Few drivers know what to do if valves or hydraulic compensators on a VAZ 2112 16 valves are knocking. This is a fairly common situation. But most people do not know the reasons for such phenomena and are afraid of them. In fact, this may be quite common and should not be a cause for concern. Depending on the characteristics of the knock, we can draw a conclusion about its nature and danger to the engine. Some types of knocking are quite harmless. You can ride with them, but this problem may lead to others. Therefore, it is still better to eliminate the cause immediately. Moreover, in most cases this does not require any special costs.
How to understand that the hydraulic compensators of the VAZ 2112 are knocking?
It is very easy to check the hydraulic compensators: you need to remove the valve cover, bring the crankshaft to a position where the cams will not act on the compensators, and then press on the piston. If the hydraulics are working properly, the piston will move down, if not, it will stop!
This often happens due to insufficient oil. You can understand what exactly is knocking in the engine by the following characteristic signs:
- If the knocking noise disappears only at high speeds, it means that there is a faulty ball piston hidden somewhere, it must be detected and the failed compensator replaced
- When it starts knocking on a warm engine, this is a sure sign that the hydraulic valve has worn out and has completely exhausted its service life.
- If knocking occurs at high speeds, there is most likely excess oil in the system. The lubricant gets onto the cylinder head and disrupts the functioning of the compensators
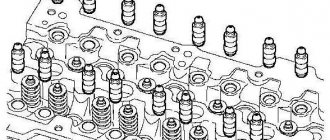
Device
What to do if valves or hydraulic compensators on a VAZ 2112 16 valves are knocking? Before answering this question, it is necessary to understand the structure of the hydraulic compensator, which mechanics often abbreviate to “hydric”. It is from the peculiarities of its structure that the reason for some knocks follows.
The hydraulic compensator itself consists of a cylindrical piston, whose bottom receives the force from the camshaft pusher. There is a plunger located inside it. With its help, force is transmitted from the camshaft to the valve stem. The plunger moves quite freely in its seat. This is necessary to ensure a thermal gap. When the engine is running, the camshaft cam pushes the piston, which opens the valve through a plunger. The thermal gap is adjusted using oil supplied to the head under pressure. Accordingly, adjustment occurs by changing the pressure. To avoid oil leakage from the hydraulic valves during parking, a ball valve is used.
How to eliminate knocking on a VAZ 2112?
The reasons for the appearance of knocking noise from hydraulic compensators are quite clear: natural wear, low-quality engine oil, lack or excess of lubricant in the system. Monitor the engine oil level; if necessary, top up, don’t skimp. Also, you don’t need to save on oil changes - it’s more expensive for yourself.
As practice shows, repairing expansion joints is a waste of nerves and time. It is also impractical and, in the end, unprofitable. Check all the elements again, most likely one of the hydraulic valves is knocking. Replacing hydraulic lifters is a simple job.
For normal operation, hydraulic compensators require an uninterrupted supply of oil, which is supplied under pressure. The supply occurs through a special channel with a check ball valve, which prevents oil from draining from the channel after the engine is stopped. In addition, there are channels located on the lower plane of the bearing housing, which supply oil to the camshaft journals.
Hydraulic compensator design:
To enlarge the image click on the image!
The disadvantage of hydraulic compensators is their excessive sensitivity to the quality and purity of the oil. The presence of mechanical inclusions and other foreign elements in the oil leads to rapid failure of the hydraulic compensator plunger pair. This malfunction is most often accompanied by increased noise emission and intense wear of the camshaft cams.
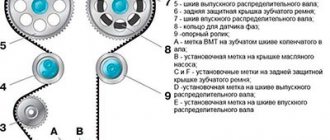
Replacing the timing belt: instructions
Let us note a slight difference in the procedure for replacing the belt on a Priora with and without air conditioning. You will need to first remove the belt and tensioner pulley of the generator (not to be confused with the timing tensioner) in order to dismantle the protective covers of the drive of the timing mechanism itself.
Using a 15 mm socket, unscrew the tension roller of the generator, remove the belt itself (it is recommended to replace it together with the timing belt), access is open; Using a T-30 bit (asterisk), or a hexagon, unscrew 5 bolts of the upper cover (plastic casing) and 2 bolts of the lower timing drive cover; Disconnect the crankshaft sensor by disconnecting the corresponding chip located near the top cover; If it is necessary to replace the cooling system pump, you will have to lift the right drive wheel into the air with a jack. All this is needed to compare the marks of the camshaft pulleys with the marks on the block body; We rotate the raised wheel in 5th gear, or turn the crankshaft pulley with key number 17. Having matched the camshaft marks with the marks on the block body, it is necessary to turn on the neutral gear to avoid failure of the mark settings. Check the markings on the flywheel by removing the rubber plug at the top of the flywheel housing. Under the plug you can see part of the flywheel and the crown on it; align the flywheel mark with the triangular mark on the left side of the housing; If it is necessary to replace the pump, at this stage it is necessary to loosen the fastening of the 2 camshaft pulleys in order to avoid deformation of the valves when the gas distribution consumable is dismantled; To gain access to the crankshaft pulley, you need to turn the steering wheel as far as possible to the right or remove the wheel. You will need a helper to remove the crankshaft pulley.
Engage 5th gear, hold down the brake pedal, and use a 17mm key to unscrew the fastening bolt;
ATTENTION! Left hand thread! Remove the pulley and thrust washer. Head 15mm; unscrew the bolts securing the tension and thrust rollers, after dismantling which you can remove the timing belt
Install a new timing drive consumable. You need to apply tension by turning the tension roller with an offset center (the cutouts of the race and the tension roller bearing bushings must match). When reassembling, carefully monitor the marks on the camshaft pulleys and engine flywheel. When replacing a part, the support and tension rollers are changed immediately.
Let's summarize. Hydraulic lifters are knocking - reasons
- Hydraulic lifters can knock due to problems with oil, including the fault of a faulty oil system, as well as as a result of a mechanical malfunction of the hydraulic compensator itself.
- If hydraulic compensators knock when cold , but the knock disappears when hot, then, according to experienced mechanics, there is nothing wrong with this; this phenomenon occurs in most car owners.
- If the hydraulic compensators knock when hot , that is, after the engine has warmed up to operating temperature, this is a clear sign of a malfunction that must be eliminated immediately.
Knock of hydraulic compensators of Lada Vesta when cold. What to do, reasons
The nature of the knock and the periods of its occurrence strongly depend on the reasons that caused extraneous sounds from the timing belt. The following reasons are typical for knocking on a cold VAZ 21179 and VAZ 21129 engine:
- Physical wear of the hydraulic compensator. Like any mechanism, a hydraulic plunger has its own resource. Especially those hydraulics that are installed on Lada Vesta from the factory. As a rule, they last from 20 to 30 thousand mileage, after which the clattering and knocking begins on a cold engine. This indicates wear of the plunger pair, wear of the hydraulic housing or subsidence of the return spring. In many cases, the knocking of hydraulic compensators on Vesta is associated with coking of the structure due to the use of low-quality oils.
- Quality and service life of motor oil. We remember when we changed the engine oil. If more than 5-6 thousand have passed since that moment, the reason for the knocking of the hydraulic compensators most likely lies in oil wear. It loses its properties, loses viscosity, and only harms and clogs the engine. Hydraulics, including. In this case, we wash the engine and change the oil and filter.
- The design of any hydraulic compensator is such that after stopping the engine, the full volume of oil must remain in the pusher housing in any case. The hydraulic compensator bypass valve prevents oil from flowing out after stopping the engine. If it is clogged, the spring has sagged, or the valve itself is worn out, the oil will leak out, and the compensator will wait for a new portion after the engine starts. Hence the noise when starting when cold. If the knocking noise disappears after warming up, the problem is in the hydraulic tappet valve.
- Dirt and carbon deposits in oil channels. Hydraulic compensators are also susceptible to oil starvation. Especially at startup. Coked oil channels both in the cylinder head and in the hydraulic compensator provoke oil starvation of the plunger, which leads to increased wear of the pusher and knocking from under the hood. If there is a suspicion of coking of the oil channels, chemical agents will only help to delay mechanical cleaning of the engine. True, this applies to a greater extent to engines with a mileage of 100-130 thousand, running on cheap low-quality oils.
- Oil . We got to it, because the wrong viscosity or type of engine oil for the Lada Vesta is first noticed by the hydraulic compensators. Oil that is too thin or too thick for the wrong season will certainly cause knocking noise from the hydraulic tappets.
- Oil filter. Again, low-quality filters may not withstand the service life of the oil itself. The knocking sound of hydraulic compensators when cold can also indicate a problem with the filter - it may be clogged, or the pressure reducing valve may be damaged.
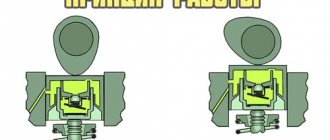
The hydraulic compensator is a small cylinder, inside of which there is a spring and a pair of even smaller cylinders - plungers, as well as a check valve. The operating principle of the engine is such that it achieves maximum efficiency when the chamber contains a “clean” mixture - exclusively fuel and air.
When gases remain there after one cycle, the mixture becomes increasingly less pure and the engine produces less power. In order for gases to leave the chamber in time, the operation of the valves must be harmonious. There are hydraulics for this - they constantly adjust the position of the valves. And oil enhances their work and helps fight friction.
The oil enters a small gap under the plunger, presses on it, and after that the pusher exerts force on the valve. When at rest (during the so-called “break” when the cam moves), the pusher is constantly in contact with the camshaft cam, which is ready at any moment to move it down so that the valves open even more.
On Priora, the knocking sound of hydraulic compensators appears when the trajectory of their movement changes. That is, when they have to change the position of the valve, they move “crookedly”, and their efficiency approaches zero. There can be several reasons for problems with hydraulics and valves. Diagnostics may lead to the discovery of other faults.
Problems in the oil system that can cause knocking in hydraulic compensators:
- Clogged oil channels (dirt in the channels, plaque);
- Airy oil system (air present in the system increases the compression ratio of the oil). Air in the oil can occur as a result of high or low oil levels;
- Clogged oil filter;
- The wrong oil has been filled in (does not match: viscosity, fluidity, quality, temperature characteristics);
- There may be interruptions in the operation of the oil pump;
- Overheating of the engine, as a result of which the oil burned, losing its viscous and lubricating properties.
How to check hydraulic compensators - video
How to solve the problem of knocking hydraulic compensators?
- You can try changing the oil if it has been changed for a long time or looks bad (dark brown color, bad smell, etc.). As a rule, after replacement, the knocking of hydraulic compensators disappears. If the knocking does not disappear, you will have to take out the main battery and see what’s wrong.
- If adding oil did not lead to anything, and washing the engine did not give any result, you can try another way to solve the problem of knocking hydraulic valves. The principle is to remove the main hydraulic valves, perform a visual inspection of them, in case of insignificant wear and normal condition, you can disassemble and wash the hydraulic compensators. When removing, I recommend remembering or writing down where which hydraulic compensator was installed. After washing, everything is assembled and the operation of the engine is checked; if washing the hydraulic compensators does not lead to anything, the only way out is to replace the hydraulic compensators .
Eliminating knocking
Sometimes car owners make attempts to independently solve the problem of knocking hydraulic compensators. I have nothing against it, since it’s quite possible to wash or repair the element with your own hands.
Be prepared that the work will take a lot of time and effort. It's not worth going there without experience in car repair. You should not rely entirely on flushing, since it does not always restore normal operation of the compensator. This is due to the fact that the knocking may be caused by oil or malfunctions in other engine systems.
Let’s not forget about situations where you can hear a knock when it’s cold, but it disappears when it’s hot. The reason here is definitely not the low oil temperature. This phenomenon is common. Therefore, car owners often ignore these symptoms, since the knocking soon disappears.
When tapping one hydraulic compensator, you can try this repair method:
- turn the crankshaft so that the valve suitable for the problematic main valve opens;
- turn the valve with the spring at an angle so that you can move the elements that are not positioned correctly;
- start the engine.
If after this the knocking does not disappear, you cannot do without a full-fledged professional diagnosis. A similar repair technique is relevant for VAZs and Prioras, for example.
When the engine is not warmed up and knocks, there is nothing terrible. Most likely, the lubricant is still thick and has not had time to warm up. That is, knocking when cold is acceptable and you can safely drive on with it. If the sound does not disappear after warming up, then leave the car alone until the problem is resolved.
Replacement procedure
If you decide to install new expansion joints, you should not be afraid to take on the work. The procedure is not the most complicated and is typical for almost all engines. That is, the instructions presented will help you regardless of what kind of car you have.
But it’s still worth having an official repair and maintenance manual on hand. And then you will say that it’s all my fault.
Please note that when replacing parts on some machines it is necessary to additionally replace the cover gaskets. Otherwise the replacement principle is identical
Act according to the plan and do not deviate from the sequence of stages:
- remove the valve cover;
- remove the sprocket from the camshaft (use a wire, carefully picking up the desired part and pulling it up);
- check the tensioners and dampers for wear (if these elements are already well worn, it is better to replace them immediately);
- remove the bed, having first removed the fastenings from the crankshaft;
- remove the rockets and place them in the same order as they were located in the engine (label, for example);
- dismantle all the compensators one by one and place them in front of you in the order of installation in the car;
- clean and rinse the oil pipeline and installation sites of new hydraulic compensators;
- screw in new or cleaned compensators according to the purchased tickets;
- when tightening, be careful with force, do not overdo it (use a torque wrench);
- it is better to clean or replace the valves;
- Reassemble the parts in reverse order.
That's all. At this point, the work of replacing hydraulic compensators can be considered completed.
To avoid such procedures in the future, be careful when choosing oil. It is because of this that hydraulic compensators most often knock. If the problem is not there and even after changing the oil the sound does not go away, then I advise you to additionally consult with specialists and carry out diagnostics at a service station.