Design Features
The motor is cooled in a closed loop by circulating coolant. The operating principle of the cooling system is forced.
The operation scheme of the lubrication system is combined - splashing plus supply of engine oil under pressure.
The operating order of the cylinders is as follows: 1—3—4—2.
The internal combustion engine device allows for major repairs of the VAZ 2106 engine and additional tuning of the VAZ 2106 engine.
The VAZ 2106 engine is replaced after familiarization with the new prices for this type of engine. Before you start replacing the engine, you need to find out how much the VAZ 2106 engine weighs.
The power unit of the sixth model is installed on VAZ 21074, NIVA, VAZ 2106 vehicles. UAZ vehicles are not equipped with these engines.
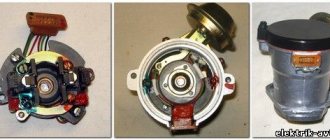
Power and ignition system
To supply fuel on early versions of the 2106 engine, a Weber system carburetor was used. With the start of production of more modern devices such as “Ozone”, they began to be installed on the “sixth” engine. With the new carburetor, the engine became a little more economical, but also lost several horsepower. In the early 2000s, engines began to be equipped with a fuel injection system. Vehicles of the “fifth” and “seventh” models were equipped with such power units.
On carburetor cars, ignition was used with pulse distribution from a mechanical device mounted on the side of the crankcase. The injection version is equipped with an electronic module that distributes ignition pulses according to signals from the engine shaft position sensor.
Sixth engine - description of technical characteristics
Main technical characteristics of the motor:
- The 2106 cylinder block is made of cast iron.
- Power is supplied using a carburetor circuit.
- Engine type: gasoline, in-line.
- The number of cylinders in the block is 4.
- Each cylinder with a diameter of 79 mm is equipped with two valves.
- The piston stroke is 80 mm.
- The compression ratio of the engine is 8.5 atmospheres.
- Engine power of the VAZ 2106 is 75 hp.
- The speed is 5400 rpm.
- The torque is 116 Nm.
- Recommended fuel is AI 92.
- The assembled weight of the VAZ 2106 engine is 121 kg.
- Changing the oil in the VAZ 2106 engine - the required amount is 3.5 liters.
- Types of recommended brands of motor oil: 10w-40.5w-40, 15w-40, 5w-30.
- Tuning VAZ 2106 - horsepower is 200.
Each engineering improvement led to a significant improvement in the design, as evidenced by the presented characteristics of the VAZ 2106 engine.
In what models was the VAZ used?
Improved engine characteristics made it possible to equip VAZ cars of the following models with it:
- 2103 Zhiguli sedan;
- 21054 Zhiguli sedan (only for the FSB, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate);
- 2106 Lada sedan;
- 21074 Lada sedan;
- 2121 Niva carrying a 5-door station wagon or 3-door hatchback.
VAZ 21054 for special services
Due to the following difficulties in manufacturing some parts, management considered the 2106 motor to be economically unprofitable and it was discontinued.
What we managed to significantly improve
Improved characteristics of the VAZ 2106:
- Using a new cylinder block of improved design with a changed diameter.
- The VAZ 2106 engine has increased power due to an increase in the total volume of the power unit and improved characteristics and properties of the cylinders.
- The use of new gaskets due to changes in cylinder diameters.
- Equipped with pistons with a diameter of 79 mm, borrowed from the eleventh model.
- Ensuring uniform heating of the pistons thanks to cylindrical wells in the motor and the use of steel temperature control plates on the pistons.
Special temperature control plates installed in the pistons are made of high quality steel.
Basic modification
Due to its wide distribution and low price, the “six” engine often becomes the target of tuning. The 2106 engine is equipped with a new camshaft with changed timing and valve opening height. In this case, valves with an increased diameter are installed, which improves the filling of the cylinders.
The channels themselves for supplying and discharging working gases inside are carefully polished, since irregularities on the walls create turbulence in the flow of moving gases and worsen operating parameters. These two methods are the most basic ways to increase the power of a 2106 engine.
2106 Powertrain Maintenance
To determine possible problems in the operation of the car, it is necessary to carry out regular diagnostics of the entire car. With the help of a master, standards for the functioning of all mechanism systems are established.
Repair work is divided into categories of complexity depending on system defects and wear of engine components and parts. In the process of detailed diagnostics of systems, studies are carried out under power loads.
Successful repair of a VAZ 2106 engine with your own hands is carried out by acquiring certain experience and skills. To help craftsmen, a special manual book has been published, which can be purchased online in stores that sell automobile spare parts.
VAZ 2106 repairs, assembly and disassembly are carried out if you have experience, you also need a full set of tools and necessary spare parts.
Features of the VAZ 2016 engine
Experienced car enthusiasts know the main technical characteristics of this engine: in the classics - gasoline, four-cylinder, cylinder diameter 79 mm, two valves for each cylinder, displacement 1568 cm3, power 75-77 hp. s., torque 3000 rpm, piston stroke 80 mm, compression ratio 8.5 atmospheres, weight 121 kg.
The engine is a four-stroke with a carburetor system and an in-line engine; the cooling system has forced circulation of liquid. Around 2002, the carburetor began to be replaced with an injector, which somewhat improved the technical characteristics of the engine. This “six” scheme is not very common in the secondary market: a lot of problems arise when re-equipping the device, and primarily of a financial nature, although in one and a half to two years of intensive use of the car the costs are more than recouped.
The most common breakdowns of the sixth engine
Car owners most often encounter the following defects in engine operation:
- The internal diameter of the cylinder increases by 0.15 mm after traveling more than 5 thousand km. This defect occurs if the engine lubricant is not replaced in a timely manner.
- The camshaft is worn out.
- Sound effects in the form of tapping in the engine. This defect can be eliminated by adjusting the valves and replacing the fuel with higher octane fuel. If these measures do not help, then you need to contact the nearest service station, where the pistons and connecting rod bearings will be diagnosed and repaired.
- Oil pressure drops. In this case, the lubricant does not reach the rubbing surfaces, as a result of which the friction force increases, causing the gaskets to burn out, accelerated wear of the working parts, and the device becomes unusable.
- Creaks indicate a breakdown in the timing chain tensioner, damper or pump bearing.
- If the engine stalls while driving, you need to look into the ignition or power systems.
- The engine turns off at idle when there is a failure in the idle speed or air damper adjustments.
- Engine trouble, with this defect it is necessary to adjust or replace burnt valves and cylinder head gasket. The cause of tripling can also be fuel with a low octane number.
VAZ 2106 engine malfunctions and their symptoms
No matter how reliable the “six” engine is, it, unfortunately, sometimes fails. There can be any number of reasons for the breakdown of the power unit, ranging from a banal break in one of the wires and ending with wear of the piston group parts. To determine the cause of the problem, it is important to understand its symptoms.
Signs that the VAZ 2106 engine requires repair may be:
- impossibility of starting (no matter cold or hot);
- tripping, “floating” speed, unstable idle;
- reduction in power at start, under load;
- overheat;
- the appearance of extraneous noise (knocking, clattering);
- change in exhaust color (thick white or bluish smoke).
It should be borne in mind here that any of these symptoms cannot directly indicate a malfunction of a specific unit, mechanism or system, therefore, diagnostics should be approached comprehensively, double-checking your conclusions.
The engine does not start at all
If, with a charged battery and a normally working starter, the power unit does not start and does not “grab”, you need to check:
- ignition coil;
- breaker (Hall sensor, switch);
- distributor cap slider and contacts;
- high-voltage wires with lugs;
- spark plug;
- gasoline pump;
- filter on the carburetor fuel intake fitting;
- idle valve.
The absence of signs of engine life is a consequence of problems either in the ignition system or in the power system. It is better to start diagnostics with the ignition, “ringing” the circuit with a tester and checking whether there is voltage on each element. As a result of this test, you should be sure that there is a spark at the spark plugs while the starter is rotating. If there is no spark, you should check each component of the system.
More information about the spark on the VAZ 2106: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/elektrooborudovanie/zazhiganie/net-iskry-vaz-2106.html
The essence of checking the system is to understand whether fuel is reaching the carburetor and whether it is entering the cylinders. To do this, you need to disconnect the outlet pipe of the fuel pump from the carburetor, insert it into some container, and crank it with the starter. If gasoline flows into the container, everything is fine with the pump and filter.
To check the carburetor, simply remove the air filter and the top cover. Next, you need to sharply pull the accelerator cable and look into the secondary chamber. At this point, a thin stream of fuel should be visible directed into the intake manifold. This means that the carburetor accelerator pump is operating normally. There is no flow - the carburetor needs to be repaired or adjusted.
It's worth checking the idle air valve as well. If it malfunctions, the engine will not start. To check it, you need to unscrew it from the carburetor cover and disconnect the supply wire. Next, the valve must be connected directly to the battery terminals. During connection, the click characteristic of the operation of the electromagnet should be clearly audible, and the rod of the device should move back.
Video: why the car won't start
The engine is running rough and there is a problem with idle speed.
Troubleshooting of the power unit and idle speed problems can be caused by:
- failure of one or more spark plugs;
- breakdown of a high-voltage wire;
- burning of distributor cap contacts;
- clogging of the fine fuel filter;
- obstruction of the filter on the carburetor inlet fitting;
- incorrect carburetor adjustment.
As in the previous case, here it is better to start diagnostics with the ignition system. You should immediately check the spark at the electrodes of the spark plugs and measure the resistance of each of the high-voltage wires. Next, the distributor cap is removed and the condition of its contacts is assessed. If they burn, you need to clean them from carbon deposits or replace the lid.
Diagnostics of a fine filter is carried out by determining its throughput, as described above. But as for the carburetor filter, you need to unscrew it from the cap and, if necessary, blow it with compressed air.
If after these diagnostic steps the symptoms remain, it is necessary to adjust the carburetor, namely the quality of the mixture and the fuel level in the float chamber.
Video: why the VAZ 2106 engine troits
Reduced engine power
The deterioration of the power qualities of the power unit is caused by:
- clogged fine filters or carburetor;
- fuel pump malfunction;
- improper adjustment of the quality of the combustible mixture;
- violation of valve timing;
- incorrect adjustment of the ignition timing;
- wear of piston group parts.
If there is a noticeable decrease in engine power, the first thing you should do is evaluate the performance of the fuel system by checking the filters, fuel pump and adjusting the quality of the mixture. Next, you need to determine whether the timing drive marks on the crankshaft and camshaft sprockets match the marks on the engine and camshaft covers. If everything is in order with them, adjust the ignition timing by turning the distributor body in one direction or another.
As for the piston group, when its parts wear out, the loss of power does not appear so clearly and quickly. Measuring the compression in each cylinder can help determine which piston is to blame for the loss of power. For the VAZ 2106, indicators in the range of 10–12.5 kgf/cm2 are considered normal. It is permissible to operate the engine with a compression of 9–10 kgf/cm2, although such figures indicate obvious wear of the piston group elements.
Video: why engine power decreases
Engine overheating
Violation of the thermal regime of the power plant can be determined by the coolant temperature indicator. If the arrow of the device constantly or periodically goes into the red sector, this is a clear sign of overheating. It is not recommended to continue driving a car whose engine is prone to overheating, as this can lead to burnout of the cylinder head gasket, as well as jamming of the moving parts of the power unit.
Violation of the thermal regime of the motor can be a consequence of:
- insufficient refrigerant level in the system;
- thermostat jamming;
- obstruction (clogging) of the cooling radiator;
- cooling fan failure;
- liquid pump malfunction.
If signs of overheating are detected, the first thing you should do is pay attention to the coolant level in the expansion tank and, if necessary, add refrigerant. The functionality of the thermostat can be determined by the temperature of the radiator pipes. When the engine is warm, they should both be hot. If the lower pipe is hot and the upper pipe is cold, it means that the thermostat valve is stuck in the closed position and the coolant is moving in a small circle, bypassing the radiator. In this case, the device must be replaced, since it cannot be repaired. The permeability of the radiator is also checked by the temperature of the pipes. If it is clogged, the top pipe will be hot and the bottom pipe will be warm or cold.
The cooling fan on the VAZ 2106 usually turns on at a coolant temperature of 97–990C. Its work is accompanied by a characteristic buzzing sound produced by the impeller. It can fail for several reasons, including poor contact in the connector, sensor failure, and malfunction of the electric motor itself. To test the device, just connect its contacts directly to the battery.
It is quite difficult to diagnose a breakdown of a liquid pump without dismantling it, so it is checked last. Most often, its malfunction is associated with damage to the impeller and wear of the rotor bearing.
Video: why the engine overheats
Extraneous sounds
The operation of any power unit is accompanied by many sounds, so only a specialist, and not everyone, can distinguish by ear what is extraneous noise and what is not. To identify “extra” knocks, there are special car phonendoscopes that allow you to more or less accurately determine the place from where they are coming. As for the VAZ 2106 engine, extraneous sounds can be produced by:
- valves;
- main and connecting rod bearings;
- piston pins;
- timing chain.
The valves produce a high-frequency knock that comes from the valve cover. They knock due to incorrect adjustment of thermal clearances, wear of the camshaft cams, and weakening of the valve springs.
Main and connecting rod bearings make similar sounds. The reason for this is their wear, as a result of which the play between them and the connecting rod journals increases. In addition, knocking can also be caused by low oil pressure.
The piston pins usually ring. This phenomenon is often caused by detonation inside the cylinders. It occurs due to incorrect adjustment of the ignition timing. A similar problem is solved by setting a later ignition.
The noise of the timing chain is similar to a loud rustling or clanging, the cause of which is its weak tension or problems with the damper. Replacing the damper or its shoe will help get rid of such sounds.
Video: engine knocking
Exhaust color change
By the color, consistency and smell of exhaust gases, you can generally judge the condition of the engine. A working power unit has a white, light, translucent exhaust. It smells exclusively of burnt gasoline. A change in these criteria indicates that the motor has problems.
Thick white smoke from the exhaust pipe under load indicates the combustion of oil in the cylinders of the power plant. And this is already a sign of wear on the piston rings. You can make sure that the rings have become unusable or “stuck” by inspecting the air filter housing. If lubricant gets into the cylinders, it will be squeezed out through the breather into the “pan”, where it will settle in the form of an emulsion. A similar malfunction is treated by replacing the piston rings.
But thick white exhaust may also be a consequence of other problems. So, when the cylinder head gasket breaks down (burns out), the coolant enters the cylinders, where it turns into white vapor during combustion. In this case, the exhaust will smell like coolant.
Video: why white smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe
Why does the engine get hot?
The most common defect of the 2106 engine is its overheating. The engine operating temperature is just before +96°C.
The reasons that the engine began to get very hot may be malfunctions of the following systems and components:
- thermostat, air lock;
- radiator, its clogging;
- low quality of liquid used for cooling;
- the fan has failed.
If engine overheating is detected, you must immediately stop the car and carry out a thorough examination and eliminate the cause. If the engine begins to heat up due to a broken thermostat, then this device must be replaced with a new one. .
If there are defects in the radiator, it is necessary to give time for the coolant to cool completely and only then begin diagnostics, drain the antifreeze and repair the damage.
Injection modification
The first in the line of internal combustion engines of the AvtoVAZ manufacturer, the 2106 engine received tuning in the form of distributed injection. At the same time, the owners received a headache:
- intense heating, since the mixture is lean, the manufacturer’s cooling system cannot cope with temperature loads;
- increased fuel consumption up to 13 l/100 km in winter.
Injection 2106
A positive feature is the low budget for major repairs within 10,000 rubles.
Check and adjustment
The table shows that after installation in the 4th cylinder TDC, the 8th and 6th valves are checked and adjusted. That is:
- We are looking for the 8th valve. To do this, we count from the camshaft drive gear. shaft, that is, from the front of the engine. It turns out that valve 8 is the last;
- We install the dipstick between the rocker and the camshaft cam. With a normal gap, it should fit between them with a slight interference, that is, there should be a small but noticeable resistance;
- If the measuring plate does not fit, or vice versa, does not experience any resistance, then adjustment is performed;
- On the side of the rocker there is a 17 wrench nut, which is screwed onto a bolt with a 13 head. This bolt allows for adjustment, and the nut prevents unauthorized unscrewing of the adjusting element. To adjust, loosen the nut by 17, holding the bolt with a second wrench. Then we rotate this bolt, which allows us to change its length, and as a result, the gap between it and the lever. And since the rocker is located on the axis, the gap on its other side will change. By rotating the bolt, we achieve the required clearance (the feeler gauge moves with force), hold it in this position and tighten it with a nut.
- We check the correctness of the adjustment. If, when tightening the locknut, the bolt still moves and the gap is broken, repeat the adjustment steps.
- We move on to valve 6 and do the same thing - check the gap, adjust if necessary and check again.
This described the procedure for adjusting the VAZ-2105 valves using the example of one crankshaft position and two valves . But there are still 6 valves left and, according to the table, 3 crankshaft positions.
To adjust the next two valves - the 4th and 7th, you need to turn the knees. shaft by 180 degrees, which will correspond to TDC of the 3rd cylinder. At the same time, it will be inconvenient to control the rotation angle along it. This is where a marker comes in handy. The fact is that 180 degrees. The rotation of the crankshaft corresponds to the rotation angle of the distributor slider by 90 degrees. That is, on the end of the housing you can put 4 marks spaced at the same distance around the circumference, starting from the zero position (TDC of the 4th cylinder).
And then, using the existing marks, we first set the crankshaft angle to 180 degrees. (check and adjust the 4th and 7th valves), then 360 degrees. (1st and 3rd valves) and 540 deg. (5th and 2nd).
After all the adjustment work, we install the removed elements on the engine.