Mariuse › Blog › Removing, checking, installing hydraulic compensators for VAZ 21213, VAZ 21214
Hello
. My story will be in several points.
1. Design and operation of hydraulic compensators 2. Check 3. Installation (2 methods) Video will be attached So: 1. Design and operation of hydraulic compensators
Hydraulic compensators were first introduced to the domestic market back in 1989. Then they seemed very effective for improving Zhiguli engines. The use of these parts had positive results, so after a while the manufacturer of these mechanisms modernized his creation so that it was possible to install a hydraulic compensator on the Niva, which became the right decision.
The principle of operation of such a device is that instead of screws regulating valve clearances, plunger pairs are screwed into the block head. It is to these vapors from the lubrication system that oil from the lubrication system is carried through additional tubes, which forces the rocker (or lever) to constantly press against the camshaft cam. This eliminates the need, which was constant before installing this part, to check and adjust valve clearances.
Experts say that hydraulic compensators for Niva and other car brands help maintain valve timing, as a result of which the parts of the gas distribution mechanism not only make less noise, but also have a significantly longer operating period. It is noted that after installing the hydraulic structures, they cease to experience shock loads. Also, exhaust toxicity and, very importantly, fuel consumption are reduced to some extent.
True, this mechanism still has some disadvantages that are insurmountable on the way to their conveyor installation. The main thing, perhaps, is that installing hydraulic compensators on the Niva requires incredibly fine adjustment and great care, which means that it will take much more time, and for a factory conveyor, time is an unaffordable luxury.
And at service stations such work is not profitable enough. In addition, there is another significant drawback, which is that after removing the head, you will need to disassemble the entire block, which means that you will have to change the gaskets, because it is not possible to assemble the block with the old ones.
When might a device need repair?
There are quite a lot of reasons leading to the need to carry out such a process as car repair. A hydraulic compensator malfunction is one of them. The damage can be either minor or very serious. Most often, repair of hydraulic compensators is caused by the use of low quality motor oil. Insufficiently frequent changes of lubrication system filters can lead to the same consequences. Turbo kit for Niva Oil contamination causes various troubles. The gaps inside a mechanism such as a pair of bushings and plungers increase. As a result, the volume of oil leakage will constantly increase or the hydraulic compensators will not have time to automatically select the size of the gaps in the gas distributor mechanism. The most obvious sign of this deviation is the knocking of the hydraulic compensators. The ball valve wears out and becomes clogged over time. As a result, the valve does not close tightly enough and oil leakage from the plunger cavity increases. The plunger pair of the Chevrolet Niva car begins to jam. Moreover, if at first it may be almost imperceptible, then gradually this deviation can completely disable the mechanism. As the load on the gas distributor increases, it is also necessary to replace the hydraulic compensators on the Chevrolet Niva. Repair is necessary if the hydraulic lifters are knocking and all their parts wear out too quickly.
2. Check
Of course, if there is a problem with the hydraulic valves (usually a simple knock), you need to check them. Having removed the valve cover, you can check it with a simple screwdriver, putting it between the hydraulic valve pusher and the rocker, try to push the plunger, it should press in and then return to the reverse position.
If you disassemble, then put the rocker and hydraulics in the same sequence as it was on the engine.
Checking on removed hydraulics is also easy. Taking the hydraulics in your hand, press the plunger with your thumb. It should squeeze and return back, and not hang in the middle. (
CHECK IS DONE ON A WASHED, READY HYDRAULIC)
To wash the hydraulic compensators you need: a container for gasoline (preferably of course), an awl, a screwdriver, a rag, and your hands)
Device
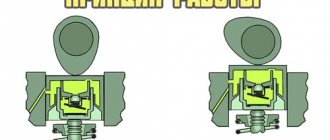
The operating principle of this unit is that the mechanism can automatically change its length by an amount equal to the clearance in the valves. The movement of the component elements in the assembly is carried out due to springs and oil, which comes from the car’s lubrication system. Let's see how the hydraulic compensator works. We already know what it is. So, a compensator is a housing in which a plunger pair is installed. She can move. In turn, this part consists of several elements:
Cylindrical pushers, parts in the cylinder head, and levers in the drive can be used as a housing for the hydraulic pusher.
There is a hole at the bottom of the plunger that is closed by a ball valve. The operation of the hydraulic compensator is possible due to the spring located between the plunger and the bushing. Almost all elements are arranged this way. VAZ hydraulic compensators are no exception (Priora 2172 is also equipped with them).
Niva hydraulic compensators: what they are and how they work
The hydraulic compensator in the engine is a device that allows you to “select” the thermal clearance of the valves automatically, that is, without additional interventions. For example, mechanical adjustments performed with washers or bolts must be carried out regularly, since the gap “goes away” over time, deviating from the recommended values.
In turn, the hydraulic compensator (HC), located between the camshaft cam and the valve, “selects” the gap automatically. The hydraulic compensator itself is a plunger; engine oil is supplied to the chamber, thereby maintaining an optimal thermal clearance.
It turns out that the lubrication system is quite overloaded, while the oil pump remains almost the same as on the old “classic” VAZ. Perhaps it was for this reason that the manufacturer replaced the old-style hydraulic compensators with new ones.
Description of the hydraulic compensator device and its principle of operation
Hydraulic compensators are designed to automatically regulate the thermal gap between the valves and the engine camshaft. The hydraulic attachment is provided by oil, which enters the expansion joints under pressure, and a complex and incredibly precise set of springs provides the necessary clearance.
Hydraulic compensators, which have been installed on Chevrolet Niva in recent years, give them a tangible advantage:
- there is no need to periodically adjust the valves;
- now the timing belt works more clearly and correctly;
- The noise when the engine is running has decreased significantly; it begins to knock less;
- The service life of timing parts has increased significantly.
Main details of the unit:
- Plunger pair.
- Frame.
- Plunger bushing.
- Plunger spring.
- Plunger ball valve.
The operating principle of the unit is relatively simple and consists of three main functions:
- There remains a small gap between the camshaft cam and the compensator, which is filled with oil. The plunger spring pushes the plunger out of the sleeve, the oil fills the gap under pressure, reaches the desired level, and the ball valve shuts off the oil supply. After these actions, the gap disappears.
- By turning, the cam moves the compensator down. Due to the accumulated oil, the plunger pair becomes rigid and presses on the valve, opening it.
- As the plunger moves down, it loses some oil and its pressure drops. As the cam moves further, the cycle repeats.
Hydraulic compensators for Niva: hydraulic supports of the old and new type
Initially, GM supplied its own hydraulic compensators for the first engines (2002 - 2005). At the same time, such GCs are reliable, the motors operate without problems. However, later they began installing compensators on the Niva, the origin of which is unknown. Problems began with these elements.
The same thing happened later, when they began installing hydraulic compensators of a new type on the engine. The first batches in 2008 turned out to be of high quality and reliable. Then the quality began to deteriorate, the GK cups were of poor quality, etc.
Please note that when installing hydraulic compensators (for example, INA), it is also important to change the cups. Ignoring this recommendation leads to the fact that after 40-60 thousand km. exhaustion appears, oil pressure drops and a knocking noise appears.
Why are they knocking?
It's easy enough to hear. The knocking of hydraulic compensators on a cold or hot engine begins to appear directly during engine operation and has a direct impact on the stability of its operation.
The reasons that the element is knocking “hot” are as follows:
- The oil pump has failed. The system does not create the required pressure.
- The hydraulics of the hydraulic compensator are broken, that is, the system does not have the required amount of oil or, conversely, there is an excess of it.
- The landing site of the part has increased significantly due to the heating of the engine, during which the metals expand.
These causes of malfunction are typical only for a warm engine. It is worth noting that the sound of these elements on a hot engine is quite rare.
Most often, the hydraulic compensator knocks “when cold”, and for both modes the sound may appear due to low quality oil. It also occurs due to a contaminated lubricant purification system.
When to change hydraulic compensators: signs
It is important to pay attention to indirect signs of problems with hydraulic compensators. If the oil level and its quality are normal, then the following symptoms indicate faulty oil coolers:
- strong knocking in the valve mechanism when cold;
- after warming up the knocking does not disappear;
- the knocking intensity decreases with increasing engine speed;
- Changing the oil and flushing the oil system does not solve the problem.
You can accurately determine that the Chevrolet Niva hydraulic compensators need to be replaced after removing the camshaft. In such a situation, it is necessary to disassemble the engine, remove compensators, perform troubleshooting or immediately make a complete replacement, etc.
We hear a bell, but we don’t know where it is.
The owner of a VAZ-21214 complained about constant knocking in the engine. Sometimes they last a very long time, sometimes not so long, but most often they happen on a cold engine. While we were standing and talking, the knocking appeared again and the engine began to feel feverish. It seems as if he is “trotting.” The knocking continued for no more than a minute and then disappeared. The client left the car and left. We agreed with him that I would call myself when I fixed the problem.
Based on the nature of the knock, it was obvious that one of the eight hydraulic compensators was faulty. But which one!? I didn’t want to change everything, or the first one that came to hand, so I used the “First Look” sensor.
It doesn't have such a name for nothing. If we translate it literally into Russian, we get – “First Look”. So it is, the name speaks for itself! Being in the diagnostician's arsenal, it can always be used first to quickly identify a malfunction. The sensor is installed on the section of the exhaust pipe of the muffler. Based on the pressure pulsation in the exhaust system, the quality and uniformity of operation of the engine cylinders is analyzed, an ineffective or faulty cylinder is localized, and the quality of the mixture is determined (lean or rich).
What tools are needed
Having determined that the hydraulic compensators and hydraulic supports are knocking and need to be replaced, and also having selected a suitable hydraulic compensator 21214, you can proceed to replacement.
To change the hydraulic compensators of a Chevrolet Niva, you need to prepare the following tools for replacement: a set of keys, screwdrivers (flat and cross), a metal brush and a medical syringe, as well as wire (can be replaced with a plastic clamp).
- ratchet wrench with extension and set of attachments;
- socket wrench (tube) “10”, “12”;
- torque wrench;
How to install new hydraulic mounts
At the initial stage, it is necessary to remove the air pipe and disconnect all elements connected and attached to it from the valve cover. Next, you need to remove the cover and replace the hydraulic compensators.
To remove hydraulic compensators on a Chevrolet Niva, you will need:
- Remove the 8 valve cover bolts. Next, after removing the cover, you need to press the rocker. If the pushrods drop easily, this clearly indicates problems with the main valve.
- Next you need to insert a flathead screwdriver between the camshaft housing and the rocker. Then, turning the crankshaft as the engine rotates, you will need to align the mark of the camshaft gear with a characteristic casting (made on the bed body).
- Now, having loosened the gear, you should remove the chain tensioner. Next, the chain (in the same position as the placement on the sprocket) should be tied around with a wire or clamp. This will maintain some chain tension, and the sprocket itself can be removed from the shaft.
- The next step is to unscrew the camshaft bed nut. Afterwards, you can dismantle the rockers and hydraulic compensators (the hydraulic supports are unscrewed using the “24” socket).
- Now the hydraulic compensators on the Niva are being replaced, and the new elements should be tightened with a force of 2 kgf. Having replaced all the main components, the engine is reassembled in the reverse order of removal.
- You should be prepared for the fact that after replacement, the first start of the engine may be accompanied by noise. Normally, the noise should stop after a short period of time when the new compensators are filled with engine oil. To minimize wear, idle speed should be raised to 2-3 thousand.
Main types of faults
We answer the question of how to check hydraulic compensators for functionality. It can be noted that there are four reasons for the occurrence of malfunctions:
- Increasing the size of the gaps in the areas indicated by the arrows in the photo below. Gaps are formed between the plunger and the plunger bushing. The result will be increased oil leakage. The compensator simply will not have time to “select” the thermal gap;
- In rare cases, the check valve does not close tightly. Which, at a minimum, makes it impossible to create sufficient pressure generated between the sleeve and the plunger;
- The bushing should move freely relative to the plunger. In the areas indicated in photo 3, a blockage may appear, and then the plunger pair jams;
- Clogged engine oil passages are another reason why compensators stop working.
Points 1-3 are illustrated in the photo:
The first failure always occurs as a result of abrasive wear. If you use low-quality oil, you will get the appropriate result. The second malfunction is the result of wear or clogging. The latter, by the way, is more common. Well, jamming can occur due to gradual coking or due to the appearance of deposits.
Each of the reasons received a number from 1 to 4. Next, links are made that say which reason causes this or that effect. Read carefully.
Testing process from start to finish
Let's consider the answer to the question of how to check the serviceability of hydraulic compensators in practice. You need to open the hood, start the engine and listen:
- Let's say that immediately after starting the engine increased noise appears, and after 5-6 seconds it disappears. Conclusion: the compensators are working properly, oil just leaked out of their cavity;
- At idle there is an intermittent noise. As the speed increases, the noise disappears completely. Conclusion: there is a malfunction, but it is due to the second or third reason (see above);
- When a warm engine is idling, a continuous noise may occur. As the rotation speed increases, the noise goes away. Conclusion: the cause of the malfunction that occurs is indicated under number 1;
- Similar symptoms were mentioned above. But the engine may behave differently: noise appears at high speeds and disappears at low speeds. This means that the cause of the malfunction is oil foaming;
- Let's say there is a characteristic noise from one or more valves. The effect does not depend on the rotation speed. Be aware that this malfunction can be caused by any of the reasons listed in “Chapter 2”;
- Sometimes you can hear noise in idle mode, which increases with increasing frequency up to 1500-2000 rpm, but no more. This effect is not related to the operation of hydraulic compensators.
Now we just have to figure out what causes the oil to foam. In fact, both a lack and an excess of engine oil leads to the effect. Advice: you need to add consumable fluid to the MIN mark or get rid of its excess.
Increased noise levels do not always indicate a malfunction. From some of the hydraulic compensators, if the car is left on a slope, oil may leak out completely, but the deficiency will quickly be replenished with the engine running. You can get rid of the unpleasant effect in a few seconds. Why is the engine started?
From all that has been said, a simple conclusion is drawn: you should park your car on a slope only when necessary. All experienced car owners know about this.
Recommendations
- It should be noted that not in all cases Niva hydraulic compensators need to be replaced. The fact is that often their thin channels simply become dirty, as a result of which the valve mechanism begins to knock heavily. For this reason, you can wash old hydraulic mounts in gasoline.
- Also, upon inspection, it often turns out that only one Niva Chevrolet hydraulic compensator makes a knocking noise. This means that replacing the entire set is not required. In this case, all hydraulic supports are also washed, and only one faulty Niva hydraulic compensator is replaced.
Installation
Several times they sent me links from forums about the fact that they installed German hydraulic compensators, but it became little better than it was. The issue is not with the INA hydraulic compensators, but with the cups. If you look at how the hydraulic compensators are installed in the cylinder head, you will see that the vector of application of force by the camshaft cam goes vertically, and the hydraulic valves and cups are at an angle to the vertical. The cups are traditionally made from shit of poor “half-baked” material, so after a while (50-70 thousand km) an elliptical groove begins to appear, along which the oil pressure required for the hydraulics begins to disappear. Therefore, if you want to update the system and install German hydraulic compensators, install new glasses.
How to check and find out which hydraulic compensator is knocking
Domestic cars tempt car owners with their ease of repair. Most service and repair work can be carried out independently, without contacting a service station and significantly saving the family budget. But before proceeding directly to the repair, you need to correctly diagnose the cause of the malfunction.
Using a Chevrolet Niva car as an example, we will tell you how to find out which hydraulic compensator is knocking on the engine timing belt.
You can first determine which hydraulic compensator you need to work closely on in a simple way. Those hydraulic compensators that are set at top dead center need to be lightly pressed down with a screwdriver, which is used as a lever.
If the hydraulic compensator “falls” under light pressure, it means that it is not adjusted and makes a knocking noise. You can even, for the “purity of the experiment,” quickly press the screwdriver lever and tap the hydraulic compensator.
After checking the hydraulic lifters alone, rotate the camshaft sprocket 180° so that the crankshaft rotates 360° accordingly. And proceed to check the next group. “Correct” hydraulic compensators “stand still” and do not respond to light pressure from a lever screwdriver.
After first identifying out-of-adjustment hydraulic lifters, make sure there is no error. This is easy to check; there is an old, “old-fashioned” method. After removing the camshaft box cover, press the “loose” hydraulic compensators with your finger. If there is no error, then they will press easily.
On the website of the sponsor of this entry it is possible to buy a new refrigerator.
Something else useful for you:
Adjusting hydraulic compensators does not always give the desired result. It happens that they turn out to be very worn out, and adjustment is simply not enough. The solution in this situation is to replace them with new ones.
Verification methods
Now the motorist is faced with the task of finding out whether the expansion joints on his car are working or not. What is the best thing to do in such a situation?
There are two verification options.
- The first option involves removing the valve cover. The method is more visual and allows you to almost certainly guarantee the correct diagnosis. But implementation is more difficult due to dismantling work;
- The second option does not require the elements to be dismantled. But here you need good hearing. To improve it, it is better to use a phonendoscope. By listening to the operation of the main engine in different modes, you can find the source of the problems.
Which option should I choose? It's up to you to decide.
Both verification methods have their strengths and weaknesses. For a beginner in such matters, I would recommend starting by listening to the hydraulic compensators. If wiretapping does not yield anything, then open the valve cover and more clearly examine the condition of the elements.
Wiretap check
The preparation for the procedure is extremely simple. You need to place the car on a flat surface, open the hood, start the engine and listen.
Even perfect hearing does not always allow one to clearly recognize a non-working compensator. It is better to take an auxiliary medical instrument to help. It's not difficult to find.
And here we will consider several situations. Depending on the result of the check, we will draw appropriate conclusions.
- After starting the engine, the noise appeared at first, but disappeared after a few seconds. Everything is fine with compensators. Lubricant just temporarily leaked out of the cavities of the main body. The engine turned over and filled them;
- The speed is idle, and the noise from the compensators is intermittent. As soon as you raise the speed, the noise goes away. There is a problem. It lies in the bushing or blockages;
- The engine is warm, the speed is idling, the noise is continuous. By increasing the speed, the noise disappears. This means that the gap has increased;
- The symptoms are similar to the previous point, only at low speeds there is no noise, but at high speeds there is. Here you are faced with foaming of the oil;
- One or several knocking noises occur at once, regardless of engine speed. Any of the above malfunctions are possible here.
By applying the wiretapping tool one by one to the area where each of the compensators is located, you can understand where exactly the problem is.
If the noise of one HA differs from the others, you have found the source of trouble. All that remains is to figure out the reasons and eliminate the malfunctions.
Disassembly check
To check these elements for their functionality, you can remove the valve cover. Next, you will have to rely on your own feelings when checking elasticity.
You will have to turn the crankshaft using the center nut to do this. This will set the shaft in motion.
When the pusher cam is directed in the direction opposite to the main body, check the elements one by one for their elasticity, whether there is free play.
You can use your hands or available tools. When the compensator is loose and moves too softly, it is faulty. Needs renovation.
Installation of hydraulic compensators on a VAZ 21214
To work you will need:
— Clean motor oil
— Tweezers (can be replaced with a slotted screwdriver)
Before installing the HA, they must be disassembled and thoroughly washed in gasoline. Dry and put back together. After that:
- We check the hydraulic supports. To check, you need to press your thumb on the assembled hydraulic support; it should squeeze and move apart freely (without jamming)
- The next step is to install the oil supply ramp and screw in the dry hydraulic mounts by hand
- Using a torque wrench, tighten the hydraulic mounts (22 N per m). Again we check that when pressed it is pressed all the way, and then returns to its original position. If it sticks:
a) swap the hydraulic support with the neighboring one
b) reduce the moment to 18 n per m
c) replace with a new one
!All hydraulic clamps must be tightened to the same torque
4. Next, you need to fill each hydraulic mount with oil. To do this: take out the plunger and put it in a clean place, use tweezers to take out the piston with the ball and also put it aside; We fill the engine oil into a syringe and fill it into the hydraulic support housing to the brim, after which we lubricate the piston and insert the piston into the housing, pressing the valve ball with an awl. Fill the plunger with oil and insert it into the body.
All steps have been completed and the hydraulic mounts have been installed, then you need to get the engine into working condition. After that you can safely start!
Preparing for washing
So, if there is a knocking sound, but the hydraulic fluids are in good working order, then you should wash them. To do this, remove the air filter and cylinder block cover. The rocker arm axles, where the hydraulic compensators are located, are also dismantled. They are carefully removed from their seats. Before washing, prepare three containers, which together have a volume of about five liters.
Before washing, you should let the car sit in the garage for a day. During this time, the oil will drain from the hydraulic fluid into the pan. Flushing hydraulic compensators will be successful and effective if done indoors, where there is no dust and wind. Kerosene or A-92 gasoline can be used as a flushing liquid. But you can also use specialized products.
Reviews from Chevrolet Niva owners
Advantages: Price and quality
Disadvantages: Body is not protected from rust
Advantages: high ground clearance, suspension, climate control, insurance coverage, inexpensive maintenance, undemanding to the quality of roads
Disadvantages: small trunk
Advantages: If this American Niva did not break down, then it would not have a price. Overall this is a very good car.
Disadvantages: The car has many disadvantages, like any domestic horse, it requires attention and constant repairs. I got the impression that by the 130 thousand mileage I had replaced almost everything, and much of it several times. I repaired the transmission and transfer case several times at the very beginning, not to mention minor repairs (balls, tension rollers, belts, thermostat, generator, pump...). I also had to change the brakes three times. The engine cylinder head was repaired twice.
Advantages: Cross-country ability, high ground clearance
Disadvantages: High consumption, calipers rattle
Advantages: good cross-country ability 2.1 ground clearance good handling comfortable spacious interior good heater good air conditioning airbags high-quality paint
Disadvantages: the gearbox is a little tight (especially the first six months), it’s noisy (but moderately), the engine is too weak for it
Advantages: 1. good cross-country ability 2. roomy 3. good sound insulation 4. good light 5. warm stove 6. starts well in winter 7. air conditioner cools well
Disadvantages: 1. weak engine 2. when the air conditioner is turned on, there is a large loss of power 3. knocking noises when changing gears 4. it is difficult to turn on, and then the lock turns off.
Advantages: Definitely cross-country ability, in this regard it has never let us down. The cabin is quite spacious and comfortable. It's good that there are plastic body kits. Accidentally drove into a concrete fence, so for the hell of it, I wiped it off with polish and that’s it. In general, they are head and shoulders above their VAZ counterparts. Good paint quality.
Disadvantages: There will be more of them. If you are not a hunter, not a fisherman or a forester, if you can drive up to your house in a puzoter, then drive a puzoter, not a Shnivo. He eats a lot, which is even more noticeable in winter. Quite dumb. The track is not for her. I drove it to Sochi, I was tired as a dog, it doesn’t accelerate, sometimes an empty truck accelerates faster. The transfer case grunts and sometimes creaks. After 10 thousand km. the panel creaked. From the moment of purchase, the right front wheel squeaks at 30-60 km/h (according to the owner's manual this is normal). Small trunk (5-6 cm spare tire is not enough to fit). The spare tire is easy to remove, mine was hanging down in 3 minutes, until I tied it with chains and installed the secrets. The stove does not warm my feet well. The lack of air conditioning (my fault) in the hot summer of 2022 was worth a lot, in the cabin it was 35-40 grams.
Advantages: Compared to other VAZs, the interior is made of better quality, there are no creaks or rattles of plastic. It is convenient to get into the car. There are no complaints about the operation of the air conditioner; it has virtually no effect on the car’s response. When you press the accelerator pedal a little sharply, it turns off and turns on again when you stop accelerating.
Disadvantages: Oil leaks from all components and assemblies wherever it is present, and this is not considered a warranty case, because GM-AVTOVAZ believes that oil dripping with an interval of one drop no more than once every twenty seconds is the NORM. All rubber products, such as CV joint boots, ball joints, silent blocks, rubber seals and others, are covered with cracks and have looks like it was 20 years ago, with a mileage of 11,000 km. The bridges and transfer case howl. There is a lot of play in the transmission, dull knocks are heard when starting off and shifting to higher gear.
Advantages: Comfortable, convenient, you can’t squeeze into it (my weight is 110) in service almost like 21213, although the cross-country ability is a little worse, but you quickly get used to it and already make allowances for this. Consumption suits me, city 11.2 highway 8.8.
Disadvantages: The suspension is rather weak. On our roads I change ball joints once a year. Prices for spare parts are 50% higher than for 21213. It’s a shame to crawl through the bushes for hunting and fishing.
Advantages: Large, high interior where I sit without bending over and don’t rub my shoulder against the front passenger. It’s nice to drive off-road without fear of touching the crankcase and the bottom, steady bumps pass smoothly.
Disadvantages: Weak engine, to drive in fifth you need to accelerate the car to 110, there are no differential locks, it doesn’t go into the mud, it spins one front and one rear wheel, the luggage compartment is small, the heater does not heat well even in comparison with the old VAZ classics, there is airflow all winter It’s aimed at the windshield, it eats gas like a crocodile 15l/100km on the highway. The gear levers are difficult to shift, especially the transfer case, it’s just terrible when you turn on all-wheel drive, you then catch the moment to switch to rear-wheel drive.
Disadvantages: - in the first years, everything that can break breaks... - low quality of components - huge costs for constant repairs
Advantages: 1. High cross-country ability. 2. Good dynamics. 3. Cheap body repairs.
Disadvantages: 1. Delays are possible with spare parts, as for foreign cars 2. Externally, it is a Chevrolet Niva (turns into an advantage if you are encrypted)
Advantages: 1. High cross-country ability 2. Good dynamics 3. Indestructible suspension
Disadvantages: 1. Old design (for whom show-off is needed) 2. most of the disadvantages are from the old Sh-Niva
Hydraulic compensators or adjusting bolts
Hydraulic compensators installed from the factory are not always of high quality, and can begin to knock even after a short mileage. In some cases, the cause of the knocking is an untwisted main valve, that is, it was not tightened with the proper force during installation (tightening 2-2.2 kgf). But if the parts are already inoperable, the question arises - how to replace the faulty hydraulic valves.
The most reliable in the automotive market are considered to be the hydraulic compensators of the German company INA; also for the Chevy Niva, hydraulic compensators are produced by AvtoVAZ, and the hydraulic compensators are of the old and new type, they differ in the cylinder heads (cylinder heads became different for cars produced after 2008).
Hydraulic compensators are mainly sold individually, but they are not cheap - the price of one AvtoVAZ group is approximately 330-400 rubles, while an adjusting bolt costs only 30-50 rubles. If the driver agrees to adjust the valves every 10 thousand km, then it is better to install the bolts - there are fewer problems and the repair is cheaper.