The popularity of diesel engines is explained by a combination of economy and high efficiency. One of the reasons for the impressive performance characteristics was the development of the Common Rail injection system, which is deservedly one of the most progressive and advanced technologies for supplying fuel to the power plant. Today, almost all diesel internal combustion engines are equipped with it, which are used in vehicles of various types, from cars to powerful agricultural or road construction machines.
Definition
Common Rail is a fuel injection system for a diesel engine. The main distinguishing feature is the common line or ramp located between the fuel injection pump and the injectors. It was she who gave the name to the device, since common rail is translated in English as “common path” or “common highway”. This design allows diesel fuel to be supplied under pressure, increasing the overall efficiency of the engine.
The date of appearance of the system is considered to be 1996, when the Bosch development was first installed on a production car. The popularity of engines equipped with Common Rail is explained by their ability to achieve the required power with low diesel fuel consumption. According to standard estimates, the use of the system reduces diesel consumption by 15% while increasing engine power by 40%.
An additional and, in modern conditions, very important advantage of the fuel supply design under consideration is compliance with modern environmental standards. A noticeable reduction in exhaust gas toxicity and a low level of noise emitted during operation are two more equally serious reasons for the demand and widespread use of diesel engines using Common Rail.
Cleaning
As already mentioned, it is possible to extend the service life of Common Rail injectors and avoid making repairs ahead of schedule if you periodically clean them by adding a special product to the tank. Such cleaning should be carried out every 25-30 thousand kilometers of distance traveled. If this is not done, then the entire fuel system, including the high-pressure fuel pump, may become unusable.
Many people know that repairing the entire fuel system is very important, because without a working fuel system the car will not be able to drive. You can do this cleaning of Common Rail injectors yourself. The second cleaning stage does not require removing them from the machine. In this case, cleaning the Common Rail injectors is carried out by blowing air into them under pressure, which can clear clogged nozzles.
There are such blockages when even the second option does not help, in this case the last stage of cleaning the injectors will come to the rescue. The cleaning process in the third option is based on the fact that the device is immersed in a special chamber, where, under the influence of ultrasound, all particles that clog the nozzles are destroyed. The only disadvantage of this cleaning option is that in this case you will need to remove them from the car and take them to a service station where such work is carried out.
Don’t think that you can clean completely clogged nozzles yourself. If you clean it yourself, you can completely damage the atomizer, channels or body of the device. In this case, a complete replacement of nozzles or even injectors will be required, which will have a negative impact on the driver’s wallet.
Design features
The Common Rail device is largely reminiscent of the fuel supply system in injection gasoline engines. Before diesel fuel is injected into the cylinders, pressure accumulates, as a result of which this design is often called a battery fuel system.
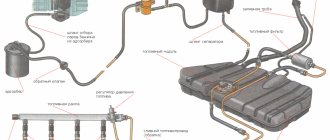
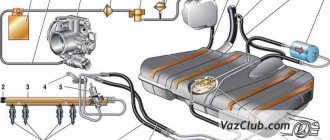
The Common Rail design includes three main elements: high and low pressure circuits, standard for any diesel engine, as well as an electronic monitoring and control unit that complements them. The low pressure circuit is practically no different from conventional systems and consists of a standard set of parts, including:
- fuel tank;
- fuel filter;
- booster pump;
- set of connecting pipelines.
The main differences between Common Rail and a conventional diesel engine are the design of the high-pressure circuit, consisting of the following elements:
- a pump that replaces the standard injection pump and is equipped with a control valve;
- accumulator unit or ramp, also equipped with a pressure monitoring sensor. It is made in the form of a fairly long two-layer pipe on which fittings are placed for fixing the injectors;
- nozzles;
- set of connecting pipelines.
The operation of the electronic control unit or ECU is important for the effective operation of the system in question. It includes several sensors that automatically transmit signals about the following engine parameters and characteristics:
- camshaft and crankshaft positions;
- gas pedal position;
- boost pressure level;
- air and coolant temperature;
- fuel pressure level;
- mass air flow.
The analysis of the received data is also carried out by the ECU in automatic mode, resulting in the determination of the required amount of fuel, injector opening time and other operating parameters of the system. After this, a command is given to start injection and the cycle is repeated again.
Fuel supply
It has already been mentioned that the Common Rail injection system uses multiple supplies of diesel fuel into the cylinder during one engine operating cycle. In total, three types of injection are used - preliminary, main and additional.
Pre-injection “prepares” the medium. A small amount of fuel injected a little earlier leads to an increase in pressure and temperature in the combustion chamber. In the future, this ensures easy and smooth ignition of the main part of the combustible mixture. Thanks to this injection, the noise level of the diesel power plant is reduced.
During the main injection, a working portion of diesel fuel is supplied to the combustion chamber, which ensures the operation of the power plant.
Additional injection occurs already during the power stroke cycle, after the mixture has burned. The purpose of this injection is to increase the temperature of the exhaust gases, ensuring the combustion of soot particles in the particulate filter. This improves the environmental friendliness of the exhaust.
Fuel injection schedule
Interestingly, the ECU can regulate multiple injections, adjusting the supply to certain operating conditions of the power plant. For example, at idle there can be two preliminary fuel injections to provide better conditions for the combustion of the main portion of diesel fuel. At an average load, fuel is pre-supplied only once, and at maximum load, preparation is no longer required.
As you can see, the driver has virtually no influence on the operation of the Common Rail system. Even when pressing the accelerator pedal, it simply sends a signal to the ECU, which is then processed and taken into account when generating an impulse to open the injectors. The entire operation of the power system is fully controlled and regulated electronically.
Operating principle of Common Rail
The Common Rail device described above ensures simple yet efficient engine operation. First, the booster pump, part of the low-pressure circuit, sucks diesel fuel from the tank. It is then cleaned by passing through a filter and entering the high-pressure circuit.
The fuel is then moved to the battery assembly, where its pressure increases. The maximum value of this indicator is 135 MPa and is controlled automatically. After receiving an injection command from the computer, the control valve opens and fuel enters the tank through pipelines connected to the injectors on the ramp. Each injector has a separate solenoid valve or solenoid that controls its operation, which is another important distinguishing feature of the system.
The presence of an ECU in the system allows you to control both fuel pressure parameters and the amount of fuel burned with a high level of accuracy. The consequence of this is maximum efficiency during fuel combustion, which is accompanied by a decrease in its consumption while simultaneously increasing the efficiency of the diesel engine. As a pleasant and useful bonus, exhaust emissions are reduced.
Is it easier or more difficult to operate equipment with Common Rail?
This is precisely one of the key points that causes a negative reaction to Common Rail. But why him?
It's simple: this is the inertia of users (mechanics) and sometimes owners, a common reaction to something new. Because for those who are familiar with CR, have studied how it works, how to maintain it, how to monitor the condition of the fuel system, it is easy to work with. For those who are not familiar with it, it, like everything unknown, causes fear. The system is not cheap, and enterprise mechanics are already afraid to blindly repair and configure it without understanding it.
Moreover, only in Komatsu equipment the CR system has been working for the second decade, including in the most severe conditions in the Far North. And in the automotive market, more than 80% of diesel engines are already equipped with electronically controlled injection. That is, the system has proven its viability through comprehensive operating experience. The only question is to learn how to work with it. And here's what it can do.
Electronic system = better controlled system. Its condition is easier to track, it is easier to prevent breakdowns, and problems can be tracked before they affect the operation of the machine. For this purpose, Komatsu has the KOMTRAX monitoring system. Since the injection system is electronic, it means that KOMTRAX can take many indicators from it, unlike the old diesel engine, which can only show the total fuel consumption. The owner of the equipment or his mechanics receive data from the monitor and see if there are any injection irregularities. You can take action before repairs become too expensive: on your own or in time to contact the service of an equipment distributor. The system is still working, and we can already predict repairs, order sprayers, choose the time for repairs in order to minimize equipment downtime. Everything is in full view, the main thing is to learn how to use it.
And on the mechanics we see either white smoke - the equipment is working, or black smoke - it no longer works, it’s time to buy spare parts, but the equipment and work are standing still.
Conclusion
The popularity and widespread use of Common Rail is explained by the obvious advantages of the system over any alternative options. Most of the advantages have already been announced above, however, for greater clarity, it is advisable to pay attention to them again. So, the most important advantages of the system under consideration are:
- high engine efficiency, which is achieved through more efficient fuel combustion;
- significant (up to 15%) reduction in fuel consumption;
- an even more serious (up to 40%) increase in engine power;
- reduction of exhaust gas toxicity, which allows the engine to fully comply with modern environmental standards.
The combination of such impressive characteristics is the best and very clear explanation for the fact that almost all diesel engines today are equipped with Common Rail. Moreover, the capabilities of the technology are far from exhausted, which allows us to hope for further improvement of the system.
What is this technology?
Common Rail is a special fuel injection technology using high pressure. It uses fuel storage and is used in diesel engines. Over time, direct injection was used for diesel engines, many details of the technology were transferred to such engines (fuel injection pump). The main element of Common Rail is a fuel accumulator that operates under high pressure.
Device history
The first prototype for a battery injection system was built by Robert Huber in 1964. At that time, electronics was not yet widely developed, so the development was quickly abandoned. The same thing happened with the works of engineers at the Kolomna Plant, who also did not receive recognition.
In 1994, Denso of Japan installed the first working model of battery injection technology on a production truck from Toyota. A year later, the Italians began to use this technology. Already in 1998, the market saw the flagship Mercedes Benz model E220 CDI with this system.
Railway loading and unloading ramps and platforms.
A railway ramp is a structure designed for loading and unloading operations. One side of the ramp is adjacent to the warehouse wall, and the other is located along the railway track.
A platform is a structure similar to a ramp. Unlike a ramp, on one side of the platform there is a railway track, and on the other (opposite side) there is a car entrance or another railway track. From the platform, cargo is usually transferred from a train to a car, from a car to a railway car, or from one car to another.
The mark of the edge of the loading and unloading ramp or platform for motor transport on the vehicle access side must be equal to 1.2 m from the surface level of the roadway. And from the side of the railway track, the difference in height between the edge of the ramp and the rail head is 1.1 m.
Loading and unloading ramps and platforms for railway rolling stock must comply with GOST 9238-2013 Dimensions of railway rolling stock and the proximity of buildings.
The width of loading and unloading ramps and platforms must be taken in accordance with the requirements of technology and equipment and ensure safety measures for loading and unloading operations.
The transverse slope of the coating of loading and unloading ramps and platforms should be taken equal to 1% towards the edge.
The length of the loading and unloading ramp or platform should be selected depending on the warehouse capacity or cargo turnover.
Loading and unloading ramps and platforms must have at least two dispersed stairs or ramps.
The width of ramps for the passage of floor-mounted vehicles must be at least 0.6 m greater than the maximum width of a loaded vehicle. The slope of ramps should be no more than 16% when placed indoors and no more than 10% when placed outside buildings.
The structures of ramps and canopies adjacent to buildings of II, III, IIIa and IVa degrees of fire resistance must be made of non-combustible materials.
Loading and unloading ramps and platforms must ensure protection of cargo and loading and unloading mechanisms from precipitation.
The canopy over railway loading and unloading ramps and platforms must overlap the axis of the railway track by at least 0.5 m. Over automobile ramps, the canopy must overlap the vehicle passage by at least 1.5 m from the edge of the ramp. When using a canopy structure supported on columns, the pitch of the columns when located along the outer edge of the ramp must be at least 12 m.
Published 2 years ago. Views since posting on the site 5043
Also, you may be interested in:
Post category: Important to know Standards for stowing cargo in railway cars Over the 4 years since publication, the article has been read 1983 times. The post has 2 comments
Post category: Important to know Railway dead-end stops. Their types and features. Over the 3 years since publication, the article has been read 7938 times. The post has no comments yet
Post heading: Important to know Instructions on the procedure for maintaining and organizing traffic on a non-public railway track. Over the 4 years since publication, the article has been read 7479 times. The post has no comments yet
Invite to tender
If you have a tender and need more participants:
Select from the list the type of work that interests youIndustrial safety auditIdentification and classification of hazardous production facilities, obtaining a license to operate hazardous production facilitiesDevelopment of plans, action plans, documentation related to the readiness of enterprises for civil emergency situations and fire safetyInspection and examination of the industrial safety of buildings and structuresWork on lifting structuresWork on boiler inspection and power equipment facilitiesWorks at gas supervision facilities Work at chemical and petrochemical facilities Work at facilities related to the transportation of hazardous substances Work at production facilities for the storage and processing of plant raw materials Work at metallurgical foundries Work at mining plants Conformity assessment of elevators, technical examination of elevators Development of a safety justification for a hazardous production facility Development of documentation for an industrial safety management system Development of industrial safety declarations securityWork at the facilities of the Ministry of Defense (special purpose production of military units) and the facilities of the Federal Penitentiary Service of Russia (special purpose organization of correctional institutions) Design Repair and installation work Electrical repair and electrical measuring work Development and production of safety devices for industrial facilities Development and production of non-standard metal products and equipment Non-state examination of design documentation (engineering surveys) Pre-certification training according to the rules and safety standardsVocational training (blue-collar professions)Training in labor protection, fire safety and electrical safety, heat and power engineeringSpecial assessment of working conditions (SOUT) (until 2014 certification of workplaces)Accreditation and certification in the industrial safety examination systemCertification of equipment, declaration of conformityEnergy auditDevelopment of heat supply and water supply schemesOther workAdvanced training, professional retrainingInspection of shelvingCopy the link to your tender into this field, to do this, go to the browser, open your site, highlight and copy the address line, then paste into this field. If it doesn’t work out, just write the tender number and the name of the site. personal data
Camshafts
The timing belt pulley is only present on the exhaust camshaft. The intake camshaft is driven by a gear drive. The exhaust camshaft gear is composite, with a mechanism for compensating the gaps between the teeth - this design reduces the noise of this gear train.
You can select and buy a cylinder head for a Volkswagen 2.0 TDI engine, a cylinder head for a Skoda 2.0 TDI engine, for an Audi 2.0 TDI or Seat 2.0 TDI engine in our catalog of contract spare parts.
Oil pump
A block of balancer shafts with a built-in oil pump has been migrated from a 2-liter engine with pump injectors to a Common Rail engine. One of the balancers is driven by helical gears. The second is driven from the first by another pair of helical gears. The oil pump is driven from the second balance shaft via a hexagonal drive (“pencil”).
This design is still used today on all 2.0 TDI engines, but with one important change: the hex driver has been increased in length to 100 mm and made of high-quality steel. This improvement appeared in November 2009.
Up to this point, the length of the “pencil” was 77 mm. And on 2.0 TDI engines with Common Rail in the first two years of production, this leash was poorly made. By the mileage of 150,000 - 200,000 km, its edges were worn out. At the same time, shavings like rags of foil fell into the oil pan. It settled in the oil intake.
By the time cars with these Common-Rail engines appeared on the market, everyone had already heard about hexagon wear. The owners changed it themselves every 150,000 km or immediately after purchasing a car with an unclear service history.
You can choose and buy an engine for Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, Seat in our catalog of contract engines.
Here, using the links, you can see the availability of specific Volkswagen cars, Seat cars, Skoda cars or Audi cars at the dismantling shop and order auto parts from them.