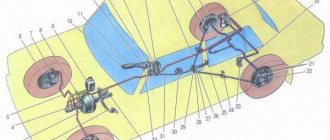
The chassis of a car is an extremely important element that ensures the movement of the vehicle. Of course, the same can be said about the engine, generator or transmission. However, it is the vehicle's chassis that converts the energy from torque directly into movement. Parts of the chassis rotate the wheels, which leads to the movement of the car.
Of course, the node also has other tasks. From this article you can find out what a walker is, what are the features of its functioning and diagrams.
What does the chassis consist of?
To ensure normal movement, the main elements of the chassis are attached to the car body. The result is a multifunctional design of units that connects the wheels to the body. The list of chassis functions includes:
- softening movement;
- damping of body vibrations;
- reception of transverse and longitudinal forces, shocks.
Thanks to the installation of elastic suspension parts, the vehicle is not subject to shaking or excessive vibration.
The suspension is responsible for the level of comfort of movement
The chassis of the car looks like this:
- frame;
- bridge beams;
- front and rear suspension;
- wheels.
Chassis elements
The first dimensional part of the chassis is the steering axle. The element is made in the form of a beam of increased strength. It has rotating axles mounted in it, which are fixed using special hinges. This design is also equipped with special connecting parts.
The steering bridge is based on a rigid stamped beam. With this structure, the bridge in the front of the car is represented by a transverse beam to which the steered wheels are attached.
Torque from the motor is not supplied to this unit. The bridge is not driving and serves as a supporting structure. Controlled systems come in various types and are used in both passenger cars and trucks.
The list of what is included in the chassis of the car is quite large. The key elements are the elastic suspension parts. Details allow you to soften strong shocks and shocks while driving. Also, these units are able to reduce vertical acceleration and dynamic load on the structure.
Thanks to the variety of elastic elements, the car body is practically not exposed to the harmful effects of unevenness on the road surface. Driving becomes smooth and controlled.
The following chassis elements can be used on many types of cars:
- leaf springs;
- springs;
- pneumatic parts;
- hydropneumatic shock absorbers;
- rubber parts;
- guide spare parts;
- guide element lever.
Independent suspension
History of appearance
Attempts to make the movement of a vehicle softer and more comfortable were made in carriages. Initially, the wheel axles were rigidly attached to the body, and every unevenness in the road was transmitted to the passengers sitting inside. Only soft cushions on the seats could increase the level of comfort.
Dependent suspension with transverse spring arrangement
The first way to create an elastic “layer” between the wheels and the carriage body was the use of elliptical springs. Later, this solution was borrowed for the car. However, the spring had already become semi-elliptical and could be installed transversely. A car with such a suspension handled poorly even at low speed. Therefore, springs soon began to be installed longitudinally on each wheel.
The development of the automotive industry has also led to the evolution of the suspension. Currently, there are dozens of their varieties.
Node Role
What is the purpose of a car's chassis? The main role is to ensure the movement of the vehicle. At the same time, it is specially designed in such a way as to provide comfort to the driver and passengers. Without this unit, the car engine and transmission simply have nowhere to transmit torque.
It is worth noting that the safety of surrounding road users depends on all elements. If you ignore any symptom and do not take appropriate measures in a timely manner, the consequences will not be rosy. It is impossible to count how many accidents have already happened due to the fault of this mechanism.
Car transmission
The main function of this part is this: it transmits torque from the engine shaft to the wheels of the car. The transmission consists of the following components:
- Drive axles.
- Gearbox.
- Clutch.
- Cardan transmission.
- Hinges.
The clutch is necessary to connect the shafts of the engine and gearbox. With its help, smooth transmission of torque is ensured. The gearbox is needed to change the gear ratio and reduce the load on the engine. The bridge is either installed in the gearbox housing or serves as a rear beam. Depending on this, the car is front-wheel drive or rear-wheel drive. The cardan transmission connects the box to the axle or wheels.
Node device
Now let's move on to what is included in the chassis of the car. This unit is formed by several mechanisms and elements. In this case, each component has its own role. But all together they pursue a common goal - to minimize (as far as possible) vibrations, shaking, including other negative impacts when the vehicle is moving. But the road is not always perfectly smooth.
The driver himself does not need to know exactly the structure and operating principle of the entire “suspension”, nor does he need to comprehend the basics of repair work. However, if something happens, this knowledge will allow you to fix some breakdowns yourself. There are some moments where the driver is able to cope on his own. But it’s better to entrust complex problems to the experts, since they require relevant skills that not every car enthusiast has.
Now it’s time to find out how the car’s chassis works and what parts are present in this unit.
skeleton
The skeleton is the foundation of the machine, connecting all the mechanisms into a single whole. It can be framed, semi-framed or frameless. In passenger cars, the role of the frame is performed by the body, called the supporting body. A short frame attached to the body floor is used to mount the engine and front suspension.
Bridge
This node, and usually there are several of them, has more than one role:
- Firstly, it is responsible for connecting two wheels.
- Secondly, it performs a supporting function for the base of the machine.
- Thirdly, it supports the weight of the car.
As you can see, bridges perform important tasks and are subject to significant loads. Therefore, only durable material is used for their manufacture. They must also undergo appropriate processing to withstand the effects of aggressive external conditions. This is especially true when it comes to corrosion. This is a fundamental factor in the occurrence of major chassis malfunctions.
Bridges can be attached directly to the frame structure, which is important for freight transport. Another option is to the body, which suits most cars.
Body types
Currently, the most common types of car body devices are:
• three-volume body with two or four side doors sedan; • three-volume body with two or four side doors and with a partition behind the front seat separating the driver from passengers - limousine; • body with a soft folding awning and removable side windows - phaeton; • two-volume body with a rear door with a cargo area not separated by a partition from the passenger compartment - a station wagon; • a two-volume body with two or four side doors, having a rear door - a combi (hatchback); • a utility vehicle body with an open platform, retractable side seats and a closed two-seater cab - pickup.
Frame load-bearing bodies of passenger cars have a special frame to which base parts made of thin-walled profiles are attached, forming a rigid welded spatial form on which the cladding panels are attached. In frameless bodies used on modern mass-produced passenger cars, sufficient rigidity is achieved by appropriately connecting the cladding panels , into which steel reinforcement from thin-walled profiles is molded. Comfortable passenger cars with high-power engines usually have a frame structure. A good view of the road in the immediate vicinity of the car is facilitated by the low-lowered engine hood. To protect passengers and the driver from dust, moisture, low and high temperatures, the body must be sealed. For this purpose, special insulation is used.
Mover
The following types of propulsion are distinguished:
- wheeled
- tracked
- half-track
The wheel propulsion system consists of wheels with pneumatic tires. In a caterpillar propulsion system, the support rollers roll along a smooth artificial path, which is formed by an endless caterpillar chain. The half-track consists of a rubber-metal track installed between a drive wheel with a pneumatic tire and a tension wheel.
The pneumatic wheel consists of:
- disk
- rims
- elastic tire
Tires are classified according to their design:
- chamber
- tubeless
The main parts of a tube tire are the tire, the tube with valve and the rim tape. A rim rubber band is placed between the tube and the rim to prevent friction between the two. Rim tapes are used only in truck wheels.
Tubeless tires are widely used on cars, trucks and tractors. In such tires, the space filled with air is formed as a result of a sealed connection between the wheel rim and the tire, and the valve is placed on the rim. The tight fit of a tubeless tire on the rim is achieved using a special bead design that is tightly pressed against the edges of the rim by internal air pressure.
Tubeless tires can be standard, wide-profile or arched. Arched tires help improve the vehicle's maneuverability in difficult road conditions. These are low pressure tires (0.05...0.08 MPa).
The internal air pressure in car tires ranges from 0.17...0.5 MPa, tractors - 0.08...0.25 MPa.
Suspension
The frame is connected to the wheels by a suspension. It is designed to soften the shocks and impacts that occur during movement, increasing the smoothness of the machine.
There are two main types of suspensions: dependent and independent. In a dependent suspension, both wheels are suspended from frame 4 (Figure a) on a common axle 1, as a result of which each of them moves together with the axle. In an independent suspension, each wheel is suspended from frame 2 (Figure b) independently of the other using levers 1, 4 and strut 5. Springs, springs, torsion bars, rubber cylinders, etc. are used as elastic elements in various suspensions. In cars, the front wheels are equipped with suspension and rear axles, for tractors - only front axles, since their rear axle forms part of the frame.
Truck suspensions are dependent. They are most often performed on leaf springs. Such a spring is a beam resting on the frame at two points - supports, one of which is made in the form of a hinge, and the other allows some movement. The middle part of the spring is connected by 12 stepladders to the front or rear axle.
Drawing. Tractor and car suspension diagrams: a - dependent: 1 - front axle; 2 — wheel axle; 3 - spring; 4 - frame; b - independent: 1 - upper lever; 2 — car frame; 3 - spring; 4 - lower lever; 5 - stand; c — with individual wheel suspension: 1 — front axle; 2 — bracket; 3 - guide; 4 — spring spring; 5 — wheel axle.
When a car moves over uneven roads, vibrations occur, which are partially damped by friction in the springs. However, this friction is relatively small, and to effectively dampen vibrations, special devices are used - shock absorbers 7. The most common are double-acting hydraulic shock absorbers. Their work is based on the fact that during relative movements of the sprung and unsprung masses of a car (tractor), the liquid in the shock absorber flows from one cavity to another through small flow sections, as a result of which resistance is created that absorbs vibration energy.
Drawing. Front suspension of the ZIL-130 car: 1 - front bracket; 2 — step-ladder eye; 3 - spring; 4 - frame; 5 — spring buffer; 6 — overlay; 7 — shock absorber; 8 — buffer on the frame; 9 — clip; 10 - clamp; 11 — rear bracket; 12 - stepladders.
Additional items
In addition to all of the above, the “suspension” includes other necessary components, without which it would also not function. We are talking about the following parts, assemblies and mechanisms:
- shock absorbers;
- levers;
- ball joints;
- brake units;
- springs;
- silent blocks;
- anthers.
All these elements also perform their specific duties. Most of the possible malfunctions of the car's chassis are caused by them. At the same time, some of these parts are deservedly awarded the title of consumables, since after a certain time they must be replaced so that the unit works properly and for as long as possible.
Main functions
The chassis of the car performs several main functions:
Connects wheels or axles to the body.
Provides transmission forces that arise when the wheels interact with the road surface.
Provides the necessary movement of the wheels in relation to the body (load-bearing part) of the machine.
Reduces vibrations and vibrations when moving.
Provides comfort and safety.
That's all that Auto-Gurman.ru wanted to tell you about the chassis of the car
.
Do not forget to regularly diagnose the suspension and other components. A fault found in time can protect you not only from large financial costs, but in some cases, save your life. After all, the chassis of a car is the main element responsible for traffic safety. A car's chassis and suspension are synonymous words.
The purpose of the car chassis is to move the car comfortably along the road. The chassis of a car is a set of mechanisms that interact between the wheels of the car and the load-bearing part. We will talk about the importance of this part of the car in the article “What is the chassis of a car definition.” The suspension serves to dampen and soften vibrations when driving on uneven roads. The body produces longitudinal, vertical, angular and transverse angular vibrations. All these vibrations determine the smoothness of the car. The wheels of the car should not be rigidly connected to the body. The suspension must ensure maximum driving safety. And this requires the suspension to be strong and durable. The hinges used must turn easily.
Suspensions can be dependent or independent. With a dependent suspension, both wheels of the same axle are connected to each other by a rigid beam. This applies to the rear wheels. When one of the wheels hits an obstacle, the second one will tilt at the same angle. With an independent suspension, the wheels of one axle are not rigidly connected to each other. This applies to the front wheels. When such a wheel hits an uneven surface, one of the wheels may change its position, while the position of the second wheel does not change. Depending on the type of elastic suspension elements, there are spring, spring, torsion, pneumatic, etc.
Literally every suspension has its pros and cons. Dependent suspension is simpler and cheaper. It has a constant track. But you can’t call it easy. Independent suspensions have great advantages. Independent suspensions are distinguished by the location of the wheel swing plane and the number of levers. Separately, there is a semi-independent suspension. This is a twist beam suspension. Most often it can be found as the rear suspension of inexpensive front-wheel drive cars.
Types of pendants
According to its purpose, the suspension is the part that is responsible for the vertical movement of the wheel relative to the body. It is this design that directly interacts with the body and the road surface.
Currently, there are two main types of suspensions used in the automotive industry:
- dependent;
- independent.
Also, some cars have semi-independent suspension. However, this pattern is most often classified as a dependent circuit.
Previously, dependent structures were widely used in various vehicles. Now this model is gradually fading into the background. Most often, the beam system is installed on trucks, which are constantly exposed to heavy loads. The beams have also found application on frame-type SUVs. In the photo, the pendant is distinguished by its simple structure. However, the main advantage is reliability. It is cheap and easy to maintain.
The main part of the dependent system is the spring. The unit is presented in the form of a package of sheets, which are made in a curved shape. Most manufacturers use spring steel when creating springs, which does an excellent job of balancing the body.
Independent suspension. Device, features
Independent suspension
The second type of suspension is independent, characterized by the fact that each wheel of the axle has its own fastening and vibration damping system, which does not transfer the movement of one wheel to the other. In fact, in an independent suspension there is no wheel axle (beam, bridge) as such.
The most widely used independent suspension is the MacPherson type. The design of such a suspension is quite simple - the wheel hub is hinged to the car body using levers. The types of these levers and their location may vary. There are A-arms, single, double, lower and upper. The simplest independent suspension consists of one lower control arm.
MacPherson strut suspension
Additionally, the hub is attached to the body with a shock absorber strut, which also acts as a steering knuckle. The main elements of this strut are a coil spring and a shock absorber. The strut itself is a housing in which the shock absorber is placed, and a spring is located on top of the strut.
At the top the rack rests against the body. Between them there is a rack cushion, on which it rests. A thrust bearing installed inside allows the rack to rotate around its axis. This makes it possible to turn the wheel.
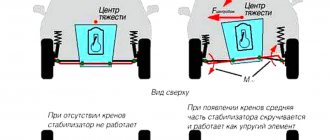
No matter how well the shock absorber strut works, there is the possibility of transmitting vibrations to the body. This can cause lateral sway of the body. To prevent this from happening, the design includes an anti-roll bar that connects both wheel suspensions. By working in torsion, this stabilizer dampens lateral vibrations.
These are the main elements of an independent suspension. But there are also a large number of auxiliary elements that you cannot do without. Such an element, for example, is the counter cushion. These also include all rubber elements:
- silent blocks;
- ball joints;
- bushings.
All of them are also involved in damping vibrations. Silent blocks, ball joints and bushings are placed wherever the connection of suspension elements is made - levers with the body and hub, anti-roll bar with hubs and subframe, etc.
MacPherson type
90% of automobile companies use the most reliable type of suspension - MacPherson strut. This is an independent example of a system that has proven itself best on various types of transport. The chassis elements form one integral circuit, which is highly reliable. This node looks like this:
- put a wheel rim on the hub;
- the hub is hingedly fixed to the body;
- The role of holders is performed by rigid levers.
There is a wide variety of levers that can be arranged according to different patterns. The most common are single, double, and A-arms. The parts can be top and bottom. A simple independent suspension includes one lever located at the bottom.
What else applies to the system:
- hubs;
- ball joints;
- brake discs;
- swing arms;
- support cups located below;
- springs;
- compression buffer;
- upper rack supports;
- nuts;
- rods;
- steering knuckles;
- drive shafts;
- protective covers.
The element that dampens hub vibrations is the strut. The part consists of a shock absorber and an outer spring. High-quality fastening of the rack to the body is ensured by a cushion. Inside, the unit is equipped with a thrust bearing, thanks to which the rack can rotate around its axis.
Over time, the strut begins to transmit more and more vibrations to the body. If the strut fails, you can check it yourself by rocking the body. If there is strong rolling, the faulty unit does not stabilize the body.
How does the anti-roll bar work?
When the car turns, one rack rises and the second lowers, that is, they move in opposite directions, the middle part of the stabilizer, which is called the rod, begins to twist.
As a result, on the side where the car “listened” to its side, the stabilizer raises the body, and on the opposite side, it lowers the body. The greater the tilt, the greater the resistance of the stabilizer. Then the car is leveled, the roll during turning is reduced and the quality of wheel grip on the road improves.
If you want to understand the operation of the anti-roll bar in more detail, this information will be useful to you.
To create vehicle roll resistance, a torsion bar is used, which is mounted in the wheel hub assembly.
The torsion bar works to twist, creating resistance to the vehicle's roll. The torsion bar is attached to the hub assembly of the left wheel, then passes in the direction of travel to the hinge attachment to the body, then in the lateral direction to the opposite side of the car, where it is mounted in a mirror image similar to the first side. The torsion bar sections running in the direction of movement act as levers when the suspension operates in the vertical direction. In the absence of roll, both segments rotate at the same angle, the torsion bar does not twist and rotates in the attachment points to the body as a whole. When the car rolls, the left and right sections of the torsion bar rotate at different angles, twisting the torsion bar and creating an elastic moment that resists the roll. On dependent rear suspensions this is often absent, instead the trailing arms are attached to the beam by a rigid connection capable of transmitting torque. Thus, the entire beam assembly with trailing arms acts as a torsion bar.
On McPherson-type front suspensions, “lever” sections of the torsion bar are often used as one of the 2 lower suspension arms, also transmitting longitudinal (in the direction of travel) forces from the hub to the body.
Stabilizers can be installed either on both axles, or only on one (usually the front).
Dependent suspension. Types, design features
In total, two types of suspension are used on vehicles - dependent and independent. At the moment, this type of suspension, such as dependent, is considered somewhat outdated, but it is still used quite widely on trucks, full-size frame SUVs and ordinary passenger cars. Dependent suspension has received such application in transport due to the simplicity and reliability of the design.
Spring suspension
The main element of this suspension is the spring. It consists of a package of spring steel sheets, slightly bent into an arc. Moreover, this package often has a pyramidal shape. The ends of the spring are attached to the car frame, and the axle is attached to its central part. Each car uses two springs, installed closer to the wheels. These springs, thanks to the springy steel, absorb road unevenness, allowing the wheel to move relative to the body.
Rear dependent suspension of a front-wheel drive car
However, this also has a negative quality - the work of the spring is accompanied by inertial oscillatory movements. That is, when the spring perceives unevenness in the road, it receives energy, which leads to its oscillatory movements. And although over time the amplitude of the vibrations will decrease until it fades, they will be transmitted to the frame. The car will sway even on a smooth road after passing a bump.
To significantly reduce the oscillation time of the spring, shock absorbers are included in the suspension design, which absorb oscillatory energy. To put it simply, the shock absorber stops the spring after an unevenness, preventing it from rocking the car.
Spring suspension
There is another type of dependent suspension - spring. This suspension uses coil springs instead of springs. They are more convenient to use because they have significantly smaller dimensions.
Operating principle of the chassis
And so, it’s time to talk about how the car’s chassis works.
To prevent a car from overturning when a wheel hits a hole, there is a suspension. The wheel will go down, stretching the shock absorber attached to the suspension, and when it comes out of the hole, the shock absorber will return to its original place and will remain there in the process of small vibrations.
The wheels on one side are tightly attached to the suspension, but on the other side they are not, and in case of slight vibrations in the road the car goes smoothly. The interaction of the suspension with other parts contributes to this.
Since the chassis is the shell that keeps the car moving, it is important for every driver to listen to the sounds of his car, namely, creaks and knocks. This way, you can detect a malfunction in time and have it repaired at a service station.
Principle of operation
The main role in creating a comfortable ride is played by the suspension. This device dampens vibrations arising from uneven surfaces.
When a wheel falls into a hole, the car should not roll over; this is the main task for the suspension. The wheel moves down, thereby stretching the shock absorber, which is attached to the suspension. After leaving the hole, the shock absorber returns to its original place and remains there in the process of slight oscillations.
Elements of the chassis that ensure high-quality contact with the coating
There is an opinion that the quality of contact with the road surface depends only on tires, elastic and damping units (shock absorber, springs).
In practice, additional elements of the chassis that interact with each other and the kinematics of the guide devices are no less important.
Thus, to ensure a sufficient level of safety and comfort, the following elements must be located between the body and the covering:
- Tires are devices that are the first to take on the negative effects of holes or “growths” on the surface of the road surface. Thanks to a certain elasticity, tires reduce vibrations and play the role of indicators of the suspension condition. If the pattern wears off unevenly, this indicates a malfunction of the chassis elements (for example, a decrease in the resistance of the car’s suspension).
- Elastic parts (springs, springs) are devices whose task is to hold the vehicle body at a certain level and maintain a high-quality connection between the vehicle and the surface. Long-term use of these products leads to gradual aging of the metal, its “fatigue” due to regular overloads. As a result, the characteristics of the car, which affect the level of comfort, deteriorate. The ground clearance, load symmetry parameter, wheel angles and other parameters are subject to change. It is important to understand that springs, not shock absorbers, support the weight of the car. If the ground clearance decreases and the vehicle “sags” without load, it’s time to install new springs.
- Guide parts. These elements of the chassis include torsion bars, springs and a lever system, which ensure the kinematics of interaction between the body part and the wheels. The main function of the units is to maintain the wheel moving up or down in the same plane of rotation. In other words, the latter should be in approximately the same position, 90 degrees to the road. If the geometry of the guide units is violated, the car becomes unpredictable on the road, the tire tread quickly wears out, and the service life of shock absorbers and other suspension elements decreases.
- Auxiliary elastic components of a car. These include rubber-metal hinges, which are often called compression buffers. Their task is to suppress vibrations and high-frequency vibrations arising from the interaction of metal elements of the chassis. The presence of these components helps to increase the service life of car suspension parts, namely shock absorbers. This is why it is so important to check the condition of the rubber-to-metal parts that provide the suspension connection. The better the auxiliary elastic elements perform the job, the longer the shock absorbers last.
- Anti-roll bar (SST) is an element of the vehicle's chassis, necessary to improve handling and reduce the level of vehicle roll when entering a turn. During a sharp maneuver, one side of the vehicle is pressed against the road surface, and the other, on the contrary, “comes off” from the surface. The task of the SPU is to prevent this separation and ensure that the “breakaway” side of the car is sufficiently pressed against the road. In addition, if the vehicle hits an obstacle, the control gear is tightened and guarantees a quick return of the wheel to its original position.
- A damping element (shock absorber) is a device of the chassis that provides damping of body vibrations arising from hitting uneven road surfaces, as well as due to the appearance of inertial forces. The shock absorber also limits the vibrations of uncontrolled elements (beams, axles, tires, hubs and others) in relation to the body. As a result, the quality of contact between the wheel and the road surface improves.
We looked at the main elements of the car's chassis, which are structurally different from each other on different car models, but ultimately serve the main purpose - to ensure comfortable and safe movement of the vehicle.
Car chassis diagram
To give our article greater practical value, we will consider the design of the chassis using the example of one of the most popular cars among domestic motorists - the VAZ 2109.
Front axle
The front axle of the “nine” has a telescopic suspension equipped with coil springs and hydraulic shock absorbers. The transverse arm is of lower design, equipped with braces and anti-roll bars.
Due to the use of a front-wheel drive design on this car model, the technical complexity of the front axle, as one of the main elements of the chassis, is quite high, despite the relatively small number of components that make up the design. It consists of:
- Struts with shock absorbers.
- Cross arm.
- Steering knuckle.
- Stretch systems.
- Mounting units to the body (transmission).
Rear axle
The design of the rear axle is much simpler, since it does not contain elements associated with the transmission (with the exception of rear-wheel drive vehicles). In addition, the rear axle bears a smaller load than the front part of the chassis. The relatively mild operating mode allowed the developers to significantly simplify both the circuit diagram of this unit and its design.
The rear axle of the VAZ 2109 consists of the following elements:
- Central beam.
- Hydraulic shock absorbers and a pair of springs.
- Trailing arms.
- Brackets that secure the axle to the vehicle side member.
- Flanges for fastening wheels.
As the name suggests, the center beam serves as the main element of the rear axle. It is a combination of three separate parts (a connector and two longitudinal arms), connected by welding seams using reinforcing pads. Shock absorbers and wheel axle flanges are mounted to brackets welded to the arms.
Car body
The supporting system of the car. It is the skeleton of the car, to which all the parts are subsequently attached. Usually the body is attached to the frame, but there are also cars with a frameless design, and then the body simultaneously performs the functions of the frame. The car body structure is:
- single-volume, when the engine, passenger and cargo compartments are located in one volume (an example would be minivans or vans);
- two-volume, in which the engine compartment is provided, and places for passengers and cargo are combined in one volume (station wagons, hatchbacks, crossovers and SUVs);
- three-volume, where there are separate compartments for each part of the car body - cargo, passenger and engine (pick-ups, sedans and coupes).
Depending on the nature of the load, the body can have three types:
- carrier;
- semi-supporting;
- unloaded.
Most modern passenger cars have a supporting structure that absorbs all the loads acting on the car. The general structure of a passenger car body includes the following basic elements:
spars, which are load-bearing beams in the form of a rectangular profile pipe, they are front, rear and roof spars;
Body load-bearing system. This system allows you to reduce the weight of the vehicle, lower the center of gravity, and therefore increase driving stability.
- pillars - structural elements that support the roof (front, rear and middle);
- beams and cross members, which are located at the roof, side members, under the engine mounts, and each row of seats, there is also a front cross member and a radiator cross member;
- thresholds and floors;
- wheel arches.
Car spar
Basic faults and diagnostics of the suspension
Since the suspension, no matter what it is - dependent or independent, moves the wheels relative to the body and dampens all vibrations, it experiences significant loads, leading to failure of one or another element.
In dependent suspension, the most common malfunctions are loss of shock absorber performance due to oil leakage and physical damage. It is also often necessary to change all the rubber elements that are also present in this type of suspension. Over time, the rubber component “aging” occurs - it shrinks and begins to delaminate. It is quite possible that the springs or springs may be destroyed; due to significant loads, they may burst.
In the independent suspension the faults are the same:
- wear of rubber elements and ball joints;
- shock absorber release;
- destruction of the spring or anti-roll bar.
Therefore, you need to constantly monitor the suspension, promptly replace consumables, and monitor the condition of shock absorbers, springs and springs.
- Why are silent blocks needed in a car?
- Operating principle and design of torsion bar suspension
- Car shock absorber - what is it for and how does it work?
Repair of chassis
The chassis often malfunctions, so repairs are important and must be carried out in a timely manner, otherwise there is a risk of getting into a critical situation on the road. Based on the diagnostics conclusion, it becomes clear which parts of the chassis need to be repaired or replaced. The most common segments of chassis repair work are:
- Front suspension;
- Rear suspension;
- The need to replace the strut, spring or shock absorber
The following chassis components may need to be replaced:
- Silent block;
- Spherical bearing;
- Steering end;
- Steering rack;
- Steering gear;
- Wheel bearing;
- Grenade.
It is very important to purchase original spare parts for your car, otherwise repairs can become a nightmare for the car owner, and a waste of money - useless. By purchasing a low-quality or unsuitable part for a device, you can get a pig in a poke. The part may not fit, may not work as expected, or may fail very early without serving its useful life.
You should not skimp on diagnostics and repairs - a serviceable car is the key to your safety on the road.
Importance of the diagnostic procedure
In order for the “suspension” to work properly for a long time, it is necessary to check it regularly. But when should this be done? This question interests every car enthusiast, especially beginners. Of course, it is not necessary to perform this procedure every day; twice a year is enough. That is, when the time comes for the car to change its shoes - change the type of tires from winter to summer and vice versa.
However, if the mileage is already approaching or has reached the 10,000 km mark, then it’s time to visit a car service center. At the same time, it is not at all necessary to wait for the counter to rewind the desired range, because everything depends on the condition of the road surface, and it is not always ideal.
Often the reason for a visit to a service station to inspect the “suspension” is when you hit a hidden hole under a puddle. That is, the result of such an impact can be the appearance of a knock, play in the steering wheel, or a hum. In addition, the car may begin to pull to the side. With such symptoms, it is hardly possible to avoid repairing the car's chassis, and its price will depend on many factors.
What is a suspension check?
This mandatory procedure can be of different types, depending on each specific situation:
- emergency or emergency;
- planned;
- pre-sale
Emergency diagnostics of the vehicle's chassis are carried out in cases where there are extraneous sounds when turning the steering wheel, and clunking is heard from the suspension. This is also caused by strong body roll when cornering. And when the car picks up speed, and the steering wheel pulls to the side, this should also be alarming. These and other undesirable symptoms clearly indicate wear of some component of the “suspension”. Then they need to be replaced or repaired. The urgency will depend on the intensity of the signs of a particular “disease”.
The planned procedure is performed within a planned period of time and does not depend on the technical condition of the elements. This could be a planned off-season check before the onset of summer or winter. This is very important, since during this time there will still be some kind of breakdown that needs to be fixed as soon as possible. Of course, the best option to check the chassis of a car is to visit a service station.
As for the pre-sale inspection, it applies to used vehicles that pass from one owner to another. In this case, the initiator can be both the seller and the buyer. Although, honestly, the latter is more interested in this than the latter.
Vibration stand
What is a vibration stand and what does it have to do with service stations? Only a beginner can ask such a question today, while people with experience understand perfectly well what we are talking about. Some car repair shops have the ability to diagnose the vehicle's chassis using this equipment. It is made in the form of a rocking platform equipped with various sensors and connected to a computer.
After the car is on the vibration stand, it begins to sway, simulating movement on the road. In this case, the vibration range of the platform reaches 25 Hz, and the frequency increases gradually.
Such computer diagnostics have special software that controls the operation of the vibration stand. As for the cost, the price for such a service ranges from 700-1000 rubles, even in cities such as Moscow, St. Petersburg and other similar megacities. This cost may seem high to some, but checking car parts on a vibration stand is worth the money!
List of works when checking the unit
What is included in the diagnosis? Regardless of the type of such procedure, the same steps are performed. Many of these manipulations can be performed by the owners themselves, without the involvement of an experienced worker. However, a professional will do a better job, since it is important to inspect many details and identify flaws and flaws.
But what exactly does a service station employee examine during a detailed inspection of any vehicle? These elements need to be carefully reviewed:
- tires with rims;
- hub bearing;
- ball joints;
- brake system;
- stabilizers, torsion bars, springs, etc.;
- CV joint;
- levers with silent blocks;
- shock absorbers with springs.
Despite the fact that the owner of an iron horse is able to perform some diagnostic manipulations independently, the master issues a conclusion regarding the further operation of the unit, mechanism or part, based on the technical condition. And only he determines what is included in the repair of the chassis.
Car chassis repair
The importance of the functions performed by the elements of the chassis of any car requires its timely maintenance and repair. But the need to perform repair and restoration work, as well as their volume, and level of complexity are determined in the process of diagnosing its condition.
So, let's look at the main signs of a malfunction of the chassis and the symptoms of the most common damage to its elements:
- Leakage of special technical fluids in the area where the chassis system elements are located. The main causes of this defect are increased wear of the oil seal or mirror of the hydraulic shock absorber rod.
- The occurrence of extraneous knocks while driving, impaired vehicle control, or “yaw.” As a rule, this symptom is a clear indication of wear and, therefore, weakening of the fastening points.
- Impaired suspension performance, expressed in insufficient resistance of the shock absorber cylinders to the force applied to them. The reasons for this phenomenon are quite varied: unacceptable level of wear of shock absorber elements (oil seals, rod, fluoroplastic bushing), malfunction of the valve mechanism, small amount of technical fluid.
- The occurrence of hard “breakdown” impacts felt on the steering wheel when operating the vehicle on an uneven road surface. The symptom is characteristic of springs that have lost the necessary elasticity due to “fatigue” of the metal. In addition, a similar picture appears when the shock absorbers are not operating correctly.
Summarizing the above, we will specify several basic rules that help to avoid serious material costs for repairing the chassis of a car:
- Adopt a non-aggressive driving style.
- Operate the vehicle carefully, especially in off-road conditions.
- Timely and fully carry out vehicle maintenance work recommended by the manufacturer and the necessary diagnostic and repair measures.
How to find out that a unit needs service or repair
Of course, every driver must regularly service the vehicle. However, unforeseen situations occur when this cannot be done. If you notice the following characteristic changes during vehicle operation. Then you should definitely contact a professional technician at the service station:
- While driving, the car begins to skid to one side or the other. This may be due to a violation of the wheel structure. With a sharp change in pressure readings, severe wear or a violation of the location of the front axle.
- The car's suspension begins to knock while driving. The cause may be faulty shock absorbers.
- Vibration has noticeably increased when driving on poor-quality road surfaces. In this case, the cause may be a damaged shock absorber or spring, usually due to wear.
- When braking, a creaking noise is heard. The cause may be a breakdown of the shock absorber, spring, stabilizer or shock absorber mounting.
This simple information will help you get an idea of what the chassis of a vehicle is. How it works and how to determine if it is faulty.
Locomotive chassis
The chassis of different types of locomotives is designed differently, depending on the type of power plant. Currently, all locomotives rest on two bogies, which provide the locomotive with maximum smoothness and fit into curves. Carts can be four-wheeled or six-wheeled. Six-wheeled bogies are made for powerful locomotives with high traction force. If it is necessary to further increase the power, the locomotive is made two-section, that is, it is made in the form of two locomotives connected to each other.