Why does the car jerk?
There can be simply a huge number of problems due to which a car can drive jerkily (twitch), and they are individual for each car. These could be problems with the fuel system or transmission problems. Let's look at each of the reasons.
Fuel problems
Problems related to fuel supply to the engine.
Gasoline pump
All cars with injection engines are equipped with a fuel pump that pumps pressure into the fuel system. The normal operating pressure of the pump reaches 10 kg/cm³. Over time, the pump may lose its former power due to aging or dirty filters, fine and coarse fuel cleaning, which will undoubtedly lead to a loss of pressure and improper operation of the internal combustion engine.
Injectors
Another important indicator in the fuel system is the injectors. They spray fuel into the engine cylinder head, mixing it with air and feeding it into the combustion chamber. Over time, the injector nozzle becomes clogged with dirt and carbon deposits, which contributes to incorrect and even insufficient fuel atomization, which leads to uneven operation of the entire internal combustion engine.
Ignition problems
Problems associated with the formation of a spark in the engine.
Candles
To ignite the fuel mixture in a car, spark plugs are used, which produce sparks in the combustion chamber, thereby igniting the air-fuel mixture. Over time, due to the low quality of fuel, which is abundant in the vast expanses of the Russian Federation, spark plugs become covered with soot or, due to exposure to high temperatures, change their gap, which leads to improper operation of the internal combustion engine.
Wires
Spark plug wires also play an important role in engine operation; they transmit high voltage from the coil to the spark plug. The insulation of these wires is made of silicone and, under the influence of high temperatures and time, is subject to drying out and, consequently, cracks. High voltage, passing through a wire with a crack, can make its way to the body and thus does not even reach the spark plug, this is especially noticeable at high speeds and when the car is running under load.
Reels
The ignition module is the element that produces a spark to the cylinders; when it fails, the cylinders fail, but it often happens that the module can turn off due to temperature or load. By the way, the ignition module is no longer available in more modern cars; it was replaced by individual ignition coils, which helped get rid of wires and their problems. The IKZ is put directly on the spark plug and produces a spark for exactly one cylinder in which it is installed.
Transmission problems
Problems related to the gearbox, drives and wheels.
checkpoint
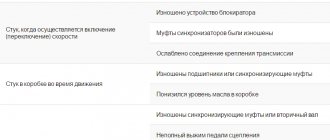
The gearbox is responsible for moving the car. Breakdowns are possible very often, especially if it is a rather complex automatic transmission, in which you have to frequently change the oil and monitor its quality. Failures in the gearbox can be in bearings, shafts, or clutches.
Drive
Car drives or cardans, which transmit rotation from the gearbox to the wheels, can also be the reason why the car jerks. Wear of constant velocity joints can create backlash between the gearbox and the wheel, which will lead to jerking. It’s the same with the cardan transmission, whether it’s on a crosspiece or a CV joint, its wear promises knocks and jerks.
Wheels
Wheels that have uneven wear, namely ellipse, can create jerks on the car when it moves at a certain speed, this is most noticeable on a flat road at a speed of 40 km/h.
Bad spark plugs and/or coils
Sharp jerks during acceleration can occur when something is wrong with the fuel ignition. A faulty spark plug or failed ignition coil will cause misfire in one of the cylinders. This may cause slight jerking, especially when you are trying to accelerate.
In addition, unstable idling will be additional confirmation of problems with the spark plug or coil.
Troit twitches and does not go when cold - logbook FIAT Ulysse Sweet cherry 2003 on DRIVE2
I’ve been fighting with the car for over a month now and still nothing... Symptoms lately: When you start it cold, the engine runs fine for 5-10 seconds, then it starts to twitch, the revs fluctuate, and it stalls. If you start it right away, you hear a pop from below, but if you hold it in the second position for 2-3 seconds, there is no pop. When driving, it stalls, if you turn it off, you start it right away, then it may start again, this happens haphazardly. It barely moves, again there is a popping sound from below - it seems like the fuel is burning out. you drive like this for 5-10 km, everything becomes normal, the car works like a clock, it drives calmly, only at xx there is a slight twitching at regular intervals. If it sits for a long time or in the morning everything repeats again. Diagnostics at the beginning of a permanent error in the camshaft sensor - changed it. I changed the spark plugs. Eliminated air leaks - installed new gaskets on the intake manifold, turned off the injectors that were not working. Changed the main lambda. Nothing remains as it was. I exclude injectors, since everything works the same on both gas and gasoline. Cleaned the throttle valve. The coil isn’t even a year old yet, the devil doesn’t know what to do. I’ll send it in for diagnostics again, let them figure it out...
PS: Does anyone have any thoughts?
What does the term "troit" mean?
Four-stroke internal combustion engines are installed on cars and trucks, the design and operation of which, as well as the most common malfunctions and their causes, we talked about in these articles:
- The car stalls at idle.
- The car starts and immediately stalls when cold - what could be the reasons.
- It stalls when hot.
The term “troit” appeared in the era of four-cylinder engines, when there were no power units with six or more cylinders. And it meant that one of the cylinders had stopped working, only three were functioning. As a result, the sound that the engine makes changes: instead of an even rumbling sound, some kind of dissonance appears.
In addition, the power of the power unit and the stability of its operation drop sharply, and fuel consumption, on the contrary, increases noticeably. Often such a power unit stalls when operating in various modes, including when the driver smoothly or sharply presses the gas pedal. Another manifestation of this defect is strong vibration with a jagged rhythm.
The problem with tripping can occur no matter what mileage the car has and what condition the internal combustion engine is in.
It doesn’t matter what mileage or condition the internal combustion engine is in, this problem can still occur.
Remember, if the car jerks, jerks and stalls due to any actions by the driver or for no apparent reason at all, then the source of the problem is always one of the cylinders that is not working normally. To ensure that the engine is running rough and to locate the faulty cylinder, do the following:
- On gasoline engines, remove the ends of the armored wires with the spark plug one by one. If after removing the wire the engine began to work worse, it means that this cylinder is working, but if the operation has not changed, then the defective cylinder has been found.
- On diesel power units, unscrew the glow plugs by first removing the common wire from them and placing it on a dielectric surface. When you find a defective cylinder, the engine will react in no way or very little to unscrewing the spark plug.
The movement of the motor is always accompanied by vibration, which can be felt with your hands or even seen
The mass air flow sensor (MAF) is faulty
If the MAF sensor sends incorrect information to the ECU, the air/fuel mixture may not be ok. It will either be too rich or too lean, causing the car to stall, jerk, shake and generally irritate the driver. The mass air flow sensor can be cleaned, but it usually requires replacement if such failures occur.
Dying fuel pump
Another part that can cause your car to jerk when accelerating is the fuel pump. If it is about to die, it may not be providing the optimal level of pressure to the fuel injection system. This will result in insufficient fuel delivery and jerking.
Why does the car engine shake during warm-up, and how to fix it?
Warming up the vehicle. This topic is as old as the World. Go to any car forum, and you will see that there are a lot of people writing about how their car behaves strangely while warming up. This article will also talk about warming up the engine, or more precisely about why it shakes for the first minute after turning on the ignition.
Every person who knows at least a little about cars knows that on a fully functional engine, the tachometer needle should lie at the lowest extreme point and not move. At the same time, the power unit should not make any extraneous sounds. But it happens that during normal warm-up the engine jerks. This lasts from 30 seconds to one minute.
It would seem that it won’t last long, and therefore there is no need to worry. But in reality, this causes tension for the owner of the vehicle. As practice shows, owners of cars produced by the Volkswagen concern face this problem more often than others.
Impact of jerks on the car
Whether jerking the car is beneficial or harmful is a rhetorical question. It’s the same as poking a person with a knife and asking if your health is improving. Any kind of jerking of the car is harmful, be it just a jolt when driving or a consequence of changing gears.
The main impact falls on the transmission unit and the engine part. First of all, the load on moving elements (bearings, switches, gears) increases. Each impact can deform, leave a crack or completely break any of these elements. Repairs can take a long time and cost the car owner a significant amount of money. That is why it is important to initially determine the reason why the car began to twitch and eradicate it.
Dirty throttle
Jerking when accelerating can also occur if the throttle valve is dirty. The car will lack power and may stall after you press the gas pedal once and then let it idle. You can use special products from auto stores to clean the throttle body, but be careful. Excessive throttle body cleaning in older vehicles can result in high engine idle speed due to wear on the throttle body. Sometimes minor repairs to this unit may be required.
Jerks when cold. Cured. — logbook of Toyota Avensis 2000 on DRIVE2
The mustachioed man is sick. But the point is this: I start up in the morning, warm up the engine a little (by the way, I always do this, regardless of weather conditions or the degree of lateness for work), and start driving. When accelerating in first and second gears, the engine begins to twitch. You release the gas a little - it accelerates smoothly, if you go too far - there's more twitching. And not a series, but one-time ones. When the engine reaches operating temperature, everything levels out and becomes as it should.
At the first appearance of symptoms, I strongly scolded myself for refueling at the PTC. I chalked it up to shitty low-quality gasoline. But everything happened again when we returned to our native Gazprom Benz.
Who thinks about this? Where to dig?
One of these days I’ll replace the spark plugs, although I think I installed new original ones in the spring. Update: cured The problem turned out to be in the old high-voltage wires. Today I temporarily installed the Russian equivalent and the problem went away. At the same time, I waved the candles before winter. Usatiy is back in action!
Thanks everyone for the advice. Although the car is far from the first, I really didn’t know where to dig!
Price: 3,000 ₽ Mileage: 249,000 km