If necessary, dismantling the ShPG engine can be done on the car without removing the engine.
For complete information on dismantling and disassembling and assembling the ShPG, see engine disassembly
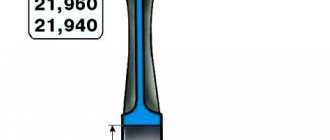
Main dimensions of the connecting rod and piston group
Piston and connecting rod markings
1 – arrow for orienting the piston in the cylinder; 2 – repair size; 3 – piston class; 4 – hole class for piston pin; 5 – connecting rod class based on the hole for the piston pin; 6 – cylinder number
Places where it is allowed to remove metal when adjusting the mass of the upper and lower connecting rod heads (to the specified dimensions)
Classes of connecting rods based on the weight of the upper and lower heads
| Mass of connecting rod heads, g | Class | Marking color | |
| top | bottom | ||
| 186+2 | 519+3 | A | white |
| 525+3 | IN | blue | |
| 531+3 | WITH | red | |
| 190+2 | 519+3 | D | black |
| 525+3 | E | violet | |
| 531+3 | F | green | |
| 194+2 | 519+3 | G | yellow |
| 525+3 | N | brown | |
| 531+3 | I | orange | |
We carry out the work on an inspection ditch or a lift.
Remove the engine oil pan (see here).
Using a 14mm socket, unscrew the two nuts securing the connecting rod cover (the piston must be at BDC).
Using a hammer with a plastic head (or a hammer with a soft metal head), apply light blows to the side surfaces of the cover to loosen its seat on the connecting rod bolts.
Remove the connecting rod cover.
Move the connecting rod up.
Using the wooden handle of a hammer against the connector of the lower head of the connecting rod, push the connecting rod upward until the piston exits the cylinder.
. and remove the piston and connecting rod assembly.
Similarly, we dismantle the pistons with connecting rods of other cylinders.
We install the ShPG in the reverse order (see also Engine Overhaul). (
Tuning options
When refining a Niva engine, a new crankshaft, cylinders and piston system are most often installed.
As a result, the car receives excellent speed characteristics and cross-country ability. There are two types of Niva engine tuning. The first includes chip tuning, and the second includes mechanical modification of the element. Chip tuning includes software upgrades, and is carried out only on new, fuel-injected SUVs. It includes flashing the control unit settings. It is performed by specialists quite quickly - within half an hour, but requires knowledge of software and additional electronic equipment.
Mechanical modifications are possible on any Niva, and this is the most popular type of tuning of a car’s power plant. With its help, you can significantly improve the technical characteristics of vehicles, and it is based on making some changes to the vehicle systems.
Pistons VAZ 21213, f 84.0 mm, offset 2.0 mm (set of 4 pieces)
Article: FR-00001106
Pistons for VAZ 21213, 21214, 2123 engines. The piston size is 84.0 mm, the hole for the 22 mm piston pin is offset by 2.0 mm. Compression height 35.9 mm. Designed for installation with an 84 mm crankshaft. The engine capacity in this configuration will be 1862 cc.
Specifications:
| Dimensions in packaging (LxWxH), mm | 180x170x90 |
| Weight, kg | 2 |
Also interesting: Turbocharging on the Niva’s fuel-injected engine
Main characteristics of internal combustion engine 21213
| Volume, cm 3 | 1690 |
| Main fuel: | gasoline AI-92 |
| Max. power, l. With. | 83 (at 5200 rpm) |
| Max. torque, Nm | 127 (at 3000 rpm) |
| Cylinder block configuration: | in one row |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Max. speed, km/h | 153 |
| Acceleration time to 100 km/h, sec. | 17 |
| Combined fuel consumption | 11,5 |
| Econorm | Russia-83 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 82 with deviation up to 0.05 |
| Piston stroke, mm | 80 |
| Repair dimensions of pistons and cylinders, mm: | |
| first repair (marking on the piston - triangle, on the rings - 40) | 82.4 |
| second repair (marking on the piston - square, on the rings - 80) | 82.8 |
| Repair measurement of the diameter (for boring) of the crankshaft supports | 54.52 with deviation up to 0.013 |
| Compression ratio | 9,4 |
| Supply system | two-barrel carburetor |
| Cooling | liquid |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Presence of liners in cylinders | not provided for by design |
| Head material | aluminum alloy |
| Resource before major overhaul, km | 80,000 (actual ≈ 120,000 km) |
| Number of bars | four |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Max. speed, rpm | 8000 |
| Weight, kg: | 117 |
Home Cars - VAZ VAZ-21213 (Niva all-terrain vehicle) - maintenance and repair manual
search site copyright holders
content .. 11 12 19 ..VAZ-21213 (Niva). Connecting rod and piston group2.8.1. Features of the device GENERAL INFORMATION Main dimensions of the connecting rod and piston group Marking of the piston and connecting rod |
| 1 – arrow for orienting the piston in the cylinder; 2 – repair size; 3 – piston class; 4 – hole class for piston pin; 5 – connecting rod class based on the hole for the piston pin; 6 – cylinder number |
Places where it is allowed to remove metal when adjusting the mass of the upper and lower connecting rod heads. Piston
The piston is cast aluminum.
During manufacturing, the weight of the pistons is strictly maintained. Therefore, when assembling the engine, it is not necessary to select pistons of the same weight group. According to the outer diameter, the pistons are divided into five classes (A, B, C, D, E) every 0.01 mm. The outer surface of the piston has a complex shape. It is conical in height and oval in cross section. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the piston diameter only in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin, at a distance of 55 mm from the piston bottom. Based on the diameter of the hole for the piston pin, pistons are divided into three classes (1, 2, 3) every 0.004 mm. The classes of piston diameters and holes for the piston pin are marked on the bottom of the piston (see Fig. Marking of the piston and connecting rod). Repair size pistons are manufactured with an outer diameter increased by 0.4 and 0.8 mm. The bottoms of these pistons are marked in the form of a triangle or square. The triangle corresponds to an increase in the outer diameter by 0.4 mm, and the square - by 0.8 mm. The arrow on the piston crown shows how to properly orient the piston when installing it into the cylinder. It should be directed towards the camshaft drive. Piston pin
The piston pin is steel, hollow, floating type, i.e.
rotates freely in the piston bosses and connecting rod bushing. The pin is secured in the piston by two steel retaining rings. According to the outer diameter, the fingers are divided into three classes every 0.004 mm. The class is marked with paint on the end of the finger: a blue mark is the first class, a green mark is the second class, and a red mark is the third class. Piston rings
Piston rings are made of cast iron.
The upper compression ring has a chrome-plated barrel-shaped outer surface. The lower compression ring is scraper type. Oil scraper ring - with chrome-plated working edges and with an expansion coil spring (expander). Repair size rings are marked digitally “40” or “80”, which corresponds to an increase in the outer diameter by 0.4 or 0.8 mm. Connecting rod – steel, forged. The connecting rod is processed together with the cover and therefore they are individually non-interchangeable. To avoid mixing up the caps and connecting rods during assembly, they are marked with number 6 (see Fig. Marking of the piston and connecting rod) of the cylinder in which they are installed. When assembling, the numbers on the connecting rod and cap should be on the same side. A steel-bronze bushing is pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod. Based on the diameter of the hole in this bushing, the connecting rods are divided into three classes every 0.004 mm (the same as the pistons). The class 5 number is stamped on the upper head of the connecting rod. Based on the mass of the upper and lower heads, connecting rods are divided into classes (see table. Classes of connecting rods based on the mass of the upper and lower heads), marked with paint on the connecting rod rod. Connecting rods of the same weight class must be installed on the engine. The weight of the connecting rods can be adjusted by removing metal from the bosses on the heads to a minimum size of 16, 5 and 35.5 mm (Fig. Places where metal can be removed when adjusting the weight of the upper and lower connecting rod heads). Classes of connecting rods based on the weight of the upper and lower heads
| Mass of connecting rod heads, g | Class | Marking color | |
| top | bottom | ||
| 186 ± 2 | 519 ± 3 | A | White |
| 525 ± 3 | B | Blue | |
| 531 ± 3 | C | Red | |
| 190 ± 2 | 519 ± 3 | D | Black |
| 525 ± 3 | E | Violet | |
| 531 ± 3 | F | Green | |
| 194 ± 2 | 519 ± 3 | G | Yellow |
| 525 ± 3 | H | Brown | |
| 531 ± 3 | I | Orange |
VAZ-21213 (Niva). Selection of piston to cylinder
GENERAL INFORMATION
The calculated gap between the piston and cylinder (for new parts) is 0.025–0.045 mm. It is determined by measuring the parts and is ensured by installing pistons of the same class as the cylinders. The maximum permissible gap (if parts are worn) is 0.15 mm. If a used engine has a gap exceeding 0.15 mm, then it is necessary to re-select the pistons to the cylinders so that the gap is as close as possible to the calculated one. Spare parts include pistons of classes A, C, E. These classes are sufficient to select a piston for any cylinder during engine repair, since pistons and cylinders are divided into classes with a slight overlap of sizes. For example, a class C piston may be suitable for class B and D cylinders.
content .. 11 12 19 ..
Oil pump work
Due to the low engine efficiency and low wear resistance, mechanical tuning of the Niva 4x4 engine is almost mandatory. Such work is called work to change the geometry of the power plant. You should start modifying the power plant by upgrading the carburetor. We do the following:
- We change jets with an indicator of 1 kam to a jet with an indicator of 2 kam;
- Renewing the accelerator pump nozzle.
If there is dirt or carbon deposits in the carburetor, we clean it manually. To do this we need a rag, gasoline and physical strength. If the dirt is very stubborn, a high-pressure cleaner or other device designed for washing the car will help. You can also use special “baths” to remove dried dirt from parts. In this way, the fuel supply to the gas distribution mechanism can be significantly improved.
If you are the owner of an injection Niva, then independently modifying the injector is unacceptable. Only a professional with knowledge of software can perform such tuning of the Niva engine.
Lubricant supplied through the oil pump extends engine life. To improve the performance of the oil pump when tuning the Niva engine, you need to take another pump and cut off part of the housing with the parting plane from it. The thickness of this “pancake” should be about 11 cm. Using milling, cut off the excess and leave a thickness of 10 mm.
Next, do the following to remove chamfers on the edges of the teeth:
- We compress, that is, remove, the drive gears.
- We trim one of the gears by 0.75 mm on each side.
- We cut the second gear to 11.5 mm (after trimming).
- We repeat the operation with the remaining gears (driven).
Let's start working on the body. To do this we do the following:
- We release the driven gear axis from the housing.
- We form a longer axis from the drive roller.
- We insert the resulting axle into the body.
- We press the narrow gear onto the second drive shaft.
- Press on the wide gear.
- We fix the wide driven gear in the housing.
- We install a narrow gear into the housing.
This sequence will prevent the gears from turning relative to each other. You can also improve the oil receiver of the Vase by cutting it a centimeter from the bottom. After this, we adjust the end gap and connect the entire structure with bolts.
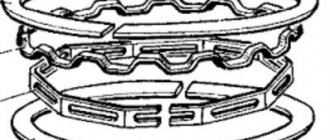
4.8.5.6 Checking the clearances between the piston grooves and piston rings
Checking the gap between piston rings and grooves
3 – set of feeler gauges
Location of piston rings in the piston grooves of the engine mod. 2106
2 – upper compression ring;
3 – lower compression ring;
4 – oil scraper ring
Tool for removing and installing piston rings
Check the height gap between the grooves and rings as shown in Fig. Checking the gap between the piston rings and grooves by inserting the ring into the corresponding groove.
Check the gap in the piston ring lock with a set of feeler gauges, inserting the rings into a gauge having a hole diameter equal to the nominal diameter of the ring with a tolerance of ± 0.003 mm. If there is no gauge, it is possible to check the gap. by inserting the piston ring into the cylinder where it will work, and pushing it with the piston to a depth of 20–30 mm from the bottom edge of the cylinder.
The gap should be between 0.25 and 0.4 mm for all rings. If the gap is insufficient, the joint surfaces should be filed down, and if it is too large, the rings should be replaced.
Heights and end installation gaps of piston rings
Piston ring kits
As spare parts, rings are supplied as a set for one engine.
Rings of nominal size are used when replacing worn rings for cylinders of nominal size. To reduce the break-in period of rings in cylinders that have already been running, compression rings that are not coated with chrome are installed in the upper grooves of the pistons.
Rings with an increased diameter are installed in cylinders bored to repair size, or they are used to replace worn rings in such cylinders.
The rings are installed in the piston grooves so that the groove on the outer surface of the second (scraper) ring faces down, and the chamfers on the outer surface of the oil scraper ring face up (Fig. Location of piston rings in the piston grooves of the engine mod. 2106 ).
If this condition is not met, oil may penetrate through the rings into the cylinder, which will lead to carbon formation on the walls of the combustion chamber, smoky exhaust from the muffler and increased oil consumption. Putting rings on the piston, as well as removing them, should only be done in a special device or with special pliers (Fig. Device for removing and installing piston rings ), ensuring the same bending stress around the circumference of the ring.
After replacing the piston rings, the vehicle speed should not exceed 60 km/h within 1000 km.
Source
Repair dimensions of cylinders and pistons of the VAZ 21213 engine during major repairs
| Repair cylinder size, mm | Piston and cylinder class | Piston diameter, mm | Cylinder diameter after boring, mm | Cylinder diameter after honing, mm |
| 1 repair | ||||
| 82,4 | A | 82,34-82,35 | 82,37-82,38 | 82,40-82,41 |
| B | 82,35-82,36 | 82,38-82,39 | 82,41-82,42 | |
| C | 82,36-82,37 | 82,39-82,40 | 82,42-82,43 | |
| D | 82,37-82,38 | 82,40-82,41 | 82,43-82,44 | |
| E | 82,38-82,39 | 82,41-82,42 | 82,44-82,45 | |
| 2 repairs | ||||
| 82,8 | A | 82,74-82,75 | 82,77-82,78 | 82,80-82,81 |
| B | 82,75-82,76 | 82,78-82,79 | 82,81-82,82 | |
| C | 82,76-82,77 | 82,79-82,80 | 82,82-82,83 | |
| D | 82,77-82,78 | 82,80-82,81 | 82,83-82,84 | |
| E | 82,78-82,79 | 82,81-82,82 | 82,84-82,85 | |
Refinement of the gas distribution mechanism
After replacing the jets and accelerator pump, you can proceed to the second stage of tuning the VAZ-2121 engine. It includes modification of the gas distribution mechanism (GRM), namely, an increase in the diameter of the valves with their subsequent sealing. Such tuning of the Niva 2121 engine will increase the power of the power plant by almost ten percent.
It makes sense to replace the pusher (with a new one with a diameter of at least 1 mm) during the modification of the Niva engine. Work is being done to increase the pusher wells of the intake and exhaust channels. The result of such modification will be especially good for the Niva 4x4.
Subsequent work concerns the replacement of injectors and the control unit itself. Tuning the VAZ-2121 engine will be incomplete unless the standard crankshaft is replaced with an advanced modification, which will significantly increase the power of the power plant. This is due to the increase in piston stroke. It is also recommended to replace the piston rings with new ones.
Such tuning repairs are capable of:
- increase smoothness;
- reduce wear of parts;
- increase power.
Chip tuning engine Chevrolet Niva or 21214
There is no point in writing about this for a long time because the Niva chip is useless, the atmospheric engine cannot be stirred up with a chip, and all the rave reviews are nothing more than an attempt to justify a waste of money, let’s move on.
Read news about the new Niva
- Increasing Chevrolet Niva engine power: description, characteristics, options
- VAZ 2121 Niva: description, engines, automatic transmission, technical characteristics
- Engine VAZ-2121 technical characteristics. Lada VAZ-2121
- Niva Lynx 4x4: the better the simple Niva "
- Installation of kenguryatnik on Niva 2121
- All-terrain vehicle fracture 4x4: photo of step-by-step assembly video of a trip on an all-terrain vehicle
- All-wheel drive Renault Duster 4x4, operation diagram, cross-sectional photo of the gearbox with clutch - Dustershop77
- UAZ-469 Military repair manual
Weaknesses of the VAZ 21213 power unit
- Water pump;
- Engine, manual transmission and transfer case oil seals;
- Generator;
- Starter;
- manual transmission;
- Valve cover gasket;
- Cooling system pipe connections;
- Radiator;
- Thermostat;
- Expansion tank;
- Vacuum brake booster.
The water pump (pump) is characterized by frequent failures on new cars after 2,000 km.
Due to poor quality, oil seals require more frequent replacement than required according to the operating manual.
Specifications
The Niva engine has high technical characteristics, and the car itself has increased cross-country ability, since there is a 4x4 option. Over the history of production, the VAZ 2121 has had different engine versions installed, from a carburetor version to an injector and even a diesel version.
So, let's look at the main characteristics of modifications to the Niva power unit:
VAZ 2121
| Name | Index |
| Engine capacity | 1.6 liter (1580 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Fuel | Petrol |
| Injection system | Carburetor |
| Power | 80 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 12.2 l/100 km |
| Cylinder diameter | 79 mm |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
VAZ 21213
| Name | Index |
| Engine capacity | 1.7 liter (1690 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Fuel | Petrol |
| Injection system | Carburetor |
| Power | 82 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 11.0 l/100 km |
| Cylinder diameter | 82 mm |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
VAZ 21214
| Name | Index |
| Engine capacity | 1.6 liter (1580 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Fuel | Petrol |
| Injection system | Injector |
| Power | 83 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 8.4 l/100 km |
| Cylinder diameter | 82 mm |
| Econorm | EURO-4 |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
VAZ 2131
| Name | Index |
| Engine capacity | 1.8 liter (1779 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 16 |
| Fuel | Petrol |
| Injection system | Injector |
| Power | 94 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 9.2 l/100 km |
| Cylinder diameter | 82 mm |
| Econorm | EURO-4 |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
Engine XUD9SD manufactured by Peugeot
| Name | Index |
| Motor type | Diesel |
| Engine capacity | 1.9 liter (1905 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Fuel | Diesel fuel |
| Power | 75 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 7.1 l/100 km |
The power units of the VAZ 2121 were equipped with 4-speed manual and 5-speed manual transmissions.
Causes of oil waste
Well, in general, this is the second question. First you need to find out where the oil goes from the engine if the leak is not visible from the outside? The debate about the natural waste of oil has been going on for many years. There is only one conclusion - if you don’t want the engine to “eat up” the oil, don’t fill it at all! The point is this. The service life of the engine is ensured by good lubrication, and even more so by the lubrication of the piston rings and, as a consequence, the surface of the cylinders in the form of an oil film. So much for natural insanity.
When designing a modern engine, oil loss due to waste is initially 0.1-0.3% of the volume of fuel used . In addition, with different types of operation (river transport, cars, generators), oil burn readings vary significantly! Well, since the engine of the VAZ 21213 is frankly “weak” and, due to the specifics of the vehicle’s operation, operates under increased loads, the passport parameter for oil waste does not last long, after which oil consumption begins to increase significantly. Why? In addition to the mentioned natural burnout, there are several other reasons:
- Oil release through the internal combustion engine ventilation system. The wear of the CPG (cylinder-piston group) directly depends on the pressure of the crankcase gases, whose speeds increase, which contributes to a greater extraction of oil into the atmosphere (in modern cars for “afterburning”);
- A trivial leak in places where engine components do not fit tightly.
Attention: In general, if you see all of the above defects in your car. If you are convinced that the CPG is worn out (by measuring the compression - at least 8 kgf), then replacing the piston rings of the VAZ 21213 is the most economical option for you. In case of such wear of the internal combustion engine, a good owner will, among other things, check the wear of the cylinders, connecting rod liners and, if necessary, replace not only them, but also the entire piston group with valve stem seals. Everything here is limited only by the price of the repair issue.
Basics of overhaul
Engine overhauls, except for diesel engines, are carried out typically for all models of Lada power units. So, if you do not take into account the 2131 model with a 16-valve engine, then all versions have a timing chain instead of a belt.
Taking into account the design and manufacturer's manuals, the Niva has a low engine life compared to passenger versions of VAZ cars. So, on average, the mileage before major repairs will be 100-120 thousand km.
Therefore, in order not to spend extra money, many vehicle owners try to repair the engine on their own. Considering the weight of the engine, you will naturally need helpers, at least to remove the engine from the car.
So, what manipulations need to be performed to carry out a major overhaul of the power unit.
- Removing the engine from the car. To carry out this operation, you will need to disconnect all auxiliary systems and components.
- Disassembly and diagnostics of the motor. At this stage, the head, pan and valve cover are separated from the cylinder block. Also, you will have to remove the piston mechanism and crankshaft. Don't forget about disassembling the cylinder head.
- Next comes the process of boring the cylinder block, which is carried out on a special boring and honing wall. Also, the surface of the block is often polished.
The size of the piston group for VAZ 2121 engines with a standard piston size of 82 mm:
| Repair | Size |
| Standard | 82.0 mm |
| 1 | 82.5 mm |
| 2 | 83.0 mm |
| 3 | 83.5 mm |
| 4 or more | Block sleeve (installation of sleeves of standard size 82.0 mm) |
- Next, you need to grind the crankshaft to the appropriate size. Also, at this stage, the liners, both main and connecting rod, are tried on.
Decarbonization of piston rings
If the engine starts to smoke, there is a possibility that there are rings stuck in the piston grooves. Nowadays, there are many different modern means for decarbonizing piston rings, and many drivers use them to restore engine performance. Among the most popular compositions are:
Motorists believe that if the engine starts smoking, you need to use a decarbonizer, and the engine will work as before, without oil consumption and without smoke. Indeed, sometimes these remedies help, but only in cases where the motor has stood motionless for a long time (for example, after winter), and moisture has accumulated in it. If the car is subject to long-term preservation (put in a garage for winter storage), you should remove the spark plugs and pour oil into the cylinders, and plug the spark plug holes with plugs. With such prevention, the spark plugs will not become damp and rust will not accumulate on the sleeves.
But if, after all, a forgetful car owner has not taken preventive measures, you can use a decarbonizer. We get rid of rust in cylinders as follows:
- pull off high-voltage wires;
- unscrew all spark plugs;
- rotate the crankshaft so that all pistons are in the middle position;
- pour 45 ml of liquid into each cylinder, install spark plugs;
- leave the cylinders to “soak” for 6-7 hours;
- why do we turn out the spark plugs, turn the starter a few revolutions so that all the dirt flies out of the engine;
- We put the removed parts back in place and start the engine. At first it may smoke a lot, but then the smoke will go away.
Car owners should remember that decarbonization is not a panacea for all ills, and if the piston rings are worn out, then only replacing them will help.
Engine tuning
Tuning a VAZ 2121 engine is an art. Since the car has the characteristics of an SUV, the engine is tuned accordingly. The air filter duct is installed as high as possible, and the motor from below is protected by a special tray, the purpose of which is not to allow water to pass through.
So, the modification of the Niva’s power unit is designed to increase cross-country ability and traction capabilities, since the vehicle is mainly designed for operation on rough terrain. So, many car enthusiasts bore the power unit in such a way as to add not only horsepower, but also traction.
As practice shows, tuning of VAZ 2121 engines and its modifications is carried out by tuning studios that are well versed in which unit needs to be modified.
Also, in the process of refinement, the ignition system and fuel injection are being modernized. For carburetor engines, an additional carburetor can be installed to increase the amount of fuel entering the combustion chamber.
For injection versions of engines, chip tuning is carried out, which can be aimed at increasing power or the balance between consumption and traction capabilities. Many car enthusiasts install additional sensors that help control the operation of the power unit.
Maintenance
For normal operation, engine 21213 should be serviced within the specified periods:
- 10,000 km - change the oil along with the filter;
- 20,000 km – checking the functionality of the thermostat, updating the cabin filter;
- 30,000 km – replacement of the fuel and air filters;
- 60,000 km – spark plugs and batteries are renewed and the crankcase ventilation is cleaned;
- 100,000 km – reinstallation of the oxygen sensor;
- 200,000 km - the timing chain may need to be replaced.
Despite the fact that the internal combustion engine device is copied from longitudinal engines with a much higher service life, it is used on an SUV with non-disconnectable all-wheel drive, so the components wear out more intensively.
Also interesting: Dynamic vibration damper @ Niva 4×4