Regardless of the design of the internal combustion engine, this important element of the car needs careful cooling to avoid overheating and, as a result, breakdown of moving structures. Modern internal combustion engines are equipped with coolant (coolant) circulating through a water pump. To prevent it from boiling, a special radiator is used, consisting of several thin tubes and lamellas.
During the movement, air hits the metal surface and passes between the lamellas, which helps cool the metal. As a result, the temperature of the liquid gradually decreases. In order to prevent a critical situation from occurring, it is important to quickly determine the location of the breakdown and find out why the cooling fan does not work.
General understanding of the cooling fan
The design is presented in the form of an ordinary electric motor, which is powered by 12V from the on-board network. The shaft has a special impeller, through which an air flow is formed, directed to the surface of the radiator. The fan is attached to the front of the frame, and is covered with a radiator grille on the reverse side.
Using the VAZ as an example, it is worth noting that most often there is only one fan in the system, but there are exceptions among the domestic auto industry, as well as foreign cars. For example, NIVA is equipped with an impeller with two independent electric motors. This design helps to increase the cooling rate of the liquid, which is an additional guarantee of engine safety.
Checking the Coolant Switch or Coolant Sensor
If both fans run when you short them, the problem is somewhere between the current flow at the fuse and the fan motors. On older systems where the fan is driven by the coolant temperature relay, disconnect the relay connector. Make sure this is the connector you need, as some vehicles have up to three connectors: one for the instrument panel warning light, one for the windshield control panel, and one for the engine management computer.
With the engine running and the coolant relay disconnected, the fan should work because the engine management computer on most systems will register a fault code from the inoperative switch and turn on the fans. If the fan does not work, and the switch is normal, it remains open until the temperature rises, then it closes to turn on the fan. To double check, simply ground one wire terminal of the disconnected connector using a jumper wire. The fan should start spinning. Many older Japanese cars have electrical circuits with relays closed in the normal state. They open at high coolant temperatures to turn on the fan, so when simply disconnected (with the ignition on), the fans should always operate in this configuration.
Many newer models have coolant temperature sensors. It is not a switch (relay), but a temperature sensitive resistor (thermistor) that sends a signal to the engine computer. The computer, which also exercises some control over the operation of the air conditioning system, decides when to turn on the fan and at what speed. You may not get a response by simply disconnecting the sensor connector or grounding it. Instead, check its calibration by connecting an ohmmeter.
Connecting an ohmmeter is a reliable way to test the thermistor.
The thermistor creates lower resistance when the temperature rises and increases pressure when it falls. If the sensor reads a thousand ohms or more (indicating low temperature) when the engine coolant is warm, it is out of calibration. Replace it. It's even easier to use a scanning device that will give readings in degrees (C or F).
How the device is activated
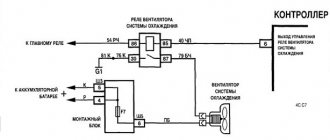
The cooling fan can be activated in several ways. It all depends on the make and configuration of the vehicle. If the car has a carburetor engine, then the fluid temperature should reach the range of 105-107 degrees. Then the sensor is automatically turned on, sending a signal to the relay. This, in turn, supplies power to the electric motor and closes the circuit.
Machines equipped with an injector have a slightly different cooling system and fan operation. All processes are started by an electronic control unit. Initially, information from the sensor is processed by the controller and then transmitted to the relay.
Operating principle of radiator fan
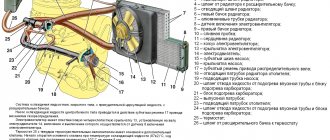
Before considering this issue, let us discuss in general what the water cooling system of an internal combustion engine is, shown in the figure below. It will allow us to remember the principle of its operation.
In cases where cold liquid passes through the motor jacket, it picks up excess heat, while the engine cools and the water heats up. Then it passes through the radiator, where it releases the resulting heat into the atmosphere, and again enters the engine.
The radiator design is a set of thin tubes that create a large cooling surface. The incoming air flow, passing through it, carries away excess heat that is stored in the liquid. In cases where there is no incoming air flow (engine idling, traffic jams and other similar situations), or it is not enough to cool the water to the desired temperature, the cooling radiator fan is provided for.
For this purpose, there is a special control circuit, the basis of which is the thermal switch of the radiator fan. It controls the temperature of the liquid. When it exceeds the established limits, the sensor is triggered and, based on its signal, the radiator fan is turned on, which creates the necessary air flow. This flow cools the heated water, and when its temperature reaches the required value, the sensor is triggered again and turns off the blowing.
This is how you can describe the basic principle by which the radiator fan works - it turns on when the water temperature exceeds the set temperature, and turns off after it drops to the desired value.
Causes of malfunction
When the fluid temperature rises to a critical level, this means that the cooling fan does not work. The main goal is to locate the fault as quickly as possible and eliminate it. There are a number of the most common reasons why the cooling fan does not turn on:
the electric fan motor has stopped working;
violation of the integrity of the wiring, which provides continuous power to the electric motor and connection to the power sensor;
the contact between the sensor and the electric motor is no longer reliable;
the fuse is blown;
the fan relay turned out to be faulty;
the sensor is broken;
The expansion tank valve fuse operates intermittently.
It is possible to determine the malfunction in each case independently. Let's look at each point in more detail.
If the fan motor is broken
If the cooling fan does not work, then first of all it is important to check the condition of the electric drive. To do this, you will need to take 2 wires, make a connection to the fan and organize power from the battery directly. If the startup was successful, it means that the element is working and you need to carry out further diagnostics.
It is also worth paying attention to the connectors and contacts in the electric motor. Sometimes a malfunction occurs due to the accumulation of dirt and dust, as well as oxidation of metal elements.
If nothing happens after connecting to the battery, then the problem is in the electric drive. Failure occurs for several reasons:
the brushes are worn out;
the collector collapsed;
The rotor winding is closed.
In the first option, it is enough to install new brushes. In the second and third cases, the situation cannot be corrected. Need a new fan.
Wiring check
An equally common reason why the cooling fan stops working. A wire break or short circuit may occur. To check, it is enough to use an ordinary tester and first activate the detector mode. Check the wiring that connects the controller to the fuse, relay and electric motor.
Checking the fan fuse and relay
First you need to check the fan fuse. As a rule, it is located in the mounting block under the hood. Most often marked with the designation F7. Check it using a tester. If everything is in order, you need to find the power relay. To find the required relay, it is recommended to use the vehicle manual. There should be 3 relays under the hood.
In handicraft conditions, it is almost impossible to determine operability, so the easiest way is to plug the relay into an adjacent socket.
Power sensor test
Another popular reason why the fan does not work is a sensor malfunction. It is possible to accurately determine that the sensor is broken only in cars with injectors. If you turn off the power, the electronic system will perceive this as a malfunction and start the fan in emergency mode.
When the fan switch sensor fails, you should be careful. The check should be carried out as follows: warm up the car until the fluid temperature reaches 100 degrees. Next, turn off the engine, open the hood and disconnect the sensor by disconnecting the connector. Next, start the engine. If the fan starts working, then the problem is a sensor malfunction.
It is important to note that in cars with carburetor engines, it is impossible to check in this way. In this case, you can only replace a new sensor and warm up the engine to operating temperature.
The fan does not turn on - reasons
- Motor. Problems with the electric motor that drives the fan is one possible problem. Such a breakdown will completely immobilize the blades and the cooling of the motor will be disrupted. You can check the operation of the electric motor by connecting it directly to the battery power, bypassing the on-board network. If, after applying power directly, the fan is immobilized, the electric motor is most likely faulty and requires replacement.
- Sensor. If everything is humming with the electric motor, but the fan does not spin, you need to check the coolant temperature sensor (DTOZH). The reason may be that the sensor is faulty and does not report the coolant temperature to the ECU or provides incorrect information. You should check the DTOZH and replace it if necessary.
- No power, open circuit, fuse. If the cooling fan does not rotate, the problem may be a simple open circuit or poor contact. Check the wiring and contacts, this may be the problem. Also check the fuses that are related to this unit.
Changing the safety valve
Another equally common problem that can lead to fan interruptions. If the above checks have been previously performed and all elements are in order, then you need to check the safety valve of the expansion tank.
The main function of the valve is to maintain the operating pressure above atmospheric pressure. Thus, the water present in the liquid does not boil when the temperature reaches 100 degrees. If the valve stops working, the pressure becomes the same as atmospheric pressure, and the liquid will begin to boil when it reaches a certain temperature.
The sensor will only work at 105-107 degrees. The liquid will begin to boil and the fan will not work. It is impossible to check the operation of this element in artisanal conditions. But it’s realistic to buy a new part and make a replacement.
If you need to replace the sensor, it is important to buy the same model with identical characteristics. Otherwise, the cooling system will start working too sooner or later. You can do the replacement yourself using the following procedure:
disconnect the battery terminal;
empty the radiator of liquid;
disconnect the two wires that are connected to the sensor. Use a 30 mm wrench;
Apply sealant to the new sensor and install it in the appropriate place;
do not tighten the sensor too much;
Fill with coolant, start the engine and wait until the temperature rises.
If all steps are done correctly, the procedure does not take much time. On average, replacing a new sensor takes no more than 30 minutes. You can contact a specialized center, but a simple procedure can be expensive.
Checking the fan motor
Is the fuse ok? The most practical approach is to go to the end of the chain, that is, directly to the fans. Most cars have two fans. Disconnect one of the fan wiring connectors and (referring to the electrical color code diagram) short the wires to the fan motor connector. Route one jumper cable from the terminal to supply current to the positive terminal of the battery. Connect the second connecting wire to the other terminal of the connector, and connect it to ground. The fan should work. If this does not happen, the fan motor is obviously faulty.
Try connecting the battery with a jumper wire directly to the fan to see if it will work.
Some cars have one fan that runs at two speeds. In such cases, the connector may have: • two terminals (one from the dual voltage supply - through a drop-off resistor circuit for low speed and a bypass resistor circuit for high speed - plus a second for ground). The circuit has a splice or connector for dual voltage supply. If you test by shorting the wires on the fan motor itself, it will start running at high speed; • three terminals (one for low speed current supply, the second for high speed current and ground). Test each of the power supply terminals separately, using a common ground line in each case; • four pins (high speed, low speed and two ground). Connect each pair individually using jumper wires.
Electrical circuit of the fan
The electrical circuit of the fan consists of two parts - an electric motor with a starting capacitor and a unit for switching on and adjusting the speed of rotation of the blades.
The electric motor is a metal casing (stator) in which windings made of copper wire are fixed and connected according to the diagram shown above. A rotor is also fixed in the housing in sliding bearings, which, in response to the appearance of an electromagnetic field as it passes through the stator windings, rotates.
By applying supply voltage to the windings L1, L2 or L3 using interconnected switches S1, S2 and S3, you can regulate the air flow speed. The motor winding L4 and the capacitor C1 attached to the motor housing are used to start the motor.
If winding L4 or capacitor C1 is broken, the engine will not start when turned on in automatic mode. But if you turn the impeller clockwise by hand, the blades will begin to rotate. In this way, you can determine the malfunction of this chain.
In some fan models, to protect the windings from overheating in the event of a malfunction, a thermal fuse (indicated St° in the diagram) is installed at an operating temperature of about 125°C.
When heated above the design temperature, the thermal fuse breaks the circuit and the supply voltage is not supplied to the motor windings. This prevents them from burning out if the rotor jams when the lubricant is produced. The thermal fuse is usually installed at the end of the stator windings.
There are two types of thermal fuses - disposable and self-resetting. The latter, when heated above the temperature indicated on their body, break the circuit, and when they cool down, they close again. This avoids the need to replace them in the event of a jammed rotor.
Checking the electric motor
If the cooling fan does not work, the first thing you need to do is check its drive (electric motor). It's easy to do. It is enough to take two wires, connect them to the fan and power it directly from the battery. If it starts, then the problem is not with it. We need to look for it further. At the same time, you can check the contacts in the motor connector. Sometimes it happens that the problem is in them. The ingress of dirt and dust, as well as oxidation of metal surfaces can cause contact failure.
If the electric motor does not turn on after connecting to the battery, most likely it is the battery that has broken down. The reason for this may be:
- worn brushes;
- reservoir destruction;
- short circuit of the rotor or armature windings.
In the first case, it is enough to replace the brushes with new ones, and the fan motor will work like new again. In the case of destruction of the commutator or short circuit of the windings, repair may not help.
Read also: Why do people become alcoholics?
Checking the serviceability of the electric fan start relay and fuses
First, check the electric fan fuse. It is usually located in a block under the hood of the car. You can find the right fuse using the car's owner's manual, although there are often markings on the cover of the mounting block with the location of the fuses. We check using a tester. If no problem is identified, move on. We find the electric fan switch relay. It will not be possible to check it with a tester; to check it, you will need to replace this relay with a working one.
How to check the thermostat
The function of the thermostat in an internal combustion engine is to regulate the flow of coolant, directing it in either a small or large circle. While the engine is cold, its valve blocks the flow of coolant into the cooling radiator. This allows the engine to warm up faster.
Check the thermostat by determining the temperature of its pipes by touch. When the engine is warm, they should all be hot. If the pipe leading from the thermostat to the cooling radiator is cold, the locking device is faulty.