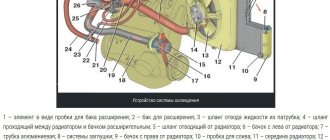
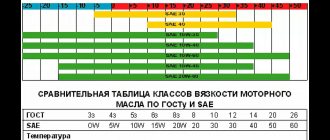
Home » Diesel » Diesel engine operating temperature - monitoring and warming up 419
Hello dear friends, nowadays modern diesel engines with rapid warming up to operating temperature are gaining more and more popularity.
Before you begin to consider any specific parameters, you need to have an idea of what a diesel engine actually is. In 1824, the theory was first put forward that a body could be heated to the desired temperature if it was subjected to a change in volume. In other words, apply rapid compression.
This was not put into practice until several decades later. The first diesel engine unit was released in 1897. It was developed by German engineer Rudolf Diesel. The operation of such an engine is based on the fact that atomized fuel, interacting with air (heated as a result of compression), self-ignites. Today, diesel engines are used only in cars and agricultural equipment; they have also found their place in tanks and ships.
Diesel engine features
This type of engine was invented back in 1824 by a French physicist who put forward the theory that by changing the volume of a body, it can be heated, that is, it can be rapidly compressed.
This hypothesis found practical application only 70 years later. It was then that the first diesel engine was released. Its operating principle is as follows: self-ignition of the injected fuel occurs, which interacts with air during the compression process.
The diesel engine has a wide range of applications, from passenger cars, agricultural equipment to military equipment (tanks, sea vessels).
general characteristics
Diesel has the highest thermal efficiency of any practical internal and external combustion engine due to its very high expansion ratio and inherent lean combustion, which allows heat to be dissipated by excess air. A small loss of efficiency is also avoided without direct injection, since unburned fuel is not present when the valve closes, and fuel does not flow directly from the intake (injection) device into the exhaust pipe. Low-speed diesel engines, such as those used on ships, can have thermal efficiencies in excess of 50 percent.
Diesels can be designed as either two-stroke or four-stroke. They were originally used as a more efficient replacement for stationary steam engines. Since 1910 they have been used on submarines and ships. Use in locomotives, trucks, heavy equipment and power plants followed later. In the thirties of the last century they found a place in the design of several cars.
Advantages and disadvantages of a diesel engine
Like all other engines, diesel has a number of both positive and negative aspects. Main advantages:
- Firstly, diesel engines can consume any fuel, so there are no serious requirements for it.
- Secondly, the greater the mass and concentration of carbon atoms, the greater the calorific value of the engine and its efficiency.
- Thirdly, vehicles with diesel engines are more responsive due to the high torque at low speeds. Therefore, owners of fast sports cars prefer the diesel engine option.
- Fourthly, the carbon dioxide content in the exhaust is an order of magnitude lower than that of similar gasoline engines.
- Fifthly, the diesel engine is more economical, since the cost of diesel fuel is less than the cost of gasoline.
Despite such an impressive list of advantages, the diesel engine also has a number of disadvantages:
- Firstly, the cost of a diesel engine is higher than the cost of a gasoline engine, since due to the high mechanical stress that occurs during operation, the parts must be of high quality and durable.
- Secondly, the power of gasoline engines exceeds the power of diesel engines.
- Thirdly, in winter, diesel fuel is more likely to solidify than gasoline.
- Fourthly, the operation of a diesel engine must be extremely careful and careful, since if you do not take care of it, you will have to carry out repair work, which will cost a lot of money.
The first stroke is intake.
Modern engine structure
car, design of systems and mechanisms
The piston moves from TDC to BDC, and purified air enters the cylinder through the open intake valve (due to the vacuum created by the piston). The air is mixed with a small amount of exhaust gases remaining from the previous cycle, the temperature rises and at the end of the intake stroke reaches 300-320 K, and the pressure 0.08-0.09 MPa. The cylinder filling coefficient is 0.9 or higher, i.e. more than that of a carburetor engine.
Combustion phases
The engine's operating process is divided into four parts. The first is the injection of a combustible mixture into the combustion chamber, in which there is high pressure.
Second, this mixture begins to ignite and burn. The third part is the formation of unspent mixture droplets, which then turn into soot. In phase 4, the combustion of fuel residues occurs in order to limit atmospheric pollution from them. Here a lack of oxygen is manifested, this is due to the burnt mass of fuel in the previous parts.
Other nuances
Diesel combustion is known to be very lean with an A/F ratio of:
- 25:1 at peak torque.
- 30:1 at rated speed and maximum power.
- Over 150:1 at idle for turbocharged engines.
However, this additional air is not included in the combustion process. It gets quite hot and depleted, resulting in poor diesel emissions. Even though the average air-fuel ratio is lean, if proper care is not taken during the design process, areas of the combustion chamber can be fuel-rich and result in excessive smoke emissions.
Parameters of diesel engines
Many car owners ask the question what the operating temperature of a diesel engine should be. But to answer it, you should pay a little attention to the main parameters that affect the operation of the motor. The number of strokes is important in the operation of the motor, that is, there are two- and four-stroke.
The power of the unit also depends on the torque. The operating temperature of a diesel engine is determined by the degree of compression of the gas-fuel mixture, so the temperature is directly proportional to compression. Thus, as compression increases, the temperature will also increase, as a result of which the intensity of this process will increase, increasing the efficiency. It is worth remembering that the most efficient work is done when the fuel mixture burns evenly.
An important parameter to achieve the best possible performance is the operating temperature. The operating temperature of a diesel engine must be maintained based on the design and purpose of the engine. This fact determines whether the temperature is normal or not.
The fourth measure is release.
The piston moves from BDC to TDC. Through the open exhaust valve, the exhaust gases are pushed out through the exhaust pipe into the environment. At the end of the exhaust stroke, the gas pressure is 0.11 -0.12 MPa, the temperature is 850-1200. After this, the diesel operating cycle is repeated. In two-stroke engines, the time allotted for the working cycle is used more fully, since the exhaust and intake processes are combined in time with the compression and power stroke processes. The operating cycle occurs over 360 degrees (one revolution of the crankshaft).
When the piston moves from TDC to BDC, expansion and exhaust processes occur simultaneously with purging of the cylinder, and when the piston moves back from BDC to BDC, intake and compression occur. Changes in cycle parameters (pressure and temperature) correspond to changes in four-stroke engine parameters. A comparison of the operating cycles of four- and two-stroke engines shows that with the same cylinder dimensions and crankshaft rotation speed, the power of two-stroke engines is 1.5–1.7 times higher. It is simpler in design and more compact. The disadvantages of a two-stroke engine include the limited gas exchange time, which impairs the cleaning of the cylinder from exhaust gases, increases the loss of part of the fresh charge, and reduces efficiency.
Source
Volkswagen operating temperature
What is the operating temperature of a Volkswagen diesel engine? This question is asked by many owners of these cars. As you know, each make and model of car, depending on the type of engine, has its own operating temperature.
As a rule, the operating temperature of a Volkswagen diesel engine is in the range of 90-100 degrees Celsius. Sometimes it happens that the dashboard shows a temperature higher than it actually is. This often happens on certain brands of Volkswagen cars. But there is no need to rush to change the equipment; first you need to contact the service for a technical inspection and determine the cause of the malfunction.
Mercedes operating temperature
The operating temperature of a Mercedes diesel engine depends on many factors. First of all, these are the operating conditions of the car. Then the thermostat type. Also, depending on the region of residence, be it Siberia or more southern regions, the thermostat is adjusted to the optimal temperature.
The normal operating temperature of a Mercedes diesel engine can range from 80 to 100 degrees. On powerful engines from 220 horsepower, set the thermostat to 75-78 degrees Celsius. For cold regions, on the contrary, up to 97 degrees and above.
Opel operating temperature
The operating temperature of the Opel diesel engine, due to the fact that it is under high pressure, can sometimes exceed the normal level by several points. Usually it fluctuates around 104-111 degrees Celsius.
Opel cars have a cooling system. When the upper operating temperature limit is exceeded, the fan turns on and quickly cools the engine to the minimum value.
Kinds
Many engines use resistance heaters in the intake manifold to heat the incoming air and for starting or until operating temperature is reached. Electric engine block heaters connected to the mains are used in cold climates. In such cases, it must be turned on for a long time (more than an hour) to reduce startup time and wear.
Block heaters are also used for emergency power supplies with diesel generators that need to quickly shed the load during a power failure. In the past, a wider variety of cold start methods were used. Some engines, such as Detroit Diesel, used a system to inject small amounts of ether into the intake manifold to initiate combustion. Others have used a mixed system with a resistance heater burning methanol. An improvised method, especially on non-running engines, is to manually spray an aerosol can of essential liquid into the intake air stream (usually through the intake air filter assembly).
KamAZ operating temperature
A very popular question among owners or those planning to become owners is what is the operating temperature of the KamAZ diesel engine. The answer to this question is the range of 95-98 degrees Celsius.
At a given temperature, the fuel burns completely, and most of the allowable clearances in the engine are selected. If the operating temperature is too low, engine performance may be adversely affected.
Diesel engine oil
The main task of oil and other lubricants in the engine is to significantly reduce friction between parts, which increases their service life. The choice of lubricant depends on the type of engine and the tasks assigned. The operating temperature of the oil in a diesel engine depends on the engine coolant. The difference is 10-15 degrees Celsius. The upper threshold of his normal temperature is 105 degrees.
In addition to temperature, the oil must also have optimal parameters to ensure maximum useful engine operation: viscosity and lubrication. Viscosity should be determined based on weather conditions and air temperature. Because if you choose the wrong oil with the wrong viscosity, the operation of the engine and its parts may be disrupted. Lubrication has two types: boundary, hydrodynamic. Boundary lubrication involves removing used oil from engine parts, and introducing a portion of new oil to them. Hydrodynamic is that the oil is constantly renewed, lubricating the parts. More modern engine models use the first lubrication option.
Common diesel problems: injection timing and compression
If the compression of the mixture in the cylinder is insufficient, noises and metallic knocks can be heard while the engine is running. The fact is that in this case the mixture needs more time to heat up to the ignition temperature.
It turns out that reducing the compression of a diesel engine increases the time before the charge ignites.
In this case, there will be more unburnt mixture in the cylinder than necessary. As a result, at the moment such a charge ignites, the combustion process becomes explosive, the pressure increases sharply, a shock wave and detonation appear, destroying the CPG and placing significant loads on engine parts.
Then the piston goes down, the temperature and pressure are further reduced, there are no conditions for combustion. It turns out that unburned diesel fuel evaporates and then enters the exhaust system
The same thing happens if the diesel fuel injection is too late. In other words, the compression in the cylinders is normal, but the supply of fuel late leads to the fact that the piston is already going down, there is no necessary compression and pressure for self-ignition.
If the exhaust is black, this may indicate that the injectors are “overfilling”, that is, fuel is being supplied in a larger volume than necessary. In simple words, there is a lot of diesel fuel, but there is simply not enough oxygen for such an amount of fuel.
The available oxygen allows only part of the fuel to burn out, and the unburned residues turn into carbon, which manifests itself in the form of characteristic black smoke from the exhaust pipe.
We also note that similar problems can be caused by insufficient air supply (for example, a clogged air filter), airing of the diesel engine power system, etc.
As a result, if the normal process of mixture formation is disrupted, this naturally affects the moment of ignition and the subsequent efficiency of combustion of the fuel charge in the cylinders.
Increase in operating temperature
A sudden increase in engine operating temperature can cause more harm than under-temperature. In this case, the engine parts begin to operate in a hydrodynamic lubrication mode, which leads to a decrease in oil viscosity. Then the oil does not completely cover all parts, which subsequently leads to damage to the engine mechanism. Oil levels will be normal thanks to constant top-ups. When the engine overheats, the housing and bearings first become unusable, but the pump remains normal. This phenomenon is similar to problems caused by insufficient lubrication.
Starting diesel engines in winter conditions
Almost all people know that it is necessary to warm up the car engine before driving. Especially during the winter period. If we consider this warming up process in detail, we will see the following: first of all, the pistons begin to heat up, and only then the cylinder block. If you start driving with a cold engine, then the oil, which has a thick consistency, will not flow in the required quantities. And in the end, this event can lead to breakdown.
It should be noted that excessive heating of the car for wear and tear is very harmful. This reduces the service life of engine parts and the entire vehicle. In order to warm up the car correctly, you need to bring the fluid temperature to 50 degrees Celsius using idle speed. After this, you can safely start driving without exceeding 2500 rpm. After heating the oil to the operating mark, you can add gas.
By fulfilling these conditions, you can keep not only the engine intact, but also your budget. If the engine refuses to start, then specially invented additives should be used. Due to their composition, they are not waxed. They are added not only as independent additives, but also in combination with fuel, maintaining optimal proportions.
Compression ratio
A diesel engine operates on the principle of self-ignition of the mixture from contact of atomized diesel fuel with air heated by compression. The more the air in the cylinder is compressed (heated), the more intense the flash occurs after fuel injection, while the amount of fuel supplied remains the same.
It is also worth considering that the compression ratio is increased only to certain limits. The fuel-air mixture in the cylinder should not explode upon contact with heated air, but burn evenly. A strong increase in the compression ratio can lead to uncontrolled ignition of the fuel, which causes detonation, local overheating and accelerated wear of the cylinder-piston group.