The braking system of any car is responsible for safety on the road. That is why it is important to keep it in proper condition so that its malfunction does not cost the life of the driver or passengers. In this article we will tell you how to diagnose faulty brake system seals, as well as how to replace the brake cylinder seal.
The device of the VAZ brake system
The brake system of Togliatti-made cars is quite simple; the vehicle consists of the following main parts:
- pedals, which are pressed to achieve braking;
- brake master cylinder (MBC), it transmits the force of pressing the pedal through hydraulics to the working cylinders, respectively, to the wheels. GTZ VAZ - dual-circuit, the circuits are divided to transmit fluid pressure to the front and rear wheels;
- a vacuum booster that makes it easier to press the pedal;
- tubes that connect the elements of the vehicle;
- brake working cylinders (RTC);
- pads (drums) and discs;
- brake distributor (pressure regulator).
When you press the brake pedal, the piston in the brake fluid compressor compresses the brake fluid and transmits its pressure to the brake pedal. The pistons of the working cylinders are expanded under the influence of hydraulics, moving the pads towards the discs or drums. The movement of the wheels slows down, and thus the car slows down.
How does the GTZ function?
The unit consists of the following parts:
- metal housing with holes for supplying brake fluid, pedal rod and connecting the expansion tank;
- 2 pistons with rubber seals;
- 2 return springs;
- guide bushings;
- end plug with gasket.
An expansion tank is attached to the top of the main distributor body, where excess fluid goes through compensation holes. Inside, the element is divided into 2 cylinders with separate pistons standing on the same axis.
The blind end of the housing is closed with a threaded plug; on the other side there is a flange for attaching to the vacuum booster. The brake pedal rod is attached to the first piston. The brake circuit pipes are connected to the lower holes - separately for the front and rear wheels.
Malfunctions occurring in the brakes
From time to time, various malfunctions occur in the vehicle, and the working and master cylinders also often fail. The following breakdowns occur at the RTC:
- the piston gets stuck in one of the positions;
- the inner surface wears out;
- The sealing cuffs fail (tear or swell).
The main sign of a faulty condition is the appearance of smudges (leaks) of brake fluid (FL) from the RTC. If the pads are worn down to bare metal, the pistons in the RTC extend too far, and as a result, the brake fluid may leak and the brakes will fail.
In the GTZ, the piston can also jam, the internal cavity of the mechanism can wear out or rust, and the cuffs can leak. Symptoms of a GTZ malfunction are as follows:
- when braking, the brake pedal (BP) “fails”, the effectiveness of pressing disappears, this usually happens when there is a small leak from the turbocharger;
- braking occurs at the very end of the pedal stroke, and you have to press the PT several times to brake;
- there are no brakes on the front or rear wheels, this happens if one of the GTZ circuits does not work.
You cannot drive with faulty working and master brake cylinders; the parts should be replaced immediately.
Disassembly
To replace and repair a damaged master brake cylinder, you need to remove it from the VAZ 2110; to do this, you should carry out several steps:
- Carefully disconnect all pipelines from a part such as the main cylinder;
- Disconnect the block equipped with wires from the emergency brake fluid indicator. They are connected by terminals;
- It is necessary to prevent fluid leakage and contamination of the mechanism; to do this, it is necessary to cover the openings of the unit and pipelines;
- Next, you need to remove it along with the tank; to do this, unscrew the fastening nuts that secure it to the vacuum type amplifier;
- After the VAZ 2110 fluid level sensor is removed, you need to drain all the brake fluid from the cylinder and basque;
We can only add to this that if there is no great need, you should not remove the reservoir from the master cylinder. To completely disassemble it, you need to remove the tank. Assemble and then install in place in exactly the reverse order.
Before you begin assembling the unit, all components must be washed with purified brake fluid or isopropyl alcohol. After this, everything must be carefully dried using a compressor, and then each of them must be wiped with a dry, clean cloth.
The main thing is not to get mineral oils directly or indirectly on the components; it is also dangerous for the front components of the main type brake cylinder, kerosene and diesel fuel to get on them.
If you find that the brake pedal has increased travel, it is recommended to bleed the brakes. The intricacies of the procedure can be found in this article: https://vazweb.ru/desyatka/tormoza/kak-prokachat-tormoza.html
Replacing the master brake cylinder
Replacing the GTZ on VAZ classic cars (2101-07) is not difficult; you can do this work yourself. To perform such an operation you will need the following tool:
- 10mm wrench (or special bleeder wrench);
- Phillips screwdriver;
- combination wrench for 13 (you can additionally use a head with a knob and a ratchet for convenience).
It is not necessary to use a pit or a lift to perform the work; replacement can be done outside in dry weather or in the garage. The work should be performed in the following sequence:
- unscrew the three brake pipes from the bottom of the device (key for ten);
- loosen the clamps of the two hoses (at the bottom of the GTZ), pull off the hoses;
- unscrew the two nuts securing the GTZ to the vacuum booster (you need a 13mm wrench or a socket with a wrench);
- We dismantle the part, install the new gas turbine unit in place, and reassemble it.
After the operation, you should add fluid to the vehicle reservoir, then be sure to bleed the brakes well.
Required Tools
If you plan to do the repair yourself, then you need to check the availability of the following tools and materials:
- Screwdriver Set.
- Brake fluid.
- Special wrench for disassembling brakes “10”.
- Socket wrench “17”.
- Plug fittings.
- Pliers.
- Rubber caps.
- A set of keys.
- Socket wrench "13".
Advice! If in the VAZ 2110 mechanism, in addition to the sealing rings, other parts are damaged, then only replacing the GTZ will help. If the remaining elements are fully operational, you need to buy new rings and install them in place of the damaged parts.
Replacing brake cylinder 2114
The work of replacing the GTZ on VAZ 2108-15 models is carried out approximately the same way, there are only some design differences.
We make the replacement as follows (using the example of the VAZ-2114):
- Unscrew the four tubes on the sides (two on the left and two on the right). It is better to use a special pipe wrench; you can roll up the edges of the nuts with an open-end wrench;
- unscrew two thirteen nuts securing the GTZ to the “vacuum”;
- We remove the old spare part and install a new one, not forgetting to bleed the brakes at the end of the work. At this point, the replacement of cylinder 2114 can be considered complete.
Replacing the brake cylinder repair kit
If in the GTZ 2114 the inner surface of the cylinder itself is not yet worn out, you can replace the insides of the mechanism by installing a new repair kit. The repair kit consists of four cuffs:
- three cuffs are the same, they are the same as on models 2101-07;
- one o-ring 2108.
Changing the repair kit is very simple:
- pour the liquid out of the GTZ;
- dismantle the plastic tank;
- unscrew the front stopper (made in the form of a plug);
- we take out all the contents (pistons, o-rings, springs), change the cuffs, and install the entire mechanism in the reverse order. Nothing should be mixed up here, otherwise the unit being repaired will not work.
Repairing the GTZ on VAZ models is not always advisable - if the mirror surface inside the mechanism is worn out, replacing the brake cylinder repair kit will not solve the problem, the GTZ will also leak. Most often, on VAZ cars, the entire master brake cylinder is replaced - a new assembled part costs around one thousand rubles, and the repair turns out to be unjustified.
Disassembly and assembly of wheel cylinders
Disassembly and assembly of VAZ 2107 wheel cylinders
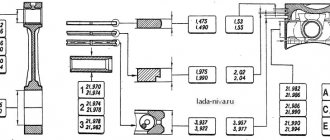
Rice. 7–16. Wheel cylinder: 1 — pad stop; 2 — protective cap; 3 - cylinder body; 4 - piston; 5 - seal; 6 — support cup; 7 - spring; 8 - crackers; 9 — thrust ring; 10 - thrust screw; 11 - fitting; A - slot on the thrust ring
Remove protective caps 2 (
Rice. 7–17. Wheel cylinder parts: 1 - piston assembly; 2 — cylinder body; 3 - thrust screw; 4 - thrust ring; 5 - crackers; 6 - spring; 7 — support cup; 8 - seal; 9 - piston; 10 - protective cap
Install the piston assembly with the automatic device on a special device so that the protrusions of the device cover the head of the thrust screw 3 (Fig. 7–17). Using a special screwdriver, turning piston 9, unscrew the stop screw 3 from the piston. Remove seal 8 with support cup 7 and crackers 5 from the screw. Separate thrust ring 4 and thrust screw 3.
Assemble the automatic device for adjusting the gap between the shoes and the drum and the wheel cylinder itself in the reverse order, taking into account the following:
— tighten the piston thrust screws with a torque of 3.9–6.9 N·m (0.4–0.7 kgf·m); Slot A (see Fig. 7–16) on the rings should be directed vertically upward; deviation from the vertical is allowed no more than 30°. This arrangement of the slot ensures more complete removal of air from the wheel brake drive when bleeding the brake;
— to pre-compress the thrust rings, press the pistons into the cylinder body using a special device shaped like a cylinder with a conical internal hole;
— the force of pressing the piston into the cylinder must be at least 343 N (35 kgf); if the force is less than 343 N (35 kgf), replace the thrust ring;
— when pressing the piston into the cylinder, it is necessary to maintain dimensions of 4.5–4.8 mm and 67 mm (maximum) (see Fig. 7–16) for a free fit of the brake drum;
— before installing parts into the cylinder body, lubricate them generously with brake fluid.
After assembly, check the movement of each piston in the cylinder body. They should move easily within 1.25–1.65 mm. Replace the protective caps 2 last.
Replacing brake cylinder 2107
If the replacement operation on a VAZ classic is not performed on a car lift, it is more convenient to do the work sequentially - first on one side, then on the other side of the rear wheel. To perform the work, the vehicle must be placed on a level surface, then proceed as follows:
- We turn off the engine, set the car to speed, and put chocks under the front wheels. Don’t forget to fully release the handbrake;
- loosen the wheel nuts of the rear wheel, jack up the car and remove the wheel;
- To prevent the car from going anywhere, it is advisable to place a “tragus” next to the jack;
- remove the brake drum - use a 12 mm combination wrench to unscrew the two guides;
- the drum usually comes off tightly, so it should be tapped from behind with a hammer through a piece of wood. You cannot hit the part with an iron hammer; the drum can split;
- unscrew the brake pipe from behind the cylinder, also 2 ten bolts securing the RTC itself;
- pull out the cylinder, freeing it from the pads;
- We install the part prepared for replacement (it is important to get the pads into the slots on the RTC pistons, we fasten all the removed parts in their places;
After the work has been done, it is necessary to top up the fuel injection system reservoir and bleed the brakes.
Replacing the brake cylinder VAZ 2109
The RTC on the rear axle of the 2109 wheels is changed according to the same principle as on the VAZ classic; the wheel and drum are also removed, the tube and two cylinder fastenings are unscrewed with a ten key. It often happens that the tube and RTC bolts on the support disk boil; to remove them carefully, you need to spray the connections with WD-40, and wait 15-20 minutes before unscrewing. The brake pipe nut will be easier to unscrew if you gently tap the metal around it with a hammer. When tapping, it is important not to break the bleeder fitting.
Replacing brake cylinder 2109 is not a difficult task, and many drivers can do this work themselves.
Replacing the front brake cylinder
The following calipers are installed on the front wheels of VAZ cars:
- in a VAZ classic car, two front brake cylinders (FTC) are attached to the caliper brackets;
- on VAZ 2108-15 models, one PTC is installed on each side of the front axle.
Replacing the front cylinder 2109 is not difficult, it is also easy to do yourself:
- we put the car on a flat area (the work can be done without a pit and a lift), we put tackles under the rear wheels;
- jack up the car, take off the front wheel;
- unscrew the two caliper fasteners with a hexagon;
- loosen the brake hose nut;
- bend the locking washers on the upper and lower bolts, unscrew the cylinder fastenings to the caliper bracket
- we move the PTC to the side along with the bracket;
- disconnect the cylinder from the bracket, then from the hose so that the brake fluid does not leak; after disconnecting the PTC, it is better to immediately direct the hose upward;
- we install another, new spare part, and perform the assembly.
Replacing the brake cylinder VAZ 2101-07
On VAZ classic cars, the PTC changes a little differently than on front-wheel drive VAZ cars. The front caliper on the “Classic” can be changed as a whole assembly, but it is also possible to replace only the cylinders. The work is carried out as follows:
- We also put the car on the platform, remove the front wheel;
- unscrew the bolts securing the caliper itself;
- move the caliper to the side, disconnect the hose;
- We take out the pads from the caliper and twist the brake pipe from it.
- if the pins for securing the pads cannot be removed, they will have to be cut with a grinder, then installing new fasteners;
- the brake cylinders are mounted on a bracket in the guides, and they are removed either with a pry bar or by gently tapping with a hammer;
- we install other cylinders, a tube and pads with pins, and complete the assembly.
Replacing the brake cylinder cuff
If desired, on VAZ cars you can not change the entire rear working cylinders, but only replace the cuffs. To do this, you need to disassemble the RTC - remove the pistons and spring, remove the old cuffs from the pistons and install new ones. It is advisable to repair the RTC only if the cylinders did not last long, but they began to leak. The thing is that on VAZ cars the RTCs are very inexpensive, it is advisable to change the rear cylinders as a whole - replacing the cuffs is often unjustified.
Leveling up
After replacing any cylinder in the vehicle, it is necessary to bleed the brakes. Bleeding on any car always begins with the furthest wheel from the GTZ. On all VAZ cars, first of all, they start pumping the brakes from the rear right wheel, then move to the rear left, right front, and the front left wheel is pumped last. If the brake pedal takes at the very end or is hard, bleeding should be repeated, the work should be done according to the same scheme again.
Some tips
- If you start having problems with the brakes, first of all you need to carry out an external inspection of the vehicle: check the fluid level in the reservoir, make sure that the front/rear cylinders are not leaking. There should not even be stains of brake fluid in the brake hydraulics.
- “Brake fluid” must be filled with the same brand; it is recommended to completely replace the brake fluid at least once every two years.
- If faults are identified in the gas turbine engine, and it has already served for at least a year, it is more advisable to replace it completely than to repair it. The same can be said about the rear working cylinders.
- Before changing the turbocharger, the brake fluid should be removed from it; this operation is usually done using a syringe.
- Usually a leak in the master cylinder is not visible, but if there is any suspicion that this part is faulty, you should remove the main cylinder - there will be traces of leaks at the rear, and this indicates its faulty condition.
- If, during an external inspection, cracks were found on the brake hoses, it is better not to take risks and immediately replace the defective parts.
For every motorist, a car breakdown is a disappointment, but many problems can be solved without a service station thanks to a ready-made repair kit. Such sets also exist for master brake cylinders, but we’ll figure out how to use them below.
Functions of the master cylinder
This element can rightfully be called the heart of the entire braking system. It converts the force applied to the pedal into hydraulic pressure. Essentially, it performs the functions of a hydraulic pump and is responsible for the correct supply of fluid to each wheel. Structurally, it is divided into two sections, one is responsible for the operation of the front wheels, and the second - the rear. Thus, even if the performance of one of the circuits is impaired, the second will still complete the task. On rear-wheel drive vehicles, these sections are divided along axles.
The main elements of the brake master cylinder (MBC) are a body, two pistons, return springs and a reservoir, it also contains a lock washer and rubber gaskets. The principle of operation of the node is as follows. The piston moves along the cylinder and closes the compression hole; pressure is created in the first circuit, causing movement of the second circuit. The resulting void is filled with liquid. The spring acts as a limiter and returns the pistons to their original places.
GTZ VAZ 2110 signs of malfunction, purpose of the device, performance check replacement
Despite the fact that these two units are inextricably linked with each other, in our material we will consider them separately. This will allow you to understand in detail all the nuances and features of the operation and repair of the two devices.
I – main cylinder body; 2 – low pressure sealing ring; 3 – drive piston of the “left front-right rear brake” circuit; 4 – spacer ring; 5 – high pressure sealing ring; 6 – pressure spring of the sealing ring;
7 – spring plate; 8 – piston return spring; 9 – washer; 10 – locking screw;
II – drive piston of the “right front-left rear brake” circuit; 12 – connecting sleeve; 13 – tank; 14 – brake fluid emergency level sensor; A – gap
Causes of breakdowns and their symptoms
One of the main reasons for brake master cylinder failure is uneven distribution of fluid in the system, leading to circuit failure. The wear of the sealing collars located at the points where the rod enters the cylinder has a negative effect. It is also possible that scuffs may appear on the pistons and deformation of their return springs with rubber cuffs.
In addition, the compression hole becomes partially or completely clogged. The above malfunctions can be caused by poor-quality brake fluid. Any failed part should be urgently dismantled and a new one installed in its place; if the cylinder mirror is faulty, the entire assembly must be replaced. Moreover, you cannot hesitate, since the correct operation of the gas turbine engine is one of the keys to your safety.
Much can be understood by the performance of the brake pedal. So, if it has a reduced stroke, then most likely the reason lies in the compression hole. It may be clogged or blocked. It may also be due to the lack of clearance between the gas turbine seal and the piston. When the piston gets stuck, the channels are blocked and the cuff is deformed, the pedal does not make a full stroke. But if it moves too easily, then the cause is a hydraulic fluid leak, and the rubber bushings need to be replaced. Sticking of the piston is indicated by the wheels braking when the pedal is released.
Basic faults
Failures in the master brake cylinder are practically excluded, and all malfunctions are associated with the passage of fluid through the seals:
- wear and aging of the sealing cuffs on the rod side, the liquid goes into the cavity of the vacuum booster or, in its absence, into the passenger compartment, onto the driver’s feet;
- similar malfunctions of the cuffs on the pistons, the cylinder begins to bypass one of the circuits, the pedal falls, braking worsens;
- jamming of the pistons due to corrosion of the pistons themselves and the cylinder bore, as well as loss of elasticity of the return springs;
- an increase in travel and a decrease in pedal stiffness when braking due to airing of the brake line.
For some cars, repair kits with pistons and cuffs are still preserved in spare parts catalogs. As well as recommendations for removing cylinder surface defects with sandpaper.
In practice, this activity does not make much sense; it is unlikely that it will be possible to noticeably extend the life of an exhausted turbocharger, and driving with an unreliable hydraulic brake cylinder, which is not for nothing called the main one, is unpleasant and dangerous. Therefore, in the vast majority of cases, the cylinder is replaced with a new assembly.
Diagnostics and repair - replacement of repair kit
Where to start diagnosing the brake system and GTZ? First of all, it is necessary to carry out a visual inspection, since any damage - drips, wet spots on the body, cracks, etc. - are very alarming signs. Are there any external defects found? Then you should check the brake pedal travel, it should be smooth and soft, jamming and failure are unacceptable. If everything is in order, then the next step is to test the braking system in action. You can check the dismantled master brake cylinder for leaks only at a service station or if you have a special stand. All its elements are treated with alcohol, and for rubber gaskets only replacement is suitable. Pay special attention to the GTZ mirror; chips, scratches and other damage are not allowed on it.
If damage incompatible with life is detected, you can replace the brake master cylinder repair kit yourself. Naturally, the first thing to do is dismantle the part. It is installed in the engine compartment housing. Having reached the unit, drain the brake fluid; to do this, you need to pry off the corresponding clamps with a screwdriver and pull out the pipes. After which the studs are unscrewed and the GTZ can be freely removed.
Nuances of repair
O-rings require special attention. The time the rings are in isopropyl alcohol should not exceed twenty seconds, after which they should be dried immediately using a compressor.
The surfaces of the mirror, as well as the piston elements, must be completely clean and free of rust. Every disassembly and repair of a faulty brake master cylinder must be accompanied by replacement of the O-rings, even if they are in good condition. The cuffs of the device also require attention; if they are swollen and frayed, they must be replaced.
Brake hoses are used to supply brake fluid from the master cylinder. If there are cracks or abrasions, they must be replaced. Details: https://vazweb.ru/desyatka/tormoza/zamena-tormoznyh-shlangov.html
After all, it is necessary to check the elasticity of the piston springs; this should be done under load. The length of the spring under load should be 39.01–45.9 N (3.8–4.8 kgf) - 41 mm, with another option the following indicators should be 82.01–99.48 N (8.35–10 .15 kgf) – 21 mm. When free, the spring should have a length of 59.8 mm. If the springs do not have such indicators, then they must be replaced.
When to change cuffs?
Any brake system contains a large number of metal pipes connected using metal fasteners and sealed with cuffs. The seals prevent brake fluid from leaking through moving parts and provide a sealed brake system.
The main signs of a cuff malfunction are a decrease in braking efficiency and a decrease in the level of brake fluid in the reservoir. First you need to find the specific location of the leak. To do this, you need to examine each wheel of the car one by one. If there are traces of brake fluid on it, then this is a clear sign that this brake cylinder has a faulty seal that needs to be replaced. After this, the brake lines and master cylinder are subject to diagnosis.
Found traces of brake fluid indicate a violation of the tightness of the element, which occurs due to worn out seals.
Symptoms of GTZ failure
The main symptom or sign of brake cylinder failure is uneven supply of fluid to the wheels, which causes the brakes to malfunction.
Wear of the seals affects the pressure. If the rubber seals are not tight, the pressure in the system is already less (see the video below for more details).
If there are particles of abrasive substances (sand, pebbles) in the liquid, then scuffing will appear on the piston and cylinder and the rubber sealing cuffs will quickly wear out.
As you can see, low-quality brake fluid, that is, not clean, containing impurities, will clog the holes and make scratches and scuffs on the contacting rubbing surfaces.
If symptoms or signs of a malfunction in the brake system are detected, it is necessary to find, repair or replace it urgently, since this is a safety and transport control system.
How to change the brake master cylinder cuff + Video
If the fault affects the master brake cylinder, then you need to purchase a special repair kit, because it contains more than one cuff.
- Set the vehicle to speed and drain the brake fluid from the reservoir and brake cylinder. To do this, unscrew the drain bolt with a spring at the end of the cylinder, and press the pedal vigorously to squeeze out the remainder.
- Next, you need to unscrew the lines from the brake master cylinder. Their fastenings are made in the form of metal fittings that can be unscrewed with a wrench. Now unscrew the cylinder fasteners and remove it.
- This will be followed by disassembling the cylinder and replacing the old parts with new ones. Pay attention to the location of the cuffs inside the cylinder. Their installation must be strictly identical, otherwise you risk reducing braking efficiency many times over.
During the installation process, be careful and do not use too sharp tools. This is due to the fact that the slightest crack in the seal will lead to its rapid wear, which, in the best case, will force you to tamper with the brake system again, and in the worst case, scrap the broken car.
After repairing the cylinder, it is installed in place, and the line fittings are connected to it. Fill the brake fluid and bleed the system to get rid of air, which also impairs braking.
This completes the replacement of the master cylinder cuff. As you can see, it's not difficult at all.
Replace brake caliper seals
We're working with a two-piston floating caliper, but the principles apply to most calipers. The first tricky task is to remove the pistons. Remove the caliper from the motorcycle but leave the hose connected. Remove the pads and plates, then slowly pump the brake lever to force the pistons out. If one sticks out further than the others, hold it down with a block (or blocks) so that the pistons come out evenly. Pay close attention to the evenness - when they almost pop out, you can pull them out by hand. But if only one piston pops out, the pressure will be lost, and it will no longer be possible to squeeze out the rest.
Of course, with four- and six-piston calipers it is more difficult. But take your time and everything will work out. If you get really stuck, you can buy a brake piston puller that will lock the piston inside and help you pull it out. In the case of two-piece calipers, sometimes you need to halve them by unscrewing the bolts - do not forget to buy new seals for the channels between the halves.
Each piston has two seals: an outer boot and an inner oil seal. The first prevents dirt from getting inside, and the second has two tasks: it keeps the brake fluid inside and at the same time holds the piston itself in the right place. When you press the brake lever, the fluid pushes the piston out and it presses the pad against the disc. When you release the lever, you need to push the piston back. The seal does just that: it flexes a little under pressure as the piston moves out, and then retracts it back in when the pressure is released. As the pads wear, the oil seal releases the piston further and further, opening the gap that appears.