speed.
Everything that happens is under the constant control of electronics, the operation of which also has some interesting features.
Crunching in the gearbox, causes
If we compare different types of transmissions, oddly enough, the most problem-free is the “mechanics”; the manual transmission outperforms the classic “automatic” and many of its varieties in terms of resource. However, as we know, nothing lasts forever, and “mechanics” during operation present surprises, the most common of them. The appearance of a crunch when changing gears. Of course, this unpleasant phenomenon does not cause the car to become completely immobilized, it is only the first sign of a possible serious breakdown, it indicates that problems have already arisen in the manual transmission and we need to start solving them as quickly as possible.
Causes of crunching
A manual transmission, although a rather complex unit, is nevertheless more conservative compared to an automatic transmission; it has much fewer sensors than an automatic one, and accordingly the control system is less complex. Therefore, breakdowns are most often of a mechanical nature, that is, associated with wear and tear of individual parts and elements.
So, why does the crunch occur?
1. failure of the synchronizer.
This device, by equalizing the rotation speed of gears during gear shifts, ensures a smooth transition from one speed to another. Before the use of synchronizers in manual transmissions, drivers were forced to change the throttle, which added complexity to driving; modern drivers do not have to perform such a mandatory action, they are helped by the synchronizer, but only while it is working. With severe wear, the part is no longer able to synchronize the speed of rotation of the shafts. Therefore, when the gears engage, a crunching sound appears. If this phenomenon occurs when only one of the gears is engaged, then the synchronizer is most likely to blame, which needs to be changed. It must be said that the problem with such a breakdown often arises among owners of front-wheel drive VAZs; the thing is that the engineers of the Volga plant, when designing a manual transmission for a whole family of cars, made a gross mistake, namely, they unsuccessfully selected the gear ratio of the second gear. As a result, when switching speed to second, the transmission elements experience increased loads, primarily the synchronizer.
2. Shaft wear.
Such a phenomenon as a crunching sound in the transmission can occur when the primary and secondary transmission shafts wear out. When teeth on gears wear out or bearings fail, alignment may be disrupted. If there are problems with the primary and secondary shafts, a crunch will occur when you engage not one, but several gears at once; it can also be heard while the car is moving in any gear.
By the way, the problem with wear of the shafts can also be determined by the temperature effect, if the gears are switched on smoothly when cold, without crunching, and after the oil in the box has warmed up, it appears, the reason most likely lies precisely in them.
3. Lack of oil in the box.
The reason, which in practice is not so rare, oil leakage can occur due to depressurization of the gearbox, if for some reason it has received mechanical damage, wear of the oil seals, or spontaneous failure or unscrewing of the oil drain plug. For example, on many Renault models, the gearbox and the inner CV joint of the left drive are connected to each other; oil can also leak through the CV joint. Owners of cars of this brand should take this circumstance into account. Repairing a manual transmission on such a car is much more difficult than, for example, replacing the hood on a Renault Logan ().
4. Clutch basket malfunction.
During long-term use, the petals of the basket wear out. They may even break off; in such cases, the clutch will not disengage completely, which will create a problem when shifting gears, although the gearbox will not be to blame here.
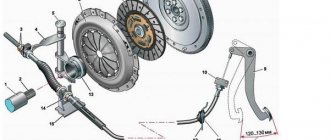
5. Problems with the clutch drive.
Much depends on what type of drive is used in the car (cable or hydraulic), there can be many reasons for the malfunction and the appearance of a crunching sound, for example, a broken cable, leakage or clogging of hydraulic fluid. Just like with the clutch basket, the gearbox is not directly to blame here, but if the clutch does not disengage completely, smooth gear shifting will also be impossible.
Typically, clutch problems affect not one, but all manual transmission gears. By this sign, you can determine that the source of the problems lies precisely in this node.
It should be noted that a crunching sound when engaging a gear is not always a sign of a breakdown; on some budget cars, for example, on the same Renault Logan 2 (there is no synchronizer in reverse gear. Therefore, if you engage reverse gear too sharply, even before a complete stop, you will hear crunch This characteristic feature cannot be eliminated, but the driver can adapt to it: do not engage reverse until it comes to a complete stop, do not do it too sharply.
Repairing a manual transmission or clutch is a costly and difficult task, but the cause of a crunching noise during gear shifting is not so difficult to determine. You need to start identifying the cause with the simplest thing, first check the oil level in the box. It is important to make sure that the rubbing parts are properly lubricated. If the oil level is okay, you will have to remove the gearbox and check the clutch. If the problem was not identified during the initial inspection, you will have to troubleshoot the unit with further replacement of worn and damaged elements, since they can be purchased separately without purchasing a complete gearbox or clutch.
Often the drivers themselves, especially inexperienced ones, provoke early wear of the manual transmission through their inept actions.
How to extend the life of a manual transmission and clutch:
1. Change the oil in a timely manner. Almost all operating instructions for modern cars with a manual transmission state that the oil poured into the transmission is filled with the expectation of the entire service life of the car. Therefore, some car enthusiasts are of the opinion that changing the oil after a certain mileage is only relevant for automatic transmissions; it is not required for mechanics. In fact, this is not entirely correct. Although a manual transmission is less critical to the purity of the transmission oil than an automatic transmission, wear products that inevitably appear over time inside the transmission reduce its service life, so it is still necessary to change the oil. How often should this be done? Opinions vary, but the most authoritative recommendations agree on mileage figures of 80-100 thousand.
2. Select the right gears. Shifting abruptly from too high to too low revs is detrimental to any gearbox, including manual ones.
3. Do not hold the clutch for a long time. Long squeezing creates additional load on individual clutch elements, reducing the life of the entire assembly; release the pedal smoothly without delay, this will save you from serious damage.
A crunching sound when shifting gears is an unpleasant, irritating phenomenon, it can be a harbinger of a serious malfunction and expensive repairs. If a problem arises, try to pay attention to it in time, and best of all, do not let it happen by following the above simple recommendations.
The transmission is noisy in neutral and howls at speed.
Main causes of malfunction:
- insufficient oil level in the manual transmission. If there is a lack of transmission fluid, the lubrication of the rubbing pairs deteriorates. Thermal expansion and dry friction leads to noise and howling when moving. If the car has covered hundreds of thousands of kilometers, you should not be alarmed by slight noise when operating in neutral. We recommend limiting yourself to only changing the oil in the manual transmission.
If extraneous noise from the gearbox occurs when the clutch is depressed, the release bearing is faulty.
- gear wear. The reason is the development of gear teeth at the contact points. In this case, only replacing worn parts will help eliminate noise and howling;
- wear of the bearings of the driven, drive or intermediate shaft. As a result of oil starvation, heavy loads, increased torque after boosting the engine, or natural wear, abrasions, scuffing and uneven performance appear on the rolling elements and bearing races;
- production of differential parts for front-wheel drive cars. In such cases, vibrations are common when accelerating.
Some VAZ models are worthy of a special note, in which the manual transmission begins to make noise, howl and vibrate at relatively short distances. Many people attribute the malfunction to a design defect and the quality of manufacturing of transmission parts, which makes the idea of any repair very doubtful.
Gears engage poorly and with a crunch
Difficulty shifting gears and a metallic grinding noise at the moment of shifting are clear signs of a malfunction of the manual transmission synchronizers. But before removing the gearbox for repairs, check the gear selector and clutch. Play in the gearshift lever, cable jamming, and incorrect adjustment of the gear selection mechanism lead to unclear and often poor gear shifting. And incomplete disengagement of the clutch after pressing the pedal (the clutch is moving) will cause crunching and grinding sounds. Driving with such a malfunction will quickly damage the synchronizers.
If your car only shifts into second or, for example, third gear with a crunch, then the problem is most likely with the synchronizers. These elements are intended to equalize the rotation speed of the output shaft and the gear engaged in the transmission. Wear of the conical friction part leads to slipping of the blocking ring and rigid engagement of the clutch with the gear teeth. When disassembling and troubleshooting, you should also pay attention to gears, gear clutches and their forks.
Knocks out the speed
The synchronizer blocking ring and gears have specially shaped teeth with which the clutch engages when changing speeds. If the coupling splines, teeth on the ring and gear are ground down, then when the load is applied and the gas pedal is released, the transmission spontaneously switches off. In this case, it will not be possible to limit yourself to replacing synchronizers; you should definitely change the gear of the damaged transmission and the gear shift clutch.
Clutch depressed
Many car enthusiasts systematically hold the clutch pedal depressed for a long time. For example, when they are standing at traffic lights or just stopped.
This, at first glance, harmless action leads to increased wear of the clutch disc, but what “suffers” the most is the release bearing, which is tirelessly forced to rotate under load.
As a result, it quickly becomes unusable (it buzzes), as a result of which it will require immediate replacement, because there is a risk that it will “scatter” right on the move.
By the way, to replace it you will have to remove the box, which is not a cheap pleasure.
Hand on the lever
Many drivers, when moving, keep their hand on the gearshift lever, as if on an armrest.
On the one hand, it seems to be convenient, on the other hand, it loosens the mechanism and “kills” the forks that directly move the clutches in the gearbox.
Those who want to save the box must understand that while driving the car oscillates chaotically and the driver does not consciously hold on to everything his hands are on.
As a result, the load on the lever turns out to be not so small, and the box loses its original “tightness”
Released clutch
As you know, the clutch is an integral part of a manual transmission. It is involved in the process of shifting gears (discussed above) and “taking off” from a place.
The most detrimental thing is slipping of the clutch disc at the moment of start. Because the entire assembly gets very hot and simply wears out due to friction.
Some drivers do not know about this and use the clutch incorrectly, thereby significantly reducing its service life.
For example, when standing on an incline in a drag, they hold the car in place by not fully grasping the clutch (the clutch pedal is not fully released) or they drive onto a curb/obstacle not due to inertia (at low speeds), as needed. And due to the moment of clutch engagement. Alas, the clutch will not serve its intended life this way. And the work to replace it will cost a pretty penny, because you will have to pay not only for new spare parts, but also for dismantling the box.
Engaging reverse gear without coming to a complete stop
A classic of the genre, the driver tries to quickly turn around in the yard, in a hurry, first and then reverse gears. We hear an unpleasant grinding noise when we obviously try to engage the rear.
The reason is simple: the pilot is trying to engage reverse without making a full stop. This has an extremely negative effect on the teeth of the reverse gears, which slowly become unusable due to licking off on one side. If such an error becomes permanent, the reverse gear will engage worse and worse from time to time, until it completely fails.
Crunching noise when shifting gears caused by breakdowns
Crunching when breaking is not very good. After all, you need to intervene in the structure of the gearbox, and this is a rather complicated repair. The gearbox is a very complex technical mechanism; it is better not to do it in garages, but to turn to professionals.
First reason. The main reason is the breakdown of synchronizers; they serve to make our shifts smooth. If they wear out, they need to be replaced. Repairs are quite complex and expensive, I recommend doing them at trusted stations.
The second reason. The clutch “basket”, the paddles fall out from working for a long time, and you simply don’t engage the gear completely. Here you need to remove the box and change the basket along with the clutch disc.
The third reason for the “crunch”. Clutch faulty. On our front-wheel drive VAZs, the clutch cable breaks, and then you will not be able to engage at least one gear and move away.
Fourth reason. Gearbox shaft.
It happened to me that when the engine and gearbox were cold, everything was fine, but as soon as I drove 30–40 kilometers around the city, the oil in the gearbox would heat up and there would be a crunching sound, and a constant one, not just when changing gears.
I went to a service station, they removed it and determined that the input shaft was made of overheated iron, a factory defect, they replaced it, everything went away (it was dark blue, the craftsmen were surprised that it didn’t burst). So you still need to look at the gearbox shaft.
Shocks in the automatic transmission but no errors - why?
Most car enthusiasts, turning to specialists with a request to conduct an auto technical examination, voice the presence of problems with the automatic transmission. At the same time, they do not have fault codes that should be displayed in the automatic transmission control unit. In such cases, dealers are not in a hurry to look for a ghostly malfunction, but make the logical conclusion that since the system shows no errors, then there are no problems with the automatic transmission.
This happens for the following reasons. The presence of a knocking sound when switching is evidence of the presence of obvious problems in the system, respectively, switching. That is, a problem in fact, which manifests itself as a knock in the body, exists, but during scanner diagnostics it is not confirmed by fault codes. Unfortunately, manufacturers of automatic transmissions have not yet implemented the ability to control the processes occurring in automatic transmissions, which would include a device that measures acceleration. Such a sensor could monitor knocks and analyze the causes of their occurrence. But for now, car enthusiasts have to do without it.
- A common cause of knocking noises is a faulty torque converter.
How does a force appear that acts on the body in such a way that the driver, due to the appearance of incomprehensible knocking, begins to experience unpleasant sensations? It is clear that when switching, the shock comes from the power unit. This unit, moving on supports, creates conditions under which accumulated energy is transferred to the body. Subsequently, damped oscillations occur. What exactly is to blame for the displacement of the unit? There can be many answers here; some of the possible options are given in the list a little higher in the text.
Vibration and knocking in the automatic transmission when engaging reverse gear
So, such a force can only appear in the presence of accumulated energy, which, due to the automatic transmission switching, is redistributed, moving the unit. A considerable amount of energy accumulates in the gear that precedes the switching process. This is essentially the inertia of the turbine wheel. Everyone had a spinning top or a spinning top in childhood? Remember, was it easy to change the axis of its rotation, or just stop the movement of this toy? So it is here. It is precisely because of the change in the angular velocity of the turbine wheel (when changing gears) that the knocking (or impact) occurs. Interestingly, if you change the time interval of gear shifting, the quality of their shifting will also change.
The higher the angular speed of the torque converter turbine wheel, the greater the amount of energy that is released. And if the angular velocity does not change as intended by the manufacturer, then, naturally, the poorly controlled release of energy entails incorrect switching, accompanied by an unpleasant knock.
Any knocking noise in an automatic transmission, regardless of where it comes from, is a direct consequence of a violation of one single process - an incompletely controlled change in the angular velocity (that same top) of the torque converter turbine. Moreover, this change occurs at the moment when the gears are changed. As a result, the driver hears uncomfortable tapping sounds.
- Directory of typical automatic transmission faults
It seems that many diagnosticians, after receiving this information, will recall numerous cases of similar breakdowns that occurred with one of the German car models. In its automatic transmission, it was the torque converter that caused incorrect shifts; to be more precise, the cause was the lock-up clutch of this unit. Because of this, the angular acceleration of the turbine wheel did not occur smoothly enough.
Hopefully, we have been able to briefly explain the real causes of problematic shifting in automatic transmissions. Thanks to the awareness of the deep root cause of these processes, both ordinary car enthusiasts and professional mechanics will be able to better develop their skills in car repair, and without outside help identify even the most hidden problems, then competently eliminate them.
The appearance of a crunch due to improper operation of the transmission
It is important to note that often a crunching sound during gear shifting indicates improper operation of the transmission. Therefore, in order for the manual transmission to last for a long time, you should follow some recommendations.
It is necessary to promptly change the transmission oil. Not everyone knows that this fluid must be changed periodically in both automatic and manual transmissions. Of course, a manual transmission does not need to change the oil too often, but after the mileage crosses the threshold of 70,000 km, you should definitely visit a service station.
If this fact is left unattended, metal shavings and dirt will accumulate in the liquid, resulting in insufficient lubrication and the occurrence of a crunching sound. The same sound can also appear due to the fact that there is not enough oil in the transmission. Adding oil or replacing it will help solve the problem.
We determine which CV joint crunches, the inner or outer one
Several methods are used to diagnose CV joints. The simplest of them is a visual inspection of the anthers and checking the shafts.
The main cause of problems associated with the appearance of crunching is the ingress of dirt into the nodes, which can only occur due to damage to the boot.
If the rubber element is torn, then upon inspection there will be traces of leaking lubricant on it, from which you can understand which of the units got sand and dust.
Also, during inspection, you should try to move the drive shaft in the transverse and longitudinal directions by hand. CV joints are highly precision-manufactured units, and if it feels like they have play, it’s time to take action.
If, during a visual inspection, no leaks in the boot are detected, but symptoms of a joint malfunction appear, several simple methods can be used to identify which of the CV joints is problematic.
Diagnostics of external hinges
External hinges are tested by placing a strong load on them. To do this, simply turn the wheels all the way to the right or left and try to start moving at higher speeds. Afterwards, we carry out the same procedure again, but this time when turning the wheels in the other direction.
When checking CV joints using this method, starting to move with the wheels turning to the left will create a significant load on the right unit, and if it has play, it will begin to crunch.
By turning the wheels to the right, the left hinge is checked. But we note that a crunching noise can also be produced by the outer CV joint on the side where the turn is being made.
Therefore, when checking, it would not be superfluous to have an assistant present, who, being near the car, will establish by ear which side the sound is coming from.
Checking internal components
To determine which inner CV joint is crunching, a different method is used. To carry it out, you need a flat section of the road, but with a bump (hole).
The essence of the test comes down to driving through a hole at a moderate speed with one of the front wheels. Then everything is repeated, but with the second wheel entering the hole.
When a wheel hits a bump, a shock load occurs on the inner joint, and if there is play in it, they will manifest themselves in the form of knocks or soft crunches.
Universal method
The only drawback of the method of driving into a hole at speed is the fact that there is not always a suitable section of road with a bump. Therefore, another method can be used for diagnostics, and it is universal and allows you to check both internal and external CV joints.
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Use a jack to jack up one of the drive wheels;
- We place a stop under the car and apply the handbrake;
- We start the engine, engage first gear and gradually release the clutch pedal (we simulate the beginning of movement. At the same time, thanks to the differential, the suspended wheel will begin to rotate, and the one standing on the ground will remain motionless);
- Having gained engine speed, we begin to slow down the rotating wheel with the brakes (we do not touch the clutch pedal. Thus, with the brake mechanisms we create a load on the internal unit, and if it is problematic, it will immediately manifest itself with knocks and crunches);
- After checking the internal hinge, we determine the condition of the external one. To do this, just release the brake pedal, pick up speed, turn the wheels all the way to one side and use the brakes again. A large drive angle and brake force will create the necessary load, which will cause the external assembly to crunch if it is not working properly.
After checking on one side, we repeat similar work with the drive of the second wheel.
Gearbox repair
What problems are indicated by the appearance of a whine in the gearbox? The gearbox may howl if there is insufficient amount of transmission oil. Because of this, the bearings begin to overheat, which contributes to their failure. The fluid can be added to the existing one, or a new one suitable for the vehicle system can be filled in. If changing the oil does not help resolve the problem, it is necessary to repair this unit.
As a rule, the box begins to hum as a result of improper operation of the transmission. Regardless of what type of gearbox is installed, the owner of the vehicle must promptly replace the transmission fuel. Otherwise, metal shavings will begin to accumulate in the oil, resulting in noise in the gearbox. If the gears do not touch each other, a hum will be noted in the gearbox.
Why does the gearbox crunch when changing gear? The automatic transmission includes synchronizers, which are responsible for the smooth change of speeds. When they wear out, they cease to perform their functions, the result of which is the appearance of a crunch when changing gears. It seems possible to solve the problem by replacing damaged components with new spare parts. If the reverse gear cannot be engaged when the engine is running, instead there is a crunching noise, you should first check the clutch; it may need to be adjusted.
If you notice gearbox noise, you need to pay attention to the condition of the clutch basket. This mechanism consists of “petals”, which may begin to fall out after 100,000 km. The consequence of this is that when the gears are engaged, extraneous noise occurs. The clutch plate needs to be replaced.
The box buzzed, what should I do? In some cases, it is possible to eliminate the cause of the hum from the side of the box when driving by replacing the filter element. Also, you should check the integrity of the release bearing. The noise may vary in strength and occur in some gears.
Thus, in order not to prematurely encounter gearbox repairs, this unit requires appropriate care and checking the technical condition of the gearbox. Why does the box howl? This manifestation is due to the fact that the teeth have worn out. If the input shaft bearing is worn out, a howling noise may be heard when the clutch is depressed. Also, extraneous noise may occur if there is insufficient oil in the transmission.
Tips and tricks
As you can see, among the main causes of knocking and noise from automatic transmissions are:
- problems with oil and its level;
- malfunctions inside the automatic transmission;
- torque converter problems;
- malfunctions of the computer and electronics;
At the same time, quite often, especially if the diagnostics do not reveal errors, it is the torque converter that causes knocking in an automatic transmission. Often the blocking clutch of the gas turbine engine turns out to be problematic, which led to disturbances in the angular acceleration of the turbine wheel. It turns out that within the framework of diagnostic procedures, HDT should be given special attention.
Also, a knocking sound when engaging an automatic transmission gear may occur as a result of play (for example, in the driveshafts). By the way, experienced car owners inject them, which allows them to get rid of the knocking for a while. This method does not always work, but sometimes it is possible to temporarily delay the replacement of a CV joint, axle shaft, etc.
Another knocking sound in the automatic transmission often appears when the wrong oil is poured into the automatic transmission, or the ATF and filters have not been changed for a long time, the transmission fluid is too contaminated, etc.
As a rule, in the vast majority of cases (if no other reasons are identified), the problem can be solved by changing the oil in the automatic transmission and the automatic transmission filter. It may also be necessary to flush the valve body separately or flush the automatic transmission (for example, with diesel fuel) when changing the oil.
Finally, we note that knocks and vibrations are often caused by faulty or worn engine and automatic transmission mounts. In fact, the unit mounted on the supports “knocks” on the body or individual elements, vibration occurs, from which the box itself may not work correctly.
For this reason, it is also necessary to check the engine and gearbox mounts separately in order to eliminate possible causes of knocking in the automatic transmission at the initial stage. If you cannot localize the problem yourself, you should stop using the car and sign up for professional diagnostics, which are performed by car services that specialize in professional repair of automatic transmissions.
Elimination of crunches and knocks, restoring the operation of CV joints
How to find out which CV joint is crunching - we figured it out, now about the measures that should be taken to fix the problem, since it is undesirable to operate a car with problematic joints.
One of the disadvantages of CV joints is their non-repairability, that is, if the joint crunches, then it is worn out and requires replacement. The only thing that can be done is to “extend the life” of the node and delay its replacement.
Since the main reason for the appearance of crunches is dust and dirt, when they appear, you should immediately inspect all the anthers for damage. If none are found, we determine which CV joint is crunching using one of the above methods.
After identifying the problematic hinge, we try to extend its service life. To do this you need:
- Remove the drive from the car;
- Disassemble the CV joint;
- Thoroughly wash all components with gasoline, solvent or other means (white spirit, etc.);
- Apply new CV joint grease or equivalents (see above) and assemble the hinge;
- Install a new boot;
- Install the rebuilt drive on the car.
At the initial stage of wear, these measures are enough to get rid of the crunches, but they will eventually return (when the wear intensifies) and then the hinge will have to be replaced.
How to change gearbox oil
The work of changing the oil in the box is carried out as follows:
- Place the car on an overpass or over a pit, warm it up slightly so that the liquid is not viscous. Locate the oil drain plug on the bottom of the box.
- The unit has a rubber cap that needs to be cleaned along with the breather. After cleaning these parts from dirt, return them to their place.
- As soon as the preparatory work is completed, place the container, twist the plug with a wrench, and begin draining the transmission oil.
- The waste liquid will drain completely within half an hour.
- Screw on the plug, tighten it well, but do not strip the thread.
- Under the hood, find the transmission dipstick and remove it. In place of the probe, stretch a hose, at the other end of which a regular watering can or funnel is installed. Pour transmission oil into the box through the hose. On older units, the fill plug is located next to the drain plug.
After the work is completed, check the lubricant level with a dipstick and take a control measurement after 2-3 days. If necessary, add oil; if it becomes critically low, inspect the box for leaks.