Flushing the engine cooling system is one of the simplest procedures that even a beginner can handle.
Moreover, if you figure out how to flush the engine cooling system with citric acid with your own hands, you will save not only on workshop services, but also on expensive reagents. The car cooling system does not require constant monitoring. As long as the machine is working properly, it is enough to flush the system no more than once every two years. But if the readings of the temperature sensor of the cooling system are too high, the engine gets very hot, the fan is noisy, the pump is acting up or the heater is not working well, then it is better not to put off flushing.
How to choose a wash?
The cleanliness of the radiator on the outside is no less important than on the inside, and more dirt gets there.
The cleanliness of the radiator on the outside is no less important than on the inside, and more dirt gets there.
The safest thing to do is buy the one recommended by the car manufacturer. Or at least one whose label states that it will not harm the metals in the cooling system.
Modern cleaning products are not based on acids or alkalis - they have a neutral pH. This means that they are not aggressive to metal parts in the cooling system.
Washings can be two-component. The first component cleanses the system of metal oxides, the second - from decomposition products of old antifreeze.
Additives are added a couple of thousand kilometers before replacing the antifreeze, and they have time to wash away all the contaminants in the system, putting them in a suspended state. When replacing antifreeze, the dirt simply merges with the old one.
Important:
It is better to use branded washes according to the instructions for use. But if there is a suspicion of a large amount of sediment in the cylinder block and radiators, you can first flush with a large amount of water under pressure (from the water supply or using an electric pump).
Flushing the engine cooling system: citric acid as a cleaner
As mentioned above, the need to flush the cooling system may arise for various reasons. As a rule, cases when:
- the antifreeze in the expansion tank has darkened or become cloudy;
- “flakes” of scale and lumps of dirt are noticeable in antifreeze;
- the engine began to overheat regularly;
- The cooling fan operates frequently;
- there are problems with the operation of the thermostat;
- The interior heater (stove) is not working correctly, etc.
It is not difficult to guess that ignoring these symptoms will soon lead to more serious overheating of the internal combustion engine, which, in turn, will damage the engine. At the same time, a number of simple and accessible actions allow you to solve an existing problem yourself in advance, as well as avoid undesirable consequences in the future.
One of the most accessible compositions for flushing the cooling system is citric acid. Let us immediately note certain advantages of this method. First of all, the use of citric acid does not require any additional precautions, since the risk of chemical burns, respiratory tract damage or injury is practically absent.
It is worth adding to this that the harmful effects of such a cleaner on the cooling system itself are similarly minimized. This means that citric acid, when used correctly, is not capable of harming parts, rubber pipes, seals, etc. In other words, the composition can be safely used for cleaning radiators, regardless of the material they are made of (aluminum, brass).
It is also worth highlighting the availability of the method, since citric acid is a cheap product, especially when compared with ready-made special cooling system cleaners from various domestic and foreign manufacturers. The main thing is that the car owner needs to know how to prepare a flush and flush the cooling system with it. In other words, you need to understand in what proportions to mix citric acid and water.
It should be noted that the proportions of citric acid in the solution for flushing the cooling system are relative. Moreover, the opinion of many car enthusiasts on this matter is somewhat different. However, one should not draw hasty conclusions, since it is a mistake to believe that the more acid, the better.
Let's move on to concentration. Analysis of information from various sources indicates that drivers often use half a package or a whole package of citric acid per 5 liters of water. It is important to take into account that the packages themselves on sale can be 30g, 40, 50 or even 80g.
If you remember that to remove scale at home (for example, in a kettle), 1 30g sachet is enough. for a couple of liters of water, then we can conclude that for 5 liters. 70g will be enough. citric acid, that is, for one cleaning cycle it is advisable to immediately buy a large 80 g package.
If the cooling system is very dirty, then it is quite possible that it will have to be cleaned several times to achieve the proper effect. This means that you need to have at least two or even three large packages in stock.
What you need to know before flushing the heater radiator
Why does the heater radiator clog?
This is what a clog looks like from the inside / drive2.ru A clogged radiator is one of the most common reasons for poor performance of the interior heater.
Most often this happens due to poor-quality coolant, mixing two antifreezes of different compositions, or the use of water. All this leads to the formation of plaque on the walls from the inside. Dirt tightly clogs the already thin radiator tubes with swirlers, disrupting circulation, and there can be no talk of any heating.
How to understand that the problem is a clog
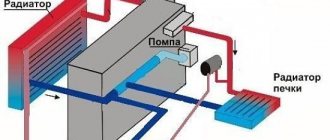
Checking whether the heater radiator is really clogged is quite simple. You need to find two thin pipes going into the cabin through the partition of the engine compartment and feel them. If one of them is hot, and the second is barely warm or cold, then this is a blockage.
In some cases, cold air will blow from the heater, even if both pipes are hot. This may indicate the following: everything inside is so clogged that the heated antifreeze enters the radiator tank and, bypassing the honeycombs, immediately leaves it without having time to give off heat.
What to do about it
The standard solution to this problem is to replace the radiator with a new one. This is what the car service will recommend. Here you will have to fork out money, since the cost of work is added to the price of a new radiator, and this is 2-3 times more expensive than the spare part itself. In modern cars, getting to the radiator is very difficult: you need to remove the trim and dashboard, unscrew the air conditioning pipes, and then refuel it.
The second option is washing directly on the machine. In this case, everything is much simpler and you don’t need to remove anything. It is enough to disconnect the pipes going to the heater, connect a pump with hoses instead and run the flushing solution through the radiator.
How effective is flushing the stove radiator?
Cleaning a radiator is much easier, faster and definitely cheaper than replacing, but this procedure also has its downsides. Flushing is not a panacea; the chances of success are approximately 50 to 50. In advanced cases, there is sometimes no effect.
Again, on older cars the radiator can leak only because the deposits that covered the holes in the tubes are washed away. Well, there is always the possibility of dirt from the cooling system getting into the washed stove again.
And yet, before changing the radiator, many car owners prefer to flush it first.
Why flush the engine cooling system?
The answer to the question is obvious: to restore its lost characteristics, improve the circulation of coolant, and stabilize the temperature regime of the engine.
Auto mechanics recommend using water first. If the degree of contamination of the cooling system is low, this will help remove all that is unnecessary and extend the life of individual components. But if the car has been in operation for five years or more, and even more so, not from a car dealership, and has changed several owners, then there is a high probability that the cooling system is not as fresh as in previous years.
Some car owners do not repair the system when there are small leaks, but simply add sealant to the coolant. It copes well with small cracks, but at the same time it can clog radiator tubes, damage the thermostat and cause a lot of other troubles if used ineptly.
How to flush the cooling system when changing the fluid?
If the check reveals that the coolant has an uncharacteristic color, or the engine begins to overheat in hot weather, then it is necessary to drain the old coolant and flush the system with water. You can find the volume of the machine's cooling system in the owner's manual or on the Internet. Usually this is about 7-8 liters for common engines with a volume of 1.5 - 1.6.
Flushing the system with water is simple: fill in the required flush volume, start the engine and wait for the thermostat to open. Let the engine idle for 10 minutes. After this, turn off and let cool. Then the water must be drained and, if possible, the system must be purged with a compressor. If the water is dirty, repeat the procedure.
At the end of the flushing, coolant is added. Every 100 kilometers you need to check its level, the absence of leaks at the joints of the system, and observe the color of the liquid. If it changes again, the system needs more serious flushing.
Why do car enthusiasts use citric acid?
- Harmless. Unlike washing with special solutions based on dangerous alkalis and acids, citric acid is a food additive and does not harm the human body if inhaled, in contact with the skin or mucous membranes.
- Cheap. To completely flush the radiator, you will need very little acid - up to 80 grams, which costs much less than other options or service station services.
- Available. Citric acid is sold everywhere - it can be found in most stores in baking supplies next to seasonings, and anyone can carry out the procedure of washing the stove with acid.
Available means
To flush the cooling system, industry today produces a number of chemical reagents. However, we all know that improvised means can often be much more effective. A separate advantage would be to note the cost-effectiveness of such maintenance methods. One of the main ways to prevent incorrect operation of the “stove” is to flush the engine cooling system with citric acid. Let's see why this method is so popular and how to use this affordable troubleshooter?
Special liquids for flushing the cooling system
Those who are not going to try drinks, descalers, as well as folk remedies as a cleaner and do not trust them, they choose auto chemical products.
Manufacturers of auto chemicals are constantly developing new products, so there is a wide range of choice.
Classification of liquids by chemical composition:
- Neutral. Neutral are those with pH = 7. You can buy a ph meter and check what kind of water we drink (it’s good to drink alkaline water), etc. Neutral liquids do not have various alkaline and acidic impurities. Such liquids by themselves cannot clean the cooling system channels well.
- Acidic. Such liquids have a pH value of 7. They effectively dissolve organic contaminants.
- Two-component. Such liquids contain both acidic and alkaline elements. Effectively dissolve and remove scale, rust, and various deposits resulting from the breakdown of antifreeze or antifreeze.
It is advisable to use only one liquid based on its chemical composition. Not so, first alkaline, then acidic, or vice versa.
Among the TOP auto chemical products for flushing the engine cooling system are the following:
- Lavr Radiator Flush Classic (Lavr Radiator Flush Classic) is a chemical product from Russian manufacturers. Effectively used for complete cleaning of the internal combustion engine cooling system. The cost of a half-liter container of Lavra is about 300 rubles.
How to use LAUREL:
- Drain the coolant.
- Pour in two-component LAUREL. Volume 430 ml is enough.
- We fill the system with water after Laurel.
- We start the engine and let it idle for 30 minutes.
- Shut off and drain the fluid.
- Fill with distilled water for rinsing.
- Start the engine and let it idle for 15 minutes.
- Drain this liquid and add new antifreeze or antifreeze.
After such cleaning, deposits of scale, rust and dirt will be removed from the system. The pump and antifreeze will last longer.
2. LIQUI MOLY Kuhler-Reiniger (Liqui Moly Kahler-Reiniger) - a product from a German manufacturer of chemicals for cars. The cost is around 500 rubles for a 300 ml can. There are no aggressive substances in the composition.
If you need to flush the radiator channels and the system as a whole from rust and oil deposits, then Liqui is perfect for this. Does not destroy rubber and plastic products.
To prepare flushing fluid for a car’s cooling system, one 300 ml bottle is enough.
How to use LIQUI MOLY:
- Drain some of the old fluid from the system.
- Pour the entire contents of the can directly into the radiator.
- Start the engine and let it idle for 30 minutes or you can also drive it.
- Drain the liquid. What usually comes out is a dirty brown liquid.
- Rinse with distilled or boiled water.
- Fill with new antifreeze or antifreeze.
Problem prevention
After completing the flushing, we recommend carefully monitoring the condition of the engine (in particular, the temperature). If noticeable heating occurs, it is necessary to immediately stop the vehicle, turn off the engine and carry out maintenance on the cooling system. Sudden temperature changes in most cases are due to the fact that the liquid inside the system does not circulate.
In extreme situations, contact a car service center for a comprehensive inspection and diagnosis of cooling system problems. Driving a car with high engine heating rates is extremely dangerous. It can lead to serious problems and the need for major repairs. Good luck on the roads!
How to solve the problem of a clogged stove?
- Radical replacement of the radiator. The method is expensive, but 100% effective if the cause of the cold air is in the radiator. You can replace the non-functioning element yourself or contact a service station.
- Dismantling and cleaning the radiator. An inexpensive cleaning option, which, however, will require specialized skills from you. If you are not confident in your abilities and are afraid of breaking the mechanism, it is better to turn to professionals.
- Flushing the radiator without dismantling. The cheapest and easiest way that even a beginner can handle. For this, you will need a simple and safe citric acid-based car heater cleaner, which will be discussed below.
Why does a car's heater get clogged?
- During the non-working summer period, the inner surface of the radiator tubes oxidizes due to the lack of fluid movement. As a result, scale forms, preventing normal heating of the elements.
- Low-quality, cheap antifreeze produced by unverified companies can cause stove failure. In this case, washing the stove radiator without removing it yourself will also help.
Citric acid into the expansion tank "techika" - radiator for release
Any technical fluid needs to be changed periodically. Antifreeze in the cooling system is no exception. How long it will last is determined mainly by the durability of the additives that inhibit the chemical activity of antifreeze in relation to the materials from which the cooling system components are made. Sergei Volkov dealt with a very unusual case.
The most common antifreezes are silicate and carboxylate. They received their names because of the anti-corrosion additives that are used in this or that coolant. In our conditions, it is recommended to change silicate antifreezes after three years of operation, carboxylate ones after five or six.
The problem is that not all car owners adhere to the recommended cooling system maintenance intervals. The older and more used the car, the more likely it is that the antifreeze has not been changed for a long time.
But now the car has a new owner. He eliminates malfunctions that exist in any used car, changes engine oil and filters, looks at what is in the power steering reservoir, brake master cylinder, and expansion tank of the cooling system.
Every more or less experienced driver knows what antifreeze should look like. If he sees a cloudy reddish-brown liquid in the expansion tank, this cannot but alert him.
Old antifreeze gets its red color due to rusting of the metal parts with which the coolant comes into contact. Turbidity and color mean that the additives in antifreeze, which are supposed to inhibit corrosion, have worn out their usefulness.
In addition to corrosion products, particles resembling grains of sand can be found in coolant that has not been changed for a long time. This is scale, as well as sediment, to the formation of which so-called silicate antifreezes are especially prone. In addition, silicate gel, solder slag, even oil and sealant are often found in old antifreezes. That's what cooling system experts say, anyway.
The appearance of used antifreeze not only indicates the need for replacement, but also raises the question of flushing the cooling system from accumulated dirt. This is what happened to the owner of a Volkswagen Transporter T4, who recently acquired a representative of the model, affectionately called “techik” everywhere in Belarus. It must be said that in addition to the color and turbidity, the putrid smell of the substance that was under the cap of the expansion tank also prompted washing.
The desire to rinse gave rise to the question “with what?” Neighbors in the garage vied with each other to offer folk remedies: lactic acid whey, vinegar, a product for descaling teapots, citric acid...
For some reason, the owner of the car chose the latter. No sooner said than done. The flushing solution was poured into the cooling system. Initially it was assumed that the car would sit with it overnight, but then plans changed. Someone suggested that we need to start the engine and let it idle until it warms up completely, and then for some more time so that the flushing mixture, adjusted by the pump and being hot, cleans all the nooks and crannies of the system properly.
Judging by the smell that accompanied the procedure, as well as the type of flushing that was drained from the system, there was a result. This made me happy, but the owner of the car found out what actually happened only after adding fresh antifreeze and a test drive.
During the trip, the level of antifreeze in the tank dropped. The saving thought that perhaps there were air pockets in the system that were expelled during the trip was not confirmed. The level continued to drop, indicating a leak.
The search for the place where the leak came from led to the radiator of the cooling system. Slowly it was clearly dripping from it.
The core of the radiator consists of many tubes through which antifreeze circulates. To increase the cooling surface, corrugated tapes are connected to the tubes. So the tubes began to flow, as if someone had pierced them in different places with the thinnest needles.
The outer surface of the tubes and tapes suffers from salt and moisture entering the core from the environment. However, from the outside, the tubes and radiator tape of the Techika did not look heavily damaged by corrosion. The only thing that bothered me was the large amount of dirt in the core, but the cause of the leak was clearly not external corrosion.
Apparently, the culprit was not so much external as internal corrosion, which thinned the walls of the core tubes from the inside. Then, during washing, citric acid was “attached” to the tubes, the effectiveness and speed of which it interacted with the tube material, apparently, exceeded any expectations.
And the last straw is the excess pressure that arises and is maintained in the cooling system during operation. With its help, the antifreeze pushed through the radiator tubes in the weakest places.
What good is a radiator that has become like a sieve, if not for emission? For a new radiator they asked from 160 rubles if it was Chinese no name, and up to 250 rubles for a product also from China, but, as the sellers assured, it was of the Behr/Hella brand, confirming the quality of the product. They bought it.
However, the story did not end there. After installing a new radiator, the owner of the Transporter discovered that the windshield fogged up during the trip, and the cabin smelled of antifreeze. This has never happened before, and these are signs that another radiator—the heater—has leaked. Apparently, the acid washing affected him too. So, there is another showdown ahead.
But how to flush the cooling system correctly, without consequences requiring repair? Experts recommend starting with a soft flush, in which a solution of fresh antifreeze with still very active additives in distilled or boiled water in a ratio of one to three to four is used as a flushing liquid. The engine should run with this solution for at least 10-15 minutes. If the liquid drained after washing is not much different in appearance from the old antifreeze, it makes sense to repeat the procedure.
When the age of the car, the color and turbidity of the drained antifreeze hint at severe clogging of the cooling system, which flushing with a mixture of water and antifreeze is unlikely to get rid of, you can try special flushing preparations from the auto chemical arsenal.
But if the system is completely clogged with deposits, nothing will help except replacing those components where the dirt is trapped, such as in the filter. But what about the old-fashioned methods of washing, known and seemingly proven since the time of Tsar Pea? Here everyone decides for himself - to take a risk or abstain...
Auto business
Flush the cooling system with citric acid solution
Many people believe that this cleaning method is too aggressive on radiator tubes and rubber hoses. It is not true. The concentration of citric acid in the solution is small.
Solution proportion: one sachet of citric acid per five liters of water. It is sold packaged in 80-100 grams in grocery stores. It's better to stock up on a dozen of these bags. It is not a fact that the solution will be able to remove all deposits from the system the first time.
It’s easy to flush the engine cooling system yourself with citric acid - the process is no different from flushing with water: add the solution, start the engine, wait for the thermostat to open, let it idle for another 10-15 minutes, turn it off, cool, drain.
After draining, it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the solution. If a layer of sediment has accumulated at the bottom of the container where it is poured, the procedure will have to be repeated. This must be done until the drained solution is as clean as possible.
There is an opinion that it is better to change the proportion in favor of reducing the acid content - add half or ¾ of a bag instead of the whole. This reduces the likelihood that scale in the system will begin to fall off in pieces and clog the radiator tubes. If it is impossible to accurately assess the degree of contamination, it is better to do just that. It is enough to reduce the concentration of citric acid in the water, but increase the number of washes.
At the end of the process, be sure to flush the cooling system with clean water, as described above. If you have a compressor at hand, blow it out. And after that you can fill in new coolant.
According to car owners who have performed this procedure, the system really begins to work better after washing with a solution of citric acid. And if in winter the stove did not warm up the interior, then washing it perfectly corrected this shortcoming.