VAZ 2107 is a five-seater passenger car of a classic layout with a front longitudinal arrangement of the power unit and rear drive wheels. The engine is a four-cylinder, four-stroke, eight-valve, in-line, carburetor or fuel injection system. The body is a supporting structure, all-metal, welded. Body type - sedan .
Overall dimensions of VAZ 2107
The VAZ 2107 car is equipped with a carburetor engine of the VAZ 2103 model with a working volume of 1.5 liters. The modification of the VAZ 21074 car is distinguished by the engine of the VAZ 2106 model with a displacement of 1.6 liters.
In recent years of production of this model, modifications of the VAZ 2107-20 car with a VAZ 2104 engine with a displacement of 1.5 liters and VAZ 21074-20 with a VAZ 21067 engine with a displacement of 1.6 liters, equipped with fuel injection, mechanical part (cylinder block, connecting rod) were produced -piston group, crankshaft) of these engines are respectively identical to the VAZ 2103 and VAZ 2106 engines. The VAZ 2104 and VAZ 21067 engines are equipped with more powerful generators and starters with planetary gearboxes. The installation of engines with distributed fuel injection in cars, as well as the use of a gasoline vapor recovery system and catalytic converters in exhaust systems, made it possible to reduce the toxicity of exhaust gases and fuel consumption, and increase the reliability of engine starting in cold weather. The body, chassis and transmission remained unchanged.
The predecessor is the VAZ 2105, the successor is the Lada Granta.
History of creation and advantages of the VAZ 2106
At the time of its creation and many years later, the “six” was an advanced car. The model based on the 2103 acquired not only an improved and more powerful motor, but also a new electrical circuit, as well as an improved external design. The car was capable of reaching a significant speed for those times - 150 km/h , while the acceleration time from zero to hundreds was only 16 seconds.
The design power of the internal combustion engine was 80 horsepower, but in practice the developers were unable to achieve this value, because the design of the original engine (VAZ 2103) was designed for a smaller volume of combustion chambers.
The salon has also changed in a positive way:
- a tachometer appeared on the instrument panel;
- sound insulation has been improved;
- the seats now have headrests and a textured surface;
- The interior has also become significantly more comfortable compared to the previous model, in which the main emphasis was on practicality.
The legendary VAZ 2106 Brezhnev.
The unique VAZ 2106 car with the popular name “Half six” was produced in 1997 on a special order for L. I. Brezhnev. The model had a slightly modified hood, and also installed seats and a radiator from the “Seven”, which at that moment was still at the development stage.
Engine optimization options
Many drivers tune the VAZ 2107 engine in order to improve performance and increase power. An important factor that affects power performance is clean injectors. Their contamination reduces engine performance, impairs efficiency, reduces the injected volume of fuel, which will lead to failures when pressing the gas pedal.
Usually the problem occurs due to the use of low-quality gasoline. Such fuel will contain heavy paraffins that build up on valve plates, injectors and the throttle valve. There are several options for cleaning them.
The first is cleaning and bench testing.
The permissible imbalance should be within 1.5%. If the deviation is more than:
- 2.5% - fuel consumption increases;
- 3.5% - unstable operation at idle, difficult cold start;
- 4% - dips occur during sudden acceleration;
- 5% - the engine does not start well, a persistent tripping appears.
The second option is to use special flushing fluid and equipment. Cleaning can be done at home. To do this, you need to dilute the flushing fluid with gasoline and add it to the power system. As a result, the deposits are corroded and enter the cylinder, where they are completely burned.
The quality of the oil used has a great influence on keeping the car in working condition.
Weaknesses of the VAZ-2106 engine
The engine of the VAZ-2106 car is a modification of the power unit from the Troika. It is quite possible that this is why its design retained a number of weak points of its predecessors. Domestic craftsmen have learned to diagnose engine problems almost by sound. As an example, we will give several symptoms of breakdowns, and also tell you which engine elements could fail:
- The appearance of loud knocking noises at idle clearly indicates the need to adjust the valves. Under normal operating conditions, this problem usually occurs no more often than once every 7-10 thousand kilometers;
- The occurrence of metal-on-metal knocking indicates that the connecting rod bearings or piston pins are worn out. Both faults must be corrected immediately to prevent serious damage to the power unit;
- the so-called ceramic knock may indicate that the pistons of the VAZ-2106 have failed. You can still get to a car service center with such a breakdown, but it’s definitely not recommended to travel around the city and beyond;
- extraneous sounds in the lower part of the engine, which are accompanied by a sharp drop in the oil level - this is a clear sign of problems with the main bearings. In this situation, it is better to immediately use the services of a tow truck, since an independent trip even a short distance is fraught with major troubles.
In addition, quite often VAZ-2106 owners encounter the following carburetor and ignition system malfunctions:
- insufficient or, on the contrary, excessive fuel enrichment;
- throttle problems;
- failure of a high-voltage wire;
- moisture entering the ignition coil insulator;
- spark plug wear.
All these malfunctions, with experience, can be eliminated in no time - you just need to remove the damaged unit, disassemble it and, accordingly, replace the worn parts.
Modifications of VAZ 2107
- LADA-2107 (engine 2103, 1.5 l, 8 cl., carburetor)
- LADA-21072 (engine 2105, 1.3 l, 8 cl., carburetor, timing belt drive)
- LADA-21073 (engine 1.7 l, 8 cells, mono injection - export version for the European market)
- LADA-21074 (engine 2106, 1.6 l, 8 cl., carburetor)
- LADA-21070 (engine 2103, 1.5 l, 8 cl., carburetor)
- LADA-2107-20 (engine 2104, 1.5 l, 8 cells, central injection)
- LADA-2107-71 (engine 1.4 l, 66 hp engine 21034 for A-76 gasoline, version for China)
- LADA-21074-20 (engine 21067-10, 1.6 l, 8 cells, distributed injection, Euro-2)
- LADA-21074-30 (engine 21067-20, 1.6 l, 8 cells, distributed injection, Euro-3)
- LADA-210740 (engine 21067, 1.6 l, 53 kW/72.7 hp 8 cells, injector, catalyst) (2010 onwards)
- LADA-21077 (engine 2105, 1.3 l, 8 cl., carburetor, timing belt drive - export version for the UK)
- LADA-21078 (engine 2106, 1.6 l, 8 cl., carburetor - export version for the UK)
- LADA-21079 (rotary piston engine 1.3 l, 140 hp, originally created for the needs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the KGB)
- LADA-2107 ZNG (engine 21213, 1.7 l, 8 cells, central injection)
The tables below show the technical characteristics of the VAZ 2107 car and its modifications.
Other characteristics of the VAZ-2106 engine
The weight of the motor is, although important, but far from its main characteristic. That is why we decided to talk about other features of the power unit installed on various modifications of the “six”. For example, engine power on carburetor models was 77 horsepower. After switching to an injector, it dropped to 75 hp. With. However, this parameter can always be increased by carrying out a number of upgrades.
The cylinder diameter of the VAZ-2106 power unit is 79 millimeters, the torque can reach 3000 rpm, and the working volume is 1568 cubic centimeters. Finally, the compression ratio of the engine is 8.5 atmospheres, and the piston stroke is 80 millimeters.
How much does a seven car weigh? Technical characteristics of VAZ 2107
VAZ 2107 Seven technical specifications
Modifications of VAZ 2107
LADA-2107 (engine 2103, 1.5 l, 8 cl., carburetor)
LADA-21072 (engine 2105, 1.3 l (1290 cm3), 8 cells, carburetor, timing belt drive)
LADA-21073 (engine 1.7 l (1689 cm3), 8 cells, mono injection - export version for the European market)
LADA-21074 (engine 2106, 1.6 l (1569 cm3), 8 cells, carburetor)
LADA-21070 (engine 2103, 1.5 l, 8 cl., carburetor)
LADA-2107-20 (engine 2104, 1.5 l, 8 cells, distributed injection, Euro-2)
LADA-2107-71 (engine 1.4 l, 66 hp engine 21034 for A-76 gasoline, version for China)
LADA-21074-20 (engine 21067-10, 1.6 l, 8 cells, distributed injection, Euro-2)
LADA-21074-30 (engine 21067-20, 1.6 l, 8 cells, distributed injection, Euro-3)
LADA-210740 (engine 21067, 1.6 l, 53 kW/72.7 hp 8 cells, injector, catalyst) (2007 onwards)
LADA-21075 (1.5 l engine, (1524 cm3 - 75 hp and 1524 cm3 - 65 hp), 1982 - 2012 onwards)
LADA-21077 (engine 2105, 1.3 l, 8 cl., carburetor, timing belt drive - export version for the UK)
LADA-21078 (engine 2106, 1.6 l, 8 cl., carburetor - export version for the UK)
LADA-21079 (rotary piston engine 1.3 l, 140 hp, originally created for the needs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the KGB)
LADA-2107 ZNG (engine 21213, 1.7 l, 8 cells, central injection)
Performance characteristics of the VAZ 2107 seven
Maximum speed: 155 km/h Fuel consumption per 100 km in the city: 8.9 l Gas tank volume: 39 l Curb weight of the vehicle: 1030 kg Permissible gross weight: 1430 kg Tire size: 175/70 SR13
Location: front, longitudinal Engine volume: 1450 cm3 Engine power: 71 hp Number of revolutions: 5600 Torque: 104/3400 N*m Power system: injector Turbocharging: no Gas distribution mechanism: OHC Cylinder arrangement: In-line Number of cylinders: 4 Cylinder diameter: 76 mm Piston stroke: 80 mm degree compression: 8.5 Number of valves per cylinder: 2 Recommended fuel: AI-92
Front brakes: Disc Rear brakes: Drum
Steering type: Worm gearPower steering: no
Drive: Rear Number of gears: manual gearbox - 5 Gear ratio of the main pair: 3.9
Front suspension: Double wishbone Rear suspension: Coil spring
Body type: sedan Number of doors: 4 Number of seats: 5 Car length: 4128 mm Car width: 1620 mm Car height: 1435 mm Wheelbase: 2424 mm Front track: 1365 mm Rear track: 1321 mm Ground clearance (clearance): 170 mm Trunk volume: 325 l
Year of manufacture: from 1982 to 2012
Dimensions of VAZ 2107
Information - How much does a car weigh?
| car model | Curb weight |
| Weight of the Oka 1111 car, weight of the Okushka | 635 kg |
| Weight of the car Oka 1113 | 645 kg |
| Weight of a VAZ 2101 car, weight of a penny | 955 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2102 car | 1010 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2103 car | 965 kg |
| Weight of the car VAZ 2104, weight of tens 2110 | 1020 kg |
| The weight of the VAZ 2105 car, the weight of the five | 1060 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2106 car, weight of the six | 1045 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2107 car, weight of the seven | 1049 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2108 car | 945 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2109 car, weight of the nine | 915 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2111 car | 1055 kg |
| Weight of a VAZ 2112 car, weight of a twelve-wheeler | 1040 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2113 car | 975 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2114 car, weight of the four | 985 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2115 car, weight of the tag | 1000 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2116 car | 1276 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2117 car | 1080 kg |
| Weight of the Niva 2121 car | 1150 kg |
| How much does a Chevrolet Cruze weigh (Chevrolet Cruze weight) | 1285-1315 kg |
| How much does a Chevrolet Niva weigh (Chevrolet Niva weight) | 1410 kg |
| How much does a GAZ (Volga) weigh, the weight of a Volga 24 | 1420 kg |
| How much does GAZ 2402, GAZ 2403, GAZ 2404 weigh? | 1550 kg |
| How much does GAZ 2407 weigh? | 1560 kg |
| Car weight Moskvich 314 | 1045 kg |
| Weight Moskvich 2140 | 1080 kg |
| Weight Moskvich 2141 | 1055 kg |
| Car weight Moskvich 2335, 407, 408 | 990 kg |
| How much does a UAZ 3962, UAZ 452 weigh, how much does a UAZ loaf weigh? | 1825 kg |
| How much does UAZ 469 weigh? | 1650 kg |
| How much does UAZ Patriot weigh? | 2070 kg |
| How much does UAZ Hunter weigh? | 1815 kg |
| How much does Nissan weigh (weight of nissan x-trail car) | 1410-1690 kg |
| How much does Qashqai weigh (weight of Nissan Qashqai car) | 1297-1568 kg |
| How much does Nissan Juke weigh (Nissan Beetle weight) | 1162 kg |
| Ford Focus car weight (how much does a Ford Focus weigh) | 965-1007 kg |
| Weight of the Ford Focus 2 car (how much does the Ford Focus 2 weigh) | 1345 kg |
| Weight of the Ford Focus 3 car (how much does the Ford Focus 3 weigh) | 1461-1484 kg |
| Ford Kuga car weight (how much does a Ford Kuga weigh) | 1608-1655 kg |
| Ford Escort car weight (how much does a Ford Escort weigh) | 890-965 kg |
| Weight of the Renault Logan car (how much does the Renault Logan weigh) | 957-1165 kg |
| Renault Duster car weight (how much does a Renault Duster weigh) | 1340-1450 kg |
| Renault Sandero car weight (how much does a Renault Sandero weigh) | 941 kg |
| Weight of the Opel Mokka car (how much does the Opel Mokka weigh) | 1329-1484 kg |
| Weight of the Opel Astra car (how much does the Opel Astra weigh) | 950-1105 kg |
| Mazda 3 car weight (how much does Mazda 3 weigh) | 1245-1306 kg |
| Weight of the Mazda CX-5 (how much does the Mazda CX-5 weigh) | 2035 kg |
| Mazda 6 car weight (how much does Mazda 6 weigh) | 1245-1565 kg |
| Volkswagen car weight (how much does a Volkswagen Tuareg weigh) | 2165-2577 kg |
| Weight of a Volkswagen Polo car (how much does a Volkswagen Polo weigh) | 1173 kg |
| Weight of the Volkswagen Passat car (how much does the Volkswagen Passat weigh) | 1260-1747 kg |
| How much does a Toyota Camry weigh (Toyota Camry weight) | 1312-1610 kg |
| How much does Toyota Corolla weigh (weight of Toyota Corolla) | 1215-1435 kg |
| How much does a Toyota Celica weigh (Toyota Celica weight) | 1000-1468 kg |
| How much does a Toyota Land Cruiser weigh (Land Cruiser weight) | 1896-2715 kg |
| How much does the Skoda Octavia weigh (Skoda Octavia weight) | 1210-1430 kg |
| How much does the Skoda Fabia weigh (Skoda Fabia weight) | 1015-1220 kg |
| How much does the Skoda Yeti weigh (Skoda Yeti weight) | 1505-1520 kg |
| How much does a Kia Sportage weigh (KIA Sportage weight) | 1418-1670 kg |
| How much does Kia Sid weigh (KIA Ceed weight) | 1163-1385 kg |
| How much does the Kia Picanto weigh (KIA Picanto weight) | 829-984 kg |
Information - How much does a car weigh?
| car model | Curb weight |
| Weight of the Oka 1111 car, weight of the Okushka | 635 kg |
| Weight of the car Oka 1113 | 645 kg |
| Weight of a VAZ 2101 car, weight of a penny | 955 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2102 car | 1010 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2103 car | 965 kg |
| Weight of the car VAZ 2104, weight of tens 2110 | 1020 kg |
| The weight of the VAZ 2105 car, the weight of the five | 1060 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2106 car, weight of the six | 1045 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2107 car, weight of the seven | 1049 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2108 car | 945 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2109 car, weight of the nine | 915 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2111 car | 1055 kg |
| Weight of a VAZ 2112 car, weight of a twelve-wheeler | 1040 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2113 car | 975 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2114 car, weight of the four | 985 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2115 car, weight of the tag | 1000 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2116 car | 1276 kg |
| Weight of the VAZ 2117 car | 1080 kg |
| Weight of the Niva 2121 car | 1150 kg |
| How much does a Chevrolet Cruze weigh (Chevrolet Cruze weight) | 1285-1315 kg |
| How much does a Chevrolet Niva weigh (Chevrolet Niva weight) | 1410 kg |
| How much does a GAZ (Volga) weigh, the weight of a Volga 24 | 1420 kg |
| How much does GAZ 2402, GAZ 2403, GAZ 2404 weigh? | 1550 kg |
| How much does GAZ 2407 weigh? | 1560 kg |
| Car weight Moskvich 314 | 1045 kg |
| Weight Moskvich 2140 | 1080 kg |
| Weight Moskvich 2141 | 1055 kg |
| Car weight Moskvich 2335, 407, 408 | 990 kg |
| How much does a UAZ 3962, UAZ 452 weigh, how much does a UAZ loaf weigh? | 1825 kg |
| How much does UAZ 469 weigh? | 1650 kg |
| How much does UAZ Patriot weigh? | 2070 kg |
| How much does UAZ Hunter weigh? | 1815 kg |
| How much does Nissan weigh (weight of nissan x-trail car) | 1410-1690 kg |
| How much does Qashqai weigh (weight of Nissan Qashqai car) | 1297-1568 kg |
| How much does Nissan Juke weigh (Nissan Beetle weight) | 1162 kg |
| Ford Focus car weight (how much does a Ford Focus weigh) | 965-1007 kg |
| Weight of the Ford Focus 2 car (how much does the Ford Focus 2 weigh) | 1345 kg |
| Weight of the Ford Focus 3 car (how much does the Ford Focus 3 weigh) | 1461-1484 kg |
| Ford Kuga car weight (how much does a Ford Kuga weigh) | 1608-1655 kg |
| Ford Escort car weight (how much does a Ford Escort weigh) | 890-965 kg |
| Weight of the Renault Logan car (how much does the Renault Logan weigh) | 957-1165 kg |
| Renault Duster car weight (how much does a Renault Duster weigh) | 1340-1450 kg |
automagadan
A small table with engine weights. It may be useful for calculating the cost of delivery of engines or for self-design.
Daihatsu, Hino, Honda, Isuzu, Mazda, MMC, Nissan, Rover, Subaru, Suzuki, Toyota
Daihatsu (petrol) EF ——— 659 cc; 90.00 kg; Daihatsu (petrol) EJ ——— 989 cc; 140.00 kg; Daihatsu (petrol) HD ——— 1589 cc; 110.00 kg; Hino (diesel) EC100 ——— 5010 cc; 360.00 kg; Hino (diesel) W06E ——— 6014 cc; 380.00 kg; Honda A18A ——— 1829 cc; 160.00 kg; Honda B16A FF injection DOHC VTEC ——— 1595 cc; 138.00 kg; Honda B18B ——— 1834 cc; 125.00 kg; Honda B18C ——— 1797 cc; 120.00 kg; Honda B20B FF SM-X ——— 1972 cc; 150.00 kg; Honda C32A 4WD coil. ——— 3206 cc; 217.00 kg; Honda D13B FF carb. 1CAM 16cl ——— 1343 cc; 105.00 kg; Honda D15B FF injection 1CAM 16cl VTEC-E ——— 1493 cc; 115.00 kg; Honda D16A ——— 1590 cc; 120.00 kg; Honda F18A ——— 1849 cc; 140.00 kg; Honda F18B ——— 1849 cc; 135.00 kg; Honda F20B FF 2CAM, DONC, VTEC injection ——— 1997 cc; 150.00 kg; Honda F22A ——— 2156 cc; 145.00 kg; Honda F22B FF passenger car 1CAM VTEC ——— 2156 cc; 145.00 kg; Honda F23A 4WD Odysey (RA4) 1 cam, VTEC ——— 2253 cc; 145.00 kg; Honda G20A ——— 1996 cc; 265.00 kg; Honda G25A FF Inspaer ——— 2451 cc; 170.00 kg; Honda H22A FF DOHC, VTEC ——— 2156 cc; 165.00 kg; Honda H23A ——— 2258 cc; 160.00 kg; Honda J25A Odissey ——— 2495 cc; 170.00 kg; Honda J25A Saber ——— 2495 cc; 170.00 kg; Honda J30A ——— 2997 cc; 190.00 kg; Honda K20A ——— 1998 cc; 150.00 kg; Honda L13A ——— 1339 cc; 100.00 kg; Honda L15A ——— 1496 cc; 100.00 kg; Honda ZC FF injection 1CAM 16cl VTEC ——— 1590 cc; 130.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4BC1 ——— 3260 cc; 320.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4BC2 ——— 3567 cc; 350.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4BD1 ——— 3856 cc; 320.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4BE1 FR truck (plunger injection pump) ——— 3636 cc; 325.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4BE2 FR truck (plunger injection pump) ——— 3630 cc; 325.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4EE1 ——— 1686 cc; 164.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4FD1 ——— 2189 cc; 270.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4FG1 injection pump ——— 2380 cc; 270.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4HF1 FR truck ——— 4334 cc; 330.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4HG1 FR truck ——— 4570 cc; 404.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4JB1 FR truck ——— 2771 cc; 192.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4JG2-T 4WD Bighorn Intercooler (fuel pump mechanical) ——— 3059 cc; 260.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 4JX1 ——— 2999 cc; 280.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) 6HE1 ——— 7127 cc; 385.00 kg; Isuzu (diesel) FE6 ——— 6925 cc; 670.00 kg; Mazda (diesel) DL-T with gearbox ——— 2765 cc; 260.00 kg; Mazda (diesel) R2 4WD ——— 2184 cc; 178.00 kg; Mazda (diesel) RF 4WD Bongo thermal front ——— 1998 cc; 180.00 kg; Mazda (diesel) SL FR truck 24v (fuel injection pump plunger) ——— 3455 cc; 254.00 kg; Mazda (diesel) TF FR Titan truck ——— 4021 cc; 356.00 kg; Mazda (diesel) VS minibus, before '95. ——— 2956 cc; 260.00 kg; Mazda (diesel) WL-T FR 4WD PROCEED ——— 2499 cc; 234.00 kg; Mazda (diesel) XA FR ——— 2522 cc; 255.00 kg; Mazda (diesel) PN ——— 1720 cc; 155.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) B3 FF Ford mono injection 1CAM 16kl, wedge. ——— 1323 cc; 115.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) B5 4WD passenger carb. 1CAM ——— 1498 cc; 115.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) B6 ——— 1597 cc; 140.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) BP ——— 1839 cc; 143.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) D5 ——— 1490 cc; 100.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) E5 ——— 1490 cc; 120.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) F8 ——— 1789 cc; 155.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) FE ——— 1998 cc; 165.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) FP FF DOHC (distributor) Capella ——— 1839 cc; 129.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) FS 4WD Capella coil side old, 16cl DOHC ——— 1991 cc; 136.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) G6 ——— 2605 cc; 150.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) HA ——— 2977 cc; 370.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) K8 ——— 1844 cc; 165.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) KF ——— 1995 cc; 175.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) KL passenger ——— 2496 cc; 171.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) LF ——— 1998 cc; 178.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) RF ——— 1998 cc; 178.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) RF-T ——— 1998 cc; 210.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) Z5 ——— 1489 cc; 125.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) ZJ FF Demio (DY3W) ——— 1348 cc; 103.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) ZL ——— 1498 cc; 118.00 kg; Mazda (petrol) ZL FF ——— 1498 cc; 145.00 kg. MMC (petrol) 4A30 ——— 659 cc; 105.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4A31 ——— 1094 cc; 105.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G13 FF injection 1CAM ——— 1298 cc; 135.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G15 ——— 1468 cc; 135.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G32 ——— 1597 cc; 130.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G37 ——— 1755 cc; 135.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G54 ——— 2555 cc; 200.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G63 4WD DONC 2CAM 16cl ——— 1997 cc; 160.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G63-T ——— 1997 cc; 170.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G64 FF injection 1CAM 16cl (distributor) ——— 2350 cc; 184.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G67 ——— 1836 cc; 170.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G91 Lancer carb. 2CAM 16cl DOHC ——— 1496 cc; 137.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G93 FF Galant carburetor. SOHC 16cl ——— 1834 cc; 150.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G93 GDI Pajero ——— 1834 cc; 145.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 4G94 ——— 1999 cc; 150.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 6A11 ——— 1829 cc; 177.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 6A11 FF passenger injection. DOHC, 24cl ——— 1829 cc; 220.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 6A12 ——— 1998 cc; 165.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 6A13 FF Legnum (distributor) ——— 2498 cc; 170.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 6G71 FF passenger car 2CAM CYCLON ——— 1998 cc; 220.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 6G72 4WD CHALLENGER, 12 valves, coils ——— 2972 cc; 195.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 6G73 FF passenger DOHC NEW (distributor) ——— 2497 cc; 194.00 kg; MMC (petrol) 6G74 ——— 3496 cc; 230.00 kg; MMC (petrol) G32B carburetor ——— 1600 cc; 120.00 kg; MMC (petrol) G37B ——— 1755 cc; 130.00 kg; MMC (petrol) G54B ——— 2555 cc; 150.00 kg; MMC (petrol) G63B-T-ECI FF Galant INTERCOOLER SIRIUS ——— 1997 cc; 150.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4D30 ——— 3298 cc; 290.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4D32 ——— 3567 cc; 300.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4D33 FR Canter 24v NEW ——— 4214 cc; 360.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4D33 FR narrow head ——— 4214 cc; 297.20 kg; MMC (diesel) 4D56-T 4WD Delica ——— 2476 cc; 193.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4D65 auto. FF F4A212-URH ——— 1795 cc; 180.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4D68-T 4WD passenger car NEW ——— 1998 cc; 170.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4DR5 FR Canter (in-line injection pump) ——— 2659 cc; 242.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4DR7 FR Canter (in-line injection pump) ——— 2835 cc; 242.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4M40-T 4WD Delica ——— 2835 cc; 239.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 4M40-T 4WD Pajero (dimensions 65cmx80cmx80cm) ——— 2835 cc; 234.40 kg; MMC (diesel) 4M51 ——— 5249 cc; 250.00 kg; MMC (diesel) 6D15 ——— 6919 cc; 400.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) A15 FR Vanette carburetor. black valve cover new image ——— 1487 cc; 135.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) CA18 DE ——— 1809 cc; 160.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) CA18 FR passenger car. 2CAM ——— 1809 cc; 130.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) CA20 ——— 1973 cc; 145.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) CG10-DE FF ——— 997 cc; 90.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) CG13-DE FF Cube (Z10) ——— 1274 cc; 105.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) CGA3 ——— 1348 cc; 110.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) CR12 ——— 1240 cc; 120.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) CR14 ——— 1386 cc; 120.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) E15 ——— 1487 cc; 131.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) GA13 ——— 1295 cc; 146.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) GA15 ——— 1497 cc; 145.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) GA16 ——— 1596 cc; 146.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) KA24 FF Pressage DOHC 16cl ——— 2388 cc; 170.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) L20 FR passenger carburetor. ——— 1998 cc; 173.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) NA16 FR Atlas carburetor. SOHC ——— 1627 cc; 117.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) NA20 ——— 1998 cc; 140.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) QG15 ——— 1497 cc; 140.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) QG16 ——— 1597 cc; 140.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) QG18 4WD 2CAM, 16cl. ——— 1769 cc; 135.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) QR20 ——— 1998 cc; 150.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) RB20 ——— 1998 cc; 181.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) RB25-DE 4WD Skyline NEO ——— 2498 cc; 235.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) SR18-DI FF Bluberd ——— 1883 cc; 150.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) SR20-DE FR Serena direct coll. down, rear distributor (no power steering) ——— 1998 cc; 160.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) VG20-E FR ——— 1998 cc; 200.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) VG30-E 4WD TERRANO ——— 2960 cc; 220.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) VG33 4WD (distributor) Terrano (LR50) ——— 3300 cc; 230.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) VQ20 FF Cefiro 24 cl ——— 1995 cc; 175.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) VQ23 ——— 2349 cc; 200.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) VQ25 ——— 2495 cc; 185.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) VQ30-T FR Cedric ——— 2987 cc; 240.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) Z16 FR Datsun carburetor. ——— 1600 cc; 115.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) Z20 ——— 1952 cc; 150.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) BD30 FR Atlas 24v ——— 2953 cc; 245.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) CD17 ——— 1680 cc; 170.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) CD20 FR Serena ——— 1973 cc; 180.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) ED30 ——— 2956 cc; 180.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) ED33 ——— 3298 cc; 220.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) FD35 ——— 3465 cc; 300.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) FD42 ——— 4241 cc; 324.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) FD46 FR ——— 4617 cc; 295.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) LD20 FR m.bus ——— 1952 cc; 190.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) QD32 12v ——— 3153 cc; 225.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) RD28 Laurel ——— 2825 cc; 220.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) SD23 ——— 2289 cc; 205.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) TD23 FR Atlas 12v ——— 2289 cc; 230.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) TD25 ——— 2494 cc; 230.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) TD27-T 4WD m.bus ——— 2663 cc; 245.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) TD42 ——— 4169 cc; 365.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) YD22 FF ——— 2184 cc; 210.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) YD25-TE ——— 2488 cc; 200.00 kg; Nissan (diesel) ZD30-TE-DDTI 4WD Safari ——— 2953 cc; 242.00 kg; Nissan (petrol) Z18 ——— 1770 cc; 150.00 kg; Rover 16K4F ——— 1589 cc; 130.00 kg; Subaru EA71 ——— 1595 cc; 155.00 kg; Subaru EA82 4WD carburetor. ——— 1781 cc; 135.00 kg; Subaru EF10 ——— 997 cc; 105.00 kg; Subaru EF12 ——— 1189 cc; 105.00 kg; Subaru EJ15 ——— 1493 cc; 130.00 kg; Subaru EJ16 4WD passenger car DOHC 16cl ——— 1597 cc; 140.00 kg; Subaru EJ18 4WD ——— 1820 cc; 180.00 kg; Subaru EJ20 4WD coil. Legasy(BG5) DOHC ——— 1994 cc; 120.00 kg; Subaru EJ20-TT 4WD coil. DOHC BOXER INTERCOOLER (BH5), 83t.km.,99y. new image ——— 1994 cc; 160.00 kg; Subaru EJ22 ——— 2212 cc; 113.00 kg; Subaru EJ25 (without power steering, generator, AC) ——— 2457 cc; 107.00 kg; Suzuki F6A ——— 657 cc; 80.00 kg; Suzuki G10 ——— 993 cc; 90.00 kg; Suzuki G16A 4WD Escudo injection 16cl ——— 1590 cc; 105.00 kg; Suzuki H20A 4WD Escudo ——— 1998 cc; 155.00 kg; Suzuki H25A 4WD Escudo coil. 24cl ——— 2493 cc; 180.00 kg; Suzuki H27A ——— 2736 cc; 200.00 kg; Suzuki J18A ——— 1839 cc; 113.00 kg; Suzuki J20A Escudo ——— 1995 cc; 135.00 kg; Suzuki K10A ——— 996 cc; 90.00 kg; Suzuki M13A ——— 1328 cc; 102.00 kg; Suzuki M16A ——— 1586 cc; 135.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1AZ ——— 1998 cc; 130.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1FZ-FE ——— 4476 cc; 300.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1G-FE VVTI FR MarkII (GX100) BEAMS ——— 1988 cc; 160.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1G-GTE ——— 1998 cc; 209.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1JZ-GE (VVT-i) 4WD ——— 2491 cc; 200.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1KR-FE ——— 996 cc; 96.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1MZ-FE ——— 2995 cc; 180.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1NZ-FE VVTI 4WD passenger car. ——— 1496 cc; 112.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1S FF Vista (SV21) single injection ——— 1832 cc; 135.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1SZ-FE ——— 997 cc; 95.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1UZ-FE rear wheel drive Celsior coil. 32 valves TRC ——— 3969 cc; 220.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1VZ-FE ——— 1992 cc; 195.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 1ZZ-FE ——— 1794 cc; 135.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 2A ——— 1295 cc; 119.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 2AZ-FE ——— 2362 cc; 170.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 2JZ-GE FR MarkII ——— 2997 cc; 230.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 2MZ FF ——— 2496 cc; 177.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 2NZ-VVTI FF coils ——— 1298 cc; 88.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 2TZ-FE ——— 2438 cc; 175.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 2ZZ front-wheel drive, Celica, Yamaha cylinder head ——— 1795 cc; 135.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 3A ——— 1452 cc; 135.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 3E ——— 1456 cc; 110.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 3RZ-FE ——— 2693 cc; 173.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 3S-FE FR Noah ——— 1998 cc; 170.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 3S-GE 4WD VVTI Caldina BEAMS Yamaha ——— 1998 cc; 155.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 3S-GTE ——— 1998 cc; 195.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 3VZ-FE FF Windom (VZV10) (distributor) 24 valves ——— 2958 cc; 199.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 3Y ——— 1998 cc; 146.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 4A-GE FF passenger Silverhead 20cl ——— 1587 cc; 145.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 4E ——— 1331 cc; 105.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 4K ——— 1290 cc; 130.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 4S-FE FF old model up to 91 ——— 1838 cc; 155.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 4VZ FF, Camry ——— 2496 cc; 190.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 4Y ——— 2237 cc; 155.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 5A-FE ——— 1498 cc; 150.00 kg. Toyota (petrol) 5E 4WD ——— 1496 cc; 120.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 5K ——— 1496 cc; 140.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 5S-FE ——— 2164 cc; 160.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 5VZ-FE Prado 24cl ——— 3378 cc; 190.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 7A-FE 4WD Carib AT-115 (distributor) ——— 1762 cc; 109.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 7K ——— 1781 cc; 140.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) 7M-GE ——— 2954 cc; 185.00 kg; Toyota (petrol) K3 ——— 1297 cc; 96.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 13B ——— 3431 cc; 290.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 14B FR DUNA 24v ——— 2660 cc; 300.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 15B FR HINO ——— 4104 cc; 295.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 1C front-wheel drive ——— 1839 cc; 157.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 1HD ——— 4163 cc; 365.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 1KZ-TE 4WD Surf CT-20 ——— 2982 cc; 280.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 1N-T ——— 1453 cc; 137.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 2C 4WD TawnAce used vacuum. ——— 1974 cc; 170.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 2L FR Haice after '89 ——— 2446 cc; 230.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 3B FR DUNA 24V (height 70, length 80, width 70) ——— 3431 cc; 294.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 3C ——— 2184 cc; 175.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 3L FR, 4WD m.bus ——— 2779 cc; 230.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 3C-E FR TawnAce with vacuum 2cyl. ——— 2184 cc; 220.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) 5L ——— 2985 cc; 250.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) B FR DUNA 24v ——— 2977 cc; 297.00 kg; Toyota (diesel) S05D ——— 4899 cc; 280.00 kg;
The continuation of the plate is on the forum in the topic “Engine weight table”
Total information
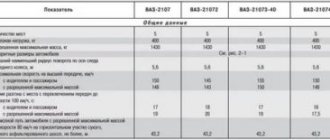
| Options | VAZ 2107 | VAZ 21074 | VAZ 2107-20 | VAZ 21074-20 |
| Weight of the equipped vehicle, kg | 1060 | 1060 | 1060 | 1060 |
| Payload, kg | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Permitted maximum weight, kg | 1460 | 1460 | 1460 | 1460 |
| Ground clearance of a vehicle with a permissible maximum weight, with tires 175/70 R13, not less, mm: | ||||
| to the front suspension cross member | 162 | 162 | 162 | 159 |
| to the rear axle beam | 157 | 157 | 157 | 154 |
| Permissible weight of cargo on the additional (top) luggage rack, kg | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Maximum speed, km/h: | ||||
| with permissible maximum weight | 148 | 148 | — | — |
| with driver and passenger | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Acceleration time from standstill to 100 km/h, s: | ||||
| with driver and one passenger | 17 | 16 | 17 | 16 |
| with permissible maximum weight | 19 | 17,5 | — | — |
| Minimum turning radius along the track of the outer front wheel, m | 5,6 | 5,6 | 5,6 | 5,6 |
| The greatest rise overcome by a car with a permissible maximum weight without acceleration in first gear, % | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 |
How much does a car weigh?
A car's directional stability and handling are also directly related to its weight. The peak of popularity of large, heavy cars abroad occurred in the 50-60s of the last century. Then the auto industry produced truly gigantic cars. For example, the Cadillac Eldorado modification 8.2 weighed almost 3 tons. Agree that for such a weight, an appropriate makeweight is needed.
But as time passed, it became clear that in order to further develop and improve the most important characteristics of the car, it was necessary to resort to reducing its overall weight. And if we compare the middle of the last century and today, cars have lost half, or even more, of their own weight. Plastic, carbon fiber reinforced plastic, light metals - all these innovations have made it possible to make the weight of a passenger car significantly lower.
Of course, for lovers of everything big and heavy, cars are produced that look like steamships that drink buckets of gasoline, but this is rather an exception to the rule.
Engines
| Options | VAZ 2103 | VAZ 2106 | VAZ 2104 | VAZ 21067 |
| Number and arrangement of cylinders | four-cylinder, four-stroke, in-line | |||
| Supply system | carburetor | distributed injection | ||
| Octane number of gasoline | 92-93 | 95 | ||
| Cylinder diameter and piston stroke, mm | 76×80 | 79×80 | 76×80 | 79×80 |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 | |||
| Compression ratio | 8,5 | 8,5 | 8,5 | 8,5 |
| Working volume, l | 1,45 | 1,57 | 1,45 | 1,57 |
| Rated power, according to GOST 14846 (net), kW (hp) | 52,5 (71,4) | 54,8 (74,5) | 50,0 (68,0) | 54,5 |
| Crankshaft rotation speed at rated power, min-1 | 5600 | 5600 | 5000 | 5000 |
| Maximum torque at crankshaft speed 3400 min-1 (3000 min-1 for VAZ 2106 engine), N*m | 103,9 | 116 | — | — |
| Minimum crankshaft rotation speed, min-1 | 850-900 | 850-900 | 820-880 | 820-880 |
| Direction of rotation of the crankshaft from the pulley side | right | |||
| Lubrication system | combined, pressure and spray | |||
| Cooling system | liquid, closed, forced circulation | |||
| Crankcase ventilation system | forced, with crankcase gases vented into the intake manifold | |||
Features of operation and maintenance
- Fuel selection
It was said earlier that many drivers cannot decide on the type of fuel used for their engine on the VAZ 2107. And if with AI-92 everything is simple, since its composition is very similar to AI-93, then with AI-95 everything is not so smooth.
Increasing the octane number leads to an increased risk of valve burnout, but gives a small increase in power. The engine begins to run smoother and more stable.
But the designers still took into account the possibility of using AI-95 gasoline. You just need to correctly set the ignition timing on your car (if you have a conventional carburetor engine) or reflash the engine control unit (if your VAZ 2107 engine is fuel-injected). But usually even this is not required. Engines of this brand are very durable and not picky about the type of fuel (within reasonable measures).
- Change of oil
Changing the oil on any engine must be approached with the utmost seriousness.
Poor quality oil can lead to not very pleasant consequences, such as accelerated wear of main components and assemblies. The ability to select oil is a real skill. Taking well-known brands is not always safe, since you are very likely to come across a counterfeit from dishonest companies. At best, you will not receive the positive qualities that this company has. At worst, you will have to carry out major repairs.
You shouldn't buy unknown brands either. In this case, you are buying a pig in a poke. You can buy oil that is of a quality that is not inferior to expensive analogues, or you can end up with expensive repairs. It is best to buy oil in specialized stores, where you can get at least some explanation and compensation.
Another important parameter is the oil class according to the international nomenclature. True, everything is simpler here. You just need to take the oil that the manufacturer himself recommends.
The manufacturer (AvtoVAZ) for VAZ 2107 engines and other models with this type of engine recommends:
- 5W-30;
- 5W-40;
- 10W-40;
- 15W-40.
You need to take about 4 liters of oil. When changing 3.5 liters of oil is usually enough. It’s better to carry the rest with you in the trunk, since oil consumption in this engine leaves much to be desired.
- Changing the oil in the VAZ 2107 engine
The procedure itself is quite simple and should not raise any questions. It is better to change the oil on a VAZ 2107 in the warm season.
- First you need to start the car and warm it up to operating temperature. Then turn it off and let the oil fall back into the crankcase. This will take about half an hour. During this time, we prepare a receiving container with a volume of 4-5 liters, as well as new oil, a watering can and a hose.
- Use a special wrench to unscrew the plug on the crankcase and wait for the old oil to drain out.
- If you change the type of oil or brand, you must also take flushing oil, which will clean the engine of the remnants of the old one. We pour it in the same way.
- Then we tighten the crankcase cover and fill in new oil through the neck on the cylinder head. We measure the level with a dipstick. It should be somewhere between the MIN and MAX marks. Please note that oil is not water and it cannot quickly sink into the crankcase, and therefore after a short stop the oil level in the crankcase will rise a little more.
Usually, along with changing the oil, the oil filter is also changed. It's even simpler here:
- We unscrew the old one using a special tool (you can also use an ordinary rope), lubricate the o-ring of the new filter with oil and screw it in place of the old one.
- Adjustment of valves
Adjusting valves is a rather complicated process and requires certain skills and tools. Actually, it is advisable to entrust the valve adjustment itself to competent specialists, but if you want to do everything yourself, then this video is for you:
Major repairs and maintenance
If valve adjustment can be done at home, then major engine repairs should only be entrusted to specialists.
During a major overhaul, all components and assemblies of the VAZ 2107 engine are checked for serviceability. They will check for you:
- Valve condition, adjustment;
- Chain, chain tension;
- Condition of oil seals, valve stem seals;
- Geometry of the cylinder block;
- Condition of the pistons, crankshaft, pins, connecting rods;
- Wear of compression rings;
- Condition of the oil pump and coolant pump.
If damaged, the part will be replaced. The cylinder block will be bored out, which will increase the combustion chamber and working volume. After this procedure, the car will be run-in for several thousand kilometers.
Typically, running-in lasts 5-10 thousand km. At this time, it is not advisable to give the engine heavy loads. After completing this procedure, your engine will make you happy.
Malfunctions
1. Engine won't start
| Cause of failure | Elimination method |
| No fuel in carburetor | |
| Fuel line clogged | Blow out the fuel line, flush the fuel tank |
| Carburetor and fuel pump filters are clogged | Wash filters and replace if necessary |
| Ignition system is faulty | Check the ignition system, replace broken parts |
| The carburetor air damper does not open at the first flashes in the cylinders | Eliminate leaks in the carburetor starting device |
| The carburetor solenoid valve does not open when the ignition is turned on: | |
| break in the wire going to the valve | Check the wire and its connections, replace the damaged wire |
| solenoid valve faulty | Replace valve |
2. Knock of the crankshaft main bearings. Usually a dull, metallic knock. It is detected when the throttle valves are opened sharply at idle. Its frequency increases with increasing crankshaft speed. Excessive axial clearance of the crankshaft causes a sharper knock with uneven intervals, especially noticeable with a gradual increase and decrease in the crankshaft speed.
| Cause of malfunction | Elimination method |
| Ignition too early | Adjust the ignition timing |
| Insufficient oil pressure | Check oil pressure |
| Flywheel mounting bolts are loose | Tighten the bolts to the recommended torque |
| Increased clearance between journals and main bearing shells | Sand the journals and replace the bearings |
| Increased clearance between thrust rings and crankshaft | Replace thrust half-rings with new ones or thicker ones |
Engine tuning
The most popular types of tuning for engines of this type are increasing the displacement, replacing the camshaft, installing a zero-resistance filter and direct-flow exhaust.
The most effective way (and the most expensive) is to install a turbo kit.
- Increase in working volume
The design of the VAZ 2103 engine allows for a good increase in displacement, since its cylinder block is almost identical to the VAZ 2106 engine block. And when this block is bored, it can be made to fit the piston and rings of the VAZ 2106 engine.
Thus, we get an increase in displacement, which increases fuel consumption and power. If even this is not enough, then they sharpen the pistons on the valve side and install a crankshaft from the Niva, which also increases the working volume. Presumably after these operations you can get an engine with a displacement of 1.7 liters, sometimes 1.8 liters.
- Installing a new camshaft
This modification does not increase engine power, but changes the nature of its operation. In most cases, they try to install a camshaft that will transfer maximum torque to as low a speed as possible. This makes the engine more responsive at lower speeds, which has a very good effect when driving at low engine speeds. The best option for such a modification is a camshaft from Niva 21213.
- Installation of direct-flow exhaust and zero-resistance filter
The most popular modification. First of all, it's pretty cheap. Secondly, it allows the car owner to show off to neighbors in the garages. In fact, it does not have any practical benefit for the stock engine. Allows you to feel a slight increase in power only at high speeds.
It is quite effective when installing Turbo, since it does not put pressure on the engine, which is now capable of developing enormous power. Direct-flow exhaust is not convenient due to increased exhaust sound. It is dangerous to use the filter in wet weather, as it can let water into the engine, causing water hammer.
- Installation of turbocharging
The most expensive and effective way to increase engine power, while its resource sharply drops by 2-3, sometimes 4-5 times.
Requires deep exhaust tuning:
- Installing T-Valves
- Imported rings and forged pistons
- Lightened crank feces
- Intercooler and much more.
It is also necessary that your VAZ 2107 engine be fuel-injected. The carburetor can simply burst due to such high pressure. This article will not describe the procedure for installing Turbo on a VAZ 2107. There is enough such information on the World Wide Web. Here we will simply indicate a price of approximately 15% of the cost of the car. If you are ready to spend your money on this, go for it.
Characteristics and principle of operation of the engine
The operation of the fuel injection system is to supply fuel separately to each cylinder. This mechanism is called distributor injection. All modern cars are equipped with a distribution or electronic injection system.
The injection mechanism is classified according to its operating principle, installation location and number of injectors. “Seven” is equipped with 4 nozzles, which are controlled by an electronic control unit. The ECU prepares the mixture depending on the engine load, throttle position and other parameters read by special modules.
The main control element of the VAZ 21074 injector is an electronic control unit. Using built-in sensors, the ECU monitors the quality of the air-fuel mixture supplied to the combustion chamber, sets the ignition timing depending on the speed, and turns the fuel pump on and off. In addition, it regulates the idle speed, controls the emission of CO in the exhaust gases and determines the operating mode of the cooling fan.
The VAZ 21074 injector works in the following order.
The pump supplies fuel from the gas tank through filters to the fuel rail. Next, the fuel is supplied to the injectors. The pressure in the injectors is maintained by a special regulator within 300 MPa. Excess fuel is sent back to the tank. The injector is a sprayer with a solenoid valve, which operates from ECU pulses.
By reading readings from the piston position module in the cylinder, the central unit determines the moment of opening and closing of the injector. The optimal quality of the air-fuel mixture is prepared based on the readings of the mass air flow sensor and the throttle position.
Other parameters are also taken into account:
- cooling system temperature - necessary to determine the degree of engine warm-up and adjust idle speed. The temperature correction affects the degree of richness of the mixture;
- oxygen concentration - used to measure the oxygen content in exhaust gases;
- on-board network voltages - read by the speed sensor to transmit pulses in a certain order.
Where is the engine number
The engine number is individual for each vehicle. This is a kind of model identification code. On injectors 7 this code is stamped and can only be placed in two places under the hood (depending on the year of manufacture of the car):
- on the lower shelf of the air intake duct on the right;
- on the cylinder block.
All markings forming part of the engine number must be clear and unambiguous.
Transmission
| Clutch | single-disk, dry, with hydraulic shutdown drive and central diaphragm spring | |||
| Transmission | mechanical, four- or five-speed, three-way, three-shaft, with synchronizers on all forward gears | |||
| Gear ratios: | ||||
| first | 3,67 | |||
| second | 2,10 | |||
| third | 1,36 | |||
| fourth | 1,0 | |||
| fifth | 0,82 | |||
| reverse | 3,53 | |||
| Cardan transmission | two-shaft, with intermediate support and elastic coupling | |||
| main gear | hypoid | |||
| Final drive ratio | gear ratio - 3.9 or 4.1 | |||
| Differential | conical, two-satellite | |||
Piston
On pistons 2112, the wells have a depth of 3.19 mm for the inlet and 3.06 mm for the exhaust.
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Diameter, mm | 82,0 |
| Compression height, mm | 37,9 |
| Volume of internal recess, ss | 0,638 |
| Weight, g | 350 |
The piston pin is steel, hollow, floating type. The outer diameter of the piston pin is 2112–22 mm, the length of the pin is 60.5 mm. The hole for the piston pin is shifted from the center plane of the piston by 1 mm.
How does a fuel injection system work?
The essence of the whole process is that gasoline is supplied under pressure into the fuel rail, in which it is mixed with purified air in a ratio of 14 to 1. The mixture is always under pressure, so when the valve opens, it enters the combustion chamber unhindered. Here ignition occurs and the piston makes a power stroke. At the same time, the crankshaft rotates and the car is set in motion.
A bunch of sensors are responsible for the normal operation of all components, which measure temperature, pressure, amount of air and gasoline, etc. All signals are sent to a microcontroller control unit. It contains a special algorithm that regulates the operation of all main components and mechanisms. This is what we will talk about the VAZ-2107 engine (injector) in our article. Or more precisely, about its components.
What does a VAZ engine consist of?
At its core, the VAZ 2106 engine is a modernized 4-cylinder Troika engine that has received more power. From now on, the car boasts 75 horsepower, which produces a torque of 116 Nm. However, the developers did not stop at just one variation, presenting several of the following modifications to the attention of car enthusiasts:
- classic car with 1.6 liter internal combustion engine;
- a product with a 1.3-liter engine, as well as a modified carburetor, the piston stroke length is 1.4 cm shorter;
- 1.5-liter engine with modified parameters of connecting rod and piston elements and block.
All variations without exception are popular, but the most popular are still models with an engine capacity of 1.5 liters. This VAZ 21061 is quite unpretentious in operation and fails less often than other modifications. In total, regardless of the design options, the VAZ 21061 - 21063 engine includes the following:
- cylinder and crankcase, at the bottom of which a special pan is usually installed;
- a piston and adjacent compression rings located directly inside the cylinder;
- the crankshaft that moves inside the crankcase bearings.
For those who are accustomed to repairing a car themselves, no difficulties arise during the operation of the “six”. It’s a completely different matter if the driver is thinking about how to increase the power of a VAZ engine. Then the process will require an order of magnitude more knowledge and, possibly, specialist consultation. Of course, if the owner really wants to improve his car, and not cause irreparable harm to it.
Brake system
Parking brake with manual cable drive on the brake pads of the rear wheels
| Service brake system: | ||||
| front wheel brake | disc, with two-piston caliper | |||
| rear wheel brake | drum, with one working cylinder and two pistons | |||
| Service brake system drive | foot, hydraulic, dual-circuit, with a vacuum booster, rear wheel brake pressure regulator and low brake fluid level sensor | |||
Scheme of operation of the injection power circuit on the VAZ 2107
There is nothing complicated here. This scheme should not cause any difficulties even for beginners.
First, the fuel system starts with a tank that stores the fuel and a fuel filter. Then, using the fuel pump, the mixture passes through the filter to the fuel rail. A special pressure regulator is mounted on the ramp, which regulates the process of supplying fuel to the VAZ 2107 injector nozzles.
Using this regulator, a pressure of 300 mPa is created, and excess fuel is sent back to the tank. The injectors open and close using electrical impulses that come from the electronic control unit. They are designed to ensure the simultaneous supply of the fuel mixture to the intake manifold of each cylinder at each crankshaft revolution.
How much of the combustible mixture enters the cylinders depends on the time at which the injectors are open. This time is adjusted by the controller based on information received from the sensors.
Sensors (VAZ 2107 injector) installed on the engine provide all the information necessary for this. For example, the crankshaft sensor provides information from which the controller calculates the time between pulses for the injectors. If the operating mode of the power unit is increased, the system increases the opening time of the injectors. The controller calculates the time based on information from the throttle valve, as well as the mass air flow sensor.
The ECU constantly monitors the voltage in the car's electrical network, so if the voltage drops, the opening time of the injectors increases. All operating modes of the motor and injector are controlled by the controller. This ensures adjustment of the composition of the fuel mixture and operation of the injectors on the VAZ 2107 “injector” car.
Technical characteristics of the “Seven” injection engine
In carburetor systems, the creation of a combustible mixture is carried out directly in the chambers of the carburetor itself. However, the essence of the operation of the injection engine on the VAZ 2107 comes down to a different approach to forming the fuel-air mixture. The injector sharply injects the fuel itself into the working cylinders of the engine. Therefore, such a system for creating and supplying fuel is also called a “distributed injection system.”
The injection model VAZ 2107 is equipped from the factory with a separate injection system with four injectors (one injector for each cylinder). The operation of the injectors is controlled by the ECU, which regulates the flow of fuel to the cylinders, obeying the requirements of the microcontroller.
The injection engine on the VAZ 2107 weighs 121 kilograms and has the following dimensions:
- height - 665 mm;
- length - 565 mm;
- width - 541 mm.
Injector ignition systems are considered more convenient and modern. For example, the VAZ 2107i has a number of important advantages over carburetor models:
- High engine efficiency thanks to precise calculation of the amount of fuel injected.
- Reduced fuel consumption.
- Increased engine power.
- Stability of idling, as all driving modes are controlled via the on-board computer.
- No need for constant adjustment.
- Environmentally friendly emissions.
- Quieter engine operation thanks to the use of hydraulic compensators and hydraulic tensioners.
- You can easily install cost-effective gas equipment on the “Seven” injection models.
However, injection models also have disadvantages:
- Difficult access to a number of mechanisms under the hood.
- High risk of catalytic converter damage on rough roads.
- Capriciousness regarding fuel consumed.
- The need to contact a car repair shop for any engine malfunctions.
Table: all 2107i engine characteristics
| Year of production of engines of this type | 1972 - our time |
| Supply system | Injector/carburetor |
| engine's type | Row |
| Number of pistons | 4 |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Cylinder head material | aluminum |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 |
| Piston stroke | 80 mm |
| Cylinder diameter | 76 mm |
| Engine capacity | 1452 cm 3 |
| Power | 71 l. With. at 5600 rpm. |
| Maximum torque | 104 Nm at 3600 rpm. |
| Compression ratio | 8.5 units |
| Oil volume in crankcase | 3.74 l |
The VAZ 2107i power unit initially used AI-93 fuel. Today it is allowed to fill AI-92 and AI-95. Fuel consumption for injection models is lower than for carburetor models and is:
- 9.4 liters in the city;
- 6.9 liters on the highway;
- up to 9 liters in mixed driving mode.
What oil is used
High-quality maintenance of an injection engine begins with the choice of oil, which is recommended by the manufacturer itself. AvtoVAZ usually indicates in the operating documents of such manufacturers as Schell or Lukoil and oils of the following type:
- 5W-30;
- 5W-40;
- 10W-40;
- 15W-40.
Video: owner’s review of the injection “Seven”
How does the fuel injection system work?
Now let's talk about how the fuel injection system works. So, from the very beginning:
- You turn the ignition key, power is supplied to the electronic control unit, all sensors and actuators.
- After the crankshaft begins to rotate, the VAZ-2107 generator (injector) starts working with the starter.
- All sensors record changes in the parameters they measure.
- The electronic control unit adjusts the quality of the mixture and regulates the ignition timing.
- The mixture is fed under pressure into the combustion chambers through open nozzles, and the ignition process and working stroke begin.
That's all - the engine has started, all its components are working. When you press the accelerator pedal, you increase the amount of air, and therefore gasoline. The crankshaft speed will also increase.
How much the VAZ-2101 weighs is affected by the wear of metal parts, the presence of additional body kit and gas equipment. It is worth noting that the vast majority of modern sedans are equipped with a monocoque body configuration. “Kopeyka” in this case is no exception. This design is a steel box, inside of which there is a compartment for passengers, driver and luggage. In addition, the body carries the working components and assemblies of the vehicle.
Tuning rules
The main goal of high-quality tuning is improved engine performance. And the desired result can be achieved using the following methods:
- boosting the engine;
- chip tuning;
- replacing the ignition system with a more powerful one.
The most difficult and one of the most expensive procedures is increasing the diameter of the cylinders and the piston stroke. The weight of the VAZ car does not change, but the output power increases significantly. The best solution in this case is to replace the cylinders, which will be both easier and cheaper to install. The overall dimensions of the components will change very slightly and will not affect the ride quality in any way. Dimensions make themselves felt only when the vehicle is overcrowded or faulty.
Another effective tuning method is to improve the dynamic performance of the engine, achieved in the following way:
- the weight of the crankshaft and connecting rod-piston system is reduced;
- adjustment of gear ratios;
- adjustment of electronic systems.
The torque of the car will not change much from such actions; the power will increase, but only slightly.
Radical methods can come to the rescue, allowing those who wish to carry out in-depth tuning.
It consists in selecting a special crankshaft to replace the factory unit. This will allow you to change the car, practically reduce the ground clearance, and increase power. After all the necessary elements have been replaced, the vehicle as a whole is repaired and debugged.
Chip tuning is a relatively new modernization method that allows you to change parameters without mechanical intervention using special software. How much the engine weighs and when it was produced does not matter. The system will cope with any, even the most difficult, circumstances.
Replacing the ignition system belongs to the category of progressive tuning techniques. The best solution is a block called non-contact and allows you to significantly gain in power.
Experimenting with your own car is, of course, good, however, when deciding on the next modification, you need to think about whether they will be the last thing that the vehicle will finish off . The range of experiments is wide, so there is no need to rush. It’s better to think carefully and choose what will really come in handy.
Design features
Regardless of how much the VAZ-2101 weighs, the car body experiences not only static stress from the equipment installed on it, but is also forced to resist its effects under dynamic load. This property of the box is called torsional rigidity. On the car in question, this figure is approximately 7300 Nm/deg.
This technical parameter is significantly influenced by the condition of the bottom, roof, and thresholds. This is due to the fact that these elements are interconnected by the front panel. In addition, the strength characteristics and geometry of the body depend on the integrity of the door pillars, window panels and luggage compartment cross member. You can check the correct symmetry and general condition of the machine yourself. To do this, take the actual dimensions of the frame and compare them with the parameters specified in the car repair manual.
Load distribution
From the above it follows that the fatigue of the VAZ-2101 body directly affects the state of the control points for fixing units and components, and is also manifested in the correct geometry of its front, rear and side openings.
When moving (in dynamics), the distribution of loads on the frame occurs as follows:
- From the front suspension parts, vibration and mechanical moments are transformed to the cross member with subsequent transfer to the sub-engine frame part.
- Next, the force is transferred to the surface of the mudguards and the front shield, which are classified as load-bearing body elements.
- In the rear, a similar picture occurs in a more simplified form. There are no motor mounts involved here; the transition goes straight from the suspension to the car frame.
Material of manufacture
With this configuration of the body and suspension, the frame material plays a significant role in the safety and stability of the car. It is logical that strengthening the weak points of the body will make the vehicle stiffer and more stable on the road. But then the mass of the car will be critical, which will make it clumsy and very heavy.
When strengthening the frame, the weight of the “penny” and the load on all structural elements increases. That is why design engineers are trying to select the rational thickness of materials, taking into account the ratio of their dimensions and cross-section. The result is a fairly durable and not too heavy body.
To reduce weight and save on costs, elements that do not bear the load are made of thinner metal. The main parts have a thickness of about one millimeter, which corresponds to similar indicators for other cars of similar class.
How much does the VAZ-2101 weigh?
The tail of the “penny” at the front and rear is welded to the frame of the vehicle, which makes it possible to include it in the supporting circuit. This also helps reduce the weight of the car. Below is a breakdown of the main parts of the first model Zhiguli (in kilograms):
- engine with associated equipment – 140;
- gearbox – 26;
- cardan shaft – 10;
- rear axle – 52;
- radiator – 7.0;
- body part - 280.
The total weight of the VAZ-2101 is 955 kilograms. It would seem that the figure is not very impressive. But if you multiply the balances by all the units, of which 4.85 million were produced, it becomes clear that every gram saved plays a significant role.
VAZ-2106 engine weight
On a VAZ-2106 car, the weight of the engine without gearbox is 121 kilograms. Therefore, it is strictly not recommended to try to remove or move this unit alone - this is a direct path to serious injury. It is best to hire an assistant who can help you during the process of dismantling or installing the motor.
With all the necessary equipment, including both the cylinder head and the ignition system, the engine weight will be even greater - 140 kilograms.
Finally, when assembled with the gearbox and the devices attached to it, this value will increase by another 26 kilograms.
As you can see, weight can be considered a significant disadvantage of the car compared to imported analogues. To reduce it, increase power, and also improve dynamic characteristics, many drivers today install parts made of light metal alloys.
In 1984, a diesel version of the “six” was released at a Bulgarian automobile company. Replacing a gasoline engine with a diesel engine didn't have much of an impact on the car's performance. Firstly, the Bulgarians failed to increase the power of the power unit. Secondly, its weight increased by about 10 kilograms, which can also be called a disadvantage of the alteration.
Additional processing measures
It is worth noting that with dimensions of 4.07/1.61/1.44 meters, the car in question has a fairly acceptable weight. The strength and integrity of the body is affected not only by how much a “penny” weighs and how thick the metal is, but also by the quality of factory and independent anti-corrosion treatment.
According to the rules, after welding procedures, before painting, the car body must undergo phosphatization. During this treatment, the entire surface of the frame was covered with a special phosphate film that is resistant to chemical attack. In addition, the effect was secured by applying a layer of primer, which was sprayed using electrophoresis. This allowed the primer to provide even coverage in the most difficult to reach areas. The bottom of the vehicle was treated with a special reinforced mastic, which reliably protects the bottom from the effects of an aggressive environment.
Interesting Facts
Classic VAZ cars have retained their original configuration and the love of the people until modern times, regardless of age and social status. The engineers of the Volzhsky Automobile Plant do not even think of stopping at the achieved result, developing and manufacturing new modifications.
It is noteworthy that of all Soviet passenger cars, only the “kopek” was delivered to the Land of the Rising Sun. The popularity of the models in question is largely due to Kimi Raikkonen, who achieved his first successes and victories on this particular car. The father of the legendary racing driver considered this car one of the most reliable representatives of its segment.
If you find out how much the VAZ-2101 and its followers weigh, you can note that over its half-century history this figure for the brand in question varied from 0.95 to 1.3 tons. There were no significant and cardinal changes in this direction.
In conclusion
“Kopeyka” is rightfully called a legend of Soviet automobile production. People appreciated this car for its reliability, practicality and affordability. This modification has not been produced for a long time, but it can be purchased on the secondary market. There are quite well preserved copies. In addition, the VAZ-2101 represents a limitless field for tuning. Craftsmen “put their hand” to literally all parts of the car, from equipping the interior to modifying the body and power unit.
Source Source https://uaz-sura-motors.ru/diagnostika-i-remont/dvigatel-vaz-21074-karbyurator.html Source Source Source Source https://labuda.blog/231364.html