This is tough, friends...
How can this be?! It took me 92,000 km, 3 (three!) years and as many as 3 (three!) timing belt replacements to find out that the reason for the constant jerking at idle is trivial! — timing marks
!
I'll start with some background. I bought a wad in 2013 with a defect - when working at XX, it shook and swayed cyclically. In a traffic jam you could feel your head swaying in time with the fawn...
Unfortunately, the video was not saved...
This confused me when I bought it, but it didn’t stop me.
.
So, the wad has been purchased, a normal discount has been requested for the uneven operation of the internal combustion engine, allowing you to immediately order the spare parts and solve the problem once and for all. We didn’t do anything with our fingers, we’ll fix everything now. Yeah. ))
Ordered spark plugs and ignition coil. I changed it - it didn't help.
Yeah, that means pillows. Ordered + replaced = did not help.
Apparently the injectors are clogged. My wynns'om three times did not help.
The diagnostician at work gives me an idea - maybe an air leak? OK, remove the intake manifold and find cracked o-rings on the intake ducts. Due to the lack of new ones, we smear the old ones with sealant, collect them - ZERO result.
Oh yes, I was undergoing diagnostics in a French repair garage (the diagnostician works for an official dealer in his free time from the garage). Verdict - “you need to remove the cylinder head, see what’s there...” (...what the hell is there - valves, pistons, what else). The idea was immediately dismissed as untenable.
By the way, usually when buying a used car, people change all the fluids and the timing belt. But the previous owner gave me a work order to replace the timing belt 15,000 km ago. Therefore, it was planned to get into the timing belt only after 45,000 km, at least.
I tried refueling with 95, 98 - to no avail.
The throttle body was washed, trained in Feng Shui, the pressure sensor in the intake manifold was washed...
A crack was found on the crankcase ventilation tube; it was successfully insulated to no avail.
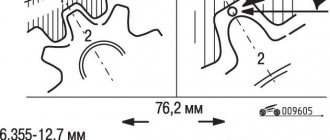
In the end, I think maybe M E T K I G R M
? ! It’s okay if I change the belt and rollers earlier, but maybe I’ll fix the problem! So, I bought a timing belt kit, read up on how to change it, where the marks are and all that, and went to change it.
I read: “We fix the flywheel with wire. There is a small hole to the right of the oil filter on the block towards the gearbox. Remove the oil filter cover and look with a mirror. We insert a steel wire there, it should go in about 5 centimeters.” And there is even a photo:
Okay, I find a plastic plug behind the oil filter,
I pick it out (I couldn’t put it back, to do this you need to at least remove the oil filter housing...), lock the camshafts with bolts, put the
the hole behind the oil filter (under the plug
), it goes there, with *hey, I got in! I think - fire!
I look, and the mark on my HF looks at 7 o’clock, but it should look at 6!
Hmm... You need to unscrew the camshaft gear and look - maybe the key has been cut off. Fuck it! The KV bolt could not be unscrewed with a pneumatic impact wrench! Well, I think, okay, so I won’t touch the HF gear, otherwise you never know!
I put the belt as it was (the mark on the HF is at 7 o'clock, and the mark on the belt is at 6 :)))), I assemble it - naturally, the engine still rocks.
I have temporarily postponed the solution to this issue, I’m driving like this for now. The wad drives, in principle, normally, confidently. Consumption is around 9 l/100 km, which also suits me quite well. In general, there is no reason to worry. Besides the fact that he still sways, the bastard...
Why is it necessary to set the labels correctly?
For the correct operation of the gas distribution mechanism of a car, it is necessary that the closing and opening of the valves occur in a strictly defined sequence. The slightest inaccuracy in the operation of the camshaft and crankshaft leads to the fact that the gas exchange process in the cylinders is disrupted, and the engine stops working in the correct mode.
A timing belt is a rubber part that during operation can wear out, crack, tear, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to replace the element in a timely manner.
When installing a new one, you should set the labels correctly. This is necessary to ensure that the engine operates correctly from the first seconds of startup. If installed incorrectly, serious problems can occur, including engine failure.
Causes
The timing belt is an important element of the car, so it needs to be serviced promptly. The reasons that lead to its jump are as follows:
Contact of oil or cooling liquid on the belt surface
As soon as traces of technical fluid appear on the product, the belt should be changed immediately. Otherwise, this can lead to slipping through the teeth, sliding off the pulley, and even breaking.
It is a serious mistake when drivers simply clean the dirty surface and continue to use this product.
Practice shows that if liquid gets on the belt, it is completely absorbed into the rubber. It loses its properties and begins to stretch.
Late replacement
Most timing belt manufacturers recommend changing their products approximately every 60 thousand kilometers. However, this figure may vary up or down, depending on the quality of the product.
Improper use
It happens that a product may jump due to errors during its operation. A common example is a weakened roller or tensioner. When the belt tension weakens, there is a possibility of slipping from the pulley grooves. In the opposite situation, if when installing the belt, it is overtightened, this will lead to its breakage.
Slippage can also occur when one of the pulleys has strong play. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the tension level of all parts of the mechanism.
The labels are set incorrectly
Sometimes the jump is not visible outwardly, but the engine does not start well and immediately stalls. This can happen if the marks were knocked down or incorrectly set initially. A shift of even one tooth can cause problems with the motor. If the engine is diesel, it will not start even if there is an error of one tooth.
Tools needed for work
Installing marks is not an easy process and if done incorrectly, you risk spending a lot of time installing the part. And that's not the worst thing. There are cases when careless drivers break the engine and other mechanisms of the car.
First of all, stock up on the necessary tools:
- Socket head.
- Jack to raise the car.
- Keys No. 17 or 19 - depends on what kind of car you have.
Advice: it is better that you have all key diameters starting from No. 10.
Large flat head screwdriver.
Labeling
Before starting work, you need to understand that it is important that during the process of replacing the timing belt, the pre-set risks do not go astray. Otherwise, you will have to go deeper into the settings and spend more than one hour installing the part.
When installing the timing belt, it is important to align the pistons so that in the first cylinder the piston is at the highest point of the first cylinder. In this position, the piston is at its maximum distance from the crankshaft. This is the position the engine is in when the marks are correctly set. In this position it is necessary to change the timing belt.
The number of marks, as well as their location, may vary depending on your engine type.
The following marks can be distinguished:
- Mark on the flywheel.
- Mark on the pulley.
- Camshaft mark (two on a 16 valve engine).
Timing belt malfunctions: signs, causes and solutions
The basis of any power unit and one of the main components of any internal combustion engine is the gas distribution mechanism. Its main function is to control the intake and exhaust valves. During the intake stroke, the intake valves open. The fuel mixture is supplied to the combustion chambers. During the exhaust stroke, the exhaust valves open and exhaust gases are removed from the cylinder. This mechanism is generally quite reliable if you follow the operating rules of the car. But sometimes it also fails. Let's look at the main timing belt malfunctions, their causes and repair methods.
Timing device
To begin with, let us briefly recall how these mechanisms work. On most engine models, the gas distribution mechanism consists of the following components and parts.
So, the valves are controlled by the camshaft. Most often it is made of steel or cast iron. It is installed in the crankcase. This crankcase is covered by the timing cover. Also on modern engines, the camshaft can be found in the cylinder head. When the shaft rotates, it acts on the cams, which, in turn, act on their valve.
The design also includes pushers - they can be steel or cast iron. Their function is to transmit force from the camshaft and cams to the valves.
The mechanism has two valves - inlet and outlet. Their task is to supply the fuel mixture to the combustion chamber and then remove the exhaust gases. The valve is a rod with a flat head. The inlet and outlet elements are different from each other. The difference concerns the diameter of the head or plate. These timing elements are made of steel and heat-resistant steel (in the case of exhaust valves). The leg is a rod with a groove. It is needed to secure the springs. The valves can only move towards the bushings. To prevent oil from getting into the cylinders, sealing caps are used. An external as well as an internal spring is attached to each of the valves. Rods in the timing device are necessary to transmit force from the pushers to the rocker arm.
The camshaft rotates due to the drive. It can be chain or belt. The drive transmits rotation from the crankshaft. The distributor makes one revolution per two revolutions of the crankshaft - this is the operating cycle of the engine.
Possible faults
Timing timing faults include incomplete valve closure and excessive clearance between the valve stem and the toe of the rocker arms. Gears, pushers, rods, rocker arm axles, bearing bushings and camshaft journals also wear out.
Let's consider the causes and consequences of some typical breakdowns of this mechanism, as well as signs of a timing belt malfunction.
Compression reduction
One of the symptoms of malfunctions is a decrease in engine compression and popping noises in the exhaust pipe. This happens after carbon deposits and shells form on the valve. Often the element may burn out. The cause of the burnout lies in the loose fit of the intake and exhaust valves to their seats. Other factors also influence the reduction in compression. These are deformation of the cylinder head, broken or worn springs, jamming of the rod in the bushing, lack of space between the valve and the rocker arm.
Power reduction
Often, timing belt malfunctions manifest themselves in the form of a decrease in power, in the form of tripping and metallic knocks. These are all signs that the valves are not opening completely. Part of the mixture of fuel and air does not enter the combustion chambers of the engine. Subsequently, the thermal gap increases and the hydraulic compensators fail. As a matter of fact, this is the reason for the malfunction of the mechanism and valves.
Worn belt or chain
This is one of the most basic timing faults, which happens especially often. In this case, the engine may completely fail. The drive belt breaks, and the pistons hit the valves that have not yet closed, as the camshaft no longer rotates. The reason lies in the wear of the belt or chain.
Timing Belt Troubleshooting
A damaged drive belt has catastrophic consequences and is a particularly common failure. Let's look at the causes of timing belt failure.
So, most often the element fails due to a break in the straight cord. This may be due to the fact that the belt was broken before installation on the engine. The second reason is the rupture of the twisted cord.
This happens if any foreign body gets between the belt and the camshaft pulley. As a result, it cut deeply into the rubber belt and the cord broke. This can also happen if the installation is incorrect. It happens that this malfunction is caused by carelessness - the camshaft pulley could be rotated with a sharp screwdriver.
Cutting teeth
This happens due to weak belt tension. Such a timing fault does not lead to catastrophic consequences, but engine operation may be disrupted. The car may not start. Among the reasons are also jamming of the camshaft pulley, as well as obstruction.
Notches on belt teeth
This occurs due to excessively low tension. This also occurs due to tension losses during operation.
Belt back cracks
Here experts highlight belt overheating and operation in low temperatures. In addition, the cause may be a worn guide roller.
Belt edge wear
If the belt is visually very worn on one of the edges, then there may be damage to the flange or wear. In this case, it must definitely be changed.
Chain
For a long time it was believed that a chain was much more reliable than a belt drive. And this is true, but the chain is far from immortal. Timing chain malfunctions also occur. If the belt breaks, then there is, albeit a small, chance to save the engine. In the case of an open circuit, the situation can be much worse. The chain is more massive than the belt, and if it breaks, it literally grinds the engine. Severe damage to valves and pistons occurs. In general, there is only one fault with the chain - it breaks.
Among the reasons include the quality of the oil. The chain's lifespan is 250 thousand kilometers, but they rarely run for that long. There are widely known cases when the chain in the engine broke after a mileage of 100, as well as 60 thousand kilometers. But this is more often a factory defect in specific cars. Often problems are associated not only with oil, but also with engineers’ mistakes.
Several symptoms will indicate a worn chain. To avoid having to overhaul the engine (which is usually very expensive), it is necessary to change the chain as it stretches.
If the engine idles roughly and unevenly, then the chain is already “fit.” This type of engine operation is due to the fact that the valve timing has changed. If the chain chirps at idle, then this is also one of the signs that irreparable malfunctions of the timing drive may soon occur.
If, after removing the cover, it is clear that the tensioner has reached its maximum distance, if wear appears on the teeth of the sprockets, then it is best to replace the chain.
Timing belt repair and maintenance
The main problem with this mechanism is worn journals, cams and increased clearance in the bearings. To reduce the gap, grinding of the camshaft journals is necessary. At the same time, the grooves for oil supply are also deepened. The necks are ground to repair size. Next, after repair, check the height of the cams.
There should not be even minimal damage on the supporting parts under the necks. There should be no cracks in the bearing housings. After cleaning and washing the camshaft, be sure to check the gap between the journals and the hole in the cylinder head support.
The chain should not be stretched or have mechanical damage. As long as it is not worn out, it can be adjusted. Unscrew the locking bolt half a turn. Then turn the crankshaft 2 turns and then tighten the locking bolt.
Otherwise, troubleshooting timing belt faults involves replacing worn elements. It is also necessary to periodically adjust the valves on vehicles that do not have hydraulic compensators.
Conclusion
As you can see, the most common problems in the timing mechanism are drive belts and chains. This is what specialists most often have to deal with during repairs. Other breakdowns occur less frequently. But it is worth remembering that it is difficult to independently diagnose this unit - often the symptoms may correspond to other breakdowns. It is also worth remembering that most timing problems will lead to a violation of the distribution phases. And then you can begin to look for the causes and ways to eliminate timing faults. You can independently adjust the thermal clearances of the valves, and it is better to entrust everything else to specialists.
Replacing a timing belt without marks
In some cases, it is necessary to install the belt if there are no marks.
For this you will need:
First of all, remove the belt protective cover and unscrew the spark plugs.
Let's take a closer look at the process of replacing a belt without marks on an 8-valve engine.
- It is necessary to align the camshaft in the overlap, for example, it is convenient to select the second cylinder. To do this you will need a caliper and a screwdriver. Slowly turn the camshaft clockwise and observe the overlap position. To do this, use a barbell. Place it on the expansion joints and rotate the camshaft until the expansion joints are at the same height. That is, the position of the barbell should be straight, not beveled.
- After determining the overlap, it is necessary to set the TDC (top dead center) of the second cylinder. Insert a screwdriver into the spark plug channel. Slowly rotate the engine, only in the direction of engine movement, so that the piston rises up. At a certain point, you will feel that the flywheel begins to rotate easily. After this, you need to feel the lower and upper points with your hand and set the upper one.
- After adjustments, put on the new belt so that it matches, you may need to turn it a little. And also pull it tight.
- The next stage is checking the belt installation. Rotate the flywheel and look for a mark on it. Set it to the top position and check the marks on the camshaft. If the adjustment is made inaccurately, the risks will disappear.
On a 16-valve engine (2 camshafts), the installation is carried out according to the same principle.
Consequences of incorrect labeling
If the timing marks are set incorrectly, serious consequences for the car can occur.
The most common cases:
- Due to misaligned timing, valves can become deformed during engine operation, and the damage will accumulate.
- The valves will become deformed - bent. Although this will not happen in an 8-valve engine.
- Due to deformation of the valves, the cylinder head may be damaged. As a result, the guide bushings will fail, and cracks may appear on the main power elements.
- The piston mechanism may burn out due to incorrect placement of the timing marks.
- There will be an oil residue on the spark plugs. Plus, the ignition moment of the fuel mixture worsens.
- And also other unpleasant consequences arise.
How to understand that the marks are knocked down, symptoms
After replacing the belt, a situation may arise that the marks were installed incorrectly. How to determine this is described below.
- Traction and throttle response disappear.
- The car begins to accelerate more slowly.
- The engine gets very hot.
At the end of the article, we would like to note that not every car owner can correctly set the timing marks. It is necessary to have information about the operation of the engine and its design features. If you don’t want to spend a single hour setting up the mechanisms, we recommend turning to specialists.
Do-it-yourself timing belt alignment
A timing belt is a relatively common solution for driving timing gear and other equipment compared to a timing chain. With all this, the designated belt serves less than the chain, in other words, it needs repeated replacement. Most drivers know that when replacing the timing belt, the drive pulleys are marked according to marks, which is necessary for precise synchronization of the operation of the engine and the gas distribution mechanism.
With all this, not many people fully understand how to correctly set the timing belt when replacing it themselves and why this is so important. Let us immediately note that if the timing belt is not aligned with the marks, then a failure of the valve timing occurs. As a result, the engine may not start after such a replacement, it will work unstably, or even the internal combustion engine may break down. In this article we will talk about what are the symptoms of an incorrectly aligned timing belt, as well as how to align the timing belt with or without marks.
Read in this article
Measures to prevent serious consequences of a malfunction
If possible symptoms of belt or chain jumping occur, computer diagnostics should be performed. The malfunction can be determined by the ignition angle being too large. In static mode, diagnostics may not show an engine error, since the electronic components remain operational.
It is necessary to measure parameters in dynamic mode. At the same time, it is dangerous, especially if more than one tooth has slipped through. When an engine is running in which the timing belt has slipped, mechanical damage to individual components is likely.
You can determine the malfunction visually. This requires access to the marks and belt drive. Older gasoline cars use a strobe light as a control device.
Aligning the belt according to the marks and how to set the timing belt without marks
Let's start with the fact that below we will focus on the general rules and instructions regarding how to set the timing belt. With all this, it should be taken into account that on cars with tuned sports camshafts, as well as on some models with 2 or only one camshaft, the order and features of the drive belt alignment may differ. To obtain clearer information, it is better to consult with specialists or separately study the operating instructions for a specific internal combustion engine model.
The timing belt jumped a tooth. Symptoms and consequences. VAZ 8 class.
In our case, the teeth on the belt are cut and the timing is off.
Before work, you should keep in mind that the main task will be to ensure that the previously set marks do not get lost during the replacement. This will help simplify the process because there will be no need for advanced configuration ahead.
- So, when installing a new timing belt, the most important step is to set the position of the pistons in the engine so that in the first cylinder the piston will be at top dead center (TDC). Then the marks are checked. Let us add that you can set the pistons to the required position using one of the available methods. The easiest way is to find a special notch on the pulley, as well as an arrow located on the timing belt casing. The indicated notch and arrow should be combined with each other. Alignment implies a position where the notch is in a vertical position and the arrow is pointing down.
- The second method, which complements the first, is to detect a special mark on the flywheel, after which the marked mark is aligned with the “tooth”. The mark is located in the control window, which is located in the upper part of the gearbox bell.
- The third and most unreliable method of aligning the pistons is to unscrew the spark plug in the first cylinder, after which a suitable screwdriver or a metal rod of suitable length is inserted into the spark plug hole. Then the rod rests against the piston, after which, as a result of turning the crankshaft, the point at which the piston is in the last upper position is determined. Please note that a similar method should only be used in this case if labeling is not feasible for some reason.
Changes in engine performance after jumping
Typically, timing belt or chain jumping occurs as a result of the simultaneous action of several factors, for example, stretching, increased load during engine starting or driving. In this case, skipping can occur through the gears (pulleys) of both the crankshaft and the camshaft pulley. After this, the ignition shifts towards late.
The amount of this displacement in angular units depends on the number of timing belt teeth or chain links. A shift of the timing belt by one tooth corresponds to a change in the ignition angle by an amount equal to the ratio of 360 angular degrees/number of teeth. For example, if the number of teeth is 100, then the offset will be about 3.6 degrees.
A delay in the engine ignition angle by this amount often does not exceed the operating parameters of the engine.
When displaced by one tooth (link), the engine usually works. The following changes are observed:
- increased fuel consumption;
- difficulty starting the engine;
- increased toxicity of exhaust gases;
- reduction in engine response.
In the case when the belt has slipped by more than a tooth, the change in the ignition angle is more than 5 angular degrees. This is a critical value. In modern cars, the control unit usually turns off the engine to prevent serious mechanical damage, especially in engines where the pistons “meet” the valves in such a situation. Experienced drivers, when choosing or purchasing a car, are specifically interested in whether pistons and valves are found in a given model of engine installed in the car.
When a belt (chain) jumps over two or more teeth (links), the following are observed:
- misfires;
- uneven engine operation, the engine naturally “sausages”;
- engine start failure;
- extraneous sounds when the power unit is operating.
Operating a car in such a situation is extremely dangerous.
Replacing the timing belt
- The process of replacing the belt is that you first need to loosen the crankshaft pulley mounting bolts, after which the designated pulley is removed. Next, the mudguard of the belt is removed; before removing it, it is recommended to fix the flywheel using the method indicated above. At the same time, you will need to remove the alternator belt and water pump pulley. The alternator belt is removed after loosening the bolts securing the pump pulley.
- Then you should unscrew the timing belt tensioner pulley bolt and remove the roller from the stud on which it is attached. Typically, the designated roller is changed in parallel with each timing belt change. After removing the roller, the belt can also be removed.
- Now it becomes possible to install a new tensioner pulley and a new timing belt. After installation, the belt should also be tightened. This is done automatically using a tension roller, and from time to time the tightening is done with a pump. The tension force itself is checked so that between the camshaft sprocket the belt can be twisted with a huge and forefinger with a small force of 90 degrees, but less than that. It is also worth considering that the belt should not be sagging.
- After tensioning the belt, it is necessary to check the alignment of the camshaft marks. In this case, if there is a slight deviation, the tension roller is loosened and the belt is rearranged. Then the roller is fixed again, after which you should turn the crankshaft bolt a couple of turns. Then all marks are checked again.
- In this case, if the marks of the crankshaft and camshaft coincide, but at the same time the marks of the distributor do not match, then the bolt that secures the distributor should be loosened. Then the distributor must be turned to a position where the center of the slider and its mark coincide. This will help to avoid such a problem when, for example, when replacing the timing belt, the ignition was set later, the ignition becomes early, etc.
Correct tension
The second most popular mistake is an incorrectly tensioned timing belt. Most often it is over-tightened, which will most likely lead to its rapid breakage. The consequences of a cliff are already familiar to you. It is no less dangerous to under-tighten - it can simply jump off at high speeds. To make sure the tension is correct, you need to try turning the long part of the belt 90 degrees. The effort should be excessive or too loose.
What's the result?
In relation to internal combustion engines with a timing belt drive, it should be taken into account that slippage of the belt even by one “tooth” can lead to malfunctions of the power unit or its breakdown. As mentioned above, if the belt breaks, there is a risk of bending the valves. As for diesel engines, a broken timing belt can render the camshaft unusable.
As a result, I would like to add that when replacing a timing belt, aligning it to the marks is the main task. In this case, if you are not convinced of your own abilities or have problems identifying the marks, then it is better to give up trying to set the belt on your own and turn to experienced specialists.
>
Repair cost
The average price for replacing a belt and roller in car services ranges from one to three thousand rubles. The price range is due to the fact that replacing parts on foreign cars costs approximately 2–3 times more than on domestic cars.
If it turns out that you also need to change the engine water cooling pump and the crankshaft oil seal, then the price will increase by another 1 - 1.5 thousand rubles.
Although there is a huge selection of products on the market at different price levels, you should only choose brands recommended by the manufacturer or their high-quality analogues. Using cheap parts can lead to serious damage and expensive repairs.
For example, if the valves are bent as a result of a belt slipping, then almost the entire cylinder head will have to be replaced. Even if the repair is carried out by yourself, the cost of replacing valves, pump, belt, filling oil and antifreeze, and other parts will be at least 10,000 rubles.