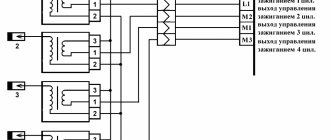
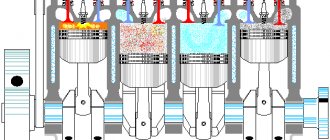
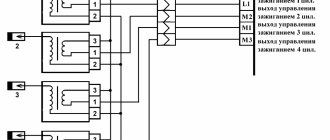
How does a mechanic diagnose trouble code P0304?
When diagnosing the P0304 trouble code, a mechanic will do the following:
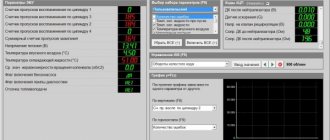
- Connects the OBD-II scanner to the vehicle's diagnostic connector and reads all stored error codes.
- Reviews all data stored in the ECM memory.
- Clear error codes from the ECM and test drive the vehicle to see if P0304 appears again.
- Inspects major ignition system components and associated wires for wear and damage, and performs a thorough check for leaks.
- Check the misfire counter in cylinder 4.
- Will check if there is an intake air leak or any problems with fuel injection.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Sometimes, when P0304 is detected, no symptoms are observed. The easiest thing to do in this case is just reset the code and see if it comes back.
If the problem manifests itself in the form of uneven idle or engine jerking, check all wiring and connectors leading to the cylinders. Next, it’s worth checking the spark plugs, wires, and coils.
In some cases, the cause is a failed catalytic converter. If you smell a rotten egg smell in your exhaust, the catalytic converter needs to be replaced. Faulty fuel injectors should also not be overlooked.
Random misfires may be due to lean fuel. This may be due to a vacuum leak in the intake manifold or air flowing past the airflow sensor. And also because of the exhaust gas recirculation valve stuck in the open position.
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0304
To properly diagnose a P0304 trouble code, a mechanic will need an advanced scanner that will not only read stored trouble codes, but also view sensor readings in real time. This data can help determine the root cause of the error.
The recommended service interval for replacing spark plugs is usually indicated in the vehicle's service book. Worn or damaged spark plugs are one of the most common causes of cylinder misfire, especially in high-mileage vehicles. If the vehicle is equipped with an ignition distributor with a cap and slider, these must also be replaced according to the vehicle manufacturer's recommendations. These components are mechanical and wear out over time. Spark plug wires are usually replaced when the spark plugs themselves are replaced.
Newer vehicles may be equipped with ignition coils, which typically last longer than the above components. To quickly determine whether the problem is a faulty ignition wire or coil, you must move the wire and/or ignition coil to a different cylinder. If the error code appears again, it is a sign that a worn or damaged ignition wire and/or coil is causing the cylinder to misfire.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0304 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi (Audi a4, Audi a6, Audi TT)
- BMW (BMW E46)
- Chery (Chery Tiggo)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Cobalt, Cruz, Silverado, Spark, S-10)
- Chrysler (Chrysler Voyager, PT Cruiser)
- Citroen
- Daewoo (Daewoo Nexia)
- Dodge (Dodge Durango, Caravan, Ram)
- Fiat
- Ford (Ford Mondeo, Mustang, Fiesta, Focus, Fusion, Expedition, F-150)
- Honda (Honda Accord, Odyssey, Pilot, SRV, Civic)
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Getz, Santa Fe, Solaris, Sonata, Tucson, Elantra)
- Jeep (Jeep Wrangler)
- Kia (Kia Rio, Sid, Sorento, Spectra, Sportage, Cerato)
- Lexus (Lexus gx470, rx300)
- Mazda (Mazda 3, Mazda 323, Mazda 6, Mazda cx7)
- Mercedes
- Mitsubishi (Mitsubishi Outlander, Karisma, Lancer, Montero, Pajero, L200)
- Nissan (Nissan Qashqai, Note, Tiida, X-Trail)
- Opel (Opel Astra, Vectra, Vivaro, Zafira, Corsa, Meriva)
- Peugeot (Peugeot Boxer)
- Pontiac (Pontiac Bonneville)
- Renault (Renault Duster, Logan, Megan, Sandero)
- Skoda (Skoda Yeti, Octavia, Superb)
- Ssangyong (Sanyeng Aktion, Kyron)
- Subaru (Subaru Legacy, Forester)
- Suzuki (Suzuki sx4)
- Toyota (Toyota Avensis, Camry, Corolla, Prius)
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Golf, Jetta, Caddy, Passat, Polo Sedan, Touareg, Tiguan, Transporter)
- VAZ 2105, 2110, 2111, 2112, 2114, 2115
- Volga Cyber
- Gazelle Business, umz 4216
- Lada Granta, Kalina, Niva, Priora
- UAZ Patriot
With fault code P0304, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common ones are: P0171, P0202, P0204, P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0305, P0306, P0308, P0354, P0402, P0420, P130A, P1399, C1201.
Signs of misfire
There are several different symptoms that you may experience when it comes to engine misfire. Here are some of the most common ones.
Uneven acceleration
When a misfire occurs, you may feel it as a slight or strong jolt coming from the engine. These misfires often occur while the engine is running under load and you are accelerating at high RPMs and high gears. Acceleration problems are a common sign that your engine is misfiring.
Unstable idle
Sometimes there will be passes at idle. The engine sensors receive incorrect readings and the air/fuel mixture becomes incorrect. This can result in a very rough idle. The revolutions can jump up and down, until the engine stops.
What's the result?
Taking into account the above, it becomes clear that in some cases it is not possible to immediately determine the cause of the misfire. It happens that a powerful spark is formed on the spark plugs, the timing is normal, the valves are adjusted, there are no comments on compression. Also, there is normal pressure in the fuel rail, and the fuel pump itself stably provides the specified performance.
As practice shows, in such cases the electrical circuits of the injectors are often to blame. For example, the engine may stall when cold, although after warming up the operation returns to normal. The complete opposite can be considered misfires after the internal combustion engine reaches operating temperature.
The fact is that it is enough that one wire to the injector “shorts”, as a result of which the injector works intermittently, and the problem itself manifests itself to a greater or lesser extent in certain operating conditions of the internal combustion engine (on a cold engine, after heating, under exposure to vibration when driving, etc.).
Finally, we add that this statement is also true in the event of malfunctions of the ECM sensors. As for spark plugs, during normal testing they may produce a good spark in the open air, but while the engine is running, there may no longer be such a spark. The fact is that spark plugs in the combustion chamber operate under high pressure conditions.
This means that the sparking process occurs when the piston compresses the mixture in the cylinder. To diagnose and check functionality, it is recommended to test the elements in a special device that creates conditions similar to the actual operation of spark plugs inside an internal combustion engine.
No matter what car you have, the reasons may be the same.
The scanner or on-board computer generated the error “multiple misfires” and the “check engine” light is on. At the same time, the motor shakes all over and works unstably and intermittently. Of course, continuing to move (if an error occurs along the way) is highly not recommended.
And even if you reset the error with a scanner or by removing the terminal from the battery, the check lamp will stop lighting for a while, but the instability of operation will remain. There may be several options here, so it’s not at all necessary to immediately get into the ignition system.
So let's take a closer look at what could have happened.
Before we figure out what the problem is, it is advisable for us to know how such an error occurs in the memory of the control unit. It is detected by a knock sensor, which compares the engine knock readings with the readings of the rough road sensor. The control unit “knows” at what moment and in which cylinder the process of ignition of the working mixture occurs.
Therefore, he can determine with 100% probability a misfire in a specific cylinder. If there is no indication of any one cylinder, namely multiple misfires, then it is quite possible that the mechanical part of the engine is to blame.
Yes, yes...mechanics can be the cause of such a fault code. And it would be more correct to say “multiple misfires.” That is, it is not correct to blame the ignition system for everything.
The valves may simply be to blame (burnt out or pinched, incorrectly adjusted). But the simplest reason is, of course, the spark plugs, unscrew the spark plugs and check on the bench. If there is no stand, then at least visually inspect for the presence of a breakdown. It is certainly rare for several candles not to work at once, but not an exception. Moreover, knowing the quality of this product. If the spark plugs are turned out, immediately check the compression in all cylinders. It is advisable that the spread does not exceed +-1bar. If in any cylinder the compression differs by more than 2, then pour 10 grams of engine oil into this cylinder and measure the compression again. If it rises to the level of the other cylinders, the cause is the oil scraper rings. If it has increased slightly, then it is still the valve.
Another “banal” reason for such an error is high-voltage wires. Which is also unlikely for several wires to fail at once. But I met this on a Nexia and an old six, because of the wires it completely stalled while driving. You can check the wires with a simple tester by measuring their resistance. Typically it should be within a few kOhms. It varies on different cars.
On old Nexias, high-voltage wires are located directly above the hot exhaust manifold. Therefore, even despite the metal protection, they constantly dry out.
RIDE IN TEST MODE
- Connect the handheld diagnostic tool to the DLC3.
- Turn the ignition switch to ON (IG) and turn on the handheld scan tool.
- Record the DTC and freeze data.
- Switch the ECM from normal diagnostic mode to active diagnostic mode using a handheld scan tool.
- Count the number of misfires for each cylinder (CYL ##1-4) while the engine is idling. If the number of misfires is displayed for at least one cylinder, skip the next test drive.
- Drive the vehicle several times at engine speed and engine load equal to the values for MISFIRE RPM and MISFIRE LOAD in DATA LIST mode. HINT: To store misfire related DTCs, the vehicle must be driven for the amount of time specified in the table below and the MISFIRE RPM and MISFIRE LOAD values are maintained in DATA LIST mode.
Engine speed Duration Idling 3 minutes 30 seconds or more 1000 3 minutes or more 2000 1 minute 30 seconds or more 3000 1 minute or more - Check for misfire by reading DTCs and freeze data. HINT: Do not turn the ignition switch off without recording the stored DTCs and freeze data. When the ECM switches to normal diagnostic mode (default), all stored DTCs and freeze data are cleared.
- Record the DTC, freeze data, and number of misfires.
- Turn off the ignition and wait at least 5 seconds.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0304 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light). It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in the ECM memory as a malfunction).
- The engine stalls or has trouble starting.
- Floating speed, as well as attempts to stall at idle.
- Jerking/misfire at idle or under load.
- Poor speed gain.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Reduced engine power.
- Smell of fuel from the exhaust.
This malfunction is considered serious and must be corrected as soon as possible. Because prolonged driving with a misfire can cause costly damage to the engine and catalytic converters.
What does error P0300 mean?
The code in question is directly related to malfunctions on the part of the ignition system.
Error P0300 indicates the presence of misfires in the ignition system, that is, the ignition order is disrupted.
Also, such a malfunction can be described as random multiple misfires that were detected in the ignition system. This is if we take the translation of the English message as a basis. A literal translation yields a similar explanation. This problem is expressed in the form of code P0300 when scanning the memory of the control unit.
If multiple random leaks are detected in the system, the air-fuel mixture ignition system will not be able to function normally. The P0300 error that appears indicates this, helping the driver roughly understand what to look for and in which area to look for a fault.
Error P0300 on some cars varies from 0300 to 0312.
This is due to the fact that certain electronic control units can independently detect in which specific cylinder misfires are recorded. Depending on the final digit in the error code, the motorist understands which cylinder should be entered.
For example, if the engine has 6 cylinders, then the error will vary from 0300 to 0306. If code 0305 appears, then the problem is, accordingly, in the fifth cylinder.
But keep in mind that not all computers determine the exact location of the malfunction, and therefore the diagnostic scanner screen may simply display code P0300. Then, through additional checks, you will have to determine which of the cylinders has leaks.
Description and meaning of error P0300
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic powertrain code. It is considered general because it applies to all makes and models of vehicles (1996-newer), although the specific repair steps may vary slightly depending on the model. So this engine code article applies to Chevrolet, Ford, Nissan, Toyota, Dodge, Honda, GMK, etc. Basically this P0300 code means that the car's computer has detected that all of the engine's cylinders are not firing properly. Diagnostic code p0300 indicates random or multiple misfire. If the last digitis is a non-zero number, it corresponds to the cylinder number that is misfiring. For example, code P0302 will tell you that cylinder number two is faired. Unfortunately, the P0300 doesn't tell you specifically which cylinder(s)/aremis are firing, nor why.
Subaru - Misfire Detected
The cars that came to us already )) had new spark plugs, coils and washed injectors. And in theory this is correct, repairs begin with this.
We, in turn, began the repair by checking the power and pulses on the coils and injectors.
And we ended up repairing the engine ECU, in each case, because the wires and connectors were intact.
Apparently a typical, but completely curable malfunction. Moreover, cars with 6-cylinder engines suffer from it:
EZ30D
- 2000–2004 Subaru Outback H6 2000–2002 Subaru Legacy GT30 2000–2002 Subaru Legacy Lancaster 6
EZ30R
- 2003–2009 Subaru Legacy 3.0R 2005–2009 Subaru Outback 3.0R 2006–2007 Tribeca
EZ36D
- 2010-current Subaru Legacy 2010-current Subaru Outback 2008-2014 Subaru Tribeca
How does error P0300 affect engine performance?
Before diagnosing, the driver can easily determine from the vehicle's behavior that the diagnostic scanner will indicate error P0300, P0301, or another of the series. Symptoms of engine operation with the error in question are characteristic of a misfire problem:
- The engine shakes violently at low speeds and at idle;
- When accelerating, the car “throws and jerks”;
- Fuel consumption increases significantly;
- There may be problems starting the engine;
- Craving decreases.
If these symptoms occur and the Check Engine light is on on the instrument panel, you can rest assured that the diagnostic scanner will show one of the P0300 family of errors.