Extreme descent is far from safe
Modern automotive industry involves the creation and use of a huge number of options designed to make the driver’s work easier and create the most comfortable driving conditions for him. And in this regard, the downhill assist system, by activating which the driver turns on the braking, which does not allow acceleration on steep mountain slopes and dangerous serpentines , fully justifies its purpose. Of course, after all, preventing, say, a heavy SUV from accelerating to the critical 15 - 20 kilometers per hour in conditions of extreme descent, descent assistance simplifies control to the limit. And this allows the driver to concentrate entirely on the road.
Essential elements
In most cases, hill descent assist is available on vehicles with an automatic transmission. This type of system is extremely rare in vehicles with manual transmissions.
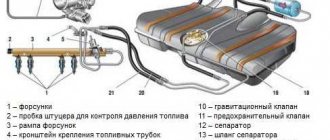
In fact, DAC is just an additional function in the vehicle's vehicle stability control system (TCS or ESP). The main elements of the mechanism include:
- a sensor that determines the position of the gas pedal;
- braking force sensor (pedal pressure);
- crankshaft speed sensor;
- vehicle speed sensor;
- ABS wheel speed sensors;
- temperature sensor;
- hydraulic unit, control unit and actuators of the TCS system;
- on/off button.
Each of the sensors helps in the full operation of the system, assessing as fully as possible all related factors that may affect automatic speed control. For example, a temperature sensor can determine what weather conditions a person is driving in.
System activation button
Options that define the functional algorithm of the braking system - for all driving conditions
Such options, which allow you to adjust the speed limit, turn out to be very relevant, especially in cases where additional assistance in driving is required by a novice, for whom even rolling downhill can be a serious test, during which there is a chance of overheating the brake pads (if, due to inexperience, the keep the brake pedal depressed). What can we say about how useful a function such as assistance when starting on a hill can be, which even an experienced driver cannot always cope with. Especially if the car is large, heavy or loaded. Moreover, purely technically, these two functions are very similar.
In one case, it is necessary for the car’s braking system to keep the wheels in a locked state until the car moves forward, uphill (this is a hill assist system), in the other, partial blocking and activation of the brake system allows you to prevent acceleration during a sharp and prolonged descent.
Advantages and disadvantages
Most motorists agree that DAC has many important advantages, however, it also has its disadvantages. Clear advantages include:
- safe passage of almost any descent;
- automatic speed control, allowing the driver not to be distracted from driving;
- assistance to novice motorists in mastering the features of driving a vehicle.
The downside is that a car with this feature will cost a little more. In addition, DAC operation is not designed for long distances. It is recommended to use automatic acceleration control on a descent on short and most difficult sections of the route.
Hill Descent Control can help the driver navigate difficult sections of the route and ensure a safe speed on the slope. This mechanism is especially useful for novice motorists. But experienced drivers should not neglect the use of DAC, because the safety of the motorist, his passengers and other road users should always remain a priority.
Manufacturers have different markings, but the functional options are similar
However, options that are functionally designed to assist the driver when going uphill, as well as downhill assist, are very popular. True, there is no specific designation for it on the international automobile market yet, and each manufacturer rather arbitrarily labels them with its own terminology.
For example:
- For European Volkswagen, BMW and Rover, it is customary to designate it with the letters HDC (this is descent assistance) and HHC (this is assistance when ascending).
- Japanese Toyota calls its system designed to provide assistance when starting off on an incline with the HAC marking (DAC is used to designate the downhill assist system).
- Japanese Nissan - DDS (descent) and USS (ascent).
- The Koreans (Hyundai) designated the automatic braking system as DBS.
DAC system: why does the driver need it?
It is believed that the DAC (Downhill Assist Control) was first introduced by engineers of the famous automobile brand Toyota. The main purpose of the new development was to provide the car with the safest descent from steep slopes, preventing unwanted acceleration and ensuring that a constant safe speed is maintained.
Most often, the English abbreviation DAC is used to denote the function of safe movement on a slope. However, there is no single generally accepted designation. Individual manufacturers may call this system differently. For example, BMW and Volkswagen use the designation HDC (Hill Descent Control) , while Nissan uses DDS (Downhill Drive Support) . The operating principle remains the same regardless of the name.
Downhill Assist System
Most often, a downhill speed control system is installed in off-road passenger cars, which can include crossovers and SUVs, as well as all-wheel drive sedans.
How do they work
However, the essence and functionality of the option does not change from the name, as well as the principle of operation. It is assumed that the car's braking system is activated to operate at a certain speed limit and, say, the help lies in the fact that if it is necessary to drive uphill, then releasing the brake pedal, the driver does not release the brake system completely. And then the car will not roll back until the brakes “feel” forward movement. Then only the brakes are “released”, and the car starts up the hill without preliminary (even the slightest rollback).
Purpose and functions
The main task of the system is to provide the car with a stable and safe speed during a steep descent. Based on information received from various sensors, the mechanism controls the speed when driving down a mountain by braking the wheels.
The DAC becomes especially valuable when driving along steep serpentines and mountain slopes. While the system monitors speed, the driver can fully concentrate on the road.
The secret of the design is a predetermined traffic intensity algorithm
The design of this option itself may vary significantly between different manufacturers. However, the meaning is the same: a predetermined operating algorithm is set, which, both when going uphill and when going downhill, automatically activates the brake pads in the mode that best suits the given program. The convenience and comfort of driving a vehicle equipped with such an option has long been appreciated by many millions of motorists around the world . And the hill-assist system, which allows even a novice to feel confident behind the wheel even on the most extreme mountain serpentine, is probably provided today on all heavy SUVs. And on other cars (sedans and others), the lifting assistance system is quite common.
Magic button - and you can safely drive off-road
Typically, the system is a special button located in the cabin, which the driver must activate before entering an off-road area. And when activated, when going uphill, it will block the wheels from reversing, “releasing” them only when forward movement is indicated, and when going downhill, it will not allow the car to accelerate beyond five to fifteen kilometers per hour. Which is the optimal speed for a steep descent downhill. When you press the button, the pressure in the brake system increases until the brake pads are activated until the vehicle speed corresponds to the specified algorithm (during a descent). When ascending, the pressure is gradually reduced in order to keep the car stationary on the rise until it moves forward.
What else is worth reading
Tire marking designation
How does an airbag deploy?
How to adjust the handbrake
Working principle of hand brake
Descent Assist System
Hill descent control is designed to prevent the vehicle from accelerating when driving on mountain roads. The presence of this system on the car increases ease of operation and safety. The hill descent assist system is usually installed on off-road passenger cars. Depending on the car manufacturer, the system has the following names:
- Hill Descent Control (HDC) from Volkswagen, BMW, etc.;
- Downhill Assist Control (DAC) from Toyota;
- Downhill Drive Support (DDS) from Nissan.
If the car is on an inclined plane, the force of gravity acting on it is decomposed according to the parallelogram rule into normal and parallel components (Fig. 1). The latter represents the rolling force FH acting on the car.
Rice. 1. Diagram of the action of forces when a car moves on a descent: FA - traction force; FG - gravity (vehicle weight); FH—rolling force; FN - normal component of gravity
If the vehicle is subject to its own traction force, it is added to the rolling force FH. The rolling force acts on the car constantly, regardless of its speed. As a result, a car rolling down an inclined plane will accelerate all the time, i.e. move faster the longer it rolls. To maintain a constant vehicle speed without hill descent assist, the driver will need to brake and/or downshift by taking his foot off the accelerator pedal. To facilitate the driver's actions in these conditions and ensure safety when descending, a descent assist system is used, which is activated when the following conditions are met:
- vehicle speed is less than 20 km/h;
- slope exceeds 20%;
- the engine is running;
- the accelerator and brake pedals are not pressed.
When these conditions are met, the system receives data on the position of the accelerator pedal, engine speed and wheel speed (which is slightly higher than walking speed) indicating an increase in vehicle speed. The system assumes that the car is rolling downhill and the braking system must be applied. The speed of the vehicle that the brake assistant must maintain by braking all wheels depends on the speed at which the descent was started and the gear engaged. In this case, the descent assist system switches on the return pump. The high pressure valves and ABS intake valves open and the ABS exhaust valves close. Braking pressure is created in the brake cylinders of the wheels, and the car slows down. The system applies wheel braking through the ABS hydraulic modulator, which creates pressure in the brake system.
When the vehicle speed decreases to a safe value, the hill descent assist system stops braking the wheels and again reduces the pressure in the brake system. If the speed then begins to increase without pressing the accelerator pedal, the system assumes that the vehicle is still traveling downhill. In this way, the vehicle's speed is constantly kept within a safe range that can be easily controlled and controlled by the driver.
The downhill assist system is deactivated forcibly (by pressing the button again) or automatically when you press the gas or brake pedal, as well as when the slope decreases to 12%.
Hill descent control is a software extension of the stability control system and uses its design elements, so at its core it is a function, not a system.