If you have never experienced oil boiling in your internal combustion engine, then I can draw one of two conclusions - either you are an excellent owner and take good care of your car, or you have simply been lucky so far. In fact, the problem is quite common. As the spring-summer period begins, our service station increases in number of clients. People ask exactly this question.
It is worth saying that even a very zealous and scrupulous motorist can cause the lubricant to boil. There are a lot of reasons for this, ranging from the purchase of low-quality lubricant to problems with the engine. Since boiling of an oil composition can lead to serious consequences, it is necessary to clearly understand the issue and know what boiling point is set for a particular oil. So, let's talk about this in this article.
The concept of operating oil temperature
During engine operation, increased pressure and a significant increase in heat occur, which negatively affect the surface of parts. And only thanks to the optimal temperature indicator of the lubricant, these negative factors are localized. According to reference literature, the operating temperature of the oil in the car engine should be +92 - +105 degrees Celsius.
Even a slight deviation from this parameter can cause serious damage to the unit. The boiling point of a lubricant depends on the use of certain brands of additives. So, some additives provide boiling at a level of +180 degrees, while others can increase this indicator to +195 degrees.
Dynamic viscosity of CCS and MRV engine oil
This indicator determines the low-temperature characteristics of the oil and also refers to the SAE J300 standard, in which it is indicated by the first number and the letter W. Most drivers determine the applicability of the oil in winter in their climate only by these two symbols in the SAE marking, but from my own experience I can say, which is not worth it. Some oils labeled 10W may have superior low temperature performance than 5W oils when considering dynamic viscosity. This indicator directly depends on the composition of the oil, that is, its base. For example, PAO has a great influence on low-temperature properties; synthetics retain fluidity better in cold weather than mineral or semi-synthetic oils. So when choosing, look at the dynamic viscosity index CCS or MRV - the further it is from the upper threshold, the better.
CCS and MRV - what is it and how is it determined
Let’s briefly define what these indicators are. CCS (Cold Crank Simular) - cold start imitation, determines the maximum viscosity at a given negative temperature, which will allow the engine to start with standard starting systems. CCS viscosity is determined at temperatures from -10 to -35 degrees Celsius, the set temperature depends on the SAE oil class, you can see the indicators for each class in the table below.
MRV (Mini Rotary Viscometer) – pumpability test. In this case, the maximum dynamic viscosity of the oil is determined, at which it is pumped through the channels into all friction pairs at the moment the engine starts. That is, the first test determines at what temperatures starting will be possible, and the second test determines at what temperatures it will be safe, without prolonged oil starvation of the parts. This indicator is determined at temperatures from -15 to -40 degrees Celsius, and also depends on the SAE viscosity class.
| Viscosity grade | Cold start simulation CCS | MRV pumpability |
| 0W | 6200 at -35 | 60000 at -40 |
| 5W | 6500 at -30 | 60000 at -35 |
| 10W | 7000 at -25 | 60000 at -30 |
| 15W | 7000 at -20 | 60000 at -25 |
| 20W | 9500 at -15 | 60000 at -20 |
| 25W | 13000 at -10 | 60000 at -15 |
Keep in mind that in tests it is the oil that is cooled to the specified temperature. In real conditions, the engine temperature rarely drops to the same value as the ambient temperature. For example, if it’s -35 degrees outside your window in winter, the engine must stand idle for two days so that the oil in it cools down to the same temperature.
Why is boiling grease dangerous?
The boiling point of 5w40 motor oil is +200 degrees and the boiling process of the lubricant itself is accompanied by the formation of many bubbles in the liquid and the formation of a significant amount of deposits that can tightly clog the gaps between parts. In addition to gaps, such deposits can clog the channels through which lubricant circulates. The boiling process can quickly turn into ignition of fuel and lubricants. In order for the oil to ignite, a temperature of + 230 - + 240 degrees is required. The boiling level also depends on the brand of oil.
But many experts argue that ignition can occur already at + 150 degrees. Indeed, during the combustion of oil, vapors are released, which cause premature ignition of the liquid.
In addition, the following negative processes can occur in the power unit:
- destruction of the protective oil layer located on the surface of parts;
- an increase in the friction force and destruction of the surface of parts or its complete failure;
- reducing the gap between rubbing parts with their subsequent jamming;
- a layer of soot forms on the surface of the parts and solids accumulate;
- failure of pistons and cylinders;
- engine tripping occurs and glow ignition occurs;
- detonation of an explosion inside the power unit.
Good to know: Rating of motor oils 2022 synthetic 5w40?
The influence of low temperatures on engine starting stability
When purchasing a lubricant, you need to familiarize yourself with the winter parameters of the fluid, since they determine the quality of starting the internal combustion engine in the cold season. If you are using a 5W-40 class lubricant, then subtract 35 from the number 5 (this is a constant number for all types of oils). We get -30 - this is the minimum temperature at which the lubricant can start the engine without problems.
Low temperature parameters
It is necessary to take into account not only the ambient temperature, but also the power unit, since the operation of the engine is determined by the vehicle’s mileage and loads.
There are low-temperature properties of the working fluid, which include:
- Pumpability. This parameter means a state in which the substance is pumped without problems through the channels of the lubrication system.
- Product rotation. This value indicates the dynamic characteristics of the viscosity of lubricants, as well as the temperature at which the lubricant becomes most liquid. In this state, starting the engine will be easier. The cranking temperature is always 5 degrees higher than the pumping temperature.
User Vlas Prudov made a video in which he talked about choosing a high-quality fluid for a machine engine.
Freezing
The value of the pour point is determined by the loss of mobility and fluidity properties of the liquid. When the viscosity parameters increase sharply, this leads to the beginning of the wax crystallization process. Oil operating at low temperatures will be less mobile. The lubricant hardens, which leads to an increase in ductility as a result of the release of hydrocarbon substances. The pour point of the motor fluid corresponds to the minimum circulation parameter. If the oil begins to solidify, starting the engine is possible, but it will be very difficult.
Solidification temperature
The solidification temperature is 3-5 degrees lower than solidification. When it gets very cold, the fluid base becomes harder, making it impossible for it to pass through the channels of the lubrication system. Accordingly, the driver will not be able to start the power unit. This problem is more pressing for residents of northern regions, who fill their cars with oils that do not meet the viscosity class for use in such conditions.
Loading …
Main symptoms of boiling
Changing thermostat data. Each car in its configuration has a special indicator on the dashboard that shows the temperature and condition of the lubricant. When the unit is normally warmed up, the indicator sensor should be in the middle position. And as soon as the car owner notices even a slight deviation towards the red line, this is a serious sign of an increase in oil temperature.
- Characteristic sound. When the lubricant boils, the motorist can hear a characteristic boiling sound, which an experienced motorist will not confuse with anything.
- The appearance of smoke . If smoke appears from the engine compartment, this may be a sign of boiling lubricant.
- Presence of black exhausts. At the initial stage of boiling of the lubricant, you can see characteristic blue-black exhaust from the exhaust pipe.
Tables with smoke points of oils and fats
Next, you can familiarize yourself with two tables: one shows the smoke points of vegetable oils, the other shows the smoke points of animal fats (including butter). They are sorted in alphabetical order.
The “*” sign next to the temperature indicates those oils/fats for which the English-language Wikipedia does not yet know reliable sources. Nevertheless, in principle, you can rely on these values - I think this information is still more reliable than what can be found on the Russian-language Internet.
If you are viewing the site on a smartphone, and the table does not fit on the screen, and even rotating the screen does not help, or simply if it is more convenient for you, then here is the table in the form of a picture.
Smoke point of vegetable oils
| Avocado | 270°C | |
| Peanut | unrefined | 160°C* |
| refined | 232°C | |
| Grape seed | 216°C* | |
| Mustard | 254°C* | |
| Walnut | unrefined | 160°C* |
| semi-refined | 204°C* | |
| camellias | 252°C* | |
| Castor | refined | 200°C |
| Coconut | virgin | 177°C |
| refined | 204°C | |
| Hemp | 165°C* | |
| Corn | unrefined | 178°C |
| refined | 232°C | |
| Sesame | unrefined | 177°C |
| semi-refined | 232°C | |
| Linen | unrefined | 107°C |
| Macadamia | 210°C* | |
| Margarine | 182°C* | |
| Almond | 216°C* | |
| Olive | extra virgin | 160°C |
| extra virgin, low acidity | 207°C | |
| virgin | 210°C | |
| refined or tasteless | 199°-243°C | |
| pomace (derived from pulp) | 238°C | |
| Palm | diffraction | 235°C |
| Sunflower | unrefined | 107°C* |
| semi-refined | 232°C* | |
| refined | 227°C | |
| high oleic, non-raph. | 160°C* | |
| Rapeseed (canola) | unrefined | 107°C |
| refined | 204°C | |
| pressed on expeller | 190°-232°C | |
| high oleic | 246°C* | |
| Rice | 254°C* | |
| Safflower | unrefined | 107°C* |
| semi-refined | 160°C* | |
| refined | 266°C | |
| Soy | unrefined | 160°C* |
| semi-refined | 177°C* | |
| refined | 238°C | |
| Hazelnut | 221°C* | |
| Cotton | 216°C | |
Smoke point of animal fats
| Butter | 150°C |
| Ghee , including ghee | 252°C* |
| Beef fat | 215°C* |
| Lard | 190°C |
Most of the types of oils listed above (as well as those not mentioned), often also having an organic certificate, you can buy in the iHerb online store (with fast and free delivery to Russia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine and other countries from $40). Including very rare oils such as avocado, macadamia, pistachio and others, as well as real organic ghee from free-grazing cows. And all products are guaranteed to be of high quality, no fakes. In general, I recommend it - I buy coconut oil, black cumin, ghee, and MCT there myself. I buy olive, flax, and sesame from us because they are of equal quality and cheaper. You can find instructions for purchasing on iHerb here→.
What to do if the grease boils?
The boiling point of 5w30 motor oil is +207 degrees Celsius. And if symptoms of lubricant boiling are noticed, then you need to immediately turn off the engine. The main thing is not to panic. But if this problem was discovered during heavy traffic, and you can’t stop right away, then you need to perform the following steps:
- reduce the load on the car engine by reducing the number of revolutions to a minimum;
- turn on the auto furnace to the maximum possible operating mode, thereby removing some of the superheated air from the working area and thereby reducing the concentration inside the engine;
- It is possible to drive at idle speed on the highway until the car comes to a complete stop.
- As soon as you manage to completely stop the car, you must immediately turn off the engine.
How to warm
This would seem to be a short recommendation - on cars with AMG engines, it is not recommended to enter power modes until the oil temperature reaches 20 °C. We are talking specifically about warming up while driving. On AMG cars this is quite simple - the oil temperature is reflected in the standard menu of the on-board computer. On regular models there is no such indication. Well, okay – that’s not the point. From the factory's recommendations, we know that only oils with 0W-40 or 5W-40 ratings are allowed in AMG engines. Oil viscosity at 20 °C is not specified anywhere, but it is approximately 200...300 cSt for 0W-40 or 5W-40 oils. Those. we know that with a viscosity of 200...300 cSt, we have every right to load the motor to its fullest without fear of damage or destruction. Another thing is that such viscosity is achieved for other oils at completely different temperatures. Since the temperature change curves for viscosity vary greatly from oil to oil, we will make the following assumption:
- XW-30 oils allow you to switch to driving mode with high loads at an oil temperature of 10...15 °C;
- XW-50 oils will have to be heated to 30 degrees, and “sixties” – to 40 °C.
It’s good for AMG owners - you can catch this moment quite accurately. What should ordinary people do in “civilian” Mercedes? After all, the oil temperature is not equal to the coolant temperature! The solution is to heat the engine with a “reserve” – up to 40 degrees (coolant temperature). This is usually the beginning of the temperature gauge scale. Those. the arrow or bar has become above the 40 mark - you can “stomp it down”.
So, we know three reference points of our graph of engine oil heating modes:
The minimum engine oil temperature point at which safe starting is possible; The point at which the engine can be brought to power modes without fear of damage. It is clear that we are talking about the second phase of warming up - warming up in motion. The point is that this phase is also divided into two parts - in the first part we “sick”, not raising the speed above 2000-2500 until the oil temperature reaches 20 °C. In the second part of the warm-up while moving, we can afford to add gas and even overtake the tram; Well, a point that is more or less clear to everyone is the normal operating temperature regime, when the oil temperature is equal to or slightly higher than the engine warmed up to operating temperature; It remains to find the fourth point. This is the temperature that the oil must be brought to before warming up the oil while driving can begin. Theoretically, this value can be found, calculated, logically assumed
But for this you will need to create a complex calculation methodology that will take into account the oil temperature at start-up, the type of engine - diesel or gasoline, if gasoline - then with or without supercharging, with injection into the intake manifold or direct injection, thermostat characteristics, cylinder block material , true viscosity characteristics of the oil and much more. Okay, well, let’s even deduce a hypothetical temperature zone up to which warming up should take place while the car is stationary, and after which – while in motion. But with the exception of AMG models, not a single Mercedes has an engine oil temperature indicator
And comparing it with the coolant temperature means introducing an additional error
But with the exception of AMG models, not a single Mercedes has an engine oil temperature indicator. And comparing it with the coolant temperature means introducing an additional error.
This is where two polar points of view appear: the first - you can’t heat it up, the starting speed has dropped - and let’s go; the second is to warm it up at idle speed at least until the coolant gauge needle comes off the stop; some warm it up to operating temperature.
Main causes of the problem
- The motorist's use of low-quality lubricant. After all, it is a low-quality lubricant that will not be able to cope with strong temperature changes, since under such conditions the lubricant loses its viscosity and begins to burn and evaporate.
- Not replacing the lubricant in a timely manner. Outdated oil is not able to perform its functions properly.
- There are malfunctions in the cooling system. If this system has problems with fan operation, a faulty fluid coupling, or contamination of the radiator, then these faults can cause boiling.
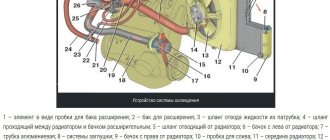
Causes and consequences of cooling failure
There are several reasons why antifreeze boils. Most common:
- Thermostat failure.
- Malfunction of the pump, radiator or fan.
- Low fluid level in the tank.
Sometimes the cause of a cooling malfunction can be an air lock that has formed. If there is visible damage to the radiator, pump, thermostat or fan, then most likely they have caused a malfunction in the cooling system. This breakdown is the easiest to identify and fix. In this case, the critical increase in antifreeze temperature will not exceed ten minutes. During such a period of time, no damage will be caused to the vehicle systems.
Low antifreeze level
Sometimes the liquid may boil due to a small amount of it in the tank. This can happen because the cooling system was not filled to the correct level. You should always look at the arrow of the tank body: it should be strictly between the minimum and maximum volume marks.
Another reason for a small amount of liquid may be a simple leak.
It is worth taking into account that the boiling point of antifreeze under pressure is higher, which means that a loss of pressure will reduce the indicator
Difficulties after changing the fluid
Over time, antifreeze can change its chemical composition and, as a result, its properties. Of course, this can cause the coolant to boil. In this case, it may be necessary to replace the antifreeze.
Even if the new fluid level is normal, problems may arise. An air lock in the engine is one of the most common. You need to get rid of it, otherwise the antifreeze will boil at a lower temperature.
Another problem after replacing antifreeze may be the low quality of the new fluid. Most often, unscrupulous manufacturers dilute antifreeze with water. Of course, such a liquid is cheaper, however, it is very ineffective.
Other reasons
Often, other causes of malfunctions are problems with an incompatible water pump, a large amount of accumulated dirt in the radiator, or impaired air circulation. For normal airflow, the water pump must have a fan with a special casing. Otherwise, heated air will flow to the pump. When replacing, it is also necessary to select the blades of the desired model. Smaller sizes may not cope, which will ultimately lead to a decrease in pressure in the system.
Possible problems after boiling
Mechanical failures of fan or thermostat systems allow you to quickly identify and eliminate boiling liquid. An emergency increase in the temperature of the antifreeze will last in this case only about ten minutes, without causing much harm to the vehicle systems.
If the engine runs on hot antifreeze for more than fifteen minutes, problems may arise. During this period of time:
- There is an increased risk of leakage in the main radiator.
- There is a high chance of damage to the cooling system pipes. This leads to antifreeze leakage.
- The rings on the piston will wear out. In this case, they will quickly shrink, which will lead to an increase in fluid consumption in the engine many times over.
- Seals and seals will no longer perform their function. The lubricant will begin to flow out quickly.
Running a car engine for a long time (more than thirty minutes) at high temperatures is very dangerous. This may cause:
- Engine explosion. This can only happen when operating at maximum temperature for a long time.
- Melting of pistons in the engine compartment. Due to the high temperature, engine elements easily burn out. In this case, major repairs cannot be avoided.
- Damage and change in the shape of the cylinder head. It will require serious repairs.
- Destruction of the partitions between the rings in the engine. The parts will weld together.
- Failure of engine valves. You'll have to replace parts.
- Damage to the cylinder head gasket. It will be necessary to replace the seal and change the bolts on the head.
- Destruction of valve seats.
Summarizing
The boiling point of motor oil has a significant effect on the operation of a car engine. As can be seen from the material presented above, an excessive increase in the temperature of the lubricant is a rather dangerous ailment that every motorist can encounter. You can reduce the likelihood of this problem occurring by performing timely vehicle diagnostics and using only high-quality lubricants.
Good to know: Boiling point of antifreeze
Every motorist should know that each brand of oil has its own boiling level. So the boiling point of 5w40 motor oil is +200, and the boiling point of 5w30 motor oil can reach + 207 degrees Celsius.
Video “Testing motor oils?”
Shelf life of motor oil
User Denis MECHANIC tested different brands of fluids in his video and talked about the test results.
If you have never experienced oil boiling in your internal combustion engine, then I can draw one of two conclusions - either you are an excellent owner and take good care of your car, or you have simply been lucky so far. In fact, the problem is quite common. As the spring-summer period begins, our service station increases in number of clients. People ask exactly this question.
It is worth saying that even a very zealous and scrupulous motorist can cause the lubricant to boil. There are a lot of reasons for this, ranging from the purchase of low-quality lubricant to problems with the engine. Since boiling of an oil composition can lead to serious consequences, it is necessary to clearly understand the issue and know what boiling point is set for a particular oil. So, let's talk about this in this article.