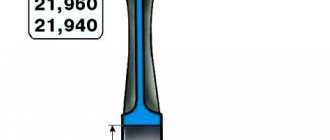
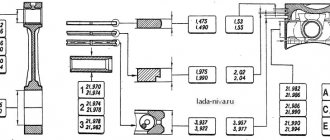
Piston size table for VAZ 2110 8 valves
The piston stroke of the VAZ 2110 car engine is standard 71 (mm), and the compression ratio is 9.9 units.
The piston is the main part of the internal combustion engine, which performs the function of converting the energy of fuel combustion into the mechanical work of the engine.
The material used for the manufacture of pistons for this VAZ model is aluminum alloy coated with tin.
Piston parameters for VAZ 2110 1.5 MT:
- Piston stroke: 71 (mm);
- Compression ratio: 9.9;
- Piston diameter: 82.0 (mm);
- Years of production: 1995 - 2007.
Important: the piston marking is located on its bottom and consists of a letter indicating the class and a number indicating the category of the piston pin hole.
Until 2014, the VAZ 2110 model was assembled under license from AvtoVAZ vehicle kits at the Bogdan Corporation automobile plant under the Bogdan-2110 brand, another name is VAZ 110.
The model is equipped with an electronic engine control system, a diagnostic unit (on-board computer), power steering, electric windows, and a new body painting technology is used.
Important: Years of production: 1995-2007.
| General view General view of the pistons |
Caution: The above data are the official figures of the manufacturer, however, please note that the information is for reference only and is not guaranteed to be completely accurate.
Source
Geometric dimensions of the “two-piece”
VAZ 2112 is one of the most popular models among the cars produced by the domestic automotive industry. It is relatively inexpensive, has a good design and different body styles.
The main geometric dimensions of the body of this car are as follows (in mm):
- length – 4170;
- width without mirrors – 1680;
- height – 1435;
- width with mirrors – 1875;
- rear door opening diagonal – 1320;
- short diagonal of the rear side window frame – 230;
- the distance between the center of the upper beam of the rear door opening to the middle of its lower beam is 1050;
- the long diagonal of the rear side window frame is 710.
The rarest body type of the 2112 is a coupe, or three-door hatchback. This is a sports model, it stands out from others, which are monotonous in terms of the geometric dimensions of the body. It was the design features of the VAZ 2112 coupe that allowed the model to become in demand at one time. However, after ten thousand examples of the 2112 coupe were produced, production ceased, so it is considered a rare model.
Several modifications of the VAZ 2112 were equipped with hatches, which greatly increased the comfort of the driver and passengers on the road. The geometric dimensions of 2112 made it possible to equip the car with many additional functional capabilities.
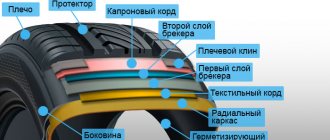
Engine piston rings
In an internal combustion engine (ICE), piston rings (PR) serve as a seal between the cylinder walls (liners) and the piston, due to which compression is created in the cylinders. If you forget to put the PC into the engine during assembly, the engine will not start, since the necessary compression of the working air-fuel mixture will not be ensured.
In passenger cars, three rings are standardly installed on each piston - two compression rings and one oil scraper ring, and oil scraper rings can be stacked, that is, consist of several elements. Compression piston rings (CPRs) are used to create compression in the cylinders and are always made of high-strength cast iron with various additives. The upper CPC has the greatest strength, since it operates in the most severe temperature conditions and experiences maximum loads.
Engine oil piston rings (OPRs) are needed to drain oil from the cylinder walls; if the rings do not perform their function, the engine will consume oil. MPKs can be either cast iron or steel, and cast iron PCs are almost always made in one piece, but steel oil scraper rings can only be assembled (composite). Steel MPC for one cylinder consists of:
- two spring steel rings;
- axial expander;
- radial expander.
Thermal clearance of piston rings
PCs are spring discs with one cut - when installed on the piston, they expand, and in the sleeve they are pressed tightly against its walls. In order to achieve maximum compression of the working mixture, the cylinder walls must be as smooth as possible (without defects), and the shape of the internal cavity must be perfectly round. On the piston, the PCs are placed in special grooves, moreover, they are not seated tightly, and on a cold piston they move freely in the grooves.
Piston rings have thermal clearances:
The clearances must be certain; if they are larger or smaller than the required value, the piston group will quickly fail. One should take into account the fact that when heated, the metal expands, and if the thermal gap of the PC is too small, the piston group will begin to overheat. With large gaps, tightness is not ensured and power losses occur.
For passenger cars, as a rule, the following clearances are established:
- between the grooves and the PDA - from 0.02 to 0.08 mm (for the upper ring the gap should be slightly larger);
- between grooves and MPC – from 0.05 to 0.06 mm;
- at the junction - from 0.25 to 0.5 mm.
As wear occurs, the gaps in the PC increase, and they should not exceed:
- between the ring and the groove – 0.15 mm;
- at the junction – 1.0 mm.
Information on the piston surface
Discussing the question of what markings on pistons mean, it is worth starting with what information the manufacturer puts on the product.
- Piston size . In some cases, in the markings on the bottom of the piston you can find numbers indicating its size, expressed in hundredths of a millimeter. Example - 83.93. This information means that the diameter does not exceed the specified value, taking into account the tolerance (tolerance groups will be discussed below; they differ for different brands of cars). Measurement is carried out at a temperature of +20°C.
- Installation gap . Its other name is temperature (since it can change along with changes in the temperature regime in the engine). Designated as Sp. It is given in fractional numbers, meaning millimeters. For example, the marking on the SP0.03 piston indicates that the gap in this case should be 0.03 mm, taking into account the tolerance range.
- Trademark . Or an emblem. In this way, manufacturers not only identify themselves, but also provide information to craftsmen about whose documentation (product catalogs) should be used when selecting a new piston.
- Installation direction . This information answers the question - what does the arrow on the piston point to? It “tells” how the piston should be mounted, in particular, the arrow is drawn in the direction of forward movement of the car. On cars where the engine is located at the rear, instead of an arrow, a symbolic crankshaft with a flywheel is often depicted.
- Casting number . These are numbers and letters that schematically indicate the geometric dimensions of the piston. Typically, such designations can be found on European machines, for which the piston group elements are manufactured by companies such as MAHLE, Kolbenschmidt, AE, Nural and others. To be fair, it is worth noting that casting is now used less and less. However, if you need to identify the piston using this information, then you need to use a paper or electronic catalog of a specific manufacturer.
In addition to these designations, there are also others, and they may differ from one manufacturer to another.
VAZ piston rings
The Volzhsky Automobile Plant produces engines for front-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive cars; piston rings for VAZ engines were originally supplied by the Michurinsky plant. The Michurins produced a lot of defects in their products, and since 1986, their own production was established in Tolyatti. Currently, there are many different manufacturers that produce PCs for VAZ engines, in particular, these are:
- AVTOVAZ (Tolyatti);
- STK (Samara);
- GOETZE (Germany);
- MAHLE (Germany);
- NPR EUROPE (formerly SM, Japan).
Signs and causes of wear (breakage) of piston rings
On VAZ cars, the engine wears out during operation, and the PCs also fail. Rings can:
- break into two or more parts;
- wear out in thickness;
- have general wear and tear.
Parts often break down due to overheating of the internal combustion engine; in this case, compression in the cylinders decreases and the engine loses power. Signs of a faulty PC are:
- bluish smoke from the muffler pipe, especially often it appears after a long period of idling when the gas pedal is sharply pressed;
- increased engine oil consumption;
- drop in power, the motor stops pulling;
- coking of spark plugs.
If there are signs of a malfunction in the piston group, the piston rings are replaced first. But replacing a PC does not always give the desired effect; often after repair the engine continues to smoke and consume oil. The reason for this is simple - there is wear in the cylinders themselves. In the block, the liners usually wear out unevenly - they take on an oval shape; due to wear, the piston rings do not fit tightly to the cylinder walls and do not provide a tight seal.
Body parts most susceptible to deformation
Sharp braking or untimely start provoke, first of all, damage to the bumper. If it is insignificant, then during repairs it is possible to achieve the performance of standard geometry. In the presence of complex deformations, this cannot be done, so it is easier to replace the damaged body part with a new one.
If the owner of the car does not take enough care of the condition of the body, then those parts that have close contact with the road surface are quickly eaten away by corrosion. And repairing the hood, doors and hidden body parts instead of timely prevention is already more difficult and expensive.
Replacing piston rings
On VAZ cars, as well as on all other models of passenger cars, it is advisable to change only the piston rings only if:
- there is no exhaust in the cylinders;
- there are no signs of damage to their inner surface.
If the liners are significantly worn, they need to be bored, and if the last size was already used before, the cylinder block needs to be relined. You can replace the PC on any VAZ engine without removing the internal combustion engine; this will require removing the cylinder head and oil sump. PCs are replaced if the gap at the joints does not exceed 1 mm.
For example, let's consider replacing piston rings on a VAZ-2114 car with an 8-valve internal combustion engine; such work must be carried out on a pit or a car lift:
- turn off the ignition, put the gearbox in neutral, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery;
- drain the antifreeze, remove the air filter housing along with the pipe (injector corrugation);
- remove the valve cover, camshaft, loosen the timing belt and move it to the side;
- disconnect the wires and cooling system pipes from the cylinder head, unscrew the head bolts;
- unscrew the nuts of the exhaust pipe of the muffler;
- We completely free the cylinder head from all fasteners that prevent it from being removed, and we remove the cylinder head;
- if there is protection under the engine, remove it;
- place a container under the engine sump, unscrew the plug on the crankcase, drain the oil;
- remove the lower hatch of the gearbox housing (three bolts);
- Using a 10 mm wrench or a socket wrench, unscrew all the oil pan bolts;
- dismantle the pan, remove the oil receiver;
- Unscrew the connecting rod nuts, remove the lower connecting rod caps, and carefully knock the pistons and connecting rods upward. Pistons should be knocked out through a soft metal drift or through a wooden block. First, you need to carefully knock out the connecting rod bolt without damaging the threads on it, then place the drift on the end of the connecting rod - in no case should you hit the bearings or the seat underneath them;
- It is recommended to remove the connecting rods one at a time, and immediately attach the caps to them; the caps should not be confused with each other, they are placed back strictly in their places, and a lock to the lock is required;
- remove the PC from the pistons, use a piece of the old ring to clean the piston grooves to bare metal. Be sure to check the cleanliness of the groove all around; there should be no coke left in it;
- We install new rings in the grooves, start with the lower MPC, then install the middle compression PK, and lastly the upper one. For installation, you can use a special device, but it is still more convenient to install the rings by hand. If the MPCs are cast iron, they cannot be bent along their axis, they can only be carefully moved apart. Compression rings also need to be bent carefully, to a minimum;
- we install the piston in place using a special mandrel, hammer it in with a wooden hammer handle or a brass or bronze drift;
- We install one piston-rod at a time, and immediately attach a connecting rod cap to each one. The connecting rod nuts should be tightened with a torque wrench, force - from 4.5 to 5.5 kg;
- then we put everything in place - the oil receiver, the engine sump, the cylinder head. We fill the radiator with antifreeze, oil into the crankcase, and start the engine to check. After replacing the PC, the internal combustion engine may initially smoke and consume oil - the engine needs to be run in for approximately 2 thousand km. It happens that despite the seemingly normal condition of the liners, the internal combustion engine continues to smoke even after replacing the rings after break-in. In this case, you will have to bore the cylinders and install a repair piston group.