Published: 01/28/2021
- Thermal clearance of piston rings
- Gap measuring device
- Rating for various ICE Lifan engines
- Functions of piston rings
- Decarbonization of piston rings
- Selection of piston rings: dimensions and materials of manufacture
- Signs of piston ring wear
- Thermal clearance requirements
- Why are there three rings on the piston?
- How to properly change and install piston rings? Detailed review
- Let's sum it up
Thermal clearance of piston rings
PCs are spring discs with one cut - when installed on the piston, they expand, and in the sleeve they are pressed tightly against its walls. In order to achieve maximum compression of the working mixture, the cylinder walls must be as smooth as possible (without defects), and the shape of the internal cavity must be perfectly round. On the piston, the PCs are placed in special grooves, moreover, they are not seated tightly, and on a cold piston they move freely in the grooves.
Piston rings have thermal clearances:
- between PC and groove;
- at the junction.
The clearances must be certain; if they are larger or smaller than the required value, the piston group will quickly fail. One should take into account the fact that when heated, the metal expands, and if the thermal gap of the PC is too small, the piston group will begin to overheat. With large gaps, tightness is not ensured and power losses occur.
For passenger cars, as a rule, the following clearances are established:
- between the grooves and the PDA - from 0.02 to 0.08 mm (for the upper ring the gap should be slightly larger);
- between grooves and MPC – from 0.05 to 0.06 mm;
- at the junction - from 0.25 to 0.5 mm.
As wear occurs, the gaps in the PC increase, and they should not exceed:
- between the ring and the groove – 0.15 mm;
- at the junction – 1.0 mm.
What should it be like?
The piston has two types of rings: compression (prevent burnt gases from passing through) and oil scraper (remove excess oil from the cylinder walls). By design, they are not solid, but have a cut that allows the rim not to jam when heated. The cut also promotes elastic pressing against the cylinder walls. The presence of thermal space in the locks plays a very important role in the operation of the rings and cylinder. Its permissible range is from 0.3 to 0.6 millimeters. Failure to comply with the range may result in missing or severe damage to the cylinder.
An oblique cut is much better valued. Since the pressure on the walls occurs more evenly due to the fact that its edges are slightly thinner.
It is useful to know about the gaps in the locks. Sometimes mechanics try to make the thermal space in locks as small as 0.2 millimeters. This often leads to scoring of rings and cylinders. And this is natural, since when the part is heated, the space in the lock becomes smaller (or completely absent) and it crashes into the walls of the cylinder.
The simplest lock with a straight cut has one drawback - its ends have high pressure on the cylinder, or rather on its walls. This leads, first of all, to oil leakage and premature wear of the walls.
In order to summarize the above, we list what characteristics the piston rings should have and what the thermal clearance of the piston rings should be:
- Temperature regulation. This is one of the most important functions, since a large mass of heat that is absorbed by the piston during the combustion period will be removed. If there is no such heat removal, the piston will melt in a matter of seconds.
- Pressure. The main function is to compact. And full implementation of this characteristic is possible only with appropriate pressure. When pressure appears, it affects the piston circles, and they, in turn, are pressed against the cylinder walls. In order for the pressure to be uniform, uniform distribution and correct clearance in the piston rings are necessary.
- Reliability and oil supply - oil scraper. They have two oil scraper bridges, which are responsible for the required amount of oil supply in the amount of 1-2 microns. If the oil is supplied correctly, then its consumption is not high, as is the fuel consumption. In this case, the wear rule will be observed as much as possible and the service life will increase.
As a result, I would like to wish every motorist and driver, regardless of whether he has diesel or gasoline, to check on his own or contact specialists in this matter. Especially when it comes to cars with high mileage and more than 5 years of constant driving.
Gap measuring device
How to properly use a micrometer to determine the size of the piston ring gap? It is necessary to measure the diameter of the piston in several places around its circumference. Then measure the width of the grooves using special feeler gauges.
After measurements, the average value of the gaps should be calculated. If the indicators differ from each other, then the piston should be replaced, if the indicators are the same, then everything is in order.
Fourth
, measuring gaps in piston ring locks. This measurement can be performed either using a special frame or with a simple cylindrical object. Indicators and parameters of the gap should be measured using a special probe. The parameters of the gap suitable for use have the following proportions - 0.25-0.45 mm.
In this case, an error of 1.0 mm may be allowed, which may arise as a result of wear of the part. If the gap size is higher than normal, the piston must be replaced. If the measured gap is less than the specified parameters (0.25 mm), then all that is needed is to simply sharpen the ends to the desired size.
Fifthly
, measuring the gap between pistons and cylinders. This measurement is based on establishing a correspondence between the already measured diameters of the piston and cylinder. Here the standard values are from 0.025 to 0.045 mm, with possible wear of 0.15 mm.
Measurement technique
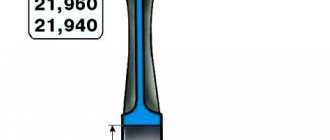
It was not said above what vertical or axial clearance is. The essence of this parameter will become clear during the following steps:
- Bring the ring to the side of the cylinder;
- Place the ring with the outer side in the slot that is intended for it;
- Using a set of feeler gauges, determine the gap size (see figure).
The diagram shows how to measure the vertical gap.
This is how the axial clearance of the rings is always measured.
Now let’s determine what gap remains on the piston rings between the ends if they, that is, the rings, are inside the cylinder. The ring itself is immersed in engine oil, and then it needs to be moved along the walls of one of the cylinders - the same one where it will “work”:
The gap is measured when the ring is clamped by the cylinder walls
To perform this operation, a piston is usually used if the latter has already been removed. The point is to bring the ring to approximately the level at which it is when the motor is running. Let's say the block was bored recently. Then the ring is moved down 3-5 mm (this is enough). And then, using a set of probes, the operation is brought to completion.
The motor oil used to lubricate the rings can be any type. Everything in the engine burns successfully!
Rating for various ICE Lifan engines
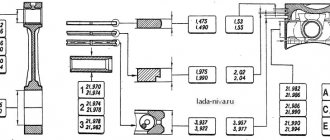
When installing new engine rings that do not have external defects, there is no need to measure the axial clearances. That is why the values of these gaps are not given in the repair literature. But the gap in the ring lock must be measured and estimated using the manufacturer's recommendations. The maximum clearance values for the lock are given below.
Solano 620
The sedan engine of the Solano 620 model is similar to the Toyota 4A-FE engine, the volume of which is 1.6 liters. Therefore, we will use the recommendations of this company (Toyota):
- Upper compression: 0.250. 0.450 (1.050);
- Bottom compression (AE-92, AT-180): 0.150. 0.400 (1000);
- Bottom compression (AE-101, AT-190): 0.350. 0.600 (1200);
- Oil scraper: 0.100. 0.500 (1100).
The maximum limit is indicated in parentheses. If it is exceeded, a major overhaul is necessary. Drill the block and so on.
X60 crossover
Here we have an engine similar to the Toyota RAV4 (1.8) crossover. So we again use Toyota's recommendations:
- Upper compression: 0.250. 0.450 (1.050);
- Bottom compression: 0.350. 0.600 (1200);
- Oil scraper: 0.150. 0.500 (1050).
We hope there are no questions here. The values are suitable for the 1ZZ-FE engine (1.8 l).
Please note that the piston parts have very high quality requirements. This is because they are affected by inertial forces, gas forces and high temperatures
Design of the kit, its dimensions and required dimensions, suitability of the selected material, precise implementation of production technologies. All this is necessary for long-term maintenance. But here we did not take into account the gap in the piston rings. Let's see what it is.
Increased oil consumption
Most modern car manufacturers increase the piston ring clearances in their engines. If for some types of internal combustion engines 1 mm is critical, but on a new engine from BVM or Audi 1-2 mm is the gap of new engine rings without mileage. Here it is necessary to deal with one important point.
The fact is that when the fuel-air mixture burns, gases are formed that enter the piston groove. Accordingly, they begin to create pressure on the inside of the ring, ensuring that it is pressed against the cylinder wall.
That is why when the internal combustion engine is operating at idle and low speeds, the clamping force is not as great as at high loads. This is due to the fact that the amount of gases in the combustion chamber is significantly different. The second compression ring partly performs the task of an oil scraper ring, removing the film from the cylinder. If it is worn out, then lubricant consumption increases significantly, especially at idle and low engine speeds.
Functions of piston rings
Piston rings are designed to perform the following functions:
- Sealing the piston space while maintaining pressure with the upper compression rings.
- Heat removal from the walls of the sleeve.
- Reduced oil consumption.
Checking the clearance in the locks inside the cylinders
The piston ring lock is the joint between two ends that are capable of being compressed to hundredths of a millimeter. The ends have a straight or oblique cut, with a rectangular profile section.
When placing the rings in the grooves, the joints are placed at an angle of 120° (if 3), and with two rings - at 180°, which limits the leakage of gases and oil into the crankcase, under the piston.
Oil scraper rings are designed to remove excess motor lubricant from the cylinder walls. They are designed to leave a thin layer of film on the mirror, so small that it is measured in microns. The design provides radial, through slots through which the oil removed from the walls is drained into the crankcase.
Available in cast iron with slots or extensions. They represent two rings (upper, lower), a pair of radial or axial expanders.
About the thermal gap
Locks are considered a common element of the rings, since the goal is to compensate for thermal expansion during operation. Locks undergo gas pressure, temperature loads, and other inert influences. This tension is absorbed by the tiny distance between the ends of the rings.
Why is the thermal factor needed?
Let’s imagine the absence of a gap between the spans of bridges, railway rails or expansion joints on main pipelines. Solar heating and expansion, for example, of the metal of rails that do not have a gap during installation, lead to their inevitable bending with all the ensuing consequences.
In the case of piston rings, the lack of butt clearance leads to breakage of the piston.
So, the free rotation of the rings eliminates butt contact inside the piston groove. The design includes cuts to prevent jamming from overheating. This feature contributes to a tight contact with the cylinder mirror.
The permissible joint interval does not exceed 0.3-0.6 mm. With a small joint gap, for example 0.2 mm, heated parts can leave marks on the cylinder.
By the way, preference is given to parts with oblique cuts at the ends. Straight ends have a lot of pressure on the walls, which prematurely damages the liner, causing oil leakage.
Compressor test
When testing a compressor on a bench, the compressor shaft rotation speed should be 1800...2000 min. The compressor must be supplied with I20A oil, GOST 20799-75
under pressure 0.25...0‚30 MPa (2.5...3.0 kgf/cm2), oil temperature 35...50 °C.
It is recommended to run the compressor at idle speed for five minutes. During the break-in process, you should make sure that there are no oil leaks, overheating of the bearings and that there is no knocking of the pistons, pins and exhaust valves.
At 800...2000 min of the compressor crankshaft and communication of the cylinder 3 with the environment through a calibrated hole with a diameter of 1.6 mm and a length of 3 mm, the pressure in the container after 50 should reach a value of at least 0.6 MPa (6 kgf/cm2).
The compressor is tested for oil throughput at 800...2000 min and an oil pressure of 0.25...0‚30 MPa (2.5...3.0 kgf/ohm2). In this case, the amount of oil flowing through the drain hole of the compressor crankcase cover (with the calibration hole open) should be no more than 220 g per minute.
The operation of the unloading system is checked by supplying compressed air under a pressure of no more than 0.5 MPa (5 kgf/cm2) into the channel of the unloading chamber, while the plungers 4 (see Fig. 8 - 11) must rise and fully open the inlet valves 8.
When the pressure is removed, the plungers must clearly return to their original position under the action of the return spring. Perform this operation at least three times.
Check the exhaust valves for leaks by connecting the compressor head to cylinder 3 (Fig. 8-13) with a capacity of 1 liter, as indicated in the diagram, at a pressure of 0.60...0‚65 MPa (6.0...6.5 kgf/cm2) . In this case, the pressure drop in the cylinder should not be more than 0.04 MPa (0.4 kgf/cm2) per minute.
Checking the tightness of connections is carried out with a soap solution at an air back pressure of 0.65 MPa (6.5 kgf/cm2).
Before installing a pressure regulator on a compressor, it must be checked, tested and adjusted to operate within the specified air pressure limits.
Decarbonization of piston rings
If the engine starts to smoke, there is a possibility that there are rings stuck in the piston grooves. Nowadays, there are many different modern means for decarbonizing piston rings, and many drivers use them to restore engine performance. Among the most popular compositions are:
- Nitrox Power;
- LAVR ML-202;
- Titanium;
- LIQUI MOLY;
- WYNN'S.
Motorists believe that if the engine starts smoking, you need to use a decarbonizer, and the engine will work as before, without oil consumption and without smoke. Indeed, sometimes these remedies help, but only in cases where the motor has stood motionless for a long time (for example, after winter), and moisture has accumulated in it. If the car is subject to long-term preservation (put in a garage for winter storage), you should remove the spark plugs and pour oil into the cylinders, and plug the spark plug holes with plugs. With such prevention, the spark plugs will not become damp and rust will not accumulate on the sleeves.
But if, after all, a forgetful car owner has not taken preventive measures, you can use a decarbonizer. We get rid of rust in cylinders as follows:
- pull off high-voltage wires;
- unscrew all spark plugs;
- rotate the crankshaft so that all pistons are in the middle position;
- pour 45 ml of liquid into each cylinder, install spark plugs;
- leave the cylinders to “soak” for 6-7 hours;
- why do we turn out the spark plugs, turn the starter a few revolutions so that all the dirt flies out of the engine;
- We put the removed parts back in place and start the engine. At first it may smoke a lot, but then the smoke will go away.
Car owners should remember that decarbonization is not a panacea for all ills, and if the piston rings are worn out, then only replacing them will help.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=uwl-MALsW-o
Comprehensive repair of CPG
The so-called “capital” of the engine implies a complete troubleshooting of the cylinder-piston group, because it is this group that is subject to the greatest thermal loads during operation. Consequently, pistons, compression and oil rings are also subject to increased wear. In some cases, when the rings have not yet reached critical wear, they are left. On most modern internal combustion engines, a gap of 1 mm is considered critical, and in this case it is necessary to replace the rings. So, when overhauling an engine, it is recommended to change all the rings on the pistons, even if they still fit. This is necessary so that after 50,000 kilometers you do not have to disassemble the engine again.
It is also worth understanding that the gap for the first and second compression rings is not always the same. A striking example of this is domestic heavy equipment. For example, the thermal clearance of KamAZ piston rings should look like this:
- first compression ring - 0.20-0.40 mm (new);
- second - 0.30-0.50 (new);
- oil scraper 0.25-0.50 (new).
In this case, the permissible wear for all types of rings should not exceed 1 mm. Even 0.9 mm can already be considered critical. Although it is often clear even without disassembling the CPG that the rings are asking for replacement.
Selection of piston rings: dimensions and materials of manufacture
A major overhaul or tuning of an engine usually involves the need to completely disassemble the internal combustion engine to replace the elements of the CPG and crankshaft. During the work, in some cases it is necessary to bore the cylinder block, then the cylinders are honed. Next, an accurate selection of pistons according to the size of the liners is required, at the same time the piston rings, piston pins and connecting rods are changed, the crankshaft is replaced or repaired, etc.
Replacing piston rings and the pistons themselves on a gasoline or diesel engine requires maximum sealing of the slot gaps. In this article we will talk about how to correctly select pistons, and then choose the right sized piston rings for them.
Read in this article
Let's sum it up
Both the service life of the rings themselves and the serviceability of the entire CPG depend on the correctly selected thermal clearance of the piston rings. Natural radial wear of the rings leads to an increase in thermal gaps, after which the sealing of the combustion chamber deteriorates.
It should be noted that a reduced clearance is much more dangerous for the engine. If the minimum gap in the locks (thermal space) is reduced to 0.2 millimeters, after the motor is heated and reaches operating temperatures, the gap in the lock may be completely absent. As a result, the ring puts a lot of pressure on the cylinder walls, ring wear increases significantly, heat transfer is disrupted, and the risk of scuffing increases.
How to choose the right piston rings. Correct selection of rings by size and materials, how to choose original rings. Useful tips.
When is it necessary to replace piston rings? How to install rings on the piston when replacing it yourself. Service life, rings, grinding in and running in.
Why do piston rings stick? The main signs for independently identifying a malfunction, diagnostics. Do-it-yourself decarbonization of piston rings.
Purpose, design features and principle of operation of piston rings of an internal combustion engine. Types of rings, gap size, main faults.
Purpose of the piston in the design of the internal combustion engine. Features and design of the piston, oil scraper and compression rings.
Purpose of the cylinder-piston group of an internal combustion engine. Design features, piston, rings, cylinder liner. CPG wear and repair.
Signs of piston ring wear
To understand whether the piston rings need to be replaced, it is necessary to study the symptoms that directly or indirectly indicate the need for such a replacement. Let us immediately note that you should not count on the amount that was initially announced by a mechanic or car service in response to a customer’s question about how much it costs to replace piston rings.
The fact is that it is often not possible to change only the piston rings and completely solve the problem, since after opening the engine, additional hidden defects are usually revealed. For this reason, it is necessary to be prepared in advance for more serious engine repair costs.
An impending replacement of piston rings is determined by the following signs:
- the engine loses power;
- the car is very bad;
- in some cases, the engine is difficult to start “hot”;
- there is an increased consumption of engine oil;
- the engine produces blue or gray smoke;
- fuel consumption increases;
The compression indicator, by which the condition of the engine can be determined, depends on the general condition of the rings and the entire CPG. Typically, with the symptoms described above, compression in the cylinders decreases and crankcase gas pressure increases.
Loss of power, increased fuel consumption and difficult starting are most often the main reasons that force the owner to change the piston rings or do a comprehensive repair of the internal combustion engine. A power unit with faulty rings has difficulty starting, especially after being idle in the cold season. When driving under load, such an engine does not “pull”.
Piston ring failures can be caused by natural wear and tear, as well as engine overheating. In the second case, even on a new motor, the rings lose their properties and cease to fulfill their intended purpose. Box-type oil scraper rings are most susceptible to overheating.
Significant engine oil consumption often occurs due to the fact that a worn oil scraper ring does not remove the required amount of oil from the cylinder walls and actively passes lubricant through leaks into the combustion chamber. The result is coking and smoking of the engine. Also, the remaining unburned oil in the engine actively pollutes the exhaust system, damaging filters and catalysts. The problem gets even worse.
To accurately diagnose the condition of the CPG, compression measurements must be supported by analysis of the color and content of exhaust gases. The fact is that the deterioration in the quality of the piston ring seal can be compensated by engine oil. In this case, the compression indicator is close to the permissible value, but oil consumption will still increase.
Remember, operating an engine with worn rings causes the wear of the cylinder bore to progress significantly. For this reason, it is necessary to change the piston rings as soon as possible after the fault has been accurately determined. This recommendation will help avoid increasing the cost of subsequent engine repairs.
Increased fuel consumption in the event of problems with the piston rings occurs as a result of the fact that compression is reduced and power has dropped. At the same time, the driver continues to drive at his usual pace, pressing the gas pedal harder to compensate for losses. As a result, an enriched fuel-air mixture enters the cylinders, which does not completely burn. Spark plugs often become flooded with fuel in such conditions.
Another unpleasant moment is the penetration of gasoline or diesel fuel through worn piston rings into the engine crankcase and subsequent mixing of fuel with engine oil. The oil in the lubrication system dilutes, loses its protective and other useful properties, and the wear of the loaded parts of the cylinder head and CV gear greatly increases.
Let us add that today the practice of using an additive to clean piston rings into oil or fuel is quite widespread. Also, owners sometimes pour so-called engine decoking into the cylinders. This is done in order to clean carbon deposits in the combustion chamber and try to restore mobility to the underlying piston rings to increase compression.
It should be noted that if obvious signs of a malfunction appear (heavy smoking, high oil consumption, low compression, etc.), an additive instead of replacing the piston rings is either a temporary measure or does not help correct the situation at all.
Where to install the camshaft
There are different options for the location of the camshaft in the engine and the design of the mechanisms that transmit pressure from the surface of the camshaft to the valve stem. However, the increase in the speed of modern passenger engines has led to the fact that a scheme with the location of the camshaft in the engine head - an overhead design - has become established everywhere in them. The proximity of the camshaft to the valves makes it possible to increase the rigidity of the system, and therefore improve the accuracy of operation.
The prototype of the first Zhiguli VAZ-2101, the Italian Fiat-124, had a solid and reliable, but no longer modern engine design with a lower camshaft. Soviet engineers decided that the engine of our new car should keep up with the times, and together with the Italians they modernized it by moving the camshaft to the head of the block.
Thermal clearance requirements
Functional requirements for thermal clearance include:
- Heat removal from the piston at the moment of ignition of the mixture. Otherwise, the piston will burn out under the temperature of the combustion chamber.
- Piston space sealing function. The resulting pressure should evenly press the rings against the cylinder walls. Achieving such touch requires setting the correct distance.
- Requirements for oil scraper discs responsible for supplying the required amount of lubricant. Compliance with this rule keeps oil and gasoline consumption at the level of factory standards.
Set gaps on rings
The established gap should correspond to 0.6-0.3 mm, and the side gap between the wall should not exceed 0.08-0.04 mm.
The value comes from the fact that exhaust gases act on the rings from the inside of the groove, pressing them against the wall. The coordinated functioning of compression and oil scraper rings allows for complete combustion of the mixture. This depends on how they are placed in the piston groove.
Therefore, a small value between the ends after warming up will lead to scuffing of the cylinder mirror.
The gap is measured with a feeler gauge and is regulated at 0.2-0.5 mm. For VAZ model engines, a value of 0.25-0.04 mm is provided on the sealing rings. Oil scrapers have 0.25-0.5 mm.
The first ring on top (compression), as loaded from alloy cast iron, is sprayed with chromium. The porous coating of this metal is capable of holding the required mass of engine oil.
Plasma coating of a layer of molybdenum on the rings promotes wear resistance and low friction with the cylinder.
The lock on the separator is painted blue
When choosing a repair size, you need to be guided by the product designation, including the engine model, kit number, product size. Additionally, the markings, which are located in a certain place of the product (close to the end), are checked. Expansion springs with a ground surface are carefully considered.
Properly selected and correctly placed rings guarantee a long service life.
conclusions
Properly selected and correctly placed rings guarantee a long service life.
We also recommend reading the article about what a hydraulic compensator is. From this article you will learn about the purpose, design and operating features of hydraulic pushers.
It is necessary to adjust the thermal clearances of the valves every 30-40 thousand km. mileage, as well as in the event of valve knocking on a cold or hot engine. The thermal gap between the piston and the cylinder, or more precisely the thermal gap of the piston rings, also requires special attention.
Why are there three rings on the piston?
The two upper rings, installed in the piston grooves, are needed to maintain compression. In the figure, these elements are indicated by the numbers “1” and “2”. And the lower ring, designated as “3”, is an oil scraper ring:
Less than 3 rings on the piston are not used in 4-stroke internal combustion engines
When the engine is running, the parts heat up, the metal expands due to heating, and the size of all gaps decreases. If the gap between the ends of the ring is smaller than recommended by the manufacturer, then after warming up such a ring will scratch the cylinder walls. Measurements must be taken without heating the part, and the ring itself must be placed in the cylinder:
Gap measurement cannot be performed without access to the cylinder block
To find out the size of the gap, use special probes (bars). Typically recommended values are in the following range: 0.2-0.5 mm. Still, be sure to check the documentation!
Operation of diesel and gasoline internal combustion engines
To better understand the importance of piston ring clearance in engine operation, let's consider how the two most common systems work. In reality, the difference between them is not that great, at least in terms of design.
The main difference is the ignition process. In diesel engines it occurs due to increased pressure. As a result, the temperature rises, after which the nozzle injects fuel inside, and ignition occurs on its own.
The gasoline engine is designed a little differently. Instead of an injector, spark plugs are installed at the top of the pistons, which supply sparks. Naturally, with such a design, normal piston ring clearance is very important.
This is interesting: Comparative characteristics of 16 and 8 valve engines
How to properly change and install piston rings? Detailed review
When repairing an engine, the question of how to properly change and install piston rings is very important. Before considering the procedure itself, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the signs that indicate the need for such repairs. Sometimes replacing the rings itself is not enough to return the engine to normal operation. Therefore, diagnostics and correct conclusions based on its results play a very important role here.
Before properly changing and installing piston rings
, you should monitor the general performance of the engine. The primary signs of ring wear are the following:
- The engine has lost power. When you press the accelerator pedal and try to accelerate the car, the engine refuses to respond, hesitates and does not pull;
- Engine oil consumption has increased. When the oil scraper rings wear out, oil enters the combustion chamber and is discharged into the exhaust system;
- Excessive fuel consumption. The symptom is a direct descendant of decreased compression. The engine loses efficiency and, as a result, fuel consumption increases.
If you have one of these problems (or all of them at the same time), you should pay attention to the condition of the piston system
To replace the rings, in any case, you will need to disassemble the engine. There are 2 options: either disassemble it on site, or remove it from the car. In any case, you should start by removing the timing cover and dismantling the cylinder head. Already at this stage it will become clear whether to replace the rings on the installed engine, or remove it completely.
If the sleeves are in good condition
, and there is no significant production on them, then you can limit yourself to replacing the rings.
After dismantling the pistons and connecting rods, you can begin to remove the old rings. To do this, you can use a special device, or simply carefully break them off, while avoiding damage to the piston. Fragments of rings can be used to clean the landing channels from soot and deposits. If this is not done, the new rings may simply not fit.
When purchasing new rings you should pay special attention. Normal quality ring kits should be from a recommended company, carefully packaged, and come with a quick labeling and installation guide.
If the purchased rings are simply wrapped in a piece of paper, then there is no need to talk about the quality of such spare parts.
Next, you can begin installing new rings.
When installing, it is very important to follow the sequence. The oil scraper ring is always put on first, then the compression rings.
It is also advisable to maintain the position of the ring in the “up-down” relationship. If there are special locks in the piston grooves, you should adhere to a uniform distribution of locks around the entire circumference.
For example
, in a piston with three compression rings, the locks should be located 120 from each other. All relevant sequences and order can be found on the ring markings and on the instructions from the manufacturer.
For better and more correct installation, you should use a special device. They can be found in automotive stores. Those who want to save money install the rings manually, using available materials and tools. At the same time, the savings are dubious, since very often with such an installation the rings break, which leads to the need to purchase a new set.
Also, often without the use of a device, the correct geometry of the rings can be disrupted. This means that if too much force is applied, the ring becomes oval. In this case, it completely loses its properties of a tight fit to the cylinder liner. The results of such repairs may be a waste of time.
When all the rings are in place, you can begin reassembling the piston system and other engine parts. A very important point in the question of how to correctly change and install piston rings during assembly is the procedure for shrinking the pistons into the cylinder liners.
Using a special device, the rings are pressed into the grooves and the piston is plunged into place. In this case, you need to be very careful not to damage the edge of the sleeve.
You should also pay attention to the correct position of the piston and connecting rod relative to the crankshaft. All subsequent assembly of the power unit and attachments is carried out in the reverse order of disassembly
What do valves do?
Valves are an integral part of the gas distribution mechanism of any engine. The camshaft, rotated by a belt, chain or gears, crankshaft, and special cams, opens and closes various valves at the right time. During the intake stroke, the intake valves are open, during the compression and operation stroke all valves are closed, and during the exhaust stroke, the exhaust valves are open. Through the intake valves, an air-fuel mixture (carburetor and injection engines) or air (diesel and direct injection) is supplied to the engine. During the exhaust stroke, fuel combustion products leave the combustion chamber. Therefore, the valves become very hot and increase in size. The thermal gap allows the valves to operate optimally.
Remedy:
Note: All piston rings supplied by Motorservice comply with the engine manufacturer's specifications. This ensures full compliance with all functional parameters.
Additional information: It is widely believed that large piston ring clearances cause increased oil consumption. However, this assumption is wrong. Increased thermal clearances of the piston rings cause a slight increase in gas blow-by, but not increased oil consumption. The following is correct: as the piston rings wear, their thermal clearances increase. The performance of a piston ring with a reduced cross-section deteriorates and as a result it no longer provides a proper seal. Increased thermal clearance and increased oil consumption are consequences of radial wear of the piston ring.
v>
A few important nuances
The service life of the cylinder-piston group and, in fact, the rings itself depends on how correctly the thermal clearance of the piston rings of a diesel or gasoline engine is selected. The appearance of scoring due to friction of the rings on the cylinder leads to a loss of not only compression, but also geometry. This is not very pleasant, since to restore the working condition you will need grinding, and in the most advanced cases, boring the cylinder block.
If radial wear of the rings occurs, the seal in the combustion chamber is significantly deteriorated. This leads to deterioration in engine dynamics and increased engine oil consumption.