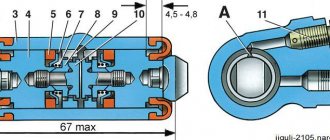
Rear cylinder design
Replacing the rear brake cylinder of a VAZ 2109
In turn, the cylinder consists of:
- Brake fluid reservoir. A special sensor regulates the liquid level;
- The housing in which the pistons and return springs are concentrated;
- Return springs, allowing the pistons to return to their original position after pressing the brake;
Note: The brake fluid reservoir does not have to be installed on the actual cylinder. It can be installed in another location if it is more convenient. It is important that it is connected to the cylinder cavity through tubes.
Replacing the rear brake cylinder on a VAZ 2109
- Sealing cuffs that create the correct pressure in the tank;
- Pistons with pushers;
- Differential pressure sensor.
Note: with its help, the driver learns about the loss of tightness in one of the circuits.
How it all works
Replacing the rear brake cylinders of a VAZ 2109
As a rule, in normal condition and under optimal environmental conditions, the cylinder works like this:
- To slow down, the driver needs to press the brake. After this, the force is transmitted along the rod to the piston. This rod moves forward, helping to close the compensation hole. Thus, the brake fluid pressure begins to increase.
Note: the same thing happens in the front cylinder, which helps the car brake quickly.
- After the car has been stopped, the driver stops pressing the pedal. As a result, the pistons return to their original positions. In addition, the pistons begin to act together with the reservoir. This helps the pressure in the second level out and become similar to atmospheric pressure. In addition, the wheels also return to their original position.
This is interesting: Repair and replacement of the gas tank on a VAZ 2108/09/14/15: how to do it quickly, accurately and with your own hands
Symptoms indicating a malfunction
The main signs of poor brake performance can be caused by all components in this circuit: rear or front circuits with pipes, malfunctions of the master cylinder or poor pedal adjustment:
- Unusual behavior of the car when braking or a “soft” brake pedal indicates that the pedal requires adjustment or that air has entered the system and needs to be bled.
- The corresponding indicator light comes on, the pads may be worn out or the entire system needs to be bled.
- There are stains under the bottom and upon visual inspection, leaks are visible. Somewhere the pipe fitting is leaking hydraulic fluid, or the cuffs are worn out.
- When checking the pressure in the circuits, it does not coincide with the control figures - the main roller is unstable, namely, the fitting unevenly bypasses the liquid or it flows in one of them. The cause may also be poor quality hydraulic fluid; replacing and pumping in this case may help.
If some of these signs are detected, there is no need to rush to conclusions that the master brake cylinder needs to be replaced; perhaps bleeding the system can help, but even if this does not give results, do not rush to change it, perhaps it can be repaired. You can always find spare parts on sale in the form of a master brake cylinder repair kit, which may include: a fitting, pistons, cuffs, springs, retaining rings, etc.
Some tips
- If you start having problems with the brakes, first of all you need to carry out an external inspection of the vehicle: check the fluid level in the reservoir, make sure that the front/rear cylinders are not leaking. There should not even be stains of brake fluid in the brake hydraulics.
- “Brake fluid” must be filled with the same brand; it is recommended to completely replace the brake fluid at least once every two years.
- If faults are identified in the gas turbine engine, and it has already served for at least a year, it is more advisable to replace it completely than to repair it. The same can be said about the rear working cylinders.
- Before changing the turbocharger, the brake fluid should be removed from it; this operation is usually done using a syringe.
- Usually a leak in the master cylinder is not visible, but if there is any suspicion that this part is faulty, you should remove the main cylinder - there will be traces of leaks at the rear, and this indicates its faulty condition.
- If, during an external inspection, cracks were found on the brake hoses, it is better not to take risks and immediately replace the defective parts.
Brake master cylinder device
The principle of operation and design of the brake master cylinder is similar to the clutch master roller, given that in many cars one mechanism performs double duty. But in many cars, there are two pistons located in the brake drum to operate the front and rear or left and right circuits, depending on the make of the car. After disassembling the brake master cylinder, you can see the following main spare parts:
1, 2 — Tank cover with gasket. 3 - Brake master cylinder reservoir. 4 - Bushings for the bypass fitting. 7 - Tank body. 10, 28 — Return springs. 12, 26 — Internal cuffs. 13, 25 - Bypass valves. 14 - Piston that activates the front brakes. 15, 16 — External cuffs of the front drive brakes. 20, 22 — Outer cuffs of the rear brake drive. 24 - Piston responsible for operating the rear brakes.
Operating principle of the brake system
The operating diagram of the hydraulic drive of this system is simple: a depressed pedal that acts on the vacuum booster (if provided), or directly on the main brake cylinder, the latter, creating pressure on the hydraulic fluid, sends it through the pipes to the working rollers that release the brake pads.
It follows that the main unit in this diagram is considered to be the main cylinder; to understand how to repair the main brake cylinder with your own hands, you need to study all its components.
Replacing the drum
How to replace the brake master cylinder? All actions are carried out as during its repair. Pump out the hydraulic fluid from the reservoir, disconnect all the pipes from the housing, disconnect the roller itself from the vacuum booster or car body and from the brake pedal. Installation of the master cylinder is carried out in the reverse order. After completing all repairs, you should bleed the brakes. Bleeding is carried out according to the following scheme: rear right and left wheels and then the front ones. After bleeding, the brake pedal height is adjusted.
We also recommend watching videos on the topic:
GTZ malfunctions
Main malfunctions of the main brake cylinder:
- wear of rubber sealing elements;
- formation of scratches and rust on the inner surface of the GTZ;
- air entering the GTZ.
During braking, the temperature in the working cylinders increases greatly, which leads to strong heating of the brake fluid. After 1–2 years, the properties of the fluid begin to change, which leads to increased wear of the rubber seals. After all, particles of metal oxides and hydroxides, as well as microscopic fragments of rubber seals, get into the liquid. As a result, the seals, and often the inner surface of the turbocharger, wear out, which leads to brake fluid leaks.
If there is even a small leak somewhere in the brake system, the fluid level in the reservoir will continually drop. When a critical value is reached, air may enter the GTZ, which will greatly reduce braking efficiency. The more air, the worse the system works. In some cases, the brakes only work after 4–5 presses of the pedal.
Manufacturers of repair kits
Popular manufacturers of brake master cylinder repair kits used in our country are the following companies:
- JSC "Volzhskrezinotekhnika" The company produces repair kits for domestic cars - “Zhiguli”, “Moskvich” and other popular brands (for Moskvich 2140 it consists of 3 pairs of cuffs, each of which has its own cat. no. 412-3505045, 042 and 036).
- FENOX Global Group (Belarus). The company produces a wide range of repair kits for domestic and foreign cars. In particular, for VAZ-2101, 2106, 2107 and VAZ-2121, the catalog number of the GTZ repair kit is KPT1963C3, the price of the repair kit is $1.3...1.7. And for Moskvich 2140-3505032.
- PJSC “Balakovorezinotekhnika”. Manufacturer of rubber products, producing more than 6,000 items and ensuring uninterrupted operation of VAZ, KamAZ, GAZ automobile conveyors (catalog number for the GTZ repair kit for VAZ 2108-09 cars is 21080350503300, repair kit from the manufacturer, price - about $1).
- Basalt company. Russian manufacturer producing GTZ repair kits for domestic cars.
- SEIKEN. A manufacturer from Japan that produces repair kits mainly for Japanese cars (for example, HONDA, kit catalog number - SK62811, price of a brake master cylinder repair kit - $16...18).
- Aisin Seiki Co Ltd (or simply Aisin). Another Japanese company producing components for car assembly plants. It produces a lot of products for Toyota.
- SEGURIDAD INDUSTRIAL, SA (SEINSA), Spain. Manufactures products, including GTZ repair kits under the AUTOFREN trademark. Used in many European cars. (for example, the catalog number of the set is D1298, the price is $2...3).
- DELPHI company, USA. Its repair kits are used on both American and European cars (for example, Mercedes).
- ATE, Germany. Produces repair kits for European cars (for example, catalog number 03037030232, the price of a GTZ repair kit is $20...25).
I would like to remind you that...
Using the GTZ repair kit, you can eliminate only minor malfunctions in its operation - brake fluid leakage, smooth operation of the pedal, adjustment of the brake system. If the cylinder is physically damaged, then in most cases it must be completely replaced, and unfortunately, replacing the cuffs is not enough.
Upon completion of the work on replacing the master cylinder repair kit, do not forget to bleed the brake system to ensure that it is tight and free of air. And before heading out on the road, test the effectiveness of the braking system near the garage, while observing safety rules.
Repair
Replacing rear brake cylinders on a VAZ 2109
If the brake cylinder is leaking, it must be replaced. But you don’t always have to buy a new one to do this. You can simply repair the old one. To do this, you need to buy cuffs in advance. As a rule, they are sold together with a boot and a pump. To do this, you need:
- Raise the car using a jack.
Note: To prevent the car from rolling away, place bricks on both sides under the wheels.
- Remove the wheel, but before doing this it is advisable to unscrew all the nuts that hold it in place. The key for 19 will help with this.
Note: the removed wheel must be put in its place, but not vertically, but horizontally. To equalize the height of the wheel with the height of other wheels, you can place some objects. Now you can lower the car and put the jack aside.
- Then the disk is removed.
Replacing the rear brake cylinder of a VAZ 2109
Note: under no circumstances should you hit the edge directly with a hammer, as you may break off the shells. It is advisable to do this through some kind of attachment (this is a small object that is adjusted to the edge, and then hit with a hammer).
- Unscrew all the nuts that hold the drum. Afterwards you can easily remove it.
Note: The brake cylinder will now be accessible.
- Remove the brake cylinder.
- Before you start repairing it, you need to lubricate the cuffs and boot with brake fluid so that they become slippery.
Replacing rear brake cylinders on a VAZ 2109
- Replace old cuffs with new ones. Insert the boot into place.
Note: After this, tighten it using a pump that was created specifically for this (it is included in the kit).
- Return the cylinder to its place.
Note: You need to press it lightly. To make it easier to fall into place, it needs to be shaken a little.
- You can twist it. To do this, you need to use a key of 10.
Note: the disadvantage of the rear cylinder is that there is no way to screw it with a head, which would be much easier.
- After this, you need to take a flat-head screwdriver and place the cylinder straight.
- Then you need to start screwing on the brake pads.
Note: The ends of the shoes must connect to the holes in the cylinder.
- Screw the pads so that they are stationary. The pads must be connected using springs.
- Return the drum, disc and wheel itself to their place.
This is interesting: Car suspension diagnostics on your own
What does brake diagnostics at a service station include and provide?
The car's brake system is diagnosed in six stages to ensure an accurate and correct result:
- from the interior, check the pedal travel and the correct adjustment of the handbrake;
- check the level and condition of the brake fluid. Then the main cylinder and the tubes that come from it are inspected;
- inspect the wheels for oil stains;
- inspect the working cylinders (calipers), hoses and tubes for corrosion, visible damage, deformation and fogging;
- check brake discs, drums and pads. If the thickness of the element approaches critical, the worn parts are replaced;
- check the car's brakes while driving, measure the braking distance and the degree of deceleration. They also make sure that the car does not deviate to the side.
A common mistake drivers make is not wanting to go to a car service center. Instead, the owner of a salvage vehicle decides to check the brakes himself and misses 9 out of 10 problems because he does not know what to look for or where.
For example, there was a problem with the brake caliper jamming. First of all, the driver will check the general condition of the pads, disc, caliper and, with a 95% probability, will not find the true cause, for example, a malfunction of the guide brackets, which have rusted and soured. The elements are protected by elastic covers, on which it is almost impossible to notice a crack. If the boot bursts, the guide rusts and the bracket moves worse. The result is that the disc mechanism wears out faster and soon you will need to buy a brake caliper, and with it new discs and pads for the damaged axle.
If moisture has accumulated on the guide boot and rust is visible on the bracket, the auto mechanic will disassemble the caliper and check the condition of the assembly elements. Thus, the cost of repairs will be 2-3 hundred hryvnia (the price of a pair of guides and a repair kit) instead of 3-5 thousand (the price of a new caliper, disc and pads). The price difference is noticeable and makes you wonder - is it worth the risk?
At the slightest sign of a brake system malfunction, take the car for diagnostics. Based on the test results, the technician will provide a report on the condition of the brakes and offer options for solving the problem. If the damage is minimal, repairs will be limited to replacing the caliper repair kit, brake fluid and bleeding the brakes. You may need to change the pads, discs or hose, but this is cheaper than the cost of a new disc or drum brake assembly.
An additional plus to regular diagnostics is that if, based on the diagnostic results, the client decides to have the brakes repaired at the same car service center, the auto mechanic will not charge a penny for the inspection.
Dismantling and repair of GTZ
After dismantling the GTZ, it is necessary to carefully inspect it for fluid leaks. If the rear oil seal is damp or damp, most likely some of the brake fluid has entered the VUT and is corroding its membranes. It is necessary to pump out the liquid from the VUT using a syringe and a thin tube.
To disassemble the GTZ, drain the liquid from it, then carefully clamp it in a vice so that the holes for installing the tank are at the bottom. Remove the locking screws that prevent the pistons from returning too far. Remove the GTZ from the vice and use a puller to remove the retaining ring from the VUT side. Pull out the first piston and spring. Often the second piston comes out with difficulty, so you have to either knock the gas turbine engine on a wooden block, or plug one of the holes in the far cylinder using a suitable bolt and connect a compressor with a pressure of at least 6 atmospheres to the second hole. When removing the pistons, be sure to remember how the rubber seals are installed and how the pistons are located, this will greatly help during assembly.
Carefully inspect the inner surface of the GTZ. Any scratches lead to a decrease in braking efficiency and are therefore unacceptable. If scratches are found on the inner surface, the body or the entire GTZ must be replaced. After making sure that the internal surface of the GTZ is not damaged, buy the appropriate repair kit. When choosing a repair kit, give preference to products that are manufactured by partner enterprises of major automakers. Often original repair kits from one brand or model fit another.
Remove all old rubber seals from the pistons. Wash the pistons with water and dry with compressed air. Install new seals from the repair kit. Before installing, be sure to lubricate them with brake fluid, this will make them easier to fit into place and prevent damage. Do not confuse the direction of installation of the cuffs. Before assembling the GTZ, wash its body with water and detergents, dry it with compressed air and lubricate it generously with brake fluid. Do not use gasoline or other petroleum products for flushing; if you do not wash them off properly, they will corrode the rubber seals. Reinstall the pistons, tighten the retaining bolts, and insert the rear oil seal and retaining ring.