The fuel pressure regulator, or simply abbreviated as (FLS - approx.) on the VAZ-2112, is designed to ensure that operating pressure is constantly maintained in the vehicle’s fuel system. And if this element malfunctions, it may require replacement. We described in detail how to do this correctly below in our article.
The video describes in detail the process of replacing the fuel pressure regulator on the VAZ-2112 (and other cars of the LADA family):
Signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator
Every engine fuel system contains a fuel pump.
Electric fuel pumps have recently been installed in gasoline engines; mechanical models are already outdated and are no longer used on modern vehicles. Mechanical fuel pumps live out their days on cars produced in the last century. The performance of the electric fuel pump must be such as to ensure uninterrupted fuel supply at any engine speed and under any load. But what to do when the engine is running at idle or low speed, and a small portion of fuel is required? After all, the pressure that is created in the engine power system for heavy loads will be excessive at idle speed. And excess pressure can lead to disastrous results - breakage of fuel hoses or other damage. For normal operation of the fuel system, there is a fuel pressure regulator.
Important nuances
There are a few things to keep in mind when cleaning your injectors. Here they are:
- You cannot save on flushing fluid. The injector is a very important part of the engine. And it is extremely sensitive to the quality of the flushing fluid. The optimal choice for washing Priora injectors is a product from Wynns, developed specifically for injection engines. The cost of a liter bottle is 700 rubles; The plastic bottle must be removed carefully after washing the Priora injectors.
What is a fuel pressure regulator?
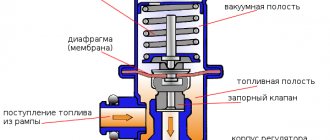
The fuel pressure regulator (FPR) is a vacuum valve that transfers excess fuel through a return hose into the fuel tank. The RTD is a housing that contains a valve, a membrane and a spring. There are also three terminals in the housing: two terminals for the passage of fuel through the regulator, the third is connected to the intake manifold. As engine speed increases, the vacuum created in the manifold (at the third terminal) overcomes the force of the spring and moves the membrane, thereby opening the valve slightly. Excess fuel gets access to the second outlet and goes back to the gas tank. An RTD is often also called a check valve.
As a rule, the check valve is located on the fuel rail; it can also be embedded in the fuel return hose of the power supply system.
Where is it installed?
There are two options for installing an RTD: on the fuel rail and in the fuel tank.
The regulator was installed on the fuel rail on cars with a 1.5 liter injection engine. On such engines, two fuel lines come from the fuel tank: direct and return.
The regulator was installed in the fuel tank on cars with a 1.6 liter engine. In such engines, the return line was abandoned. Now the regulator directly relieves pressure in the car tank.
Causes of fuel pressure regulator malfunctions
RDT may fail for several reasons. For example, defective parts are found on Russian-made cars. There are significantly fewer defects on foreign models, but you can purchase a defective RTD by purchasing a non-original spare part.
Mostly the check valve breaks down due to natural aging. Let's say this can happen after a hundred thousand mileage or more. It should be noted that check valve failures are not common. Most often, in an RTD, the membrane dries out over time, less often the valve jams, and even less often the spring breaks or weakens.
Sensor failure may occur due to low-quality gasoline. For example, in winter, fuel was filled with water, and water got into the regulator. If the fuel filter is not replaced on time, dirt gets into the parts of the power system, including the regulator. In this case, the RTD valve most often jams. It’s hard to imagine what could happen to the spring, but apparently, it still breaks sometimes.
Important nuances
There are a few things to keep in mind when cleaning your injectors. Here they are:
- You cannot save on flushing fluid. The injector is a very important part of the engine. And it is extremely sensitive to the quality of the flushing fluid. The optimal choice for washing Priora injectors is a product from Wynns, developed specifically for injection engines. The cost of a liter bottle is 700 rubles; The plastic bottle must be removed carefully after washing the Priora injectors.
Replacing injectors is a long procedure. Nevertheless, it is quite within the power of a novice driver if he has at least a vague understanding of the structure of an injection engine. When cleaning the injectors, the situation is much simpler: you just need to be able to use a drill and know where the main fuel hose is located.
Carburetor cars are slowly but surely becoming a thing of history. Float chambers and diffusers have been replaced by injectors and distributed fuel injection, the quality of which is controlled by the car’s on-board computer. On the one hand, injectors have made life much easier for motorists. On the other hand, even these reliable devices periodically fail. Fortunately, the driver can replace them with his own hands. The main thing is to know how it's done.
Characteristic symptoms of fuel pressure regulator malfunctions
By what signs can you determine that an RDT is not working:
- the engine is very difficult to start, you need to turn the starter for a long time and at the same time keep the gas pedal pressed in order for the engine to start;
- The engine idles unsteadily or the speed is very low, the engine often stalls. At the same time, it does not gain power at all; when trying to accelerate, it results in a deep failure;
- The spam engine changes speed sharply, this is especially noticeable at idle:
- Fuel is leaking from the fuel hoses. Attempts to tighten and replace clamps and replace hoses do not help.
How to check the fuel pressure regulator for serviceability
The fuel pressure regulator is not an electrical sensor and cannot be checked using instruments. It should also be taken into account that the RDT cannot be disassembled or repaired. Someone writes that the fuel check valve can be repaired. I would like to see what it looks like and where you can buy a repair kit. Typically, RTDs are inexpensive, and even for that reason they would not be worth repairing if they were repairable.
You can verify that the regulator is working properly by checking the pressure in the fuel system. This is usually done with a mechanical pressure gauge, which is connected to the engine power system.
Measurement is carried out as follows:
- connect the pressure gauge to the fuel system;
- start the engine and look at the pressure gauge readings.
The standard system pressure for a passenger car is usually within 3 kg/cm2. When stopping the engine, the pressure should not drop immediately - the regulator closes the return flow. If the pressure gauge needle quickly goes to zero, the RTD is most likely faulty.
Another way to check: if you manage to pinch the fuel return hose while the engine is running, then if the regulator is working properly, the pressure in the fuel system should increase. The indication of the arrow of the device depends on the degree of compression. But there are foreign cars where it is impossible to clamp the return line - instead of rubber hoses there are metal tubes, or the hoses are very short.
In some cases, by squeezing the return hose, you can verify that the RTD is faulty without a pressure gauge. But this is only due to one sign - when the engine idles and does not develop speed at all. If, when the return line is pinched, all cylinders begin to fire and the engine acquires the required power, then the RTD is definitely faulty and needs to be replaced.
Tips for motorists
Chassis front and rear suspension VAZ 2110 2111 2112 Removing the lever and extension of the front suspension VAZ 2110 2111 2112
Interruptions in the operation of the engine of the VAZ-2118 Lada Kalina passenger car become very noticeable in idle mode (the engine jerks), as well as when trying to quickly gain speed (the engine does not pull). There are many reasons why an engine may start to work like this. They can be connected both to ignition and power systems, and to gas distribution and crank mechanisms.
It is unlikely that it will be possible to determine immediately what caused the interruptions in engine operation. Therefore, according to the established driving tradition, the search for such a malfunction begins with checking the spark plugs and high-voltage wires. Initially, they check the reliability of the fit of the tips of the high-voltage wires on the spark plugs, and the breakdown of the high-voltage wire to ground is very clearly visible in the dark, naturally with the engine running.
If everything is in order with the high-voltage wires, then you will have to unscrew the spark plugs one by one and check them for the presence of a spark between the central and side electrodes. You need to start this work with a well-warmed-up engine, this will make it easier for you to remove the spark plugs from the cylinder head. Be sure to use a feeler gauge to check and, if necessary, adjust the gap between the electrodes, since an increased gap can lead to misfiring when the engine is running.
Also pay attention to the color of the central electrode insulator, because if there is black carbon on it, the spark plug will not work normally
The engine will operate intermittently in the event of a malfunction in the power system associated with the failure of one of the injectors to inject fuel into the combustion chamber or the pressure in the rail drops below the required level. Considering that the injectors on the Lada Kalina are electromagnetic, and if with the engine running you begin to de-energize their solenoid valve one by one, then by the changed nature of the engine operation you can find a faulty injector. A decrease in pressure in the fuel rail is possible either due to a malfunction of the pressure regulator, or is associated with a malfunction of the fuel pump. But in order to determine this you will need a pressure gauge.
Malfunctions of the gas distribution and crank mechanisms can lead to a drop in compression in one of the engine cylinders. This may be due to leaky valves, as well as breakage or coking of the compression rings.
Due to the fact that the operation of the injection engine is controlled by a controller, and it is located under the interior heater radiator, if it is not sealed, antifreeze begins to drip onto the controller body and if moisture gets inside, malfunctions may occur in its operation, leading to unstable operation engine.
The car became unstable. Although when you start it, it runs normally at high speeds, as soon as it warms up it starts to twitch, not that it shakes, but it’s really noticeable, the steering wheel is already shaking from vibrations. In addition, the engine lost some traction, not much, but noticeably. The check does not light up.
I did the following: - Replaced the spark plugs and Armored wires, also threw in another coil. - Replaced the mass air flow sensor (the old one was dead) - replaced the IAC and TPS and cleaned the throttle (during disassembly I saw a small axial play of the flap, tightened it, I don’t know if it could be from it such an effect?) -Replaced the fuel pump, mesh and filter, as well as the RTD. -I went for diagnostics, there were no errors, the indicators were normal, the mixture in the lambda was a little lean. As a result, I cleaned the lambda. I also tried to drive without a lambda, the check did not light up and there was no difference. — Compression is 13 everywhere (maybe valves? Although the previous owner says that he recently adjusted them) — We also checked the receiver for air leaks — Replaced the DPKV — I looked at the marks on the timing belt It seems to be in place, but there is no mark on the flywheel, I installed it using the old-fashioned method, by unscrewing the spark plug and finding TDC. DPKV hits the 20th tooth. But when the camshaft gear is shifted by 1-2 teeth in both directions, there is practically no difference in the operation of the engine.
The crankshaft pulley also moves a little (+-1 mm), although it has always been like this and it did not affect the operation.
Fuel pressure regulator VAZ 2112 16 valves
The fuel pressure regulator (FPR) serves to maintain constant pressure in the engine fuel system, ensuring uninterrupted operation of the internal combustion engine and its maximum performance in all modes. Most often, the fuel pressure regulator is located on the fuel rail, or on the fuel pump itself in the tank.
We are repairing a VAZ-2112 car produced in 2003, with a 1.5 liter engine with a power of 94 hp. The owner complained about difficult starting after long periods of parking and roughness at idle.
Fault diagnosis
First you should measure the pressure in the fuel system. The regulator on this engine is located on the fuel rail. On the left as the car moves. On the right side of the ramp there is a fitting for connecting a pressure gauge.
To connect the pressure gauge, unscrew the plastic cap and nipple.
The nipple can be unscrewed with a metal cap from a regular camera. The external thread size for connecting a pressure gauge is 10 mm. You can contrive to put a VAZ fuel hose on it. You must first make an internal chamfer in it, otherwise it will be difficult to put it on the fitting.
Signs of breakdown
If for some reason the fuel pressure regulator does not perform its functions, then this can be understood by the following signs:
- The engine's operation has become unstable, it may begin to stall when idling, although it would seem that the fuel level is sufficient and all systems are in working order;
- The crankshaft at idle speed has increased or, conversely, decreased speed;
- The engine, as they say, “loses throttle response”;
- While driving, dips and jerks occur in a running engine;
- Gasoline consumption increases compared to what it was before;
- The content of CO and CH in the exhaust increases;
- The engine starts with difficulty. Although this property does not always appear.
If the regulator has become completely unusable, then an increase in fuel pressure is observed. Instead of the norm for the VAZ 2110, which ranges from 2.5 to 3.3 kg/cm2, it reaches 4 – 5 and even more.
Consequently, the fuel pump supplies more gasoline by volume, which is not completely burned, and overconsumption is guaranteed. Of course, such a regulator needs replacement, and the sooner the better.
If the fuel pressure regulator does not provide the required pressure, or simply does not hold, then the lack of fuel pressure leads to the fact that normal supply does not occur, and the VAZ 2110 “chokes” when you need to increase the speed.
In addition, the starter cannot quickly spin the engine; it has to be turned on many times.
Why is this device needed?
The regulator, responsible for maintaining normal fuel pressure in the system, is in direct interaction with the power unit. According to its location, it can be located in the fuel tank or in the rail (this is where you will be able to find the regulator if you have an injection VAZ-2115). The reason for the failure of this element is often the low quality of gasoline. If you fill up at gas stations with greatly reduced prices, then it is not surprising that very soon the regulator will fail.
The fuel flows through the injectors to the intake manifold, and it is important that its pressure does not change at this moment. The regulator measures the volume of fuel required for engine operation, and also monitors the pressure in the fuel rail and intake manifold.
A fuel pressure regulator (FPR) is needed to maintain gasoline pressure in the fuel system at a constant certain level, regardless of engine operation. It is installed in the injector rail and is a diaphragm valve connected to the fuel supply channel to the injectors, the drain line and the air tube supplied from the intake manifold.
The RTD valve is affected by fuel pressure, on the one hand, and, on the other, by air pressure in the tube and spring force, adjusted to certain operating parameters in the system. When the engine is running, a serviceable RTD maintains the following indicators in the system: 2.9–3.3 kgf/cm2 (284–325 kPa).
It is quite clear that we first learn about excessive consumption of gasoline by readings from the level sensor. However, sometimes the FLS also starts to lie, and then the true consumption cannot be known.
There may be a situation when you still have half a tank of gasoline, but the FLS says that the fuel is almost empty. That is, the flow sensor itself may confuse you, and before rushing to replace the regulator, make sure that the FLS is working properly, remember that the VAZ 2110 has problems with it very often.
If you notice that it is lying, the fuel sensor may need adjustment or even replacement.
Replacing the fuse
Removing and installing the fuel filter VAZ 2110-2111-2112
One of the most common causes of breakdown is failure of the protective element. A clue that the fuse for the cigarette lighter has blown will be a non-working VAZ 2110 stove or a faulty glove compartment illumination lamp. To carry out repairs, it is necessary to replace the blown fuse in the mounting block.
To get to the box, press the button in the front panel to the left of the steering wheel. The fuse to be checked is number F18, rated for a current of 25 amperes. It is convenient to use tweezers for replacement.
A fuse of the recommended rating should be installed. Otherwise, there is a high risk of insulation melting, short circuit, and fire. After repair, you cannot connect powerful devices to the cigarette lighter socket. The maximum power is 300 watts. Calculated using the formula P=I*A, where I is the network voltage (12 volts), and A is the amperage (25 amperes).
Checking the RTD
So, your sensor is already in order, but there is excessive fuel consumption and other problems indicating that the regulator is acting up. First of all, check it.
This is done like this:
- You need to unscrew the plug of the fitting responsible for controlling the fuel pressure. Look, if the seal ring is torn or simply no longer elastic, it (or even the entire plug) needs to be replaced;
- Unscrew the spool from the fitting, this is done in exactly the same way as in any tire;
- Using a tire pressure gauge secured with a clamp to the fitting, measure the pressure while the engine is running. It should be within normal limits;
- When disconnecting the vacuum hose of the regulator, the pressure should increase slightly (by 0.2 - 0.5 kgf/cm2). If this does not happen, then there is only one solution for your VAZ 2110 - you need to replace the RTD. On average, the price of a standard RTD fluctuates around 300 rubles; an analogue of the SOATE RTD costs about 600 rubles.
When can fuel consumption increase?
It is worth paying special attention to such a sign of a regulator malfunction as increased fuel consumption. The car will require more gasoline to operate if the valve in the regulator is faulty or, conversely, it does not hold fuel. In the first case, excess fuel is not returned to the tank; the car owner may notice pressure above 2.5 kg/cm2. As a result, more gasoline enters the combustion chamber of the engine, which is not completely consumed.
If the valve does not perform its functions, fuel “staggers” through the system. The pressure in the fuel system decreases, and as the speed increases, the engine feels a clear shortage of gasoline. The power unit becomes less responsive and powerful. A valve malfunction can be noticed when starting the car for a long time - during the process, the starter has to be turned for a long time until it creates the necessary pressure.
How to replace the brake pressure regulator in a VAZ 2110?
1. The first thing to do is to release the regulator drive lever; to do this, lift the bracket up. If necessary, use a screwdriver to loosen the earring bracket. All manipulations are performed with a key of 10.
2. After disconnecting the lever, carefully remove the earring bracket.
3. Prepare a container; it needs to be placed under the junction of the regulator with the pipes; brake fluid will flow out of it. We disconnect the four tubes by unscrewing the fastening nuts. We wait until the liquid drains. We plug the holes in the tubes; this can be done, for example, with caps on the cylinder bleeder valves. It is recommended to mark the tubes so that during further installation you will not confuse them.
4. Unscrew the front bolt securing the bracket with the regulator.
5. We unscrew the rear bolt, which we hold the regulator on the side of the bracket, after which we remove the regulator (sorcerer), without unscrewing the drive.
6. If you need to replace drive parts, unscrew the bolt that holds the locking lever and disconnect the drive lever from the elastic lever.
7. When you connect the drive lever to the elastic lever, following the sequence, the clamp fork should fit into the groove on the elastic lever.
8. Next, install the brake pressure regulator in the same order as it was removed. Please note that the front mounting bolt is slightly longer than the rear one.
9. When replacing, it may be that the lever spring begins to protrude, thereby interfering with the installation of the regulator. To avoid problems, move the drive lever as far forward as possible beyond the protrusion.
10. Installation is complete, now crimp the earring brackets with pliers. To make sure that the system is working, pump and adjust the pressure.
Replacement is carried out in the following order:
- It is necessary to reduce the pressure in the fuel system, then unscrew the nut securing the fuel pipe to the RTD;
- Unscrew the bolt with a 10mm wrench securing the oil level indicator guide tube and remove it;
- Unscrew the bolts securing the RDI to the ramp;
- Remove the fitting from the fuel rail, remove the RTD;
- When installing a new regulator, experienced car owners advise lubricating the O-rings with gasoline.
In the future, do not forget to look at the fuel level sensor. If a large flow rate is detected, you may suspect that the replacement was not carried out entirely correctly, and it needs to be carried out more carefully.
How to check and replace the VAZ 2110 regulator?
In order to independently check the pressure in the system, and therefore the correct operation of the regulator, you need to take a pressure gauge, the maximum pressure in which is up to 10 atmospheres. You should not use a device with a larger scale, as its readings will have a serious error. It connects between the fitting and the fuel pipe:
- first turn off and cool the engine;
- locate the fuel rail under the hood;
- remove the plug from the fuel pressure fitting;
- unscrew the fitting nipple using a spool valve;
- wipe the surfaces if fuel splashes appear under the influence of residual pressure;
- pull a hose with a diameter of up to 9 millimeters onto the fitting and secure it with a clamp;
- Connect the second hole of the hose to the pressure gauge.
Preparatory work
- We take a pre-prepared pressure gauge, and to prevent fuel spills and air leakage, we wrap flax or fum tape around the tip.
- We are preparing a hose with a maximum internal diameter of 9 millimeters, and clamps will be needed to secure them.
- We place the prepared rags on the engine in such a way that the hose and pressure gauge fixed on it cannot roll off the surface. This is done to prevent excess fuel from spilling over the surface of the engine.
- We wrap flax or tape around the pressure gauge, then fix the hose on it and tighten everything with a clamp.
- On the ramp, unscrew the spool valve from the nipple (in this case, fuel splashes are possible due to the presence of residual pressure - approx.).
A regular wheel cap came in handy.
We put a hose with a pressure gauge on the ramp connections and secure everything with a clamp.
Pressure gauge with pipe assembly.
We place the pressure gauge on a previously prepared rag, and the preparatory work can be considered completed.
Measurement procedure
Before you start working, you can try to relieve the pressure in the fuel system. To do this, remove the fuel pump fuse (which is located on the right side of the panel, under the front passenger’s left foot - approx.). Where 3 relays and 3 fuses are located. In the photo below it is located under the number “5”. After removing the fuse, turn on the ignition and check by ear that the fuel pump is not pumping. We start the car and wait for the engine to stall.
- After everything is ready, we check the already attached end of the pressure gauge with the hose for a secure connection.
- Next, start the engine and look at the readings that appear.
Thus, we diagnose the results that appear and compare them with the results of the norm.
After all the work has been done, unscrew the hose with the pressure gauge, screw in the spool and return everything to its original state.
Note!
The peculiarity of measuring pressure using a pressure gauge is such that its initial value on the scale has a certain inaccuracy. That is, when the air analogue has a measurement period of 15-20 atmospheres, and for fuel control the required maximum value is 5-7 atmospheres, then all measurements taken will have an error equal to the initial values on the device. Therefore, pressure testing should be carried out on a pressure gauge with maximum values of up to 8 atmospheres.
Fuel pressure regulator VAZ 2110 - check and replacement
Fuel pressure is one of the most important indicators used in diagnosing the operation of a car engine. The efficiency and usefulness of all parts that make up the fuel system depend on it. That is why it is necessary to maintain the correct pressure, regardless of the functioning of the engine. This task is precisely performed by the RTD in the VAZ 2110. Every motorist must remember that it is the pressure regulator that affects gasoline consumption and engine power. A faulty regulator will not allow the engine to operate normally and should be replaced.
From this article you will learn what signs of problems with the RTD are most often found in the VAZ 2110, as well as how it is possible to independently check the regulator and replace it.
Cleaning Priora injectors
There are two options for washing injectors: with and without removing them from the car. The removed injectors are washed on special stands using ultrasound, under the influence of which even the oldest contaminants disappear. Ordinary drivers do not have such stands, so below we will consider a more popular option for washing injectors without removing them from the Priora. Here's what you'll need for this:
- liter of special flushing fluid;
- two automobile nipples;
- automobile fuel filter;
- a pair of metal clamps;
- a meter piece of rubber hose with a diameter of 12 mm;
- drill with 13 mm drill bit;
- electric pump;
- two liter plastic bottle.
Flushing sequence
- The bottom and cap are drilled into the plastic bottle. This is done with a “13” drill. Automotive nipples are inserted into the holes.
Ordinary car nipples are inserted into the holes of a plastic bottle
Priora injectors are washed using a filter and a plastic bottle
The green button is clearly visible on the Priora fuel hose
The main fuel hose of the Priora is connected to the fuel filter for flushing
The device for washing Priora injectors is assembled and ready for use
A car water pump plays an important role in the operation of a car engine. It is possible to recognize its malfunctions using the following article: https://vazweb.ru/desyatka/pitanie/zamena-forsunok-vaz-2114.html
Symptoms of a problem
Before moving directly to the process of replacing the regulator, you need to mention the signs of its malfunction.
The main one is problems in the operation of the valve, especially when the valve does not hold well, i.e. fuel circulates freely. This in turn provokes a decrease in pressure. As a result, the engine power decreases, because it does not have enough fuel to increase speed. When you turn on the engine, it becomes necessary to work for a long time with the starter (i.e., a device that spins the engine shaft in order to start it) in order to create the required pressure. If the valve is completely inoperative, fuel stops being discharged into the tank. This provokes an increase in pressure. As a result, there is excessive consumption of gasoline, as well as incomplete combustion.
In addition, there are other signs indicating a malfunction of the RTD in the VAZ 2110:
- the engine stalls at idle;
- the motor does not work at full power;
- unstable engine operation;
- the content of CO (carbon monoxide) and CH (methane) significantly exceeds the established standards;
- jerking while driving.
How to check the RTD of a VAZ 2110?
If you want to check the fuel pressure regulator 2110, you must first unscrew the special plug that closes the fitting for checking the pressure.
You should look for the fitting on the ramp block, from the end. After you have unscrewed the plug, you need to unscrew the spool from the fitting. Use the back of a metal tire cap for this.
After the completed operations, attach a pressure gauge to the fitting using a hose. You can take a regular pressure gauge that you use to measure tire pressure. Secure the ends of the hose with clamps. Now you can start checking - turn on the engine. We continue to check the pressure - it is necessary to disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure regulator. After removing the hose, the correct pressure gauge readings should be in the range of 0.2 - 0.7 cm 2. Other data indicates the need to replace the RTD.