Poor activation due to the slider
First, let's look at why first gear doesn't engage well and the problem is with the transmission.
Often the problem with turning on the speed lies in the latch and slider. The appearance of a burr near the groove for the retainer on the slide can easily prevent the ball retainer from entering the groove. When moving the slider, the latch rests on this burr and cannot overcome it without significant effort from the driver. In this case, the gears come very close to each other, but do not engage, and the teeth of one gear hit the other.
In the future, such beating can lead to flaring of the teeth, and the impossibility of engagement will be due to the fact that due to this flaring, the teeth will no longer be able to engage.
Common causes of problems with first gear on popular cars
Some car models, due to their design features, are more susceptible than others to problems with engaging first gear. In order not to cause a problem and avoid serious damage, they need to monitor potentially vulnerable components and have them serviced in a timely manner. Such cars are collected in the table below.
| Brand, model | Design flaws, weak points | How to prevent the problem |
| VAZ 2108-2115 | The gearbox supports (side and rear) often wear out, causing gears to fly out. Due to the large difference in gear ratios of 1st and 2nd gears, their synchronizers wear out more. Difficulty engaging first at speed is not yet a breakdown, but a characteristic drawback of VAZ front-wheel drive gearboxes, caused by an almost 2-fold difference in the gear ratios of 1st and 2nd gears. But it can develop into problems if you regularly engage the gear with force. A loose cardan of the rocker leads to unclear movement of the lever. |
|
| VAZ 2110-2112, Priora, Kalina | On a car with a rocker drive, the problems are the same as for Samara (weak synchronizers, wear of the cushions, the rocker). Added to these are problems with the gearbox torque rod, damage to which deprives the box and the rocker of a rigid connection. On a car with a cable-driven gearbox, there may be a problem with their tension. | |
| VAZ Classic (06,07,01) | Due to a fluid leak or incorrect stroke adjustment, the hydraulic shift drive does not completely disconnect the engine from the gearbox when the clutch is depressed. | Check the fluid level in the clutch circuit and the adjustment of the release mechanism, add brake fluid and bleed the clutch if necessary. |
| Lada Vesta | On modifications with a VAZ gearbox, the problems are the same as on earlier models: load on the 1st and 2nd synchronizers, unstable gear shift drive. | Gently shift into 1st and 2nd gears, use high-quality gear oil. |
| Volkswagen Passat (from b3 to b8) | The Volkswagen Passat uses a cable shift mechanism, which is sensitive to wear and requires maintenance. | Periodically (at least once every 10 thousand km) inspect the gear selection mechanism and its movement. Adjust cables and replace worn parts. |
| Chevrolet Aveo T250, Lacetti, Daewoo Lanos, Sens, Nexia | On the Chevrolet Aveo and a number of other models developed by GM, the weak point is the shift mechanism (“helicopter”) at the gearbox, which becomes loose. Because of this, it becomes difficult to catch the desired speed. | Monitor the “helicopter”, clean it periodically, and if noticeable play appears, change the switch parts. |
| Hyundai Solaris | The weak point is the clutch circuit. If there is a lack of fluid or air, the clutch is not fully depressed, which is why the first one is difficult to engage. The adjustment of the rocker cables may also go wrong. | Check the fluid level in the clutch circuit and the tension of the gear shift cables. Adjust the clutch drive and cables if necessary. |
| Mitsubishi Pajero | The selector switch on the automatic transmission (inhibitor) often turns sour. | Avoid heavy contamination of the gearbox, monitor its condition and clean it if it is heavily soiled. |
| Gazelle | On the Gazelle, first gear is difficult to engage due to wear on the clutch or problems with its drive. | Periodically (at least once every 10 thousand km) inspect the clutch drive for leaks. If necessary, adjust the drive and bleed it. |
| Opel Astra G (including automatic transmission and robot with 1 clutch) | The weak points on the mechanics are the lever linkage (there are plastic parts there), the “fingers” and the “helicopter” of the gear selection mechanism at the gearbox. Sometimes its settings simply go wrong and production appears. | Monitor the adjustment of the switching mechanism, adjust it in a timely manner or repair it if unclear movement or play appears. |
| Automatic transmission is sensitive to oil level and quality. | Monitor the oil level and change it regularly every 40–50 thousand km. |
Reasons for complete jamming
There are not so many reasons for a complete jamming of the gearbox. One of these reasons is the destruction of the teeth of a gear. Broken tooth fragments can become meshed with the teeth of other gears, which in turn makes the gears unable to rotate.
It is also possible that one of the internal bolts of the box may rupture or spontaneously unscrew. In this case, the bolt gets between the gears and blocks them.
To check whether the cause of jamming is the destruction that occurred inside the box, simply drain the oil from the box crankcase and check it. The fact is that if any element of the box is destroyed, a large amount of metal shavings will get into the oil.
Why do speeds slip on a manual transmission?
Any gearbox has a complex structure with many interconnected parts, and the failure of even one part immediately affects the performance of the gearbox as a whole.
So often the cause of a gearbox malfunction is such a breakdown as one of the speeds being knocked out.
In this article, we will look at the main reasons for the question of why transmissions fail.
In order to make it easier to understand the reason for knocking out a certain speed, you need to briefly consider the principle of operation of the gearbox.
Knocks out the first gear of the VAZ 2110 reasons
VAZ 2110 gearbox malfunctions
- January 11, 2009
The VAZ 2110 has been produced for several years now, because all the “sores” of these cars have long been known, both to ordinary owners of “ten” cars and to VAZ itself. The latter seems to be trying to gradually solve these problems, but very gradually. But that's a completely different story, as they say.
In addition to the diseases themselves, their symptoms are also known. In this article we will provide a list of the main possible malfunctions of the VAZ 2110 gearbox and the symptoms by which you can at least roughly identify the problem without disassembling the gearbox.
Noise in the gearbox.
Increased noise during gearbox operation can be caused by the following reasons:
- wear of gear teeth - wear of bearings - insufficient oil level in the box
Communities › Lada 2110, 2111, 2112, 112, Bogdan › Blog › First gear gearbox repair
When I start, the first gear jumps out, as soon as I hold it a little with my hand and start moving, I can remove my hand, the car calmly goes to 1st, and does not move from a place without support. Sometimes it doesn't turn on. I decided to repair the gearbox myself. I would like to hear from those who have encountered this. Besides the synchronizer and first gear, what else do you need to buy in advance? Are there any difficulties in replacing or repairing a gearbox? and one more important point: how do I find out what gearbox I have installed? an acquaintance with a 10 had the box repaired and bought spare parts specifically for the 10, but it turned out that they didn’t fit him, but only fit the 9. Thank you all for the good advice
Repair work
If the adjustment does not give the desired result, you will have to work more carefully with the box. A common problem is knocking out the gears responsible for speeds 1 and 2.
When dismantling, make sure that each individual fastener is in good working order. The latches are springs, of which there are a total of three. The first one is the longest, it is responsible for speeds 1 and 2. The second is medium in size, and its prerogative is 3 and 4 speeds. The third detent is the smallest, and its “guardian” is fifth gear.
Messages 12
1 Topic by ander_kr 2014-05-13 07:52:26
Topic: Gears don't engage well (they hit something and grind)
Hi all! I didn’t find anything similar on the forums. The situation is like this, VAZ 2110, 16kl, 04. At first, 1st gear was difficult to engage from time to time (it rested on something), then 1st and 2nd were engaged with difficulty and every other time, reverse turns on with a slight grinding noise, sometimes not the first time. Then 1.2 hardly turn on, they rest against something, then I noticed that if the gearshift knob is not pushed to the left all the way when shifting gears to 1.2, then the gears are engaged (no grinding, but like on a washboard), it turns out that 1 and 3 are very close, as are 2 and 4. The clutch pedal is slightly lowered. I pulled the cable, the pedal became slightly higher than the brake pedal, then the gears began to engage as expected in the extreme left position (again, as on the washboard), 3rd gear seems to click there. The travel of the clutch pedal has increased (very inconvenient) and the clutch engages with the engine only at the very end. YES, AND THIS IS ALL BOTH INITIALLY AND AFTER TENSIONING THE CABLE BOTH WITH THE ENGINE RUNNING AND ON STUFFED. Can anyone tell me what? They say on the forums that since they don’t shift gears when the engine is switched off, it’s definitely a case of removing and repairing the gearbox. Could there be another reason? I don’t want the service department to take the trouble to repair the gearbox for nothing. Thank you all
2 Reply from klimashov.roman 2014-05-13 08:13:06
Re: Gears don't engage well (they hit something and grind)
Well, first of all, pay attention to the clutch and in particular to the basket, and if it is already all crooked or askew, replace it. Try to adjust the rocker to the position where it will engage best and at the same time unscrew the bolts with the speed locks, there are 3 of them, well, this is more likely to calm the soul. If not, then most likely the gears have come to a halt and this is just a repair. Only if you take it to the service station, be as close as possible when they start disassembling it, otherwise they will issue you a bill for a new box; it will be easier to buy, and they can take out the good parts
Clutch basket
Over time, the clutch basket fails on all cars with a manual transmission. Sometimes it’s due to wear and tear, sometimes the petals or the so-called “spider” break. Let me start, perhaps, with the “spider”, this is a mechanically fixed release bearing on several extensions (done like this on some VAZs), if the extension breaks, then it cannot be effectively fixed to the basket - the gears do not engage.
Next, the petals of the box break, or they become weakened. This leads to the fact that it is very difficult, almost impossible, to release the clutch disc. Therefore, the “speeds” do not switch – we just change the basket.
Well, the last wear and tear is the basket disk. It has a metal disk inside, and over time, especially from high mileage, wear forms there. When starting, the car will shake, and if the wear is very large, the gears may not shift.
In any case, we need to change the clutch basket.
What's the result?
So, the main reasons why gears are difficult to engage are problems with the clutch mechanism and gearbox. However, most of them can be eliminated yourself if you have tools, spare parts and certain skills.
Why may it be difficult to engage gears or why first gear, second, reverse, etc. may not engage? The main causes of gearbox malfunctions, recommendations.
Reasons for difficulty shifting gears with the engine running. Transmission oil and level in the gearbox, wear of synchronizers and gearbox gears, clutch.
How to change gears without a clutch: driving a manual car without a clutch in case of malfunction. Tips and tricks.
Manual transmission gears (speeds) do not engage after replacing the clutch: main reasons, settings and adjustments. Diagnosis of problems, useful tips.
Clutch: basket, release, clutch disc. Purpose and design, principle of operation of the clutch basket. How to increase clutch life.
The automatic transmission does not change gears: the car does not move forward or backward, the automatic transmission does not switch to individual gears, reasons.
Source
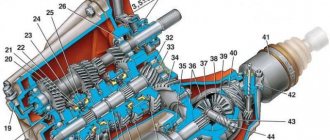
How does a manual transmission work?
A conventional manual gearbox consists of 3 shafts. These are the primary, intermediate and secondary shafts. The secondary shaft is located coaxially with the primary shaft, inside which there is a bearing into which the end of the secondary shaft fits, allowing it to rotate independently of the primary.
The intermediate shaft is a single unit with gears cast on it. It has a rigid connection through a gear to the input shaft, which causes it to rotate along with the gears of the gears.
What is it for
First of all, it’s worth understanding how a manual transmission works. In short, it is needed to transmit torque to the wheels from the crankshaft, as well as to change the gear ratio . To put it even more simply, the gearbox changes the torque, which gives the car the ability to move without problems at different speeds and under constantly changing load conditions. The gearbox is based on three shafts (primary, secondary, intermediate) and gears of different sizes. The interaction of the shafts is ensured by these same gears.
Now about the tandem of the internal combustion engine and gearbox. The essence of its engine operation comes down to the rotation of the crankshaft. When the shaft rotates, the gearbox input shaft, which is connected to the flywheel, also begins to rotate. If the driver selects neutral gear, the secondary shaft does not begin to rotate. But when the driver selects another gear, the secondary shaft gears immediately engage with the input shaft gears . The force from the unit is transmitted to the drive wheels through a chain of automotive transmission elements. Of course, the meshing of the gears should cause something like shocks. This is where the synchronizer turns out to be a very necessary mechanism.
On a VAZ 2110, it is not so uncommon for the gears to shift poorly or get knocked out. A mechanism for adjusting the speed selection drive is provided specifically for this purpose.
Adjustment may be necessary if:
- the box was recently removed for repairs;
- one of the gears falls out;
- the speeds do not engage well or simply get knocked out when the car is moving.
If you have one of these problems, try making adjustments first. Its sequence:
- Under the bottom of the VAZ 2110, find and slightly loosen the nut on the bolt that tightens the clamp that secures the rod designed to control the gearbox;
- Use a screwdriver to slightly move apart the grooves in the end of the rod and the resulting gap on the clamp itself. This is necessary to ensure easy movement of the rod in relation to the gear selection rod. Place the rod in the neutral position;
- Release the shift knob from the cover in the cabin;
- Align the lever using a special template. This is done like this: install a template in the window of the rear speed lock bracket lining. After this, insert the lever axis stop into the groove of the template, pressing it without unnecessary force in the transverse direction;
- Then adjust the axial play of the rod in the rear direction, and its axial play by turning to the left;
- Install the clamp, not reaching a few millimeters from the end of the rod. Then tighten the clamp thoroughly with the bolt.
Adjusting the gearbox, video instructions
If it is necessary to replace gears, bearings or other parts, the box must be dismantled. Usually in such cases, the VAZ 2110 gearbox is overhauled and elements that have failed are replaced. But removing the box is not always necessary.
It is known that the 10 has problems with gear shifting. In fact, the speed is knocked out.
To eliminate the problem, the unit is equipped with a special mechanism that allows you to adjust the drive.
The operation is performed in the following cases:
- the gearbox was dismantled due to repairs, for example, replacing the input shaft bearings;
- speed knocks out while driving;
- Gears don't engage or disengage easily.
If such situations arise, then adjustments cannot be avoided.
Of course, performing this procedure is much simpler than dismantling work. The work is performed in the following sequence:
- At the bottom of the vehicle there is a nut in a bolt. This fastener holds the transmission linkage in place. The fastening element does not need to be removed: just unscrew the nut a little;
- to move the grooves of the rod and the slot of the fastening clamp apart, just use a flat screwdriver;
- the rod must be set to the neutral position. Then you need to remove the cover from the gearbox handle;
- then the lever is set in accordance with the template;
- at the next stage it is necessary to adjust the backlash of the rear vector rod;
- adjusting axial play;
- At the final stage, the fastening must be installed in place and tightened.
Why is first gear difficult to engage?
The answer to the question “ why does first gear stick in poorly ?” in a specific situation directly depends on the type of transmission (manual transmission, automatic transmission, manual transmission), the conditions of such behavior (from a standstill, in motion, in a cold and warm box), as well as on the car model.
The most common reasons why first gear is difficult to engage:
Breakdown of the jet thrust is the most common problem in many gearboxes.
- faulty or unadjusted clutch;
- worn transmission synchronizer;
- broken gear shift drive (yoke);
- faulty internal selection mechanism in the gearbox;
- bearing wear;
- gearbox shaft wear;
- sagging or weakened support (pillow) of the power unit;
- breakdown of the gearbox jet thrust;
- automatic transmission solenoid failure;
- wear of friction clutches (for automatic transmission);
- Lack of gear oil or severe contamination.
When a running car has difficulty engaging first gear at the start, most often the problems lie in the box itself . If first gear is difficult to engage when driving, it makes sense to check mounts and clutch .
Reasons for poor engagement of first gear on a manual transmission
Before disassembling the gearbox for troubleshooting and replacing worn parts, you need to check:
A cable break most often occurs at the point where it connects to the tip.
- engine mounts and jet thrust;
- free movement, development of rods, shafts and bushings of the scenes, external gear shift mechanisms - “helicopter”, hinges, rods, cables (depending on the car model);
- adjusting the stroke of the clutch mechanism;
- oil level in manual transmission.
When first gear is difficult to engage in cold conditions, the problem may be an excessively high viscosity of the transmission oil - because of this, the movement of the lever and internal parts of the gearbox becomes difficult. If the viscosity is insufficient (the oil is too thin), the first gear does not engage well when it is hot - the liquid forms a thin film, so the splines of the couplings, synchronizers and gears begin to work under more severe conditions.
If you need to exert force when engaging first or reverse gear on a cold and warm engine, most often the problem is in the gear shift mechanism or in incorrect clutch settings. First of all, you should inspect the rocker and check the adjustment of the pedal and disk pressure, since finding and eliminating other causes will require dismantling and disassembling the manual transmission.
Worn synchronizer ring can also cause a stuck transmission.
Often, first gear does not engage fully due to wear or deformation of the gear selector forks, the gear selector tab on the inner shifter (in front-wheel drive models) or on the lever (in rear-wheel drive models). The couplings that the forks sit in are made of a stronger metal than the forks themselves and rarely wear out.
When the gearbox cushions and its jet thrust wear out, the power unit sags, vibrations and hums , and the gear shift lever shakes Since the box has too much free play relative to the body, it knocks out first gear when starting off, and while driving, especially on uneven roads and in corners, other speeds also slip out.
The internal reason for the difficulty of engaging first gear on a manual transmission most often lies in the wear of the bronze synchronizer ring . If it cannot slow down the shaft to equalize the speed, the splines of the gear and clutch slip, causing a crunching sound. Over time, after the splines have worn out significantly, the speed starts to drop out on bumps or when turning, and in advanced cases, it just doesn’t turn on, or doesn’t turn on at all.
Never use GL-5 gear oil in gearboxes designed for GL-4. The sulfur additives contained in such a lubricant accelerate the wear of parts made of copper alloys (bronze synchronizers). The performance properties and purpose of such oils are discussed here.
If the first gear is poorly engaged while driving, when the speed exceeds 20–25 km/h, there may be no breakdown at all. On a gearbox with a large difference in gear ratios between 1st and 2nd speeds (front-wheel drive VAZ, some Opel, Chevrolet models), the secondary shaft, when downshifting to 1st gear, rotates much faster than the primary one, so on a warm gearbox the synchronizer cannot quickly equalize the speed of the shafts, since liquid oil does not create much resistance to rotation.
The table below lists all the main reasons why first gear is hard to engage or why it slips out, mentioning symptoms that will facilitate diagnosis.
First gear does not engage well: causes of malfunction
| Cause of malfunction | What causes | How does it manifest itself on the car, except for problems with turning on the 1st | How to fix |
| Incorrect cable adjustment | Natural stretch of cables | The first gear is difficult to engage; problems with selecting other gears are possible. If the cable is set incorrectly, problems with engaging 3rd and 5th gears, as well as reverse on cars that have it to the left of 1st, are possible. | Replace worn rocker parts, adjust gear shift cables. |
| Loosening fasteners | |||
| Wear of backstage parts | |||
| Failure of the switching mechanism | Long-term absence of maintenance | It is also problematic to engage the reverse gear, the gears are knocked out when starting to move, identical problems may appear in the 1st and 3rd or 1st and 2nd gears. Appears when cold and after warming up, from a standstill and while moving. | Clean the mechanism, repair, fix or replace worn parts or the mechanism assembly. |
| Long mileage output | |||
| Wear of gearbox and motor supports | |||
| Incorrect clutch setting | Rope stretch | All gears shift poorly, with a crunching sound, the suspended wheels of the drive axle rotate in gear even when the clutch is depressed, and there may be a smell of a burnt clutch. The rear, which in most gearboxes does not have synchronizers, is also difficult to engage. It appears when it is cold and after warming up, it is especially pronounced when driving, since when starting from a standstill, the wheels hold the shafts and prevent the clutch from transmitting torque to them. | If detected in a timely manner, adjust the cable tension or the hydraulic squeezing mechanism. If the problem is severe, replace the clutch. |
| Loosening fasteners due to vibration | |||
| Deformation of parts | |||
| Hydraulic problems | |||
| Clutch wear | Natural production of discs | Detect and replace worn clutch elements (discs, release bearing, basket). | |
| Disk wear due to overheating | |||
| Overheating and/or deformation of the basket | |||
| Worn or deformed synchronizers | Natural production of parts | The first gear is difficult to engage, with a crunch. Possible transmission failure. In other gears everything can be absolutely normal. Shifting problems are constant and only affect one gear. If the synchronizers are worn out at several speeds, there are also problems with other gears, but the behavior may differ depending on the degree of wear. | Replace the synchronizer rings, preferably all at once, so that after 10–20 thousand you do not have to go through the gearbox due to similar problems at a different speed. If there is wear on the gears and couplings, they also need to be replaced. |
| Using incompatible oil (for example, GL-5 with sulfur and phosphorous additives) | |||
| Sloppy gear shifting | |||
| Worn or deformed shift fork | Natural wear and tear | If the fork is worn out, the shifting of 1st and 2nd gears is unclear, too loose. Departures, misconnections and crunching are possible. If the fork is bent, the 1st plug may turn on with difficulty, and the 2nd, on the contrary, very easily. The problem occurs equally often when starting off and while driving. | Replace the gear selector fork. |
| Consequences of engaging gears with excessive pressure | |||
| Failure of the gearbox jet traction | Age and metal fatigue | Gears are difficult to engage. When driving, they may fly out, especially when the road is uneven and when turning. The gearshift lever in the cabin vibrates and dangles. It manifests itself in motion, from a standstill everything can be normal. Warming up often doesn't play a role. | Replace the gearbox torque rod. |
| Wear of suspension elements | |||
| Consequences of driving on bad roads | |||
| Production of gearbox bearings | Natural wear and tear | Problems with gear shifting are accompanied by constant gearbox noise while driving. When parked at XX, tapping in the box area. As it warms up the noise increases. It appears both during movement and at start. | Troubleshoot the gearbox and replace the bearings. |
| Consequences of lack of oil or use of unsuitable lubricant | |||
| Chips ingress | |||
| Box shaft production | Natural wear and tear | Gear shifting problems occur all the time. Gears may fly out, including on a flat road. Appears at start and while driving. As it warms up, the noise increases due to a decrease in oil viscosity. | Troubleshoot the gearbox and replace the faulty shaft. If the shaft on which the gears rotate (usually the secondary shaft) is worn out, the needle bearings of the gears must also be replaced. |
| Consequences of lack of oil or use of unsuitable lubricant | |||
| Clogged oil channels | |||
| Lack of oil | Leakage from seals | The gearbox is noisy and there are problems shifting gears. The problem gradually progresses: noise and vibrations increase, and gears engage worse. | Fix the leak, fill the oil to the level specified by the manufacturer. If the problem is not solved, you need to replace the parts affected by a lack of lubrication. |
| Damage to seals | |||
| Insufficient filling from factory or upon replacement | |||
| Oil viscosity does not match the season | Incorrect oil selected or counterfeit lubricant used | If the viscosity is low, there may be problems with switching on, noise and vibration after warming up. With high viscosity, gears are difficult to engage in cold weather (especially in winter), and the gearbox is noisy. On a box with a rigid switch drive, the lever travel becomes tight before warming up. As the oil warms up in motion, the “symptoms” go away. | Change the oil to the one recommended by the manufacturer for viscosity and tolerances. |
| Worn power unit supports | Natural wear and tear of pillows | The motor is visually tilted forward, backward or sideways. The car “kicks” when starting, vibrations and shaking of the engine occur, the gearshift lever trembles and twitches. On uneven surfaces, gears can fly out. When starting, sharp acceleration and braking, shocks are heard, gears fly out. The problem appears regardless of the degree of transmission warming up. | Replace engine and gearbox mounts. |
| Consequences of driving on bad roads |
Reasons for problematic engagement of first gear on an automatic transmission
Failed Toyota Corolla manual transmission actuator
On a robotic automatic transmission, internal problems that cause difficulty shifting gears are similar to manual transmissions:
- insufficient or inappropriate lubrication;
- wear of synchronizers;
- wear or malfunction of forks;
- bearing wear;
- shaft wear;
- clutch malfunction.
Since the gear shifting is carried out by an electronic unit, there are no problems with the rocker and interruptions caused by wear of the pillows on manual transmissions. Instead, there may be problems with the actuators responsible for switching gears, sensors and the electronic transmission control unit.
If the torque converter automatic transmission does not engage 1st speed or engages it with difficulty, not immediately, first you need to look at the selector drive (on an automatic transmission with a cable or rod) and the selector itself (inhibitor) on the box.
The main control mechanisms are concentrated in the box itself, and if there are problems with the electronics, the car does not move or moves only at a reduced speed. If the first gear on the automatic transmission does not engage, first you need to check the oil level and assess its condition. If there is underfilling, or the transmission fluid is dirty or dark, you need to replace it, and if you have access without disassembling the gearbox, you need to replace the oil filter.
If switching problems only appear in cold or hot weather, sometimes changing the ATF helps get rid of them.
Often the culprit that causes poor first and reverse gear engagement on an automatic transmission is the torque converter (donut), which does not provide the required free play and creates resistance. Similar problems arise when the valve body channels become clogged . Due to disruption of normal fluid circulation, kicks, vibrations, and difficulty shifting gears occur.
The main reasons for kicks, jerks and gear slippage in an automatic transmission using the example of the Hyundai Solaris: video
If there is a problem with the pump, first gear is difficult to engage when driving. As the oil warms up, its viscosity decreases , making it more difficult for the pump to generate the required pressure due to the reduction in the thickness of the oil wedge.
But the reason for this behavior can also be clutches, the friction force between which decreases as it warms up. Problems with clutches can be identified by characteristic slippage and speed surges.
Due to wear on the friction discs that lock or release the gears, gears can also be difficult to shift. In such cases, the first and second gears of the automatic transmission are poorly engaged, shifts are performed with delays, and slipping and knocking are possible when starting off.
Due to the fact that it is difficult to determine the cause of problems with engaging the first gear on an automatic transmission based on symptoms, to first search for a breakdown you need to carry out diagnostics using OBD-II. Typical error codes for which the first gear is difficult to engage in an automatic transmission are:
Troubleshooting - first gear in automatic transmission does not engage: video
- P0700 – general malfunctions in the electrical part of the automatic transmission (you need to look for the exact cause manually);
- P070F – insufficient oil level;
- P0731-P0736 – problems with the planetary mechanism, indicating a lack of oil, wear of the friction clutches, clogged channels or leaking seals;
- P0745-P0774 – problems with automatic transmission solenoids;
- P0780-P0790 – faulty gear switches.
The table below contains the main reasons why 1st gear is difficult to engage in an automatic transmission.
Problems with engaging 1st gear on an automatic transmission: causes and “symptoms”
| Cause of malfunction | How does it show up on a car? | What to do |
| Lack of transmission fluid | The automatic transmission goes into emergency mode, operates unstably, and overheats. An early shift to lower gears is possible due to lack of pressure. | Add/replace ATF and filter, carry out diagnostics. |
| Unsuitable gear oil | Gears shift poorly, jerks and jolts occur when shifting. | Replace ATF and transmission filter. |
| Souring or jamming of the selector (inhibitor) | The lever travel is tight, there may be problems with gear shifting and overshoot. | Clean the selector mechanism (inhibitor) or replace it. |
| Development of a clutch package | The car accelerates worse, gears slip, or they do not engage at all. | Replace worn clutch packs. |
| Torque converter malfunction | Symptoms of “clutch slipping”, difficult starts and slow acceleration. Car jerks, vibrations. | Repair or replace the torque converter. |
| Clogged channels of the automatic transmission valve body | Vibrations, noise when changing gears. Shocks, impacts, slipping when changing gears. One or more speeds may not be turned on. | Clean the hydraulic channels of the gearbox, change the oil and filter. |
| Oil pump problems | Shifting gears is difficult, the car has difficulty shifting to higher speeds when accelerating, and gears may not engage at all. | Replace the automatic transmission oil pump. |
| Solenoid malfunction | Gears are difficult to engage, early and late upshifts are possible. | Replace faulty automatic transmission solenoids. |
| Malfunction of manual transmission actuators | Problems with gear shifting, some speeds may not engage, crunching, gear slipping. | Replace faulty actuators. |
| Problems with manual transmission clutch | On “robots” it suffers from the same malfunctions as on manual transmissions. Deformation, wear of the disk, and violation of the clamping force lead to difficulty engaging gears. Possible crunching and ECU errors. | Repair/replace and adjust the clutch if it is not self-acting. |
| Electronic lock | It does not allow you to abruptly switch to 1st while driving, limits engine power, and causes an accident. | Carry out computer diagnostics of the automatic transmission and eliminate the identified faults. |
Knocking out the speed
If it turns on, but immediately turns off, then the latch may be stuck in the squeezed position, so it no longer does its job. It is also possible that the spring that presses the ball retainer is destroyed. Without the force of the spring, it will not be able to hold the slider in the desired position.
If significant force is applied while shifting into gear, the shift fork may bend.
Poor switching may also be caused by incorrect installation of the gearshift knob. In this case, the rocker does not bring the gear to full engagement.
Methods for engaging first gear
So, if the modes in your vehicle are difficult to engage and you have already understood the reasons and theory, then let’s move on to the most important thing - methods for engaging first gear. The simplest method in this case would be to activate first gear while driving the car. You need to push the unit selector forward without any effort and do this until the corresponding synchronizer comes into operation. However, it should be noted that this method is relevant for most passenger vehicles and some trucks.
It should be taken into account that this cannot be done in most old trucks, since the design of the unit itself does not allow this, since they simply do not have synchronizers. In addition, you need to take into account that this method of activating the first speed is hardly relevant if the synchronizer on your vehicle has already exhausted its service life. This will simply be impossible.
see also
Comments 23
First check the rod spring of the first and second gears, maybe it is broken and does not hold. If the spring is normal, then change the first and second gear clutches, also change the first and second gear synchronizers and a set of new bearings and seals so that in the future you will have peace of mind and a quiet gearbox
it’s not that complicated if you know what to change, what to change, just twist the nuts and twist it
I am doing exactly the same operation, I also had problems with the first one, I showed the box to a knowledgeable person, I told him to change the first clutch first and the synchronization of the first and second ones, and the stopper on the drive gear in the main pair fell apart because of this, there were problems, tomorrow I’ll put it together and write about the result of the operation )
Great! I will be waiting you!
In general, the following were replaced:
1. First speed gear assembly with synchronizer and clutch 2. Retaining ring for secondary shaft gear 3. Second gear synchronizer
Now about what happened - because the ring of the secondary shaft gear scattered (this is the gear that transmits torque to the 17-teeth differential ring on a VAZ 2110), as a result of which the gear itself was significantly damaged (chips), and most importantly, it shifted by about 2 mm, which pulled This resulted in a displacement of the first speed gear on the secondary shaft, as a result of which the clutch was not engaged.
Issue price: about 3.5 - 4 thousand rubles. for spare parts, I did everything myself according to the book
Wow! Quite expensive! Perhaps the coupling is expensive? And thank you for not forgetting to write back!
In general, the following were replaced:
1. First speed gear assembly with synchronizer and clutch 2. Retaining ring for secondary shaft gear 3. Second gear synchronizer
Now about what happened - because the ring of the secondary shaft gear scattered (this is the gear that transmits torque to the 17-teeth differential ring on a VAZ 2110), as a result of which the gear itself was significantly damaged (chips), and most importantly, it shifted by about 2 mm, which pulled This resulted in a displacement of the first speed gear on the secondary shaft, as a result of which the clutch was not engaged.
Issue price: about 3.5 - 4 thousand rubles. for spare parts, I did everything myself according to the book
And tell me, are the 1st and 2nd gear synchronizers the same/interchangeable?
I can’t answer this, they are very similar, I just came to the store and said what parts I needed.
And tell me, are the 1st and 2nd gear synchronizers the same/interchangeable?
And the symptoms were the following: - From the beginning, sometimes the first one would be knocked out - Then I held it with my hand while accelerating - Then, at the place where the first one should have engaged, there was just the noise of the gears barely engaging, if you press further, it seemed to engage, but when releasing the clutch, it was knocked out with a loud knock
Well, I have the same thing, only it doesn’t fly out when accelerating, only when starting off. Damn, I really want to take on repairs, but it’s already cold outside to do repairs, and there’s no garage. It's not even about the money. I want to learn myself, I also need to change the clutch along the way. Well, it’s clear in general, how does the box work now? Like new I guess?
Works great! The first one is a little difficult to engage due to new parts not yet developed, and surprisingly there is no howling, although I changed the secondary shaft gear on the main pair, I thought it would howl until it was used, but there is no silence, the speed is all right, I also advise you to change the oil seals along the way drives, it won’t hurt, but in the seals, shorten the springs a little, by 3-4 turns, so that they press better against the drives, I also replaced the release valve, there was not much noise, and the clutch was still not working properly.