The brake system is a key element that ensures safe movement in a car. Brake malfunctions are highly likely to lead to accidents, so car owners are required to pay attention to the condition of the brake system cylinders and hoses. At the first hint of a brake malfunction, it is necessary to check their elements and repair or replace parts. The most important component of the brake system is the VAZ 2107 master brake cylinder.
Symptoms of a faulty master cylinder
Problems that arise with the brakes while traveling are considered critical and must be corrected immediately. The culprit of the malfunction is often the main cylinder, installed in the engine compartment and rigidly connected to the pedal. To find out the cause of the breakdown and repair the unit yourself, you need to know the structure of the brake master cylinder (MBC) and its principle of operation. During the diagnostic process, it is necessary to distinguish and filter out problems with other elements of the system.
Absolute vehicle malfunctions
During operation, the braking functions of the system deteriorate. This is due to wear and tear of components, assemblies and parts that require repair. Some vehicle malfunctions are included in a special “List...”, and driving with them is prohibited.
Inefficiency of the working vehicle
The most common malfunction of the brake system (including the VAZ-2107) is inefficiency, which is diagnosed by two main parameters (when carrying out a specialized instrumental study):
- increasing braking distance;
- increase in steady deceleration during braking.
How does the GTZ function?
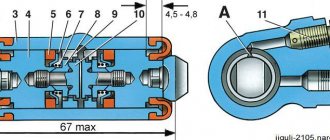
The unit consists of the following parts:
- metal housing with holes for supplying brake fluid, pedal rod and connecting the expansion tank;
- 2 pistons with rubber seals;
- 2 return springs;
- guide bushings;
- end plug with gasket.
An expansion tank is attached to the top of the main distributor body, where excess fluid goes through compensation holes. Inside, the element is divided into 2 cylinders with separate pistons standing on the same axis.
The blind end of the housing is closed with a threaded plug; on the other side there is a flange for attaching to the vacuum booster. The brake pedal rod is attached to the first piston. The brake circuit pipes are connected to the lower holes - separately for the front and rear wheels.
The operating principle of the master brake cylinder looks like this:
- When you press the pedal, both pistons simultaneously move forward and push fluid into the circuit tubes. Under its pressure, the wheel cylinders are activated, compressing the pads on the discs.
- Part of the liquid that does not have time to pass into the tubes flows into the expansion tank through special bypass holes.
- When the driver releases the pedal, the springs push the pistons back, returning them to their original position. Liquid from the tubes and reservoir refills the cylinders.
- To compensate for the expansion of the liquid (for example, from heating), another pair of holes is provided leading to the expansion tank.
Note. The GTZ acts in conjunction with a vacuum booster (not shown in the diagram), which helps put pressure on the pistons. This allows the system to respond faster and make the driver's actions easier.
Summarize
The brake system of the VAZ-2107, like any other car, is an important component of an integral vehicle control system that ensures traffic safety.
Diagnostics and timely repair of vehicles is a vital necessity.
Let's first take a look at what brake systems are available in this car model. There are only two of them:
A working vehicle is used to allow the vehicle to reduce speed and stop. The parking lock fixes the vehicle in a stationary state when the driver needs it. They do not depend on each other, but setting off on a journey knowing that one of them is faulty is strictly prohibited. Naturally, the front and rear brakes should also always be replaced in a timely manner.
Symptoms of problems
The general technical condition of the car (including the brake system) can be checked using a personal diagnostic adapter - a car scanner. These types of devices are widespread and have a wide price range. We would like to draw your attention to the budget model of Korean production Scan Tool Pro Black Edition.
At a cost of about 2 thousand rubles. This scanner is capable of fully diagnosing your car (engine, gearbox, transmission, abs, srs and much more), which will pay for itself in 1-2 trips to the service station. The adapter is quite easy to use, has Russian-language software and is compatible with most cars produced in 1993. The device will also be useful when buying a used car, as it can show its real mileage and VIN.
The fluid brake system consists of many parts that can become unusable: pipes, wheel cylinders, calipers, drums and pads. Typical signs of a faulty master cylinder:
- After pressing the pedal, the car stops slowly. The reason is that the cuffs of one or two pistons have lost their tightness - they have cracked or “floated”.
- To slow down, you need to press the brake pedal hard. The phenomenon occurs due to swelling of the rubber of the piston seals.
- The brake pedal travel is too short. The fluid inside the cylinder has nowhere to go because the compensation hole is clogged. Another option is that the passage is blocked by a swollen rubber seal.
- A common symptom is pedal failure, the brakes coming on at the end of the stroke. This indicates complete wear of the cuffs; as a result, liquid penetrates behind the piston and rushes into the expansion tank - the cylinder “bypasses.”
- The pads do not release the brake discs and drums and get very hot when driving. Options: one of the pistons is jammed or the bypass hole is clogged.
The listed symptoms of a GTZ malfunction are similar to malfunctions of other elements. Pedal failure also occurs when a large amount of air enters the tubes or loss of fluid in one of the working cylinders. Sluggish deceleration and increased force on the pedal are often caused by a breakdown of the vacuum booster - a cracked membrane or a lack of tightness at the joints of the hose that takes off engine vacuum.
There are signs that clearly indicate the performance of the main hydraulic cylinder and the malfunction of other elements:
- during braking, the car pulls to the side - the problem lies in a certain circuit or wheel;
- jamming of the brake mechanisms of one wheel;
- creaking and squeaking when braking;
- heating the discs and pads on one wheel.
If you eliminate these symptoms, it will become easier to check the brake master cylinder in a garage. This also includes obvious brake fluid leaks and the knocking sound of worn calipers.
Why did it happen so?
Perhaps the automatic requests do not belong to you, but to another user accessing the network from the same IP address as you. You need to enter the characters into the form once, after which we will remember you and be able to distinguish you from other users exiting from this IP. In this case, the page with the captcha will not bother you for quite a long time.
You may have add-ons installed in your browser that can make automatic search requests. In this case, we recommend that you disable them.
It is also possible that your computer is infected with a virus program that is using it to collect information. Maybe you should check your system for viruses.
If you have any problems or would like our support team, please use the feedback form.
A fully operational brake system of a VAZ 2107 car is a key element in ensuring safe movement in a car for both passengers and the driver. Therefore, you should pay special attention to it, and if minor signs of malfunction appear, begin repairs immediately.
The brake master cylinder is one of the main elements of the car's braking system. Basically it can have two faults. The first is the appearance of a fluid leak from the main brake, the second is a decrease in the effectiveness of the brakes, which can be determined by the failure of the pedal or its “softness”. Both of these faults can be eliminated by a not very complicated repair of the main brake; this repair consists of replacing the o-rings and boot, but in some cases the problem can only be solved by replacing the cylinder.
Diagnostics and repair
From the signs listed above, it is easy to understand that in most cases there is only one source of problems - rubber products that have become unusable. The cuffs crack and swell, as a result they leak liquid and close the discharge holes. Hence the recommendation: all “rubber bands” of the brake system should be changed at intervals of approximately 100 thousand km, without waiting for critical wear.
Reference. Many auto mechanics express the opinion that after replacing the cuffs, the main hydraulic cylinder will not last long. The statement is true if the car owner purchased cheap, low-quality spare parts or installed new o-rings in the cylinder, where internal wear has formed in the walls.
Before checking the GTZ for operability, make sure there are no other faults:
- Inspect the wheel assemblies from the inside for leakage of brake fluid from the working cylinders.
- Check the integrity of the expansion tank and the fluid level in it.
- Start the engine and at idle speed, press the vacuum take-off pipe to the amplifier. If the engine speed has increased noticeably, there is an air leak and the master cylinder is most likely working.
A clear symptom indicating a breakdown of the main hydraulic cylinder is drops of brake fluid on the body . If you discover a leak, feel free to dismantle the unit and disassemble it to look for the cause. Another common problem - fluid flowing through the seals - is diagnosed as follows:
- Open the cover of the expansion tank and place an assistant in the driver's seat.
- Listening to sounds in the tank, give the command to an assistant to press the pedal.
- If the pedal moves easily and gurgling is heard in the reservoir, liquid is entering there. The reason is that worn cuffs are unable to create pressure in the circuits; liquid seeps through the leaks and enters the container.
Also, problems with the GTZ are indicated by jamming or too little pedal travel.
Sit behind the wheel, press it several times, and start the engine while holding the pedal with your foot. If it sinks to the floor or does not budge, disassemble the hydraulic cylinder. To replace or repair the master brake cylinder, you need to remove the unit from the vehicle. Work is carried out in the following order:
- Suck out the liquid from the tank with a syringe. If the cuffs are leaking, press the pedal several times and suck out the excess fluid.
- Remove the expansion tank.
- It is not necessary to drain all brake circuits. Substituting a small container, unscrew the nut of the first tube and carefully move it to the side, plugging it with a wooden stick.
- Repeat the operation with the second tube, unscrew the fastening of the GTZ flange and remove the unit.
Further actions depend on the design of the master cylinder. If the element is completely disassembled, change the rubber seals. Otherwise, you will have to replace the pistons assemblies. Pre-wash the body and all openings with alcohol; do not use gasoline. After assembly, add fluid and bleed the brake system to remove air.
Source
Replacement
Replacing the part yourself is not difficult. To do this, you need to arm yourself with the following set of tools:
- screwdriver;
- keys 10, 13;
- 5 – with a cubic syringe or bulb;
- brake fluid;
- clamps.
If during disassembly you find that the old rubber hoses have become hard, it is recommended to replace them with new ones.
- Remove the belt from the expansion tank and put it aside.
- Using a ten key, unscrew the fastenings of the brake fluid reservoir and open the lid.
- Drain the brake fluid into a container.
- To prevent brake fluid from entering the engine compartment, it is necessary to place a piece of dense material under the cylinder.
- Loosen the clamps on the hoses extending from the tank and remove them.
- Disconnect the three brake pipes and move them a little.
- We unscrew the two nuts securing the cylinder to the amplifier, using a 13mm wrench.
- Remove the brake master cylinder.
- We clean the seat of the spare part from dirt and brake fluid residues.
- Let's move on to a new element. We remove the protective seal and install the oil seal there.
- We insert the new cylinder into place and tighten the nuts.
- We remove the plugs and use a syringe to inject brake fluid into the cylinder cavity until it is completely filled.
- We assemble the remaining elements.
The final stage of repair work will be bleeding the car's brake system.
How to check the brake master cylinder
A smooth or sharp dip in the brake pedal, or its floating and vibration during braking, usually indicates a malfunction of the brake master cylinder . Most often, the reason for its malfunction is the loss of tightness of the rubber sealing cuffs or improper operation of the bypass valves.
To distinguish its malfunctions from other malfunctions of the brake system and find out how to check whether the master cylinder is working, read the article.
Repair of the front brake mechanism of VAZ-2107
Replacing the front wheel brake caliper
Remove the front brake pads (see Replacing the VAZ-2107 pads).
Disconnect the brake hose from the caliper.
Use a chisel to bend the locking plates of the two caliper mounting bolts
Use a 17mm socket to unscrew the two caliper mounting bolts.
You can remove the caliper and brake pad assembly. To do this, simply disconnect the brake hose from the caliper and unscrew the caliper mounting bolts.
Install the caliper in the reverse order of removal.
After replacing the caliper, bleed the brake system (see Replacing brake fluid on a VAZ-2107).
How to understand that the GTZ is bypassing brake fluid?
Vehicles use a system with two separate hydraulic circuits. You can read in detail about its task and work separately. The general principle is that when the brake pedal is pressed, the vacuum booster rod acts on the first piston of the GTZ, which, by compressing the brake fluid supplied from the reservoir, creates excess pressure in circuit 1 directly, and in circuit 2 indirectly by moving the second piston.
GTZ device diagram, click to enlarge
If the piston seals are severely worn, the GTZ bypasses: the liquid passes between the walls of the housing of the first, second or both pistons in the opposite direction and returns to the expansion tank. As a result, necessary to act on the brake cylinders is not created
There are two simple ways to check the operation of the brake master cylinder for bypass of brake fluid:
Method number 1 (performed with an assistant)
- Unscrew the cap of the expansion tank in the engine compartment.
- Have an assistant press the brake pedal while observing the condition of the fluid.
- If, when pressed, the level decreases and remains until the pedal is released, the cylinder is in good condition.
- If the fluid level begins to increase when the pedal is pressed or bubbles appear and gurgling is heard, the GTZ is bypassing.
Vacuum brake booster
A rod connected to the amplifier is connected to the pedal. The design of the VAZ-2107 vacuum brake booster is quite interesting; it is shown in the figure:
The amplifier is a sealed container, internally divided into 2 chambers by means of a membrane. The chamber located closer to the pedal is called atmospheric, and the chamber separated from it by a membrane is called vacuum. The diaphragm itself is connected to the piston rod of the master cylinder.
The vacuum chamber is connected by a pipe to the intake manifold of the engine, where the vacuum comes from. The design also includes a follower valve controlled by the pedal rod, which does all the work.
When the pedal is released, this valve connects the chamber cavities through a channel, providing identical pressure. When the pedal is applied, the valve closes the channel connecting the chambers and opens the channel connecting the atmospheric chamber with the atmosphere. Since a vacuum is maintained in the second chamber, atmospheric pressure begins to put pressure on the membrane. Since it is connected to the piston rod of the master cylinder, due to the movement of the piston, fluid is displaced from the cylinder into the pipelines.
Signs of a faulty master cylinder
Among the symptoms indicating a malfunction of the master brake cylinder, the main signs can be identified:
Checking the GTZ in 5 minutes without removing it from the car: video
- pulling the car to the side when braking;
- overheating of the pads on one wheel;
- squeaks when pressing the brake pedal;
- pedal travel is too soft or hard;
- shortened pedal travel;
- brake pedal failures;
- holding the wheels with blocks after releasing the pedal;
- fluid leaks on the GTZ housing.
Most signs of a brake system malfunction appear when the brake pedal is pressed and are similar to other problems with the brake system. In particular, the failure of the pedal may indicate congestion or depressurization of the lines. Therefore, before checking the serviceability of the master brake cylinder, it is necessary to at least check the level of brake fluid in the reservoir, as well as the condition of the pads, discs and hoses .
How to Diagnose a Malfunctioning Master Cylinder
| Symptom of malfunction | Why is this happening? | Alternative reasons |
| Slow braking |
|
|
| Great force when pressing the pedal |
|
|
| Short brake pedal travel | ||
| The pedal gets stuck while driving |
| |
| Pedal failure near the end of the stroke |
|
|
| The pads continue to hold the discs |
|
|
| The pads and disc/drum on one wheel get hot |
| |
| The car pulls to the side when braking | ||
| Squeaking/creaking noise when braking |
|
|
| Slow return or stuck pedal when released |
|
|
Braking system of modern cars
The general braking scheme on modern cars suggests the presence of three main types:
The working vehicle performs the functions of reducing the speed of the vehicle or stopping it.
The spare vehicle is intended to prevent malfunction or failure of the working system.
The parking vehicle performs the functions of holding the vehicle stationary in special conditions and in parking mode. The VAZ-2107 implements a working and parking vehicle in a “pure” form.
In a modern car, braking can be performed not only by the vehicle itself, but also by the engine, electric or hydraulic transmission brake. In addition, additional systems (or devices) are often implemented that increase the productivity of braking functions:
- anti-lock braking system (the notorious ABS);
- electric brake force distribution (or EBD);
- electrical stabilization system (ESP), etc.
The described devices and systems lead to a significant increase in the cost of the vehicle, and the VAZ-2107 brake system diagram does not provide for them.
However, domestic cars have recently begun to provide similar capabilities.
FAQ
When the engine is running, the pedal slowly sinks to the floor with constant force, is it necessary to change the turbocharger?
Smooth subsidence of the pedal is a frequent sign of leaking GTZ seals. In this case, it is possible to repair the part by installing new cuffs from the repair kit.
Brake fluid leaves the reservoir, but then appears, is it the GTZ?
Changes in the level of brake fluid in the reservoir are not necessarily a sign of a breakdown of the turbocharger. The fuel fluid can also either go down or rise due to airing, boiling due to overheating of the pads, or jamming of the actuator cylinders.
Does it make sense to install a repair kit or is it better to replace the GTZ?
It makes sense to install a repair kit when only the rubber parts are worn out. If the piston is severely worn or the housing is damaged, it is better to replace the entire turbocharger.
Comments
The GTZ will need to be replaced. Thank you.
- Login to leave comments
Well written. At
Well written. With a certain amount of skill, if you are clever and quickly “close” the fittings of the main pipes when removing, you can do without pumping, or do the bleeding “by gravity.” Caps from GTZ are excellent for closing fittings.
From personal experience, I will say that the VAZ GTZ is complete nonsense at a cost of 80-100 UAH (10-15 $) and a service life of 1-1.5 years. Two main disadvantages: 1. Low-pressure nylon fittings are held in place by crown-springs (bad metal), and with a little effort they pull out of the socket - they were adjusting the valves and accidentally touched the repair belt. I used the kit as a temporary measure. 2. after 20 thousand-30 thousand km the piston in the cylinder begins to bypass. It manifests itself - the pedal is either soft or hard, there is a dependence on the ambient temperature and the intensity of the impact on the pedal, pumping the brakes does not help.
After replacing two VAZ stock units every year, I installed an Italian one (I don’t remember the name) and forgot about the existence of such a part as a GTZ in my car. The main difference from the VAZ one is the metal low-pressure fittings. issue price 25-30$
- Login to leave comments
Which cylinder to install if replacing?
To avoid problems during operation, it is better to find the original Togliatti-made GTZ, catalog number 21013505008. But since the VAZ 2107 family of cars has not been produced for a long time, finding this spare part becomes difficult, especially in remote regions. An alternative is products from other manufacturers that have proven themselves well on the Russian market:
Judging by the reviews of the owners of the “Seven” on thematic forums, defects most often come across among the products of the Phenox brand. Advice regarding the purchase of original spare parts: do not purchase them in markets and unverified stores; many counterfeits are sold at such points.
Defective spare parts were also found during the Soviet era. I remember an incident from childhood when my father took me to drive his first Zhiguli from a car dealership. We covered the 200 km journey all night, because the pads on the rear and front wheels spontaneously compressed and the rims became very hot. The reason was found out later - a defect in the factory master cylinder, which was replaced free of charge at the service station under warranty.
Removing air by pumping
If during the repair process a lot of fluid leaks from the circuit and air bubbles form in the system, the repaired hydraulic cylinders will not be able to function normally. The circuit must be pumped using the instructions:
- Place a spanner and a transparent tube directed into the bottle onto the discharge fitting.
Before removing air and during the bleeding process, the tank is replenished with new fluid. A working substance filled with bubbles and poured into a bottle cannot be reused. Upon completion of the repair, check the operation of the brakes while driving.