Faulty shock absorbers not only make an unpleasant sound on every bump, but also create a driving hazard. Because of this, the car's handling deteriorates, it wobbles on uneven surfaces, and tire wear occurs unevenly. Of course, comfort in the cabin also suffers due to constant knocking and shaking. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, this will entail more expensive repairs of various components. Shock absorbers are simple components, which, however, can create big problems. They work in harsh conditions, so their condition needs to be monitored, especially if the roads leave much to be desired. They can fail after 50 thousand kilometers or after 100 thousand, depending on driving style and road conditions.
How to eliminate knocking shock absorbers.
Service life of shock absorbers of various types
Car racks, depending on the internal structure and principle of operation, are divided into three types.
- Oil - operate due to the flow of working fluid from the cavity above the piston into the cavity below it. The simplest and cheapest type. Serves an average of 60 thousand km.
- Gas - have two sections in one cylinder, separated by a freely moving piston: gas and oil. The gas pump dumps dynamic loads and pushes the rod out of the cylinder. Oil is used to dampen car vibrations. Despite the increased number of moving parts and the addition of a gaseous working phase to the design, this type of shock absorber struts is considered more durable: the average service life is about 80 thousand km.
- Gas - oil. They consist of two cylinders nested one inside the other. The outer one is designed to store gas, the inner one is for moving the piston in an oil environment. This design is more complex and expensive to manufacture, but in terms of comfort, gas-oil shock absorbers are superior to conventional gas shock absorbers. Such racks also last about 80 thousand km.
Calipers
What can knock in the front suspension on small bumps
Each car model may have its own reasons for the caliper knocking, it all depends on their design features, but there are also similar reasons that we will focus on.
1. Anther.
This is what is checked first. If the boot is torn, the lubricant will quickly leave the guides and they will run dry. Read below for what to do with worn fingers.
2. Caliper pin.
It is inserted into the bracket and must be lubricated with high-temperature grease, for example, special for calipers or CV joints.
On the VAZ 2110, Priora, Kalina, Grant, 2114, two guide pins are structurally provided, upper and lower.
In the absence of lubrication or severe wear of the bracket holes or pins, the latter begin to knock on bumps.
To fix the problem, it is necessary to apply fresh lubricant to the parts, and if they are severely worn, replace them with similar ones from the repair kit, which is sold separately.
The new repair kit for the above VAZ models includes one guide pin with a bolt and boot. Accordingly, two repair kits may be needed.
But there are cases when the new fingers are 0.5 mm thicker than the standard ones, so you have to bore the caliper bracket to solve the problem.
READ ON THE TOPIC: Other characteristic malfunctions of the VAZ 2110.
Knock in the front suspension
Unfortunately, it is impossible to determine by ear
what actually knocks. Therefore, when performing it, you need to inspect the shock absorbers, tie rod ends, anti-roll bar, front suspension arm, steering knuckle, silent blocks, ball joints. A common cause of knocking is failure of rubber seals. All rubber parts must not be cracked or damaged. If you notice a defect, you must replace them immediately.
Work must be carried out in an inspection hole or with the vehicle jacked up.
Possible causes of knocking and their diagnosis
The cause of the knock can be any part that is part of the suspension. The most common reasons are:
Carrying out car suspension diagnostics yourself
- wear of the tie rod end;
- wear of ball joints;
- damage to rubber-metal hinges;
- deformation of shock absorber strut supports;
- wear of supports and suspension arms;
- loosening the nuts and bolts of the system components;
- wear of the cushion and rubber-metal hinges of the rod;
- production of hub bearings;
- large wheel imbalance or deformation of wheel rims;
- settling or breakage of the suspension spring.
Next, we will analyze these and other causes of knocking in more detail. You should start self-diagnosis by checking the condition of the anthers
rubber sealing parts. If they are damaged, they must be replaced.
Also pay attention to signs of oil leakage from the shock absorbers.
Malfunctions in the operation of the suspension arms
Silent block
A possible cause of suspension knocking is a malfunction of its levers
. This is usually accompanied by poor vehicle handling. Check the operation of silent blocks. To do this, use a pry bar as a shoulder to bend the levers. If there is a malfunction, you will see significant play
. For repairs, it will be necessary to replace the silent blocks. To do this, you need to remove the levers and press the old silent blocks out of the hole. Before installing new silent blocks, lubricate the seat to reduce friction. Clean it from dust and dirt in one go.
Ball joints
Spherical bearing
On old rear-wheel drive cars (for example, VAZs), problems with ball joints are considered a classic cause of knocking in the suspension. The check must begin by hanging the car on the shock absorber above the wheel where the knock is coming from. Without rotating the disk, you need to try to shake its opposite parts toward and away from you. The procedure must be carried out in two planes
, grasping the left and right parts of the wheel, then the top and bottom. If the supports are faulty, you will feel play.
Constant velocity joint (CV joint)
If the CV joint is faulty, then while driving it produces a characteristic crackling sound, especially when turning. When a CV joint breaks down, it has to be replaced because it cannot be repaired.
Uncharacteristic causes of failure
Another reason for the knocking noise could be a loose brake caliper.
. This is a fairly rare reason, since, as a rule, the caliper is mounted very securely using locknuts. But if the fastening bolts do loosen, the sound of the caliper, especially when braking the car, will be very loud, so it is impossible to confuse it with anything else. Sometimes, especially if the brake pads are of poor quality, they can make a small and dull sound. In some cases, peeling of their working surface may occur. The cause of knocking noises in the front suspension can also be the stabilizer bar bracket.
. It has bushings with rubber elements in its design. It is necessary to check their integrity.
Another reason for knocking may be a situation where the engine mounts burst.
. Because of this, a knock occurs, which is similar in appearance to the sound from the chassis system of a car. So check this option too. It is also worth checking that all the nuts and fasteners under the hood are tightened.
. This is especially true when buying a used car. Unsecured parts may rattle, producing a sound similar to a clattering suspension.
Finding out the cause of the knocking
Clunking noises in the suspension when driving over uneven surfaces: causes and solutions
data-full-width-responsive="true">
If, when overcoming bumps in the car's interior, you hear distinct loud knocks from the wheels, it's time to inspect the suspension. You should first make sure that the knocking is a consequence of a malfunction of the shock absorbers, because third-party sounds are also created by other components, for example, the brake caliper.
First of all, it is necessary to visually inspect the damping elements. One of the main reasons for loss of performance is oil leakage due to wear of the seals. The lack of working fluid inside leads to the fact that when working on compression, the shock absorber rod does not meet resistance and it reaches the bottom of the reservoir - a “breakdown” occurs, accompanied by a strong knock.
Since the oil comes out, the marks are clearly visible on the body. Detection of fluid leaks indicates a faulty unit and the need for replacement. But it is not always possible to visually assess the condition of the damping unit. Many cars use shock-absorbing struts (MacPherson struts) both front and rear. In them, the shock absorber is placed in the strut housing and it will not be possible to inspect it without disassembling the unit.
In this case, you can use the “folk” method of checking - rocking the car. At the front of the car, you need to press firmly on the fender (at the rear - on the fender, bumper, lower trunk shelf) and release. If the shock absorber is working properly, the car body will take its initial position and stop, since the damper will absorb the energy of the spring. But if the part is faulty, the body will wobble a little after pressing and releasing.
The condition of the silent blocks must also be checked, since they can also make knocking noises. And to do this, we put the car in a pit and, using the pry bar as a lever, swing the suspension components. This inspection method makes it easy to identify wear on rubber suspension parts.
And lastly, the upper supports of the shock absorber strut (in the front suspension) are checked. They can also cause knocking noises when driving. These elements are also easy to check - we put our hand between the coils of the spring and touch the shock absorber rod, and then rock the front of the car to the sides. Vibrations of the rod during swinging indicate a malfunction of the support.
Something else useful for you:
- Gas, oil or gas-oil shock absorbers - which ones are better?
- Car springs: what they are, design, advantages and disadvantages
- What is special about MacPherson suspension?
Brakes as a source of knocking
Sometimes sounds coming from the suspension are actually coming from the brakes. It happens that a car enthusiast has checked everything and replaced everything that can be replaced. The front suspension layout has already been learned by heart, but the knocking was still there.
To make a diagnosis, you need to move. If the knocking noise disappears when braking, and when the pedal is released, it resumes again, then the brake pads are to blame. The same problems can occur after installing new pads.
If the car is knocking, do not rush to repair the chassis. Perhaps the extraneous sound is caused by a completely different reason. In this case, only a complete diagnosis can help. It may be enough to replace the front suspension silent blocks and the sound will disappear forever.
A knock in the front suspension usually appears suddenly and can alarm anyone, even the most experienced driver. This problem almost never occurs in new cars, but the older the “iron horse”, the greater the likelihood of such troubles occurring. This review is about the most common sources of sound in the suspension.
The first place to start inspecting a car is with the levers. As soon as some defect occurs in the latter, the suspension begins to knock. Among the most common defects is wear of rubber-metal hinges (silent blocks). If the steering wheel begins to oscillate while driving, this can lead to deterioration in the car’s controllability, and at high speeds such a problem can even lead to a run off the road, so there is no point in wasting time checking and repairing it. In order to identify the wear of the rubber-metal hinges, you just need to shake the ends of the rods with a mounting tool. The problem in silent blocks can be eliminated by replacing them.
When checking the car, attention should also be paid to the tie rod ends. A knock may occur due to large play in the finger in the socket. Play in this area can be detected in another way, simply by shaking the steering wheel from side to side.
A knock in the front suspension can also occur due to ball joints that may have worn out a long time ago. You can get rid of such a knock only by completely replacing the worn part. The main task assigned to the ball joints is to turn the steered wheels. This part takes on the maximum load that appears on a poor-quality road surface. You cannot delay replacing ball joints - the longer you delay, the greater the likelihood that they will tear out and the vehicle will immediately lose control.
When inspecting the front suspension, look at the condition of the steering wheel caps and supports. The purpose of such covers is to protect the hinge from contamination. If the protection is defective and dirt gets on it, this will greatly reduce the service life of the part.
Often the cause of a knock can be a failed shock absorber, which often becomes unusable due to improper use, as well as in cases where the car is operated in difficult conditions. You can understand the condition of the shock absorbers on uneven roads. If after a bump the car rocks in all directions, then there is a problem with the shock absorbers.
You can also check the condition of the shock absorber after removing it from the car. After dismantling, the part is installed in a vertical position, and then the rod is pulled out/lowered several times. If, when moving the rod upward, less resistance is felt than when the same manipulations are performed in the opposite direction, this indicates a malfunction of the shock absorber. If the rod moves too freely, then there is a lack of working fluid.
If you notice a knocking sound in the suspension of your car, do not hesitate and take the necessary measures immediately. If you cannot carry out repairs yourself or doubt your abilities, contact professionals. By the way, even if the suspension does not bother you, experts strongly recommend checking its condition about twice a year.
If you liked it, please share with your friends!
We carry out repairs
Knock in the steering rack: how to determine how to eliminate the knock
Non-working shock absorbers must be replaced since they are non-separable. And they change in pairs. That is, if only one element malfunctions, the damper on the other side is also changed. Note that some car enthusiasts repair the shock absorber by cutting off the rolling of the housing in order to remove the rod with the piston. This operation allows you to replace the oil seals, install a new rod with an intact piston (from the donor), and fill in new oil. During assembly, tightness is achieved by welding the rolling area.
But restoring the functionality of an element is a labor-intensive process; it is easier to buy new dampers and install them instead of worn ones.
Mechanism design
This component is designed for a reliable and at the same time damping connection of the unsprung masses of the suspension (wheel, hub, steering knuckle) with the elastic part - the stabilizer beam. The common purpose of the stand is to provide a movable joint. In this case, the execution may be different:
- Ball joints.
The most common scheme. Provides freedom to hinges in all directions. With this design, wear occurs the fastest, since the ball joints take on a load comparable to ¼ of the vehicle’s weight. The stand is constantly in motion, experiencing forces aimed at compression, tension and bending. It is used in suspensions where the components are arranged compactly and the stabilizer beam has a complex shape. Can be installed at an angle. Practically beyond repair or restoration. - Earrings.
A primitive but very reliable scheme. Elastic elements (rubber, polyurethane, silicone) are threaded onto the pin and secured with washers. Between the rubber bands are the eyes of the suspension arm and the stabilizer beam. Some freedom of movement is provided by the rubber stops themselves, but significant deviation from the vertical is impossible. This drawback does not allow the use of such racks in complex suspensions. The advantages include the ability to withstand significant loads and high maintainability. - Silent blocks.
Such a hinge has mobility in only one plane. Transverse deviations are allowed at a small angle. The advantages include a longer service life (compared to ball joints) and relative maintainability. Disadvantage: limited use on complex suspension structures.
Do-it-yourself restoration and repair (with photo)
Faulty racks should be dismantled. This procedure is performed with a standard tool. You may need a ball joint remover. Depending on the design of the rack, it should be replaced or repaired.
- Ball joints are practically irreparable. There are repair mixtures that are injected into the hinge and, when hardened, eliminate the play. This method is questionable, the effect will be short-lived.
Advice! To prevent wear of the stabilizer ball joints, the boots should be checked regularly. If a crack or tear appears, the rubber should be replaced.
The choice of bushing material depends on the driving style and the owner’s love for comfort
If you don’t have the necessary bushings, you can find suitable bushings in the car market that are suitable in diameter and thickness. It is important to remember that the rubber bands are designed for a certain weight of the car. The same applies to replacing material. Polyurethane has a longer service life, but is harder than rubber. You can lose in comfort. When replacing the support rubber bands, you should thoroughly clean the seat (eye). Sand and dirt contribute to wear.
Upper rack support
This can also cause knocking in the front suspension over small bumps. On car forums, the topic dedicated to this knock is very popular. The reasons are different for everyone. In attempts to combat this annoying sound, car owners go through the entire suspension, but often the knock remains.
One possible cause is the upper strut support. It consists of a rubber part as a damper and a bearing. If this rubber element has lost its elasticity, then this is the cause of this extraneous knock that all drivers struggle with. In order to find out for sure whether this is so, measure the gap between the limiter and the support. In most cars this is easy to do, but in some models this unit may be closed. If measurements show that the gap is more than 10 mm, then the support must be urgently replaced. However, this gap is not always uniform. When measuring, it is recommended to focus on the average figure. It is worth checking this support carefully: on many cars this sound appears only on one side.
Checking shock absorber struts
It is very important to monitor the condition of the vehicle and know how to check the shock absorbers, since they are the ones that keep the car in the correct position on the road.
If this important suspension element fails, and the car owner postpones testing the shock absorbers until later, the accompanying chassis parts will also be susceptible to failure:
- Failed shock absorbers, coupled with wheel imbalance, will lead to accelerated tire wear and destruction of wheel bearings;
- After traveling several thousand kilometers with faulty struts, the support bearing will break down;
- If the shock absorber is in good working order, the service life of the brake pads increases, but when there are problems, the braking system is no longer reliable, since the braking distance increases and the likelihood of an accident increases.
So it turns out that timely intervention can protect not only from various breakdowns and traffic accidents, but will also significantly save the car owner’s budget - after all, it is cheaper to replace struts at the stage when the first signs of a malfunction appear than to repair the chassis or brake system later.
Main malfunctions of shock absorbers
If the cause of the unpleasant knocking sound is a faulty shock absorber, and this is definitely confirmed, you need to understand the reasons and eliminate the malfunction. The most common reasons, knowledge of which will help determine the cause of the knocking of the shock absorber strut:
- Oil leak.
- Damage to the hull.
- Piston damage.
- Poor quality oil.
In the first case, oil may leak due to wear of the seals, which are precisely what should prevent this. They wear out due to constant movement, accumulation of abrasive components inside the structure, and abrasion of surfaces. Natural corrosion also plays a role. Damage to the housing may occur from hitting an obstacle. In this case, the strut knocks because the shock absorber piston rod hits this recess when moving and its stroke is limited. This happens with single-pipe structures; in double-pipe structures, the internal tank is protected from shock.
Another reason is the poor quality of the oil inside the tank. It is this that serves as the working fluid and a lot depends on its characteristics. For example, if it is too viscous, the shock absorber will be hard, especially in cold weather. At low viscosity, the likelihood of breakdown increases, since its resistance is much lower. Therefore, you cannot use any oil, but only the one recommended for this model. You can usually check the strut and find the cause of the knock visually by inspecting it. Oil leaks and external damage to the housing will be visible. You can also detect sideways vibrations of the rod if you rock the car. The quality of the oil can be checked against the passport recommendations, if you know which one was filled.
Measuring distances and sizes
One of the simplest and most accurate ways to determine the presence of a malfunction is to measure the gaps and dimensions. The optimal solution: take it to a service station. Qualified technicians will definitely help determine whether replacement is necessary. It must be remembered that even one faulty shock absorber affects the efficiency of the vehicle’s suspension system.
It must be remembered that working with a stand in a workshop implies the need to configure it for a specific car. For example, it often happens that the data indicated almost complete wear of the car’s suspension. At the same time, on the road, regardless of speed, the car behaved perfectly. The reason was simple: the stand was simply not configured to work with a rigid suspension.
Read also: Percentage of burnt out lamps in the panel board
Why is the shock absorber knocking?
If, as a result of diagnostics, it was possible to determine that the faulty part in the car’s suspension is the shock absorber, you need to understand what exactly the problem is. The most common shock absorber malfunctions are:
A small amount of working fluid, which occurs due to its leakage. The reason for this is wear of the seals. If the seals are damaged, the shock absorber does not provide the necessary tightness, which leads to leakage of working fluid. It is worth noting that damage to the oil seal is a natural process, which is caused by the formation of corrosion, harmful chemicals from the road getting onto the shock absorber, and dust settling. On average, when driving on Russian roads, problems with oil seal leaks begin after 50-60 thousand kilometers; Physical deformation of the shock absorber body. The cause of this malfunction is a physical impact on the body
Due to the deformation, the rod cannot move in normal operating mode over the entire height required for shock absorption. Please note: If the vehicle has twin-tube shock absorbers, the deformation of the outer rod is not so critical for them.
Defects in the piston rod - chips, bends, deformation. Damage to the rod can occur under heavy loads, for example, when the car falls into a pothole while driving at high speed.
The piston tries to work off such a load, but there is not enough working fluid to absorb its movement, which leads to a collision of the piston with the bottom of the tank and its deformation. Also, piston defects are often accompanied by leaks of working fluid; Low quality oil. The performance of the shock absorber greatly depends on the quality of the oil. Low viscosity will not create enough resistance for the piston rod.
Due to its design, the shock absorber is practically irreparable. If the shock absorber is defective, it must be replaced.
Important: Replacing shock absorbers is carried out only in pairs on one axis. That is, if the front right shock absorber fails, then the front left one will have to be replaced along with it.
Some service centers offer a shock absorber repair procedure by making a cut in the housing and removing the rod and piston. After this, oil seals and other necessary elements are taken from the donor shock absorber, oil is poured in and the part is welded. From an economic point of view, such a procedure is impractical, and it is cheaper to install a new shock absorber than to repair a defective one.
Please note: It is necessary to bleed the shock absorber before installation
"De Dion"
This type of suspension got its name from the famous French engineer. As a rule, "De Dion" is used in the rear axles of cars. At the same time, suspension traction when driving along a camber in the VAZ-2121 and other cars is often encountered precisely because they use such a system.
The main difference between such a suspension will be the separation of the gearbox from the rear axle, and the transmission of torque is transmitted using half-gears. Among the disadvantages of this system, car enthusiasts note the characteristic “squatting” of the car during braking.
- To better understand the situation, it is worth considering the dependent system, which is actively used in Zhiguli cars, which are more likely than other cars to experience suspension failures.
- VAZ-2114 and other models that use similar systems also face various problems. As one of the key elements of this design, coil springs and several levers are used to fix the rear axle in the longitudinal direction and one in the transverse direction.
- Thanks to this, it is possible to achieve good technical characteristics of this suspension, although certain difficulties during its operation remain.
Semi-independent designs are also widely used, which are used by most manufacturers today and rarely get caught in the suspension when riding over cambers.
Ford Focus 2 and other cars are equipped with such systems due to their low weight, as well as the kinematics of the wheels, which distinguishes them favorably from their counterparts. But this design has its drawbacks, such as the inability to install this type of suspension on rear-wheel drive vehicles.
CAN THE NEW SHOCK ABSORBERS KNOCK?
It happens that knocking occurs on new shock absorbers that have just been installed. Due to the fact that the parts have just been changed, they are the last to be “sinned”, looking for reasons in other suspension elements. But even new shock absorbers create extraneous sounds. There are several reasons for this - a manufacturing defect in the damper, unreliable fastening, mismatch or defective rubber bushings.
Factory defects are rare, but this reason should not be ignored, and if knocking noises appear, even a new element should be checked. Extraneous sounds may appear due to unreliable fastening of the part in the rack housing. The element is fixed in the body with a nut and if it is not tightened enough or is loose, the damper will move along the stand, creating knocking noises.
In shock absorbers installed outside the strut (lever and semi-dependent suspensions), extraneous sounds appear due to inappropriate or depressed rubber bushings installed in the mounting lugs.
False signals
True, there are situations when some other knocks are mistaken for a shock absorber knock, the so-called false shock absorber knock.
This usually happens when the bushings between the strut and the car body support bowl begin to knock.
Over time, the bushings wear out, lose their original sizes and shapes, and shock absorbers begin to knock due to play.
Therefore, you shouldn’t start panicking when a shock absorber knock appears; calmly figure out the situation, maybe it’s not all that scary.
But also knocking in the wheel area may mean that the silent blocks of the levers and balls have failed, or have begun to fail, so it’s still better to contact a specialist if you don’t understand this.
MAIN FAULTS OF SHOCK ABSORBERS
So, the diagnostics showed that everything is in order and the only place where the shocks are coming from is the shock absorber. Note that the damper produces extraneous sounds not only due to loss of tightness.
The causes of the malfunction may be:
- leakage of working fluid;
- deformation and damage to the body;
- damage to the piston rod;
- inconsistency or low quality of oil.
The leakage of working fluid has already been mentioned - this is a consequence of wear of the seals - oil seals that ensure tightness. The reason for such a malfunction lies in their natural wear (the rod is constantly moving, so the edge adjacent to it wears off over time). But the oil seal is also damaged due to corrosion, scuffing and the settling of dust and sand on the shock absorber rod.
Deformation (dents) are formed due to impacts on the damper body. Because of these dents, the rod is not able to move along the entire height of the tank and, along with the deformation, the piston rests against the defect, and this is accompanied by a strong knock. But such a problem is possible only in single-tube shock absorbers (in double-tube shock absorbers, the dent occurs on the external reservoir, while the internal one, along which the rod runs, remains undamaged).
Another problem occurs in the shock absorber rods, which leads to malfunction. If the shock absorber is not securely fixed in the strut body, it moves, and under heavy loads, even minor movements can cause cracks or wear on the body.
Damage to the rod piston occurs in one case - when it hits a hole at speed, the shock absorber cannot withstand the load and a “breakdown” occurs. In this case, the piston collides with the bottom of the tank, which causes damage. As a result, the valves are damaged and the oil flow process is disrupted.
The oil in the shock absorber is a working fluid and the performance of the damper depends on its properties. If the viscosity of the oil is low, then it will not create the required resistance to the movement of the rod with the piston - it is much easier to “break through” the shock absorber. In winter, highly viscous oil creates excessive resistance.
Shock absorber knocking in winter
Reliable operation of the shock absorber in severe frosts is structurally built into it, especially in our domestic models.
But it all depends on the type of oil that is used in it. Some shock absorber manufacturers are guilty of this and do not use all-season oil, but summer oil, which freezes in severe frosts, which is why the shock absorber begins to knock.
For example, we drove a car from a warm country to the north of Russia. Situations are different and a shock absorber operating in one weather conditions may behave completely differently in a different climate.
Also read - kayaba shock absorbers, oil, gas, reviews, history of creation, review of popular models.
In this situation, the oil in the shock absorber should be replaced with non-freezing oil, then the knocking should stop.
Steering tips
Tie rod ends need to be replaced when they wear out, and the first sign of wear is the appearance of a knocking sound when the car moves over bumps and holes.
We will also carry out diagnostics using the example of VAZ classic cars, but the methods shown below may be suitable for other brands of cars.
On VAZ classic cars, internal and external tie rod ends are structurally provided and all of them need to be checked.
It is also important to understand how these steering elements are designed and how they work, so it will be easier to understand what you are doing
There is no need to jack up the car or use a pry bar; use only your hands for diagnostics.
The first thing you need to do is get to the steering rods; to do this, you can drive the car onto an overpass, a pit, or use a lift, if there is one.
Pay attention to the condition of the anthers; if they are torn, then this points to the tips as one of the reasons for the source of the knocking. Grasp the tie rod of the steering tips and forcefully, maybe jerkily, move it up and down, but it should not wobble or make sounds
Grasp the tie rod of the steering tips and with force, you can jerk it, move it up and down, but it should not wobble or make sounds.
If it openly dangles, it is most likely the cause of the knocking in the front suspension.
Do not confuse knocking with a spring movement, which is obtained due to springs inserted into the steering tip (see the device above).
On classic VAZ cars, for example, model 2106, the inner tip is attached to the steering pendulum, which can also play, namely, its bipod can hang on the bushings.
Therefore, you need to grab the bipod with both hands and use the same up and down movements to diagnose the pendulum.
Also, on the side of the steering gearbox, there may be play in the pair of the unit itself, and you will be sinning on the steering tip, which sits on the bipod of the gearbox.
As for other VAZ cars, for example, 2110 - 2115, the steering design there is much simpler, which means diagnosing the condition of the tie rod ends will also be easier.
For example, remove the front left wheel and turn the steering wheel to the right until it stops.
Grasp the caliper with your left hand and the brake discs with your left hand. When making sudden movements away from you or towards you, you can see whether there is play in the steering tip or not.
How to check: diagnostics at home
Attention! The general rule for diagnosing suspensions is to look for faults in an unloaded state. The hinges, compressed under the weight of the car, may not show any play.
An assistant may be needed to carry out the diagnosis.
Necessary tools for performance testing
- Jack. Designed for lifting and suspension manipulation purposes only. It is dangerous to carry out work when the car is supported only by a jack!
- Support stands for the bottom (frame).
- Wheel chocks.
- A pry bar or a small crowbar.
- It is advisable to have a car enthusiast's stethoscope. Without the vehicle moving, knocks in the suspension are not so pronounced; sometimes they can only be detected with the help of a stethoscope.
Using a car stethoscope, you can listen not only to suspension malfunctions, but also to engine noise.
How to check the serviceability of parts
- Inspect the geometry of the racks. Abnormal bends are a sign of a malfunction, and driving on such ones is not recommended.
- Carefully examine the condition of the front hinges. Torn ball boots, cracks in silent blocks or rubber bushings indicate critical wear.
- While under the bottom of the car (in the pit of the garage), ask an assistant to rock the body with his hands. Obvious knocking noises will be noticeable, and it will not be difficult to find out the malfunction.
- Unload the suspension. To do this, lift the car with a jack and place it on support stands. The wheels should not leave the ground. Both sides should be lifted, otherwise the elastic beam will twist. Pull the racks with a sharp movement - the play will be noticeable. Use a stethoscope for an accurate diagnosis.
How to find out the cause of knocking noises: video guide about the easiest diagnostic method
How to fix the situation?
First you need to determine the cause of the knocking. The situation can be corrected by replacing the non-functioning element, since it is impossible to disassemble the shock absorber. By the way, replacement should only be done in pairs. That is, if you changed the shock-absorbing device on the left side, change it on the right as well.
Some car enthusiasts still try to make minor repairs to a defective item. To do this, they cut off the rolling of the body. After cutting, you can remove the piston with rod. This allows you to check the rod and pistons and, if necessary, replace them - and also add new working fluid. During assembly of the mechanism, the cut rolling area will have to be welded. This is a complex process - it is much easier to buy new elements and install them.
To prevent knocking, it can be recommended to avoid “forcible” operation of the car. It is clear that the roads need to be chosen more evenly - it’s hardly worth talking about
Pay special attention to the condition of the oil. In cold weather, you should not pick up speed too quickly, because at the very beginning of movement the temperature of the working fluid corresponds to the air temperature
Excessive oil viscosity is a common cause of valve disc failure. To avoid this, it is better to pick up speed a few minutes after the start.
The service life of shock-absorbing elements is limited. But to prevent them from breaking prematurely, you must follow the rules for operating the car.
Shock absorbers, otherwise called dampers, are special devices that help smooth out vibrations during driving by converting mechanical energy into thermal energy. Shock absorber struts are closely connected and work in tandem with springs, springs, torsion shafts, cushions and several other elements of the vehicle's chassis.
Front suspension. What might be a concern?
- Wheel bearings.
Wheel bearing noise can be detected by ear even by a less experienced driver. It howls and rustles when moving and, gradually increasing, begins to drown out all other noises in the cabin. To make sure that it is the bearing that is making noise, you need to turn the steering wheel a little when driving at speeds above 60 km/h. If the rumble appears in one steering position and stops in another, it means the bearing has definitely failed. You can also check this by lifting the car wheel and spinning it. If you hear a characteristic rustling sound, it means the bearing needs to be replaced.
- Stabilizer's pole.
Stabilizer links are the most vulnerable part of the suspension. Due to the poor quality of roads, they often fail and begin to produce a slight but constant noise from under the bottom of the car. You can determine if the struts are broken by resting the lever on the subframe and shaking the stabilizer. If during these actions a knock is heard and play is felt, it means that the stabilizer links are out of order.
These parts are usually replaced in pairs, and you can do it yourself. To do this, you need to hang the front wheels of the car, and using a 16 wrench, unscrew the hinge nuts, while holding them with a 5 hex wrench on the back side so that the hinges do not turn.
- Spherical bearing
The sound of a broken ball joint can be difficult to distinguish from other suspension noises. You can check the play of this unit by moving the suspended wheel in a horizontal plane. If the fault cannot be determined, you can insert a pry bar between the subframe and the lever and press on the resulting stop. This is the easiest way to identify a loose ball pore.
At the service center, the ball joint is replaced along with the lever and silent blocks. But these parts also exist for sale as a separate unit.
Replacing a ball is not an easy operation, so you can tackle it yourself only if you have the necessary tools and metalworking skills.
- Shock absorber.
Many drivers complain about the knocking of Lada Vesta shock absorbers, but their design itself eliminates this possibility. The telescopic strut consists of two cylinders that dampen vibrations while moving on uneven roads. When they break down, the car begins to “sit down”, the road holding is poor, all the unevenness and bumps become clearly noticeable, and the steering deteriorates. In this case, the outflow of liquid or gas from one cylinder to another is disrupted, and the shock absorber rod begins to make characteristic sounds that resemble knocking.
Visually, a breakdown of the oil shock absorber can be determined by drips on the casing, in the presence of which the part must be replaced immediately. You can also rock the car, focusing on the hood. Under normal conditions, after the impact ceases, the machine should swing once and stop moving. If this does not happen, the racks do not absorb as expected.
- Upper rack support
The upper mount of the front shock absorber contains a support bearing that can knock and howl when driving. You can identify a malfunction of this unit in the following way: swing the car in a vertical plane and put your hand on the support. If a part malfunctions, rattling and humming will be felt.
Another method requires completely dismantling the rack. This check can be done simultaneously with replacing the front shock absorbers. After removing the steering knuckle, you need to rotate the strut together with the spring in a circle. The crunching and grinding sound in the upper part of the assembly that occurs during this indicates that the support is faulty.
Like shock absorbers, it is advisable to change the upper supports at the station, since the process of dismantling and installing them is quite complicated.
Where to begin?
If it's not something else that's knocking, you should first check for engine oil leaks. This generates knocking noise quite often. In this case, the knocking part should be replaced immediately. If it is completely dry, then you can do a simple test: swing the car down by pressing on its wings. If, instead of smoothly rising to its original position and stopping, it continues to wobble, then this vital part of the car is most likely broken and no longer dampens the vibrations. In this case, the car will rock much longer than it should, and you will find out the cause of the knocking. This, together with a slight imbalance of the wheels (perfectly balanced wheels do not exist in reality), leads to uneven intensive wear of the tires, reducing their service life by several times or tens of times, accelerating the wear or breakdown of suspension parts and brake mechanisms and bringing the time of the next unscheduled body repair closer.
Wear and damage
The knocking noise occurs due to wear or mechanical damage. It can be caused, for example, by a broken thread or a bent rod. In case of such malfunctions, the shock absorber must be replaced or repaired, especially if it has served at least 50 thousand km. This is the same consumable material as filters and pads, only its service life is much longer. A knock can also occur due to elementary malfunctions of its parts: damage to the pipe, rod thread or its disconnection.
Liquid leak
Another common cause is hydraulic fluid leaking into the outer cylinder. Air begins to enter the volume free from leaked oil. The problem can be eliminated by pumping it yourself or at a service station.
Freezing
Quite often, knocking appears in cold weather, and in this case it is caused not by the part in question itself, but by the oil that has frozen in it. Some car owners especially note a knocking sound in the rear shock absorbers when it gets cold. A special hydraulic fluid for cold weather and warming up the shock absorbers should help.
Bushings
If you have just installed it, and correctly, the nuts are tightened securely, there is no play in the rod, but there is a knocking noise, then the problem may be with old rubber bushings or new ones that are incompatible with its type. To avoid such cases, it is better to buy everything as a set, along with suitable bushings.
Illiterate repair
Sometimes the oil is too thick not because of the weather, but because of an illiterate “repair”, in which the working fluid was replaced with a more viscous one with the best intentions - to reduce the likelihood of leakage. As a result, the controllability and stability of the machine deteriorate: the increased rigidity of this part does not guarantee good performance under high loads. In addition, such “repairs” significantly increase the compression force, increasing the load on the body. Gradually, cracks appear near the fastening points and the rebound force increases, which also has a negative effect on the car.
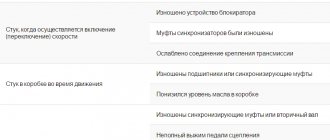
Car front suspension
Half shafts If the hum increases with increasing speed, then they are faulty. The axle shaft itself does not break, but it has a weak point - the bearing. Within 3 weeks it is necessary to repress it or replace it along with the axle shaft.
CV joint If the CV joints (grenades) are faulty, clicks will be clearly heard when turning. Especially if you turn the steering wheel from side to side at idle. In this case, urgent replacement is required.
Removing the CV joint from the axle shaft
Ball joints. If there is a malfunction, they creak or knock when driving on uneven roads and bumps. It is necessary to replace them as quickly as possible, otherwise the car will end up in the middle of the road, with the wheel unnaturally turned out.
Wheel bearings. Front wheel bearings can produce both knocking and noise. The noise occurs as a result of wear of the bearing rollers and the separator raceway, and the knocking occurs from strong play in the bearings. It is not difficult to make a diagnosis yourself. To do this, you need to jack up the left side of the car and sharply turn the wheel. If there is a hum that sounds like a metal ball rolling on a sheet of metal, the bearing needs to be replaced. Next, grab the upper inner section of the wheel with your left hand, and the lower outer section with your right hand. Now you need to shake the wheel “to the point of breaking”. If it “lobs” even a little, contact a specialist to eliminate the play in the hub bearing, otherwise its service life will be halved.
Steering. You should start with the gearbox, which sometimes knocks as a result of wear on the main pair and creaks when turning the steering wheel in different directions. As a rule, the problem is solved by lubricating and adjusting the steering shaft. And the steering ends and rods knock like ball joints, and the knocking only appears on rough roads. They urgently need to be changed.
Shock absorbers. As a rule, they do not bother you with “sounds,” but if sounds are still present, you can clearly hear them on an uneven road: they squeak and knock. Their disease is wear of cushions, rubber bushings, and oil leakage. You need to rock the car (press on the trunk and fenders) and listen for knocking noises. If the body continues to sway even after you stop the impact, it means the bushings and cushions are worn out. Driving on such shock absorbers is dangerous, because when you press the brakes sharply, the braking distance doubles. In addition, the cause of the breakdown may be an oil leak from the shock absorber, which is noticeable to the naked eye (you will see adhered dirt and smudges on the body). This shock absorber needs to be replaced.
Springs. Unpleasant sounds of rubbing metal elements are often produced by springs. The reason is incorrect installation - to fix the problem, you should contact the specialists who installed them.
Brakes. Brake pads sometimes whistle when the pedal is applied, even to the point of grinding. If the pads are new, most likely they just haven’t gotten used to it yet, and the noise will disappear after 1-2 thousand kilometers on its own. However, there is a risk that they are crooked, that is, defective. Therefore, if the sound does not disappear after some time, and the car changes trajectory when braking (it pulls to the right or left), the pads should be replaced. On cars that are expensive to maintain, they are quite expensive, so the problem can be solved in another way: remove the brake disc and sharpen it on a machine, and process the brake pads using a grinding wheel.
Why do shock absorbers knock?
There are several known reasons for shock absorbers knocking on small bumps.
Deformation of the rod. Counters and burrs on the working surface of the rod, as well as its deformation, will cause knocking. With these defects, the guide bushing breaks, and the rod “walks” in it, producing a characteristic knocking, often dull, sound.
- Lack of oil or gas in the shock absorber. After one of the working media leaks, the rack is no longer able to operate normally. Idling zones appear in which the piston does not transfer oil with resistance, as it should, but simply falls through or shoots off sharply under the influence of a spring.
- Damage to the bump stop. The bumper serves to stop the rod in its extreme position, that is, before it reaches the “dead point” and the impact falls on the rod or cylinder. If the bump stop wears out, the shock absorber strut begins to knock when driving through amplitude holes.
- Overloading the vehicle. One of the most common reasons why knocking occurs in the rear struts, especially after long runs. The free play between the bump stop and the body becomes less and less as the load increases. And when driving over even shallow irregularities, a shock appears: the beam hits the bump stop.
- Broken spring. If a spring breaks, depending on the area of damage, the strut as a solid structure loses its rigidity or stops functioning. Backlash appears between individual elements. This play causes knocking in the shock absorber strut.
Support bearing wear. The upper supports of the front shock absorber struts are designed to ensure their rotation around their own axis when the steering wheel is turned. Wear of the support bearing is one of the reasons for the appearance of extraneous sounds. Production of silent blocks. Rubber-metal bushings, through which the shock absorber is attached to other elements of the chassis or body, break over time. And if the silent block is completely destroyed, a characteristic metallic knock will appear. Incorrect installation. The design of some racks allows for errors during assembly. In this case, visually and when tested outside the working position, the rack will function normally. However, under load, play may appear.
Therefore, if after replacing the shock absorbers a knocking noise appears, you should immediately bring this to the attention of the repairman.
A common question: is it possible to drive if the strut is knocking? You can drive, but at low speed and to the nearest service station. In a MacPherson strut suspension, the strut acts as one of two mounting points that hold the hub. If the shock absorber collapses, one of the two links between the strut and the chassis will be broken, and the car will lose control.
How to correctly identify wear and malfunction
A common sign of wear is looseness of the suspension and extraneous sounds. However, there are a number of signals that relate specifically to racks:
- Unusually high roll in corners.
- When driving over bumps in a long turn, the car tries to “jump off” the trajectory.
- Characteristic knocking noises in the suspension, especially during rebound, when the stabilizer joints are unloaded.
- When braking or accelerating, faint knocking sounds are heard in the suspension.
Operating a vehicle with damaged (worn) stabilizer links can result in loss of control and an accident, especially at high speeds. In addition, when the struts constantly knock, it distracts the driver from driving the car.
Wear of the hinges in the struts is a progressive malfunction. A slight play that appears, especially during movement under load, accelerates the development of the defect and leads to unpleasant consequences.
When the first signs of a malfunction appear, you should carry out diagnostics at a service center or independently check the condition of the racks in order to later restore them or remove and replace them.
Why are the anti-roll bars knocking on a BMW E34 (video)
Can new shock absorbers make knocking noises?
A knocking noise from a recently installed rear shock absorber is a common occurrence.
But car enthusiasts pay attention to new dampers last, first of all, suspecting other elements of the chassis as the source of the knocking. Even newly installed devices can make noise
Possible reasons:
- the product is defective;
- violation of fastening;
- the bushing does not meet the specified parameters.
Manufacturer defects are a rare occurrence, but they should not be discounted. Much more often, knocking occurs due to poor-quality fastening of the device. The movement of the damper along the rack is accompanied by a knocking sound if the nut fixing the element is poorly tightened or loosened during operation. In lever suspensions, knocking can occur due to deformed bushings mounted in the mounting lugs.
Diagnostics of shock absorber struts
If there is even the slightest suspicion of a malfunction, it is necessary to urgently carry out diagnostics. How are shock absorbers checked? There are a number of activities that the car owner can carry out independently, which will become the initial testing of the rack.
Some car enthusiasts prefer to do without testing at the stand and begin to rock their car themselves to determine the wear of the shock absorbers. However, such a check is not very informative, because if the racks are already weakened but functional, rocking will show that everything is in order, but this is not the case.
Replacing the front strut support and bearing
The work is carried out in a garage. The presence of a pit or lift is not necessary.
What tools are needed to replace
- Socket wrench with curved handle.
- Special head for disassembling racks.
Select a head after consulting with a consultant, all tools are different - Long head (candle).
- Special key for the rod.
- The usual kit is a ratchet with a set of heads to match the size of the fastener.
- Torque wrench.
- Tie for strut springs.
Article on the topic: How to drain oil from an engine when changing the lubricant: pumping through a device or by gravity