A smooth or sharp drop in the brake pedal, or its floating and vibration when braking, usually indicate Master brake cylinder malfunction. Most often, the reason for its malfunction is the loss of tightness of the rubber sealing cuffs or improper operation of the bypass valves.
To distinguish its malfunctions from other malfunctions of the brake system and find out how to check whether the master cylinder is working, read the article.
Why the brake caliper jams: how to identify and fix the problem
Hi all! Any problems associated with the braking system of vehicles are potentially very dangerous. Therefore, every motorist should know why the brake caliper jams, what can provoke such a situation, how to diagnose and eliminate it. On your own or with the help of specialists, decide for yourself.
Our regular readers remember that we have previously talked about situations when the caliper knocks. Now let's consider a slightly different situation. Moreover, it is even more dangerous and unpredictable in terms of possible consequences if nothing is done after noticing the symptoms.
Let's start with the theory. The caliper on a car is part of the brake system. It is used in the design to press automobile brake pads when the corresponding pedal is pressed against the brake disc. As you understand, the node is extremely important.
But sometimes it can jam and creak because of this.
Features of work
First, let's try to imagine the ideal operation of a caliper as part of a car's braking system.
In fact, this is a mandatory component of any car, be it:
- VAZ 2110;
- VAZ 2109;
- Lada Kalina;
- Chevrolet Lanos;
- Lada Priora;
- VAZ 2114;
- Chevrolet Niva;
- Lada Kalina;
- VAZ 2112;
- Daewoo Nexia;
- Volkswagen Polo Sedan;
- Skoda Octavia;
- Mercedes E class, etc.
Regardless of whether it is installed on a Niva or a BMW, the caliper must be in constant working order.
This is the direct task of the car owner himself. Or persons responsible for maintaining the machine and maintaining it in proper technical condition.
Before determining why it does not press out and what to do to prevent the car caliper from jamming, you need to understand the principle of its operation.
In optimal condition, when the brake assembly is working properly, the operating diagram looks like this:
- the driver presses the brake pedal;
- pressure is built up inside the braking system;
- this pressure is transmitted to the piston group of the auto calipers;
- the calipers, being under high pressure, bring the brake pads to the disc;
- the braking disc is attached to the car wheel;
- friction force arises;
- wheel rotation slows down;
- the car stops;
- or reduces the speed to the required values.
As you can see, in theory there is nothing complicated. But in fact, the caliper is rightly called an extremely complex element.
For the brakes to work effectively, it is important to ensure that the pad is parallel to the disc.
Friction during active braking causes heat production. This heats up the pad, brake fluid and our caliper.
Therefore, it is extremely necessary that the car caliper be made on the basis of a material that does not change its properties and characteristics during the process of strong heating. Plus, there are increased requirements for strength.
Causes of jamming and creaking
Now directly about how to determine the presence of a problem.
The primary sign indicating a malfunction in the calipers of a car brake system is squeaking.
It is the creaking that indicates that the element is seriously worn out. In the near future, the unit must be replaced without fail, which the car literally and figuratively screams about. It is extremely difficult not to hear such a creak. But for some reason, thousands of motorists still stubbornly ignore it. As a result, they pay a rather high price. Sometimes even to the point of road accidents resulting from brake failure while driving. To prevent this, you need to understand the issue and understand the essence of what is happening.
The first step is to look at the possible causes. In fact, there are several potential problems to look for. Some of them arise due to the fault of the motorist, others are caused by the natural process of wear and tear.
In any case, the appearance of a squeak as a symptom is a harbinger that at the most inopportune moment the caliper may simply jam.
If you know the reasons, you can prevent them and troubleshoot them by contacting a car service center or solving the problem yourself.
The reasons are:
- The brake pads were initially installed incorrectly. As a result, they are not strictly parallel to the response drives. Because of this, creaking often appears;
- The brake discs are seriously worn out. The reasons are natural wear and tear and aggressive use of the car;
- There is no lubrication in the unit. Initially there was little of it, or it was used up;
- The lubricant was selected incorrectly. Many people skimp on lubricant intended for calipers, hence the consequences.
The most undesirable and dangerous situation is rightly considered when the piston does not return and the unit begins to jam during operation.
Imagine that you are driving a car, press the brake, and then accelerate again. But at the same time, the calipers do not release the front brakes. Additional resistance arises, the car tries to move, but cannot. The result is uncontrolled braking, extremely intense wear and serious overheating of the entire system.
What to do in such a situation
If you were able to diagnose creaking and signs of wedging in this unit, you need to perform a number of measures.
And here it is not necessary to contact a car service. You need:
- put the car on a jack;
- remove the wheel;
- unscrew the caliper;
- remove it;
- unscrew the problematic piston;
- remove the piston from the cylinder;
- visually inspect the element;
- check for chips, damage, corrosion;
- if there is rust, clean it;
- if severely damaged, replace;
- drain the working fluid from the element;
- remove the sealing ring;
- clean all surfaces;
- dry;
- fill in new hydraulics;
- assemble in reverse order.
When putting the assembly back together, pay special attention to not accidentally damage the old boot. If you notice cracks on it, then no restoration will help. Replacement only.
Prevention measures
I can say from personal experience that the detailed cleaning procedure is quite complicated. This will definitely take more than one hour.
To minimize the number of repetitions of such operations, be sure to lubricate the caliper twice a year for preventive purposes. It is optimal to use professional special lubricants designed specifically for this element. But regular WD40 is also an alternative. It will definitely protect against corrosion.
Plus, visually inspect the condition once a year. Make sure that the assembly is free of damage, dirt and signs of corrosion. Make sure that the boot does not rupture during operation. Otherwise, the caliper will not last long after this.
You need to monitor all brake systems, including periodic adjustment of the handbrake. After all, this is also an integral part of vehicle safety.
Source: https://pricep-vlg.ru/remont-svoimi-rukami/pochemu-klinit-tormoznoy-support/
Diagnostics and repair
From the signs listed above, it is easy to understand that in most cases there is only one source of problems - rubber products that have become unusable. The cuffs crack and swell, as a result they leak liquid and close the discharge holes. Hence the recommendation: all “rubber bands” of the brake system should be changed at intervals of approximately 100 thousand km, without waiting for critical wear.
Reference. Many auto mechanics express the opinion that after replacing the cuffs, the main hydraulic cylinder will not last long. The statement is true if the car owner purchased cheap, low-quality spare parts or installed new o-rings in the cylinder, where internal wear has formed in the walls.
Before checking the GTZ for operability, make sure there are no other faults:
- Inspect the wheel assemblies from the inside for leakage of brake fluid from the working cylinders.
- Check the integrity of the expansion tank and the fluid level in it.
- Start the engine and at idle speed, press the vacuum take-off pipe to the amplifier. If the engine speed has increased noticeably, there is an air leak and the master cylinder is most likely working.
A clear symptom indicating a breakdown of the main hydraulic cylinder is drops of brake fluid on the body . If you discover a leak, feel free to dismantle the unit and disassemble it to look for the cause. Another common problem - fluid flowing through the seals - is diagnosed as follows:
- Open the cover of the expansion tank and place an assistant in the driver's seat.
- Listening to sounds in the tank, give the command to an assistant to press the pedal.
- If the pedal moves easily and gurgling is heard in the reservoir, liquid is entering there. The reason is that worn cuffs are unable to create pressure in the circuits; liquid seeps through the leaks and enters the container.
Also, problems with the GTZ are indicated by jamming or too little pedal travel. Sit behind the wheel, press it several times, and start the engine while holding the pedal with your foot. If it sinks to the floor or does not budge, disassemble the hydraulic cylinder.
Front wheel brake cylinder sticks
18.07.2019
Issues discussed in the material:
- How do brakes work?
- What are the main causes of front brakes sticking?
- What other faults can cause the front brakes to jam?
What daily manipulations does every person who moves during the day by car do? He gets into his car, starts the engine, warms it up a little and starts driving. And here an unpleasant surprise can await him: the car does not move! If this has not happened before, then it is difficult for the driver to understand what is going on, especially if his driving experience is not yet very long. The reasons why the front brakes stick can be different. To learn how to distinguish and eliminate them, you must first understand the theoretical side of the issue.
How the brakes work
The serviceability and correct operation of the car's braking system determines whether you can drive it normally or not. The law prohibits driving a car with broken or jammed brakes, even if it is a minor problem. This is still unsafe for both you and other road users.
To understand possible malfunctions and understand why the front brakes jam, you need to have an idea of the principle of their operation. The braking system in modern cars consists of brake discs or drum pads, which mechanically, if necessary, slow down the speed of the car.
The system works like this: the brake pedal is pressed, the piston in the main brake cylinder moves, “adjusting” the brake fluid, which, in turn, passing through the lines, affects the brake cylinders of the wheels. They press pads equipped with a friction mixture against the discs or drums.
How does the GTZ function?
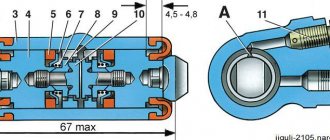
The unit consists of the following parts:
- metal housing with holes for supplying brake fluid, pedal rod and connecting the expansion tank;
- 2 pistons with rubber seals;
- 2 return springs;
- guide bushings;
- end plug with gasket.
An expansion tank is attached to the top of the main distributor body, where excess fluid goes through compensation holes. Inside, the element is divided into 2 cylinders with separate pistons standing on the same axis.
The blind end of the housing is closed with a threaded plug; on the other side there is a flange for attaching to the vacuum booster. The brake pedal rod is attached to the first piston. The brake circuit pipes are connected to the lower holes - separately for the front and rear wheels.
The operating principle of the master brake cylinder looks like this:
- When you press the pedal, both pistons simultaneously move forward and push fluid into the circuit tubes. Under its pressure, the wheel cylinders are activated, compressing the pads on the discs.
- Part of the liquid that does not have time to pass into the tubes flows into the expansion tank through special bypass holes.
- When the driver releases the pedal, the springs push the pistons back, returning them to their original position. Liquid from the tubes and reservoir refills the cylinders.
- To compensate for the expansion of the liquid (for example, from heating), another pair of holes is provided leading to the expansion tank.
Note. The GTZ acts in conjunction with a vacuum booster (not shown in the diagram), which helps put pressure on the pistons. This allows the system to respond faster and make the driver's actions easier.
Operation of the system when one of the circuits fails
Dual-circuit brake drive device
If there is a brake fluid leak in one of the circuits, the second will continue to operate. The first piston will move along the cylinder until it contacts the second piston. The latter will begin to move, due to which the brakes of the second circuit will be activated.
If a leak occurs in the secondary circuit, the brake master cylinder will operate differently. The first valve, due to its movement, activates the second piston. The latter moves unhindered until the stop reaches the end of the cylinder body. Due to this, the pressure in the primary circuit begins to increase, and the car brakes.
Even if the brake pedal travel increases due to a fluid leak, the car will maintain control. However, braking will not be as effective.
Vacuum booster
The braking system of a car certainly cannot be called perfect, so it has to be supplemented with devices that help improve efficiency. One of them is a vacuum booster.
Application and purpose
Today, a vacuum amplifier is in great demand because it is highly efficient.
Its tasks are extensive, but the amplifier copes with them all perfectly:
- The degree of resistance of the brake pedal increases;
- Reduces the load on the brake system;
- Acts as a highly efficient auxiliary unit;
- Has a positive effect on the service life of the brake system, etc.
This element has the following components:
- Dense body, for the manufacture of which a high-strength polymer is used;
- The diaphragm, which is also called the collecting node;
- Monitoring or control specialized valve;
- Pusher. It allows you to return the engine elements to their original position when there is no power;
- Main piston rod of the brake system cylinder (main);
- Switch return spring.
The body of this spring has two cellular divisions, which are divided into vacuum and atmospheric. Cells are often called chambers.
- The vacuum chamber is a cell directly connected to the brake master cylinder.
- The atmospheric chamber is a cell located opposite the brake pedal. Its open part of the body rests on the brake pedal.
It is also worth noting the diaphragm, which performs two very important tasks:
- Corrects the position of the piston in space;
- Pumps brake fluid to the main brake cylinders.
Installing a vacuum booster involves a serious change in the sensitivity of the pedal, so it is strongly recommended not to apply a large and sudden force to it in the “first couple”. Pressing should be done carefully and smoothly.
Causes of malfunction in the GTZ device
If there is a leak in one of the circuits, the pressure between the primary and secondary cylinders is lost. This leads to the fact that the GTZ functions as if it had only one circuit. The pusher will begin to move both pistons in the good circuit until the piston of the faulty one reaches the end of the cylinder body. Accordingly, the required pressure will be ensured in the depressurized chamber. If the idle mechanism is properly adjusted, the vehicle will effectively slow down the vehicle even in conditions of its inferiority.
Here are some signs of a malfunction in the GTZ device:
- depressurization of the cylinder is determined by the presence of a leak in the body and a specific smell;
- brake pad wear is characterized by a characteristic squeak and leakage of brake fluid;
- jamming of the regulator, which distributes the brake force. In this case, it is necessary to clean the cylinder body. There is a low threshold of sensitivity of the brake pedal; it has to be literally “sunk” into the floor;
- the pedal falls to the floor - this damage occurs due to non-working pistons. If they are not able to generate the required pressure, then the pads cannot compress normally;
- An increase in the brake pedal travel is a sign that the vehicle has become airy. Operating a car in this condition is dangerous, since there is a high risk of overheating the vehicle to the point of boiling. Pumping will help eliminate this problem.
If any of the above happens constantly, we can talk about damage to the vacuum booster valve or a complete loss of tightness in the system. If the metal housing itself is damaged or there are scuffs on the piston, a complete replacement of the turbocharger is required. When the gasket wears out, all components of the repair kit (sealing collars, rubber gaskets, springs) are changed.
What parameters of the brake system are checked on the stand?
There are two types of brake diagnostics: road and bench.
Road is used to calculate:
braking distance length;
car stability when braking;
brake response speed;
the maximum possible slope of the road on which the car can stand.
The bench method is used to calculate:
specific braking force;
coefficient of uneven braking capabilities of wheels.
The work is that sensors record reactive moments. Thanks to the recorded data, you receive accurate information about the condition of each vehicle element.
Symptoms of problems
The general technical condition of the car (including the brake system) can be checked using a personal diagnostic adapter - a car scanner. These types of devices are widespread and have a wide price range. We would like to draw your attention to the budget model of Korean production Scan Tool Pro Black Edition.
At a cost of about 2 thousand rubles. This scanner is capable of fully diagnosing your car (engine, gearbox, transmission, abs, srs and much more), which will pay for itself in 1-2 trips to the service station. The adapter is quite easy to use, has Russian-language software and is compatible with most cars produced in 1993. The device will also be useful when buying a used car, as it can show its real mileage and VIN.
The fluid brake system consists of many parts that can become unusable: pipes, wheel cylinders, calipers, drums and pads. Typical signs of a faulty master cylinder:
- After pressing the pedal, the car stops slowly. The reason is that the cuffs of one or two pistons have lost their tightness - they have cracked or “floated”.
- To slow down, you need to press the brake pedal hard. The phenomenon occurs due to swelling of the rubber of the piston seals.
- The brake pedal travel is too short. The fluid inside the cylinder has nowhere to go because the compensation hole is clogged. Another option is that the passage is blocked by a swollen rubber seal.
- A common symptom is pedal failure, the brakes coming on at the end of the stroke. This indicates complete wear of the cuffs; as a result, liquid penetrates behind the piston and rushes into the expansion tank - the cylinder “bypasses.”
- The pads do not release the brake discs and drums and get very hot when driving. Options: one of the pistons is jammed or the bypass hole is clogged.
The listed symptoms of a GTZ malfunction are similar to malfunctions of other elements. Pedal failure also occurs when a large amount of air enters the tubes or loss of fluid in one of the working cylinders. Sluggish deceleration and increased force on the pedal are often caused by a breakdown of the vacuum booster - a cracked membrane or a lack of tightness at the joints of the hose that takes off engine vacuum.
There are signs that clearly indicate the performance of the main hydraulic cylinder and the malfunction of other elements:
- during braking, the car pulls to the side - the problem lies in a certain circuit or wheel;
- jamming of the brake mechanisms of one wheel;
- creaking and squeaking when braking;
- heating the discs and pads on one wheel.
If you eliminate these symptoms, it will become easier to check the brake master cylinder in a garage. This also includes obvious brake fluid leaks and the knocking sound of worn calipers.
There are other symptoms indicating a malfunction of the gas turbine engine.
- When braking at speed, the car pulls to the side. This happens when one of the circuits or brake cylinders on the wheel is faulty.
- The appearance of a squeaking or knocking noise during braking. It could also be pads that are time to be replaced, but it happens that the problem is in the GTZ.
- The pads can jam, heat up and heat up the brake disc on a particular wheel.
Symptoms of problems
The general technical condition of the car (including the brake system) can be checked using a personal diagnostic adapter - a car scanner. These types of devices are widespread and have a wide price range. We would like to draw your attention to the budget model of Korean production Scan Tool Pro Black Edition.
At a cost of about 2 thousand rubles. This scanner is capable of fully diagnosing your car (engine, gearbox, transmission, abs, srs and much more), which will pay for itself in 1-2 trips to the service station. The adapter is quite easy to use, has Russian-language software and is compatible with most cars produced in 1993. The device will also be useful when buying a used car, as it can show its real mileage and VIN.
The fluid brake system consists of many parts that can become unusable: pipes, wheel cylinders, calipers, drums and pads. Typical signs of a faulty master cylinder:
- After pressing the pedal, the car stops slowly. The reason is that the cuffs of one or two pistons have lost their tightness - they have cracked or “floated”.
- To slow down, you need to press the brake pedal hard. The phenomenon occurs due to swelling of the rubber of the piston seals.
- The brake pedal travel is too short. The fluid inside the cylinder has nowhere to go because the compensation hole is clogged. Another option is that the passage is blocked by a swollen rubber seal.
- A common symptom is pedal failure, the brakes coming on at the end of the stroke. This indicates complete wear of the cuffs; as a result, liquid penetrates behind the piston and rushes into the expansion tank - the cylinder “bypasses.”
- The pads do not release the brake discs and drums and get very hot when driving. Options: one of the pistons is jammed or the bypass hole is clogged.
The listed symptoms of a GTZ malfunction are similar to malfunctions of other elements. Pedal failure also occurs when a large amount of air enters the tubes or loss of fluid in one of the working cylinders. Sluggish deceleration and increased force on the pedal are often caused by a breakdown of the vacuum booster - a cracked membrane or a lack of tightness at the joints of the hose that takes off engine vacuum.
There are signs that clearly indicate the performance of the main hydraulic cylinder and the malfunction of other elements:
- during braking, the car pulls to the side - the problem lies in a certain circuit or wheel;
- jamming of the brake mechanisms of one wheel;
- creaking and squeaking when braking;
- heating the discs and pads on one wheel.
If you eliminate these symptoms, it will become easier to check the brake master cylinder in a garage. This also includes obvious brake fluid leaks and the knocking sound of worn calipers.
Video on the topic
Problems that arise with the brakes while traveling are considered critical and must be corrected immediately. The culprit of the malfunction is often the main cylinder, installed in the engine compartment and rigidly connected to the pedal.
To find out the cause of the breakdown and repair the unit yourself, you need to know the structure of the brake master cylinder (MBC) and its principle of operation. During the diagnostic process, it is necessary to distinguish and filter out problems with other elements of the system.
| The content of the article: |