The crankshaft position sensor on VAZ 7 series vehicles is designed to synchronize the fuel injection process with the ignition system. Failure of this part leads to unstable engine operation and incomplete combustion, and hence to fuel overflow. The engine does not reach full speed or does not start at all. The article describes the reasons for the malfunction of this unit, its design, testing methods, as well as the process of removal from the engine.
Crankshaft sensor for VAZ 2107
The crankshaft position sensor on VAZ 7 series vehicles is designed to synchronize the fuel injection process with the ignition system. Failure of this part leads to unstable engine operation and incomplete combustion, and hence to fuel overflow. The engine does not reach full speed or does not start at all. The article describes the reasons for the malfunction of this unit, its design, testing methods, as well as the process of removal from the engine.
Symptoms of a problem
Problems with difficult engine starting, overfilling or incomplete combustion of fuel can arise for various reasons. A faulty crankshaft sensor could be one of them.
Symptoms of a malfunction may include:
- Noticeable deterioration in the dynamic characteristics of the vehicle. The engine is unstable at low speeds, the car accelerates slowly and does not accelerate.
- Engine speed “floats”. This is noticeable even by the tachometer needle at low speeds. The arrow moves either above or below the “800” rpm position.
- Noticeable increase in fuel consumption.
- Detonation appears when under load or stopping the engine.
- The engine does not start or stalls when starting.
The reason for such malfunctions lies in the design of the DCPV.
DPKV design
DPKV or crankshaft position sensor on the VAZ-2107 is an inductor with a magnetic core. The part is a plastic or aluminum case, inside of which there is a magnetized core on which a copper wire is wound. The core wire is insulated from the body using PVC insulation or compound resin.
Principle of operation
An inductive type DPKV is installed on fuel-injected VAZ-2107 vehicles. The sensor is located next to the “monitoring” disk. There are teeth along the entire edge of this disk. And only in one place there are no 2 teeth. It is to the position of this gap that the DPKV reacts. With each revolution, a signal is sent to the electronic control unit (ECU), thereby notifying that an empty section of the disk has passed. Next, the ECU sends a signal to the injectors, only after which fuel is injected. In addition to fuel injection, synchronization with the operation of the ECU is carried out. Based on the supplied signal, it is possible to determine:
Location
On the VAZ 2107, the DPKV is located on the cylinder block body; there is a special ebb point for it, in the ear of which it is installed, and the control circuit connector is connected to it. You can see the sensor by looking under the hood; the sensor is located near the crankshaft pulley between the engine and the radiator cooling fan.
Sensor check
In order to make sure that the crankshaft position meter is working properly, it is necessary to check it. On injection VAZ-2107 cars, the crankshaft position sensor is located on the camshaft cover bracket.
There are 3 ways to check.
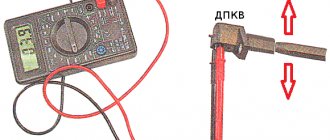
A quick check can be done using a screwdriver and a multimeter. Connect the probes of the device to the coil terminals. Set the measuring device to the “continuity” position. Place a metal screwdriver in front of the magnetic core. While the screwdriver is in front of the core, the multimeter will show the moment the contacts open.
It is important to remember that before removing the part, you must disconnect the “-” terminal of the battery. Don't forget about setting tags. This will help you easily install the sensor and start the engine.
Checking the integrity of the VAZ DPKV using a multimeter
You can check the VAZ crankshaft position sensors using the ohmmeter built into any modern multimeter. Applicable to VAZ 2110, 2112, 2114, Priora, Kalina models.
To do this you need to follow a few simple steps:
- It is necessary to carefully inspect the sensor itself before removing it from the car, or rather, check whether there is a gap between the sensor and the synchronizing disk. It may turn out that it is not there at all, due to a large amount of adhering dirt, and this could lead to malfunction.
- If everything is fine with this and there is a gap, you can remove the sensor from the car.
- Next comes the stage of assessing the external state of the DPKV. Check the housing for any signs of damage, the core must be clean, inspect the output contacts for oxidation, and the wires for deformation.
If contamination is found on the contacts of the crankshaft position sensor, before checking it, you must thoroughly wash it with clean gasoline or alcohol, then use a needle file or sandpaper to clean the connector contacts.
- After cleaning and washing, the DPUV should be thoroughly dried. Then you can start taking measurements. The multimeter must be switched to the resistance position, and the probes of the device must be connected to the output terminals of the sensor.
If the DPKV is working properly, then it should have a resistance of only 550 - 570 Ohms. If the multimeter shows a different value, then the sensor should be replaced.
Removing the sensor
Before checking the crankshaft position sensor or replacing it, you must remove this unit.
To do this you need:
The operation to replace the sensor is carried out in the reverse order.
The crankshaft position sensor on the VAZ-2107 is responsible for the stability of the injection system of the ignition and gas distribution system. These parameters affect the operation of the engine, and therefore the overall dynamics. Timely inspection and replacement of a faulty unit will help to avoid problems with bending of the intake and exhaust valves, fuel overflow and excessive fuel consumption. The engine will gain smoothness in the set of revolutions, their stability and dynamics during acceleration.
Purpose, device and principle of operation
The engine crankshaft position sensor in a car performs the main adjustment of the fuel injection system. Its presence ensures synchronous operation of each engine injector and the ignition system as a whole.
The controller consists of the following components:
Unstable operation of the controller will lead to failures in timing when supplying fuel. When the device operates, the vehicle's control module, which is a microcontroller, ensures the correct position of the piston at a specific period of time for each cylinder of the internal combustion engine.
To ensure adjustment through the device, the process is built according to the following algorithm:
If the crankshaft position sensor is working correctly, the car's engine will operate at maximum performance. To produce maximum power, the power unit will require a minimum of fuel.
Separately, we should talk about the different types of devices:
Replacing the crankshaft position sensor on a VAZ 2104, VAZ 2105, VAZ 2107
Welcome! Crankshaft position sensor - it monitors where the crankshaft is during operation and in a certain place (When the pistons are at TDC), the sensor sends a signal to the controller, which in turn pours fuel into the engine through the injectors and gives a spark through the spark plugs ignition, thanks to this sensor, all this is done together, that is, first the fuel is poured in and then with the help of a spark it is burned, if this sensor fails (completely means), then you will not start the engine because it will not be able to transmit a signal when the pistons will be at TDC, and therefore there will be no fuel or spark, so the engine will not start.
Note! To replace this sensor, you don’t need many tools, just take one Phillips-head screwdriver, and of course you will need a new sensor itself!
Where is the crankshaft sensor located? In the injection classic, it is installed on the bracket of the camshaft cover (the cover is indicated by a green arrow, and the bracket on which the sensor is located is red), it is directed towards the crankshaft pulley, in the photo below, unfortunately, the pulley has already been removed and you will not be able to see it, but on In your car it will be installed, and the pulley will be installed on the shaft itself (Crankshaft), this shaft is also indicated with a blue arrow.
When should you replace the crankshaft position sensor? Let us repeat once again, the crankshaft sensor is the only sensor in the injection classics; if it fails, the engine will no longer start, so if your “check engine” light comes on and the car does not start, then you can blame this sensor, of course, the first thing you do is check it you will have to remove and then check (we will write about how to perform the check a little later, so as you read the article you will learn how to do this), by the way, even if this sensor comes out (depending on what is broken inside it), the engine can still start, but run it will either not be smooth (the speed will float), or the power will noticeably disappear, and besides, it will most likely stall at low speeds.
How does the fuel system receive the signal from the sensor?
While the sensor is operating, the on-board computer (microcontroller inside the car) determines the specific position of the piston at a certain moment of its operation in each of the cylinders. To regulate operation using a sensor, the process is built according to the following plan:
- The crankshaft has a special gear in which 2 teeth are specially omitted.
- When the crankshaft moves, all the teeth pass next to the DPKV sensor, greatly distorting the state of its magnetic field.
- As a result, pulses are generated in the inductance coil of this device, which are sent to the on-board computer database. In this case, the missing 2 teeth are the starting or zero point, thanks to which the computer determines the initial position of the shaft.
- Next, the computer inside the car counts the number of pulses sent by the device and determines the position of the crankshaft in each period of time.
- After this, the return signal is sent by the computer to the sensor responsible for triggering the fuel injector, which already supplies fuel to the ignition system.
Thus, if the DPKV works correctly, the car will operate at the highest performance, while consuming a minimum of fuel.
How to replace the crankshaft position sensor on a VAZ 2104, VAZ 2105, VAZ 2107?
Note! Before you go to the auto store to purchase this sensor, we recommend that you check the markings on the old one, especially since you can remove it in less than a minute, or even easier, come to the auto store by car (If possible) and remove this sensor from it directly there, after that, show the seller that it is exactly like this, it’s just that each sensor has a core (If you don’t know what a core is, then study the article: “What is DPKV?”) has its own length and if it is not normal (For example, you have a longer install the sensor), then your car will not work correctly, and in general, most likely the end of the core will rest against the teeth of the crankshaft pulley, so the sensor must be exactly the same length as the old one you had, which you removed from the car, please note This!
Removal: Removal is not difficult, as we said earlier, first disconnect the main block of wires from the sensor (see photo 1), this block is secured by a latch, bend it a little and then remove the block (When you remove it, make sure there is no water it didn’t get inside), then use a screwdriver to unscrew the screw that holds the sensor itself (see photo 2) and then, pulling the sensor, remove it from the bracket in which it is installed.
Note! If it is raining outside, for example, and if you are simply afraid that a short circuit may occur if water gets into the inside of the wire block, then in this case, disconnect the minus terminal from the battery and after that you can no longer be afraid of anything, since the system is you will be de-energized, but also try to prevent water from getting into the block! (If you do not know how to disconnect the battery, then study the article in which, in paragraph 1, it is described how to remove the terminal from the battery, this article is called: “Replacing the battery on a VAZ”)
Installation: The sensor is installed in its place in the same way as it was removed, by the way, if you want to check your old sensor for operability, then read a detailed article about this, called: “Checking the DPKV for serviceability.”
Source
Electronic engine control unit
The VAZ 2107 engine control unit is the main element responsible for the proper operation of the entire internal combustion engine. The block processes a huge number of different processes. All sensors that are installed on the “seven” are directly connected to the computer. It is he who reads information from the sensors and sends signals to fuel injection with the required amount of gasoline and fuel concentration. If the ECU breaks down, the car may stop starting or have problems similar to signs of failure of any of the sensors.
The engine block is located under the glove compartment on a special bracket.
VAZ 2107 crankshaft sensor - malfunctions and testing
The crankshaft position sensor of the VAZ-2107 car, as well as other injection vehicles, is designed to synchronize the operation of the engine ignition system, as well as fuel injectors. Failure of this part will lead to one of three situations: unstable engine operation, incomplete combustion of fuel, or complete engine failure.
The most common types of crankshaft sensors are induction. This is exactly the sensor installed on VAZ-2107 injector cars. They have their own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, as well as diagnostic and repair methods. This information will be briefly presented below.
see also
The article will talk about the VAZ 2107 hall sensor, the advantages of using it, and most importantly, diagnostic and replacement methods. This is an electronic component that is used in the ignition systems of modern cars. Of course, they can be called modern rather conditionally, since Hall effect sensors in the ignition system are used only on carburetor engines. If we are talking about injection systems, then you will find a similar design in them only in revolution and speed sensors, or in alarm systems.
Crankshaft position sensor design
The design of the DPKV is simple and consists of a small number of elements. In particular, its main element is a magnetized steel core on which a thin copper wire is wound. On top they are covered by a plastic (plastic) case. Naturally, in a copper winding, all the wires are insulated from each other (this can be implemented in different ways, for example, through compound resin or conventional insulation made of PVC or other material).
The operating principle of the device is as follows. In the immediate vicinity of the sensor, a “monitoring” disk with teeth around the perimeter rotates. Two of them are missing, creating a kind of emptiness. The main task of the sensor is to record the passage of this section and send appropriate signals to the ECU. If it does this late or with a weak signal, the electronic unit will provide incorrect information to the fuel system, and a mixture of suboptimal composition will be formed.
DK (Oxygen sensor) – lambda – umbrella
It is installed either next to the catalyst or on the exhaust pipe of the muffler. Some foreign cars have two of them (before the catalyst and after). The main task is to determine the remaining oxygen in the exhaust. If detected, the fuel mixture is lean; if not detected, the fuel mixture is rich. The readings, as usual, are sent to the ECU and used to adjust the fuel supply.
This is a fairly reliable electrochemical design, however, it can also fail. If it breaks, fuel consumption increases, as well as emissions of harmful substances.
Cost from 1000 to 2500
Crankshaft sensor for VAZ 2107
In any modern car there are many sensors and devices. But only one of them has the ability to turn off the engine. Such a sensor is the crankshaft position sensor.
The crankshaft sensor is located on the camshaft cover bracket. DPKV reports data on the performance and speed of rotation of the crankshaft to the control unit. This data comes in the form of magnetic pulses. Depending on the vehicle assembly, the DPKV may differ.
The crankshaft sensor on a VAZ 2107 with an injector engine consists of a steel core, which is wrapped with copper wire. This design is located in a plastic housing. The wires that are in the sensor are separated from each other by a special polymer insulating resin.
CPPS (crankshaft position sensor) is also called a synchronization sensor. Thanks to it, electronic control works synchronously with the mechanism that provides engine gas distribution and provides a signal for clock, cyclic and angular control of fuel mixture injection and the ignition system. The operating principle of this device is not too complicated and consists in creating inductive signals.
The crankshaft sensor detects the passage of metal pulley teeth near the sensor. The pulley has 60 teeth, two of which are missing. When a gap passes where teeth are missing, this is recorded and allows for order in the operation of the ignition and power systems so that there is a clear distribution of fuel supply through the injectors. Thus, DPKV is an important link, without which stable operation of the car as a whole is impossible.
Design features
To check and replace the sensor, you need to know what it looks like. It wouldn’t hurt to talk a little about its internal structure at the same time. The design of this device is very simple. But it varies somewhat depending on the purpose of the sensor and the installation location. For example, digital ones turn out to be more complicated; they have a semiconductor crystal built into the sensitive part. Between the semiconductor crystal and the small circuit (responsible for switching) there are short sections of connecting conductors.
The semiconductor crystal in the VAZ 2107 Hall sensor must occupy a special position. The magnet is positioned so that its field lines are perpendicular to the plane of the crystal. It is due to this that induction (magnetic) occurs. In this case, some current passes through the crystal. Under the influence of a magnetic field, an electromotive force is generated and supplied to the switching circuit.
Types of sensors
After it has become clear what the crankshaft sensor on the VAZ-2107 and other cars is responsible for, it is worth highlighting the main types of DCPV. At the moment there are several varieties. The table shows modern types of crankshaft position sensors with a description of their operating principle.
| Sensor type | Principle of operation |
| Induction | Its action is based on the use of a magnetized core wrapped in copper wire. The ends of the wire are brought out in order to measure voltage changes. The sensor is mainly used in modern cars. |
| Optic | It works using an LED that emits a beam of light and a receiving device. When a control tooth passes, the beam of light is interrupted, which is recorded by the monitoring device. The collected information is sent to the ECU. |
| Hall Sensor | It works due to a magnet that is installed on the crankshaft and which is fixed. When DC movement begins in the sensor, it is immediately recorded on the synchronizing disk. |
Checking with an oscilloscope
Modern digital oscilloscopes make it possible to effectively monitor and find faults in crankshaft position sensors. Below are step-by-step steps for identifying malfunctions in the injection system using an oscilloscope.
DPKV produces a signal, which is a series of electrical pulses, their generation occurs during the rotation of the crankshaft and the synchronizing disk. At this point, the cavities between the teeth act on the magnetic field in the sensor and generate a pulsed alternating current in the sensor coil.
For greater diagnostic accuracy, the sensors should be checked with the engine running. However, this can be done by first removing the device. To start testing, you need the electronic oscilloscope itself and software for it.
Check sequence on the removed sensor:
- Connect the probes to the output contacts of the DPKV.
- Launch the oscilloscope program.
- Hold any metal object near the sensor.
If the DPKV is working properly, the oscilloscope will display an oscillogram image on the screen, according to the signal from the sensor. If it detects the appearance of a metal biter in the electromagnetic field of the coil winding, it means it is working.
More accurate diagnostics can only be carried out with the ignition on and the engine running. To do this, the probes are connected in parallel with the ECU contacts.
Replacing the sensor
The crankshaft sensor may become unusable and then it needs to be changed. But first, you should pay close attention to the signs of malfunction to be sure that the sensor really needs to be replaced. These signs are:
If the crankshaft sensor on a VAZ 2107 fails, then it must be checked for functionality. To do this, you need to prepare a screwdriver and a multimeter.
Set the position on the multimeter, which corresponds to 200 MV. The outputs from the DCPV must be connected to a multimeter. Bring an object, maybe a screwdriver, in close proximity to the core. Voltage surges should appear on the multimeter. If this does not happen, then the sensor is broken and needs to be replaced.
To install a new crankshaft sensor on a VAZ 2107 with your own hands, you will need:
First of all, it is necessary to de-energize the sensor. To do this, you will need to remove the block with wires from it.
Unscrew the mounting screw with a 10 mm socket wrench and remove the DPKV.
Install a new one in place of the broken sensor.
After installing a new DCPV, you should check the distance between the sensor core and the pulley teeth. It should be within: 1 mm +/- 0.41 mm.
If the numbers are different, this indicates that there is dirt under the device. The sensor may be pushed out or pushed back too far. You cannot reduce the distance, you can only expand it. After installing the sensor, start the engine and check its operation.
Thus, the crankshaft sensor on the VAZ-2107 is a rather important device. If the faults mentioned above occur, first of all you need to check the crankshaft sensor. It does not have a complicated device, and you can check it in the simplest way - measure the resistance of the coil. If there are no diagnostic devices, then you need to contact a professional at a service station.
Source
Methods of checking in garage conditions
Checking the operation of the DPKV can be done in three ways:
Using an ohmmeter, you can ring the controller winding to measure the resistance value. If an ohmmeter is not available, multimeters can be used. As a result of diagnostics, the resistance parameter on the working sensor should be from 550 to 750 Ohms.
The ringing process itself consists of measuring the resistance value of the coil in the inductive controller. If this element of the device is inoperative, the malfunction will affect the operating parameter of the resistance. Therefore, before performing the test, it is necessary to set the required range and diagnose the correct functioning of the device using probes.
The method of checking the crankshaft sensor using an ohmmeter is considered the simplest to implement, but it cannot give a 100 percent result.
Nikolay Vaganov demonstrated the procedure for diagnosing DPCV using a multimeter.
If signs of malfunction are detected in the operation of the crankshaft sensor, you can resort to a comprehensive check method. This diagnostic option is difficult to implement, but more accurate. To carry it out, you will need a set of instruments and equipment that is not available at every service station.
To complete the task you will need:
When performing a comprehensive diagnosis of the crankshaft sensor, it is recommended to maintain the temperature in the region of 20-22 degrees. This condition is required to ensure correct values that the equipment will produce.
Features of complex device diagnostics:
The Auto Electrician HF channel showed another unique option for diagnosing the controller - using a wrench.
This diagnostic option is the most accurate of all those described. This is because not only the spare part for the crankshaft is checked, but also its design during engine operation. The essence of diagnostics is to connect an oscilloscope to the controller and monitor signals through icons that extend from it. When performing the test, there is no need to remove the sensor from the power unit, since all actions will be performed with the internal combustion engine running.
When receiving an impulse from the controller that does not correspond to the nominal parameters, the power unit will twitch noticeably. There may be difficulties when starting the engine.
The appearance of such defects when monitoring output pulses from the controller will indicate the following problems:
It will be possible to determine exactly which component is inoperative after a complete diagnosis of the type of change in the pulse waves. Usually it is not the controller itself that needs to be replaced, but the toothed disk - over time it wears out and becomes unusable.
The Car Diagnostics channel talked about the features of checking the DPKV using a pocket oscilloscope.
The simplest and least labor-intensive way to check for a unit malfunction is diagnostics using diagnostic equipment. Diagnostic time takes no more than 5 minutes, and there is no need to go into the engine compartment. The range of diagnostic devices on the market is huge, both in functionality and pricing. Among budget devices, we can recommend a car diagnostic scanner, made in Korea – Scan Tool Pro Black Edition.
According to our personal experience, this device, despite its low price in the region of 1950 - 2500 rubles. is able to diagnose the general condition of the car by displaying error codes with their descriptions, as well as the operation of various sensors in real time. The auto scanner has a compact size and is connected via the OBD-2 diagnostic connector. Data transfer is carried out to any modern device - smartphones, tablets, PCs running Android, iOS and Windows OS.
If you do not have such adapters, then you need to remove the sensor and perform the diagnostics described below:
If the above actions do not produce results, the crankshaft sensor is dismantled and checked with a multimeter in 2 stages. At the first, the resistance between the terminals of the device is measured, which makes it possible to verify the integrity of the induction winding. Clean the contacts, turn on the ohmmeter and check the resistance between them. Normal readings are in the range of 500–700 Ohms; if the turns are shorted, you will get a zero or reduced value; if there is a break, you will get infinity.
At the second stage, the performance of the element is tested according to step-by-step instructions:
Further actions are as follows: the broken crankshaft speed meter is replaced with a new one; the part cannot be repaired. The working sensor is installed back, maintaining the gap, and the troubleshooting continues in another place.
A few words about how to check the crankshaft sensor on the road when you don’t have a multimeter or other diagnostic tools. You will need 2 wires and an LED light bulb from any car lamp (for example, an interior lamp). For convenience, unscrew the element and connect the lamp to the connector, then apply a wrench to the magnet, as described above. A working sensor will cause the LED to flash.
Crankshaft sensor for VAZ 2107 - design and principle of operation
The crankshaft position sensor or DPKV on the VAZ 2107 ensures engine operation (not stable, but overall). With its help, the ECU knows what position the crankshaft is in. From this, the control unit knows the location of the pistons in the cylinders, which directly affects fuel injection through the injectors, and the occurrence of a spark to ignite the fuel assembly.
The device in question has a simple design. The sensors installed on the seven work on the principle of inductance. The part consists of a metal cylindrical base with a wire wound on the surface (coil). The top of the coil is covered with a permanent magnet. The operation of the device is associated with a ring gear, which is attached to the crankshaft. It is with the help of this ring gear that the sensor records signals and transmits them to the computer. The principle of operation of the device is as follows: when the crown tooth is located at a level with the steel core of the DPKV, an electromotive force is induced in the winding. A voltage appears at the ends of the winding, which is detected by the ECU.
The gear wheel consists of 58 teeth. Two teeth on the wheel have been removed to determine the starting position of the crankshaft. If the DPKV fails, which is extremely rare, then starting the engine and its operation is simply impossible. The marking of the sensor, which is installed on the VAZ 2107, is as follows - 2112-3847010-03/04.
Signs of sensor failure
The main sign of a DPKV failure is the impossibility of starting the engine. Such a breakdown occurs due to a complete malfunction of the device. If the surface of the DPKV is dirty or the contacts are oxidized, the following malfunctions can be detected:
If the above symptoms are detected, then DPKV should be checked. To do this, you need to know where the crankshaft sensor is located. On the VAZ 2107, the DPKV is located on the front engine cover, where it is fixed to a bracket. On other car models, this element may be located on the other side of the crankshaft near the flywheel. If you suspect a breakdown of the DPKV, it must be checked.
Methods for checking DPKV
You can check the suitability of the crankshaft sensor on the seven in three different ways. To begin with, it should immediately be noted that the malfunction of the device can be determined visually. To do this, you should inspect the part, and if there is contamination, as well as microcracks on the magnet body, you can judge that it is broken. Contaminants are easily removed, but if there are microcracks, the part must be replaced.
The crankshaft sensor on the VAZ 2107 injector is checked in three ways:
The inductive crankshaft position sensor, which is used on the seven, creates sinusoidal pulses. They arrive at the ECU, where they are rectified into rectangular pulses. Based on these pulses, the control unit makes a decision about sending a pulse to the injectors and spark plugs at the right time. If during the inspection it turns out that the DPKV is faulty, it should be replaced.
How to replace the crankshaft sensor on the seven
Knowing where the DPKV is located on the VAZ 2107, it will not be difficult to dismantle the device. This procedure is not difficult and does not take much time. Detailed instructions on how to replace the crankshaft sensor on a VAZ 2107 look like this:
After replacing the device, you can check the performance of the engine. Despite the fact that the part rarely fails, it is recommended to always have a spare sensor in the car. If an element fails, it can always be quickly replaced to continue moving.
As a result, it should be noted that DPKV is the most important sensor. It has a simple design and rarely fails. The estimated cost of the device for the seven is about 1000 rubles. It is recommended to check the part not only when the first signs of a malfunction appear, but also periodically to clean the working surface from contamination.
Source
Types of sensors and their operating principles
Sensors are divided into types depending on the principle of operation, but despite this, they all consist of two main components:
- the crankshaft position sensor itself;
- synchronization disk.
The sensors are placed in a plastic or aluminum case and are installed next to the sync disk using a bracket. For connection to the general vehicle control system, the sensors have a standard connector. It can be located either on the sensor body itself or displayed separately on the wire. The task is to count the teeth on the synchronizing disk.
A synchro disc is a metal or plastic pulley with square teeth. The disc is rigidly fixed to the crankshaft pulley itself or to its toe. This is done in order to give the parts the same speed.
Sensors are divided into types depending on the physical principles of their operation. The three most common types are:
- inductive (magnetic);
- Hall Sensor;
- optical (light).
All crankshaft sensors have their own design features and operating principles.
Inductive DPKV
The crankshaft sensor consists of a magnetic core placed in a coil. The sensor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction in a conductor. The sensor has a constant magnetic field and in a quiet state no currents flow. When a metal synchrodisk tooth appears near the magnetic core, its field begins to change randomly, which subsequently causes the induction of currents in the coil. As a result, an alternating current of a certain frequency is generated at the output ends of the DPKV. The readings are taken and transmitted to the computer, which carries out calculations and determines the position and speed of the crankshaft.
Sensors of this type are the simplest in design, therefore they are most often used on all types of power plants. Their main advantage is that they do not need additional nutrition. Thanks to this, the connection occurs using only two wires to the control unit. Installed on all VAZ models with both 8-valve and 16-valve engines, in particular 2110, 2114, Priora.
Hall Sensor
Based on a principle discovered by scientist Edwin Hall. If you pass a current through two opposite sides of ferromagnetic plates located in a magnetic field, then a voltage will appear at their other ends. Sensors of this type are made using specialized microcircuits, which are placed in a housing with magnetic cores. There are magnetic teeth on the synchronization disk. In a quiet state, the sensor does not produce any voltage, and when a synchrodisk tooth appears in the magnetic field zone, alternating currents appear at its ends, which are supplied to the electronic control unit.
This type is a more complex sensor, but at the same time the most accurate at all speeds. To function, the device requires additional power, so the connection is a little more complicated than the previous type.
Optical sensor
It consists of two main elements - an LED that emits an optical signal and a photodiode that captures it. Between these optical elements are the teeth or holes of the synchronizing disk. During rotation, the synchro disk periodically blocks the light emanating from the light of the diode; as a result, a pulse current is formed at the ends of the photodiode, which is transmitted and converted by the measuring unit.
They are used quite rarely due to difficulties in use. Sensors begin to fail when they are highly contaminated with dust, liquid dirt, exhaust gases, etc.
Sync disk
For proper operation of the DPKV, standardized sync disks are used. They are divided into 60 teeth, which are located every 6°. To ensure synchronization of the sensor with the control unit and connected elements, as well as to set the starting point for counting crankshaft revolutions, there is no pair of teeth at a certain point on the synchronizing disk (synchronizing disk type 60-2).
According to the standard, the first tooth after the missing ones must coincide with the location of the first or last cylinder at top dead center (TDC) or bottom dead center (BDC). In addition to these, there are discs with two missing teeth located at an angle of 180° relative to one another (synchronizing disc type 60-2-2).
Mainly used on modifications of diesel power plants. Synchronizing disks for working with inductive devices are made of steel, in some cases together with the crankshaft pulley. To work with a Hall sensor, plastic disks are most often used, and permanent magnets are placed on the teeth.
It is also worth mentioning that position sensors are used not only on crankshafts, but also on camshafts. This is necessary to monitor the position of the camshaft and its rotation speed, as well as to make adjustments to the operation of gas distribution systems. Simply put, so that the brain knows into which cylinder fuel needs to be injected at the moment.