The crankshaft pulley is a part that plays a very important role in the performance of the machine. The design of the crankshaft pulley is quite simple, but periodically this unit needs to be replaced. In most cases, it is removed when the crankshaft oil seal has to be replaced.
But crankshaft pulleys are different, so now we will look in more detail at the types of crankshaft pulleys and what types of breakdowns are associated with this unit.
Pulley concept
It is designed to transmit torque from the drive shaft to the driven shaft. To operate such a drive, both shafts are placed in parallel. A flat wheel is put on and secured to each shaft; they are placed in the same plane. The wheels are connected by an endless flexible drive belt. When the drive pulley rotates, the friction force causes the belt to move, covering part of its surface. This motion is transferred to the driven pulley, causing it to rotate.
Belt drives are common among household appliances, mechanisms of low- and medium-power machine tools, and in various internal combustion engines.
It has the following advantages:
- simple device;
- the ability to transmit significant power, modern V-belt pairs transmit up to 400 kW;
- high rotation speed, up to 50 m/s;
- smooth and quiet running;
- damping of vibrations and jerks of the drive shaft during rotation transmission;
- slippage under overloads acts as a safety mechanism.
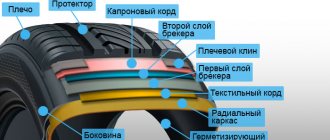
The pulley itself is a disk on a shaft. It consists of two main parts: the rim and the hub. The rim is the outer part of the part. It engages with the belt and, depending on the type of drive, can be flat or have a recess in the shape of the belt. The side projections above the rim are called cheeks. They keep the belt from slipping. If the drive is wedge, then the cheeks are made inclined; they have an additional function - they increase the engagement area.
If a gear drive is used, then teeth of the appropriate shape are made on the surface of the rim.
If several streams are used in parallel, several grooves are made on the rim.
The hub is the inner part of the pulley. It has a hole for mounting on the shaft. Often the rim and hub are cast, turned, or milled as a single piece.
To reduce the weight of the product, voids are left in the body of the pulley, forming spokes. When made from wood, the presence of knitting needles was determined by the manufacturing technology.
To ensure the interchangeability of pulleys, their standard sizes, technological requirements, and markings are standardized. They are described in GOST 20889-94. “Pulleys for driving V-belts” and in GOST R 50641-94 (ISO 4183-89).
Download GOST 20889-88
Download GOST 50641-94
Standard markings include the following parameters:
- number of streams;
- profile of the drive belt used;
- diameter (calculated by cord);
- sleeve designation.
Thus, the marking 8 SPC 500 indicates an eight-lane pulley for an SPC profile with a diameter of 500 mm.
The rules for depicting pulleys in the drawing have also been standardized. The drawing must be constructed so that the product can be manufactured to exactly the same shape and size.
How to choose
When choosing a toothed pulley, you should pay attention to the processing class, the distance between the teeth and the manufacturing shape. The tooth surfaces and the belt are subject to constant loads, so high demands are placed on the quality of cutting and processing. Cutting teeth is carried out in several stages on a milling machine or devices designed specifically for the manufacture of these parts. Cast iron products are somewhat different from other varieties; they are cast in forms that completely replicate finished pulleys for timing belts and are processed using a milling machine.
The flanges on the pulley can be either absent or located on one or both sides. They are fixed in three ways:
Types of pulleys
Over thousands of years of use, designers have developed many designs of belt pulleys. Their classification is carried out according to various criteria.
Depending on the type of belt used, there are:
Wedge-shaped
The most common type of product. Used with V-belts. The side cheeks provide additional engagement area, increasing the transmission capabilities of torque and rotation speed.
The inclination of the groove must be indicated on the part drawing.
In order to reduce the dimensions of the transmission or increase its power, several streams are launched in parallel. Such pulleys are called multi-grooved; they have the appropriate number of grooves. Sometimes a single belt with several wedge-shaped protrusions is put on such a pulley. This is a poly-V transmission.
In the drawing it is permissible to give a detailed image of one groove and indicate their number. Detailing of the rest in the drawing is not required
If the permissible load is exceeded in an emergency, slipping begins, protecting the equipment from damage.
V-belt transmissions allow you to transmit the highest torque.
Serrated
There are toothed projections on the inner surface of the belt; teeth corresponding to their pitch are also made on the surface of the rim. Gear-belt pairs do not slip and can transmit more torque. They are also distinguished by the accuracy of transmitting the angular position of the shaft, therefore they are used in gas distribution mechanisms of internal combustion engines. The downside is the lack of a protective function against overloads. The rim is made by milling. There is also production by the rolling method. The detail drawing must indicate the exact parameters of the tooth, its pitch, height, and profile.
Flat-shaft
A classic design used in the very first gears. Absorbs vibration and dynamic loads from the drive shaft. They are characterized by low noise, limited torque and rotation speed.
Using additional rollers, you can connect driven and drive shafts that are in different planes, not coaxial, and change the direction of rotation. In this way, cardan and worm gears can be replaced. The drawing of such a product is the simplest, but it should indicate the radii of the rim and cheeks, if provided. Sometimes cheeks are not provided, and the rim profile is made convex. In this case, its radius should be indicated on the drawing.
Round belt
The groove in the rim has a semicircular profile. Such belt drives are used for low transmitted torques and rotational speeds. They also allow you to change the direction of rotation and connect axes located in different planes. In the drawings of such parts, only the radius of the groove is indicated.
CVT
These are the most complex devices in design. The rim is made in the form of a cone with a conical moving cheek. The V-belt ring has the ability to move along the cone in the axial direction, from a smaller radius to a larger one. The second pulley has a reverse taper, and the drive on it moves from a smaller radius to a larger one. In this case, the transmission ratio changes. The cheeks of both pulleys can move in the opposite direction, changing the gear ratio in the opposite direction.
The advantage of the design is that the gear ratio can be changed without stopping rotation and without removing the load from the drive. It can be difficult to understand the operating principle of a device from a drawing. Three-dimensional modeling allows you to supplement models with kinematic simulations that clearly demonstrate the interaction of mechanism parts.
Pulleys are also distinguished by the method of placement on the shaft:
- Under the sleeve. Allows you to secure the drive on any standard shaft by selecting a bushing of the appropriate internal diameter. If the seat is damaged, it is enough to replace the bushing, which makes repairs easier and faster.
- Under boring. Available with a small central hole. It is bored or drilled to fit the diameter of the shaft. If damaged, it is difficult to repair.
- Fixed diameter. Usually equipped with a groove for keyed fastening or splines. Very simple and quick installation and dismantling. Requires exact matching of diameters. Allows the production of molded parts.
For the manufacture of parts, materials such as are used:
- Cast iron. Widely used for V-pulleys. It is characterized by high strength, low price of products and ease of processing.
- Steel. It is used in mechanisms subject to large temperature changes and strong dynamic loads.
- Aluminum and its alloys. Used for lightly loaded gears in mechanisms for which weight and dimensions are important. Not subject to corrosion.
- Plastics. Used in small-sized devices with low transmitted torques and speeds.
- Composite materials. They are used in advanced technology, where a combination of low weight, high strength, resistance to dynamic loads and adverse environmental influences is required. They are distinguished by their high cost.
The drawings indicate not only the grade of the alloy, but also the method of its processing, surface cleanliness, hardness, the need for hardening, etc.
Wood, as a traditional material for belt drives, has fallen out of use these days. It is used in the reconstruction of historical mechanisms and in homemade products. Drive wheels glued together from plywood rims are sometimes used as a temporary repair part in home workshops.
Important Features
The operation of individual automobile units is provided by energy that is transmitted from the rotating crankshaft. For example, the rotation of the wheels is ensured by a complex system of gears and shafts, but the pump, air conditioner, timing belt and generator rotate from the crankshaft pulley. This small part is characterized by high strength and low fault tolerance. In fact, it can last as long as a car will last until it is sent for recycling.
Read also: Cytotoxic drugs
In fact, there are many types of crankshaft pulleys for cars. At least in the sense in which the manufacturer sees it, each group of engineers has the right to resort to their own design solutions and create their own pulley options. Today there are not many varieties of this part left, but the division into types has a justification. Each pulley is adapted to certain operating conditions of the vehicle, so it is important for the driver to understand that a pair of pulleys cannot always be interchangeable. In part, this simplifies the buyer’s task, since it is enough to search for the pulley using the vehicle data or its identification number.
Application of pulleys
Wedge drives are one of the most widely used in a wide variety of mechanisms and devices with high torque and angular velocity. First of all, these are internal combustion engines. In addition, V-belt pairs are used in areas such as:
- fans and air conditioners;
- compressor units, both piston and screw;
- transport systems of buildings: elevators, escalators, travelators;
- agricultural machinery;
- road construction equipment;
- mining machines;
- industrial technological installations;
- machines;
- Appliances;
- hand power tools;
and in many other industries.
Gear drives are used in cases where it is necessary to transmit significant torque without slipping. The toothed belt drive does not require much tension for good traction. It produces significantly less radial load on the axle than other belt drives.
The following drives are used in:
- automobile engines, for the gas distribution mechanism;
- power drives of machine tools and industrial mechanisms;
- in technological installations of the food, pharmaceutical, chemical industries.
Poly V-ribbed pulleys do an excellent job in so-called serpentine transmissions, when one drive supplies rotational energy to many consumers, and at the same time follows a very winding trajectory. Poly V-ratio transmissions allow you to transmit significant torques and achieve high speeds without increasing dimensions.
They are used both in heavy engineering and in the production of household appliances.
CVT drive wheels are used wherever it is necessary to smoothly change speed and torque without stopping rotation or removing the load. They are popular in areas such as:
- transmissions of cars, motorcycles, and other wheeled vehicles;
- conveyors;
- precision machines for processing metal, wood and other materials;
- agricultural machinery.
A modern variator surpasses both manual and hydraulic transmissions in its performance characteristics.
Flat drives are used where it is necessary to transmit rotation over significant distances (up to 7-9 m) and absorb shocks, jolts and other dynamic loads transmitted from the drive shaft to the driven shaft (or in the opposite direction). They apply:
- in pressing and other forging equipment;
- in sawmill drives;
- in technological equipment of the textile industry;
- in powerful centrifugal pumps.
Round belt drives are used for light-duty transmissions in precision instruments, consumer electronics and appliances.
They also easily intersect and, with the help of additional passive pulleys, allow you to connect the driven and drive shafts, located in different planes and at an angle to each other, and also change the direction of rotation.
Description
Many vehicle systems operate using energy supplied from the crankshaft. The design of the pulley has improved over time; today several options have appeared, each of which is suitable for a specific vehicle and various operating conditions. They are fixed using bushings made of high-quality materials, thus simplifying installation and increasing the reliability of fastening.
The main purpose of a pulley is to transfer energy between shafts. It is of particular importance in the following cases:
- there is excessive transmission load on the belt;
- It is necessary to prevent belt slippage.
Dismantling
In order to remove the old toothed pulley, it is necessary to remove the cover that hides the wires of the units, thus providing free access to the motor parts that require replacement. Next, the tension of the drive chain is released. After which the tank with antifreeze liquid and the electric generator are removed. If the car is equipped with power steering, it is necessary to remove the belt for this system.
Next, all that remains is to remove the mounting bolt that secures the toothed pulley to the crankshaft, but difficulties may arise here due to the direction of the thread. While the engine is moving, the bolt is constantly tightened, so at this stage of the work a pneumatic impact wrench may be required if the manual effort is not enough.
In the absence of special tools that significantly simplify the task, it is recommended to secure a wrench to the bolt to prevent it from turning. During work, the vehicle must be on jacks or with the drive wheels removed. This is necessary to ensure that the transport does not move from its place. The bolt will be unscrewed by sharply turning the ignition key, while the starter will make several turns and all that remains is to remove the bolt. After replacing the pulley, all parts are installed in the reverse order.