↑ VAZ 2106 engine compartment photo
- – radiator;
- - accumulator battery;
- – suction pipe;
- – air filter housing;
- – oil filler plug;
- – vacuum brake booster;
- – brake system reservoir;
- – hydraulic clutch release reservoir;
- – expansion tank of the cooling system;
- – washer reservoir;
- - ignition coil;
- – radiator cap (plug);
- – electric fan;
- – upper radiator hose;
- – breaker-distributor;
- – cylinder head cover.
How to light the engine compartment video
Low beam relay
NOTE
The relay for turning on the high and low beam headlights and the relay for turning on the radiator fan of the engine cooling system are of the same type (90.3747-10 or 113.3747-10), are interchangeable and are replaced in the same way.
Relay for direction indicators and hazard warning lights on a VAZ 2106 car
The turn and hazard warning relay on the six is located behind the instrument panel. It is located approximately behind the tachometer.
Relay for wipers - glass cleaners VAZ 2106
The wiper relay on the VAZ 2106 is located in the legs on the left side under the trim. It seems to be to the left of the hood release lever and the main fuses.
Well, that's it, we've looked at the main standard relays and fuses on the VAZ 2106. Bye everyone.
Source
↑ Engine
The car is equipped with a gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, eight-valve engine with an overhead camshaft.
- The power supply system is carburetor.
- The operating order of the cylinders is: 1–3–4–2, counting from the crankshaft pulley.
↑ Differences between VAZ-2103 and VAZ-2106 engines
The VAZ-2103 engine differs from the VAZ-2106 engine in its smaller cylinder diameter (76 mm versus 79) and, accordingly, the cylinder block, the size of the pistons and piston rings, as well as the cylinder head gasket.
The cylinder heads of both engines are the same and their parts are interchangeable. The engine cylinders are arranged vertically in one row and combined into a block.
A block head common to all cylinders is installed on top of it. The bottom of the cylinder block is covered with a stamped steel pan, which also serves as a container for oil.
The pistons have two compression rings and one oil scraper ring. The crankshaft rotates in five bearings in the cylinder block. From the pulley at its front end, a V-belt drive drives the generator and coolant pump located on the right side of the engine.
In the front part of the engine there is a drive for the camshaft and a drive shaft for auxiliary units: ignition distributor, fuel and oil pumps. The drive is carried out by a double-row bush-roller chain.
On the right side of the engine, in addition to the generator, there is an exhaust manifold, starter and intake pipe with a carburetor and air filter. On the left side there is an oil filter.
General information about the car
General view of the car
Technical characteristics of cars of the 2106 family
| Index | VAZ-2106, VAZ-21065 | VAZ-21061, VAZ-21065-01 | VAZ-21063 |
| Total information | |||
| Number of seats including driver | 5 | ||
| Curb weight, kg | 1035 | ||
| Total weight, kg | 1435 | ||
| Overall dimensions, mm (length x width x height) | 4166x1611x1440 | ||
| Maximum speed, km/h: with full weight with one passenger | 148 150 | 148 150 | 143 145 |
| Acceleration time from standstill with gear shifting to 100 km/h, s: with full weight with one passenger | 17,5 16 | 19 17 | 21 19 |
| Smallest turning radius along the track of the outer front wheel, m | 5,6 | ||
| Maximum climb overcome by a vehicle with full weight without acceleration in first gear, % | 36 | ||
| Engine | |||
| Model | 2106 | 2103 | 21011 |
| Type | four-stroke petrol carburetor | ||
| Number and arrangement of cylinders | Four in a row | ||
| Cylinder diameter x piston stroke, mm | 79×80 | 76×80 | 79×66 |
| Cylinder displacement, cm3 | 1569 | 1458 | 1295 |
| Compression ratio | 8,5 | ||
| Rated power at crankshaft speed 5600* min1, kW (hp): according to GOST 14846 according to DIN 70020 | 55,5 (75,5) 56,6 (77,0) | 53,3 (72,5) 54,4 (74,0) | 47 (63,5) 48 (65,0) |
| Maximum torque at crankshaft speed 3400** min1, N-m (kgf-m): according to GOST 14846 according to DIN 70020 | 116(11,8) 118(12,0) | 104(10,6) 106(10,8) | 93 (9,5) 95 (9,7) |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 | ||
| Transmission | |||
| Clutch | single-disc dry with central pressure spring; hydraulic clutch release drive with servo spring on the pedal | ||
| Transmission | mechanical three-way four-speed with synchronizers in all forward gears | ||
| Gearbox ratios***: first gear second gear third gear fourth gear reverse | 3,24 (3,67) 1,98(2,10) 1,29(1,36) 1,00(1,00) 3,34 (3,53) | 3,75 (3,67) 2,30(2,10) 1,49(1,36) 1,00(1,00) 3,87 (3,53) | 3,75 (3,67) 2,30(2,10) 1,49(1,36) 1,00(1,00) 3,87 (3,53) |
| Cardan transmission | two shafts with an intermediate elastic support, connected to the gearbox shaft with an elastic coupling; two rigid universal joints at the ends of the rear shaft have needle bearings | ||
| main gear | conical hypoid | ||
| Final drive ratio*** | 4,1 (3,9) | 4,1 | 4,1 (4,3) |
| Chassis | |||
| Front suspension | independent wishbone with coil springs, telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers and anti-roll bar | ||
| Rear suspension | dependent rigid beam connected to the body by one transverse and four longitudinal rods, with coil springs and telescopic shock absorbers | ||
| disk, stamped | |||
| Rim size | 127J-330 (5J-13) | ||
| Tires | chamber, radial 165/80 R13 or 175/70 R13 | ||
| Steering | |||
| Steering | injury-proof | ||
| Steering gearbox | globoidal worm with double-ridge roller, gear ratio 16.4 | ||
| Steering gear | three-link, consists of one middle and two lateral symmetrical rods, bipod, pendulum and swing arms | ||
| Brakes | |||
| Service brakes: front rear | disc drums with self-centering pads, with automatic restoration of the gap between the pads and the drum, with rear brake pressure regulator | ||
| Service brake drive Parking brake | foot hydraulic double-circuit, with vacuum booster manual with cable drive on the brake pads of the rear wheels | ||
| Electrical equipment | |||
| Electrical wiring system | single-wire, the negative pole of the current sources is connected to ground | ||
| Accumulator battery | capacity 55 Ah at 20-hour discharge mode | ||
| Generator | AC with built-in rectifier, output current 42 A at 5000 min1 | ||
| Starter | with electromagnetic traction relay and freewheel, power 1.3 kW | ||
| Spark plug | A17DV, A17DVRM, BRICK L15Y, NGK BP6ES | ||
| Body | |||
| Model | 2106 | ||
| Type | all-metal monocoque four-door sedan | ||
The small class car VAZ-2106 (export version of the Lada-2106) with a four-door sedan body is equipped with a 2106 engine with a displacement of 1.57 liters and a power of 75.5 hp, located in front along the longitudinal axis of the car.
Production of the VAZ-2106 began in 1976 at AvtoVAZ OJSC; it is a modernization of the VAZ-2103 car.
The modernization of the VAZ-2106 car was carried out for the first time in 1982 and has been carried out several times since then. For example, in 1998, the thin slippery steering wheel was replaced with a Nivovsky one, and the uncomfortable leatherette seats were replaced with anatomical fabric ones.
In July 1998, production of the VAZ-2106 car and its modifications at AvtoVAZ OJSC was stopped and at the same time started at the RosLada plant in Syzran. Since the end of July 2001, the production of this model from vehicle kits began at DOAO Izhmash-Avto.
The vehicles are designed for use on roads with improved surfaces in various climatic conditions. All cars are equipped with an all-metal four-door sedan mod body. 2106 supporting structure. Cars are equipped with carburetor gasoline engines and four- or five-speed gearboxes. Front suspension: independent spring; rear – dependent spring. The braking system is dual-circuit, with disc brakes on the front wheels and drum brakes on the rear. All cars are equipped with radial tubeless tires. An anti-theft device is installed on the steering column, built into the ignition switch (lock).
The VAZ-2106 family of passenger cars includes the following main modifications:
VAZ-2106, VAZ-21065-00 - with an engine of the VAZ-2106 model;
VAZ-21061, VAZ-21065-01 – with a VAZ-2103 model engine;
VAZ-21063 – with an engine of the VAZ-21011 model.
The VAZ-21065 car is considered a “luxury” version of this family and has the following differences from the VAZ-2106 car.
A five-speed gearbox and a final drive with a gear ratio of 3.9 are installed. The gear ratios of the five-speed gearbox are as follows:
– first gear – 3.67;
– second gear – 2.10;
– third gear – 1.36;
– fourth gear – 1.00;
– fifth gear – 0.82;
– reverse – 3.53.
Some cars are equipped with a Solex type carburetor 21053-1107010 and a contactless ignition system. The wheels are used from a VAZ-2105 car, and tires are installed like EX-85 or IN-251, size 175/70 R13. The car's electrical equipment adds an electrically heated rear window, halogen headlights and a rear fog lamp. In the body, the upholstery and headrests of the seats have been changed, bumpers mod. 2105.
“Classic” VAZ models are well studied in operation, spare parts for them are available everywhere, so maintenance and repairs do not cause much trouble and expense.
Engine compartment of VAZ-2106 (top left view
): 1 – windshield washer reservoir; 2 – ignition coil; 3 – fuel pump; 4 – ignition system distributor; 5 – radiator of the engine cooling system; 6 – engine; 7 – hood lock; 8 – engine compartment lamp; 9 – main brake cylinder with vacuum booster; 10 – hydraulic brake reservoir; 11 – windshield wiper gear motor; 12 – hydraulic clutch reservoir; 13 – expansion tank of the engine cooling system; 14 – voltage regulator; 15 – relay for turning on the radiator fan of the engine cooling system.
Engine compartment of VAZ-2106 (top right view
): 1 – thermostat of the engine cooling system; 2 – air filter for the engine power supply system; 3 – engine; 4 – battery; 5 – generator; 6 – battery charge indicator relay; 7 – relay for turning on low beam headlights; 8 – relay for turning on the high beam headlights.
Engine compartment of VAZ-2106 (bottom view
): 1 – anti-roll bar; 2 – body spar; 3 – generator; 4 – engine sump; 5 – engine oil filter; 6 – axis of the lower suspension arm; 7 – lower suspension arm; 8 – clutch housing; 9 – exhaust pipe; 10 – suspension cross member; 11 – steering rods.
Main components of the car (bottom front view
): 1 – additional muffler of the first stage of the exhaust gas system; 2 – exhaust pipe; 3 – gearbox; 4 – front suspension; 5 – clutch housing; 6 – engine.
The main components of the car (bottom rear view
): 1 – rear suspension spring; 2 – rear suspension shock absorber; 3 – rear suspension transverse rod; 4 – additional muffler of the first stage of the exhaust system; 5 – cardan transmission; 6 – rear axle; 7 – additional muffler of the second stage of the exhaust system; 8 – main muffler of the exhaust system; 9 – lower longitudinal rod of the rear suspension.
↑ Suspension
To install the engine assembly with gearbox and clutch, a three-point suspension scheme is used. The two front supports are located on either side of the cylinder block and are attached to the cross member of the vehicle's front suspension. The rear support is located on the gearbox and rests on a cross member fixed under the floor of the body.
The elastic cushions of the front supports consist of rubber with vulcanized steel washers and mounting bolts. To increase the rigidity of the supports, there are springs in the central hole of the cushions, supported by insulating rings, and to soften impacts, rubber-metal buffers are located inside the springs. The cushions are attached to the brackets using intermediate plates. The right cushion is protected from heating from the side of the exhaust pipe of the mufflers by a protective casing.
The rear support is also rubber-metal, it consists of three steel plates with rubber separating them. The middle plate is attached to the gearbox, and the outer plates are attached to the cross member of the rear engine mount. Steel spacer bushings are placed between the crossbar flanges to protect the flanges from deformation when tightening the fastening bolts.
Fuses and relays VAZ 2106
Hello everyone, today I would like to talk about the fuse and relay box on the VAZ 2106 car. On the VAZ 2106, the fuses are located in the interior, but the relays under the hood are scattered in different places. By the way, in the interior of the VAZ 2106 there is also a relay, I almost forgot. Sometimes it is a fuse or relay that can cause a malfunction of one or another element.
↑ Cylinder block
The cylinder block is made by casting from special high-strength cast iron. The holes for the cylinders are bored directly in the block and additional inserts (liners) are not used in the cylinders. To obtain a special profile and surface cleanliness, the cylinders are honed. By diameter, cylinders are divided into 5 classes every 0.01 mm, designated by the Latin letters A, B, C, D and E. The class of each cylinder is marked on the bottom plane of the cylinder block.
The holes for the main bearings of the crankshaft are bored together with the bearing caps. Therefore, they are not interchangeable either with each other or with the covers of other cylinder blocks. In order not to confuse the lids, markings are made on them. The bearing caps are attached to the cylinder block with self-locking bolts, the replacement of which with any other bolts is unacceptable.
The auxiliary drive shaft rotates in two bushings pressed into the cylinder block. The front bushing is steel-aluminium, and the rear bushing is metal-ceramic, bronze-graphite. Spare parts are supplied with bushings of nominal and repair sizes with an internal diameter reduced by 0.3 mm.
↑ Piston
The pistons are cast from aluminum alloy. To improve its wearability to the cylinder walls, the outer surface of the piston is coated with a thin layer of tin. To compensate for uneven thermal expansion, the piston skirt has a complex shape. It is conical in height and oval in cross section. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the piston diameter only in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin and at a distance of 52.4 mm from the piston bottom.
Based on the outer diameter, pistons (as well as cylinders) are divided into five classes: A, B, C, D and E, every 0.01 mm, and according to the diameter of the hole for the piston pin, they are divided into three categories, every 0.004 mm. The category is indicated by paint on the end (the first is blue, the second is green, the third is red). The piston class (Latin letter) and category (number) are marked on the piston bottom.
Spare parts include pistons of classes A, C, E, which are quite sufficient to select a piston for any cylinder, since pistons and cylinders are divided into classes with some overlapping sizes.
The hole for the piston pin is shifted from the axis of symmetry by 5 mm to the right side of the engine. Therefore, there is a mark on the piston in the form of the letter P for the correct orientation of the piston in the cylinder. The mark should face the front of the engine.
Since 1986, repair size pistons for all VAZ engine models have been manufactured with an outer diameter increased by 0.4 and 0.8 mm. Until 1986, repair size pistons for engines 2103 and 2106 were produced with an increase of 0.4; 0.7 and 1.00 mm.
The pistons of engines 2103 and 2106 differ only in size (diameter).
The piston rings are made of cast iron. Top compression ring with barrel-shaped chrome-plated outer surface. The lower compression ring is scraper type, phosphated.
The piston pins are pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod and rotate freely in the piston bosses. According to the outer diameter, the fingers are divided into three categories every 0.004 mm.
The category of the finger is marked on its end with the appropriate color:
- 1st – blue,
- 2nd – green,
- 3rd – red.
The connecting rod is steel, forged. The lower head of the connecting rod is detachable; connecting rod bearings are installed in it. The connecting rod is processed together with the cap and therefore they are not interchangeable with the caps of other connecting rods. To avoid mixing up the connecting rod caps during assembly, the connecting rod and its cap (on the side) are marked with the number of the cylinder in which they are installed. When assembling, the numbers on the connecting rod and cap must be on the same side.
Tuning the exhaust system of VAZ 2106
They resort to tuning the exhaust system on the sixth model Zhiguli in order to increase power and obtain a beautiful sound. Almost every element of the system can be changed, or, more precisely, replaced with a different design.
An exhaust manifold
When tuning the exhaust system, the standard manifold is replaced with a “spider” type design. This name corresponds to the shape of the product. The collector can be long or short, and the difference lies in the connection diagram. In addition to replacing the exhaust element, you can improve the standard manifold by treating the internal surface. For these purposes, use a round file, which grinds off all protruding parts. If the intake manifold is easy to process (it is made of aluminum alloy), then you will have to work hard with the exhaust element, since it is made of cast iron.
After rough processing of the inner surface, polishing of the exhaust channels begins. For these purposes, an electric drill and a metal cable are used, which is clamped in a chuck and lubricated with an abrasive substance. Then turn on the drill and polish the channels with translational movements. When finishing polishing, a coarse cloth coated with GOI paste is wound around the cable.
Downpipe
The exhaust pipe or trousers are attached on one side to the exhaust manifold, and the other to the resonator of the VAZ 2106 exhaust system. The need to replace this part arises when installing a direct flow, and the pipe must be of increased diameter, which ensures unhindered exit of exhaust gases.
Forward flow
One of the options for tuning the exhaust system is to install direct flow. As a result, owners of “sixes” receive not only an increase in power, but also a sporty sound. If the engine was boosted, i.e. the block was bored, a different camshaft was installed, the volume of exhaust gases increases, which should be taken into account when choosing direct flow. Structurally, a direct-flow muffler resembles a resonator, inside of which there is a special sound-absorbing material, for example, basalt wool. The service life of a modernized muffler depends on how long the sound insulation is in it.
To install forward flow on a VAZ 2106 you will need a welding machine and skills to handle it. Otherwise, you will need to contact a service center, where the work will be performed by experienced auto mechanics. It is important to understand that direct flow elements, as well as their installation, are not cheap.
↑ Crankshaft
The crankshaft is cast from high-strength cast iron and has five support (main) journals, hardened by high-frequency current to a depth of 2–3 mm. At the rear end of the crankshaft there is a socket into which the gearbox drive shaft bearing is inserted. The lubrication channels in the crankshaft journals are closed with cap plugs, which are pressed in and caulked at three points for reliability.
To extend the service life of the crankshaft, it is possible to regrind the crankshaft journals when their surfaces are worn or damaged. By grinding, the journal diameters are reduced by 0.25; 0.5; 0.75 and 1.00 mm.
The axial movement of the crankshaft is limited by two thrust half-rings installed in the cylinder block on either side of the rear main bearing. A steel-aluminum half-ring is placed on the front side of the bearing, and a metal-ceramic half-ring (yellow) is placed on the rear side.
The main and connecting rod bearing shells are thin-walled, bimetallic, steel-aluminium. The shells for the 1st, 2nd, 4th and 5th main bearings have a groove on the inner surface (since 1987, the lower shells of these bearings are installed without a groove). The central main bearing shells differ from other shells in that they lack a groove on the inner surface and are larger in width. All connecting rod bearing shells are without grooves, identical and interchangeable. Repair liners are made of increased thickness for the crankshaft journals, reduced by 0.25; 0.5; 0.75 and 1 mm.
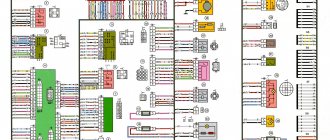
VAZ 2106 fuse box pinout, diagram
If you have any problems with electrical equipment: the low or high beams have disappeared or are not working, the turn signals, stove, cigarette lighter, fan, wipers are not working, the signal has disappeared, etc., then this could all be the reason that the fuse has blown. This means it needs to be replaced.
To do this, you need to know the location of the mounting block. And it is located under the steering wheel, on the left side. In order to understand what the VAZ 2106 fuses are responsible for, you need to look at the simple pinout of the old fuse block (FB) and see the description below.
Table “VAZ 2106 fuse designations”
| Fuse number | Current, A | What is he responsible for? |
| 1 | 16 | 1. Lamps 2. Horns 3. Power socket 4. Cigarette lighter 5. Rear lamps 6. Front door open warning lamps 7. Clock |
| 2 | 8 | 1. Windshield wiper and wiper relay 2. Wiper motor 3. Heater motor |
| 3 | 8 | Left headlight (high beam) and high beam indicator lamp |
| 4 | 8 | Right headlight (high beam) |
| 5 | 8 | Left headlight (low beam) |
| 6 | 8 | Right headlight (low beam) |
| 7 | 8 | 1. Left front marker 2. Right rear marker 3. Trunk light 4. License plate light 5. Instrument lights 6. Cigarette lighter light |
| 8 | 8 | 1. Right front marker 2. Left rear marker 3. License plate light 4. Engine compartment lamp 5. Side light indicator lamp |
| 9 | 8 | 1. Oil pressure sensor with warning lamp 2. Coolant temperature sensor 3. Fuel level with reserve warning lamp 4. Parking brake activation and brake fluid level warning lamps 5. Turn signals and corresponding warning lamps 6. Battery charge warning lamp 7. Control lamp carburetor choke control lamp 8. Carburetor shut-off valve 9. Tachometer 10. Reversing lamps 11. Glove compartment lamp 12. Rear window heating relay coil |
| 10 | 8 | 1. Voltage regulator. 2. Generator excitation winding |
| 11 | 8 | Spare |
| 12 | 8 | Spare |
| 13 | 8 | Spare |
| 14 | 16 | Heated rear window |
| 15 | 16 | Engine cooling fan |
| 16 | 8 | "Emergency" |