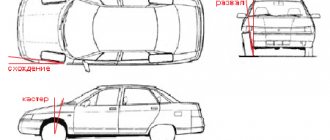
What should be the camber angles on Lada Granta FL?
To check and adjust wheel alignment angles, it is recommended to use stands whose characteristics comply with the requirements of GOST R 51709-2001.
Before checking and adjusting wheel alignment angles, the technical condition of the vehicle must meet the following requirements:
When testing under load, the applied load should be 225 ± 5 kgf.
Lada Granta must meet a number of technical requirements, including the parameters of the vehicle's front wheel alignment angles:
| Model | Front wheel alignment angles | |||||||
| Car under load | Curb car | |||||||
| Wheel camber, deg. | Angle of longitudinal inclination of the steering axis of the wheels, degrees. | Total wheel toe (linear), degrees | Total wheel toe (angular), degrees | Wheel camber, deg. | Angle of longitudinal inclination of the steering axis of the wheels, degrees. | Total wheel toe (linear), degrees | Total wheel toe (angular), degrees | |
| Lada Granta | 0 o ±30′ | 0,5±1 | 0 o 05'±10' | 0 about 35'±30' | 2 about 20'±30'* | 1,5±1 | 0 o 15'±10' | |
The angles of the rear wheels are set by design and cannot be adjusted (with the exception of Lada Granta Sport 219059 and Lada Kalina Sport 219259). If the parameter values deviate, replace the rear suspension arms.
| Rear wheel alignment angles | ||
| Wheel camber, hail | Total toe-in, degrees | |
| Lada Granta | -1 about 00'±12' | |
| Lada Granta Cross | -1 about 00'±12' | +0 o 36'±20' |
| Lada Granta Drive Active | -1 about 00'±15' | +0 o 10'±20'* 3 |
Signs that clearly indicate that your car needs to have its wheel alignment checked:
LADA service centers recommend diagnosing vehicle wheel alignment in the following cases:
How often do you adjust the wheel alignment of your car?
Source
How to choose a service station
Many service stations can assure you that they provide high-quality wheel alignment adjustments. However, if the technician immediately puts the newly driven car on the stand and begins tuning, you can freely interrupt the procedure and look for another service station.
The fact is that the correct angle of inclination of the wheels cannot be established if the car’s suspension is faulty. For this reason, a professional will first make sure that this system in the car is working properly. As a result of diagnostics, hidden problems are often revealed that will subsequently affect the position of the wheels.
Only after the technician diagnoses the suspension and chassis does he begin adjusting the wheel alignment. Serviceable parts have minimal play (and in some it should be completely absent). Otherwise, the angle of the wheels will be set incorrectly (if the technician manages to do this on a faulty chassis).
For these reasons, before allowing specialists to begin setting up the machine, you should clarify whether they do diagnostics of the chassis or not.
And one more nuance. If a driver has driven a car for a long time with a damaged camber, then the tires on it have already worn out. It happens that after high-quality tuning the machine still behaves unstable
In this case, you should pay attention to the quality of the rubber, and ideally, replace it with a new one.
To learn how you can do wheel alignment at home, watch the following video:
Camber - Toe. The old-fashioned way with your own hands. Wheel alignment without service station
Watch this video on YouTube
Camber Toe Caster
After the winter period, I changed the tires to summer ones and felt that the car was pulling to the left. I checked the ball joints and ends, visually inspected the front and rear suspensions, and saw no flaws. I checked the car's alignment and alignment. But it was not immediately possible to find reference information for Granta. I read on one of the forums that the reason a car pulls to the side can be the wheels themselves, or rather the tires on them. Sometimes it is enough to change the front right and left seats and the drift will stop. I didn’t attach much importance to it at the time, but that was in vain. In short, I drove like this for about a month, after changing the tires to new ones I was almost stunned, everything returned as it should be. Again to the forum, where they write that summer tires are changed like this: where you removed the wheel from, put it back there and don’t confuse places. I removed the right front one, returned it there in the spring, etc. all wheels. True, this advice applies to those who have not changed their camber or caster over the winter. I removed and installed wheels without any consideration of places.
Background information: This is a temporary recording, so please copy it for reference.
● Granta, under load: camber 0 degrees +/- 30 minutes caster 1 degree 40 minutes +/- 30 minutes (without ESD) 3 degrees +/- 30 minutes (with ESD) linear toe 0 +/- 1 mm angular 0 degrees +/- 10 minutes
● Granta, equipped car: camber 0 degrees +/- 30 minutes caster 1 degree 15 minutes +/- 30 minutes (without ESD) 2 degrees 20 minutes +/- 30 minutes (with ESD) linear toe 2 +/- 1 mm angular 0 degrees 10 minutes - 0 degrees 30 minutes.
● For Lada Granta, which are equipped with power steering (standard and luxury configurations), the front suspension caster is increased. It will be 2°45'.
I’ll insert the information somewhere in my blog. PS I'm saving. And I’m adding to the post.
Caster angle is the angle between the steering axis of the wheel and the vertical in a side view. It is considered positive if the axis is tilted backward relative to the direction of movement.
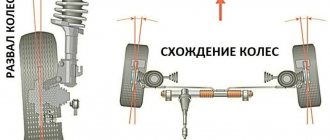
Camber
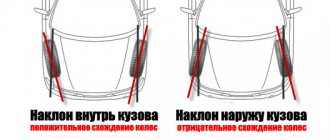
- the inclination of the wheel plane to the perpendicular restored to the plane of the road. If the top of the wheel is tilted outward of the car, then the camber angle is positive, and if it is tilted inward, it is negative.
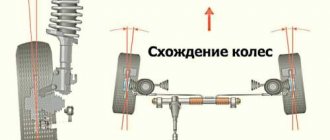
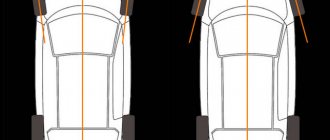
Convergence
- the angle between the longitudinal axis of the vehicle and the plane passing through the center of the steering wheel tire. Toe is considered positive if the planes of rotation of the wheels intersect in front of the car, and negative if, on the contrary, they intersect somewhere behind.
Below are experiments to understand how wheel adjustments affect the behavior of the car. The Samara VAZ-2114 was chosen for testing - most modern foreign cars do not burden the owner with a range and choice of adjustments. All the parameters there are set by the manufacturer and it is quite difficult to influence them without structural modifications. The new car has an unexpectedly light steering and slurred behavior on the road. The wheel alignment angles are within the tolerance range, with the exception of the longitudinal angle of inclination of the left wheel (caster) axis of rotation. In relation to the front suspension of a domestic front-wheel drive car, setting the angles always begins with adjusting the caster. It is this parameter, on the one hand, that is decisive for the rest, and on the other hand, it has a lesser effect on tire wear and other nuances associated with the rolling of the car. Moreover, this operation is the most labor-intensive - I think that is why they “forget” about it at the factory. Only then, having dealt with the longitudinal angles, does a competent master begin to adjust the camber, and then the toe-in. • Option 1
The master shifts the angles of the longitudinal inclination of the racks as much as possible, taking them to the “minus”.
We seem to be moving the front wheels back towards the mudguards of the wheel arches. A situation that quite often occurs on old and heavily used cars or after installing spacers that raise the rear of the car. The result: light steering, quick responses to its slightest deviations. However, “Samara” has become overly nervous and fidgety, which is especially noticeable at speeds after 80-90 km/h and above. The car has unstable responses when entering a turn (not necessarily fast), tends to venture to the side, requiring the driver to constantly steer. The situation becomes more complicated when performing the “rearrangement” maneuver. Option 2
“Correct” position of the struts (tilted to “plus”), toe and camber angles are set to “zero”.
The steering wheel has become elastic and informative, and a little “heavier”. The car drives clearly, clearly and correctly. The agility, unclear relationships and trajectory yaw have disappeared. At the “rearrangement”, the VAZ easily outperformed the previous version. Option 3
Excessively “positive” camber.
It is undesirable to change it without toe correction, therefore positive toe is also introduced. The steering wheel became lighter again, the responses when entering a turn became lazier, and the lateral movement of the body increased. But there is no catastrophic deterioration in character. However, when simulating an extreme situation, the “steering feel” is lost. With the advent of slips, unexpectedly early it becomes difficult to get into the given corridor at the “rearrangement” and the car begins to slide too early. In fast corners, the strongest slip of the front axle dominates. Option 4
Option with sporting ambitions: everything is negative, except for the caster. A car with such settings turns more confidently and quickly, as does the “rearrangement” maneuver. Hence the best result.
So, there are a lot of simple and very effective ways to change the character of a car without resorting to expensive replacements of components and parts. The main thing is not to neglect the adjustments - they often turn out to be very important. Which option should you prefer? For most, the second will be acceptable. It is the most logical for everyday driving, both with partial and full load. You just need to take into account that by increasing the longitudinal tilt of the rack, you not only improve the behavior of the car, but also increase the stabilizing (return) force on the steering wheel. The last, “fastest” tuning option is more suitable for the near-sporting public who likes to improvise with the car. When giving preference to these adjustments, it must be taken into account that with increasing load, the values of the toe and camber angles will increase and may go beyond the permissible limits.
Source
Making adjustments yourself
You also need to prepare the following tools and auxiliary equipment:
- driver's tool kit;
- a plumb cord or building level, a piece of chalk;
- folding measuring ruler or tape measure;
- a skein of strong rope or flexible wire;
- two timbers with a flat surface, 60 cm long;
- two sliding supports for car wheels (can be made from 4 metal plates, lubricating each pair of plates with grease to ensure the best sliding).
Before starting work, you need to check tire wear and tire pressure. If the treads are worn unevenly, they should be replaced and the tires should be inflated if necessary.
It is also better to perform suspension diagnostics before adjusting the wheel alignment angles.
Camber
Using a plumb line attached to the wheel arch, two distances from the wheel to the cord are measured. The difference is the camber index. With tires between 15 and 17 inches wide, a 1 cm difference is approximately 1 degree.
Alignment: working with the front axle
It is necessary to stretch a string along the perimeter of the car sills, which will become a guideline against which the wheels will be aligned. The angle is measured with a protractor.
The second method is to measure the distance from the stretched string to the wheel.
Correction of toe-in and camber indicators using special equipment
Unfortunately, statistical observations demonstrate that the computer stands used in our country often do not give very good results, since most of them are used uncalibrated.
An important role in the setup process is played by the experience and qualifications of the specialist performing the setup. Video about wheel alignment:
Wheel alignment "Grants": what it is, what it affects and how to adjust
If the tires are not aligned, this causes increased fuel consumption to overcome the additional resistance to movement due to pull to the side and uneven grip on the road surface.
By correctly adjusting the camber and toe of the Granta wheels (as well as Kalina and Priora), owners of Lada cars will provide their cars with excellent handling, fuel economy and extended tire life.
What might be required to get the job done?
But even without an adjustment stand, it is possible to set the necessary parameters quite accurately. For this you will need:
- An inspection pit with a flat, level platform. Practice shows that this is the most difficult thing to find. When arranging ordinary inspection pits, it is not customary to achieve a perfectly flat floor.
- A right-angled triangle, preferably large, with a leg length exceeding the distance from the floor to the top edge of the rim.
- Plumb. It is best if it comes with a tripod, since measurements taken using a plumb line that someone is holding in their hands will not provide sufficient accuracy.
- An accurate ruler with millimeter graduations, or better yet, a special ruler for adjusting wheel alignment. Such devices are commercially available and relatively inexpensive.
- Knowledge of the cosine theorem, which allows you to calculate an angle given the lengths of the sides of a triangle. As an alternative, you can use an online calculator, which is available in sufficient quantities on the Internet.
- Technical specification of the car with exact data of adjustment parameters.
- High-quality locksmith tools, the specific choice of which depends on the suspension and steering design of your car.
- A metal brush, an aerosol can with “liquid key” and, of course, patience.
A plumb line with a square can be replaced with a device that has the complex name “shtangen greysmas”. It is perfect for the task at hand. Some craftsmen manage to replace the ruler with a precisely calibrated laser rangefinder.
But we will have to give up goniometers and, especially, protractors. You will not be able to take accurate measurements with them. In any case, it makes sense to get down to business only when everything listed is available.
When should you do a wheel alignment? Video:
What does toe-in affect?
Technical and operational characteristics, convenience and ease of driving significantly depend on the wheel toe angle. The following indicates that it is not installed correctly:
Professional wheel alignment
The reasons for violation of the established suspension parameters may be the following circumstances:
The main factors indicating the need to check the alignment of Granta wheels are listed below.
Controllability
Correctly setting the suspension parameters guarantees stable traction in all modes, improving vehicle control.
Fuel consumption
If the tires are not aligned, this causes increased fuel consumption to overcome the additional resistance to movement due to pull to the side and uneven grip on the road surface.
Cornering stability
When negotiating a turn, the inner and outer pairs of wheels move in circles with different radii. Accordingly, forces of different magnitudes act on the inner and outer wheels, which must be taken into account by the adjustment parameters. Their imbalance leads to loss of stability when cornering.
Tire wear
Uneven tread wear indicates a problem. If everything is in order with the chassis, incorrect wheel alignment is to blame. The wear pattern of the tires may indicate the cause of malfunctions or adjustment defects:
Measuring the longitudinal and transverse angle of inclination of the axis of rotation
Of greatest interest is the measurement of the tilt parameters of the rotary axes. Their position is determined by two key characteristics: lateral inclination and longitudinal (caster).
A short video (2 min) about what a caster is
If the wheels of a car could turn 90 degrees and stand across the body, these parameters could be easily calculated using an inclinometer. But in real conditions this is impossible to do, so you need to limit yourself to a rotation of 20 degrees in both directions relative to the zero position. The difference in the obtained angles must be multiplied by an additional factor of 1.5 - this is necessary to compensate for errors that are allowed during the measurement process.
To measure caster, the bubble level bulb must be mounted perpendicular to the plane of the wheel.
To determine caster, you first need to turn each wheel 20 degrees in front of the steering axis: right to left, and left to right. In this case, you need to set the inclinometer to zero or write down the results. Next, the wheels are turned behind the turning axis: right to the right, left to the left. If the angle measured behind the steering axis is greater than the angle measured in front of the steering axis, then the caster is positive. If it's the other way around, then the caster is negative. The protractor should show a slight difference of a few degrees. This difference should be multiplied by the same factor of 1.5. For example, if the protractor showed a value of +2 degrees, then the caster value should be taken as +3 degrees.
The transverse inclination is calculated in a similar way, but the protractor is installed in a slightly different position. For additional convenience, you can use a smartphone, on which you should install in advance an application that simulates two mutually perpendicular bubble levels. An ordinary building level, preferably with a rotating bubble, will also work for these purposes.
To measure the lateral inclination of the steering axis, the bubble level flask must be fixed parallel to the plane of the wheel. Measuring the level of lateral inclination of the axis of rotation.
If the task is not to measure specific numerical values of slopes, but only to compare them (they are not adjustable on most cars anyway), then the results do not need to be multiplied by a correction factor of 1.5. The main thing is to make sure that the angles are equal on both axes (right and left).
In the process of self-measurements, it is not necessary to strictly observe the rotation of the wheels exactly 20 degrees, especially when there are no appropriate tools to determine these angles (for example, graduated turntables). You can turn the steering wheel about 3/4 of a turn. It is necessary to ensure that when turning left and right, the steering wheel is locked in symmetrical positions. To do this, you can put some marks on the bottom of the steering wheel. When the steering wheel is in zero position, the line connecting the marks must run strictly horizontally.
Another way to get accurate results is to draw corners on the asphalt near the wheels using a protractor. If you don't have this tool, you can use a square sheet of paper with equal sides. Folding it diagonally, we get an angle of 45 degrees. Then one corner is folded in half again, resulting in an angle of about 22.5 degrees, which is close to the standard 20. Next, you need to attach the sheet to the wheel and outline its edge with chalk, thereby creating the necessary marks on the asphalt.
Marking the corners for turning the wheel
Other wheel parameters
In addition to toe-in, there are two more important parameters - caster and camber, all together they position the wheel in three mutually perpendicular planes.
What is camber
Camber characterizes the degree of deviation of the wheel from the vertical in a straight-line driving position and can be positive (the tops of the wheels outward of the body) or negative (the tops of the wheels inward).
What is caster
The wheels turn right and left around an imaginary line passing through the shock absorber axis and the center of the steering knuckle ball joint. Which can be set vertically or offset, forming an angle to the surface of the road surface. The conventional point on the bottom of the tread around which the rotation is made can:
Caster when adjusting wheels
The angle formed by the conventional axis of rotation of the wheel and the normal to the road surface is called caster. This adjustment is used to maintain a given direction of travel. The change in camber angle when turning is also the merit of the caster.
We measure and correct camber
First you need to place the car on a flat surface and set the steering wheel to move in a straight line. Additional space will be required to move the machine. The further algorithm for adjusting the camber yourself is as follows:
- Chalk marks are applied to the rubber. One at the top, the other at the bottom;
- A weighted rope is secured above the wheel so that it coincides with the marks;
- The segment from the rope to the rim of the disc is measured from above and below;
- The car moves forward so that the marks move 90 degrees;
- More marks are applied above and below;
- Similar measurements are made again;
- Next, the car is rolled forward so that the first divisions move 180 degrees;
- Measurements are being taken.
The results obtained should not differ significantly from each other. The permissible deviation for a rear-wheel drive car is 3 mm, for a front-wheel drive car it is 1 mm. If the permissible deviation is exceeded, then camber adjustment is necessary.
The angle is changed using an eccentric bolt. To access it, you need to remove the wheel. Depending on the positive or negative difference, as well as its size, the direction and number of revolutions are determined. After manipulating the bolt, repeated measurements must be taken.
Cars for city traffic are set to slight negative camber. With this indicator, the car is better controlled in corners.
Camber parameters for Lada Grants
The manufacturer recommends the following angle values that must be adhered to when adjusting the wheel installation parameters:
| Car make | Angles of the front wheels of the Lada Granta (degrees) | |||||||
| Under load | Curb | |||||||
| Camber | Custer | Total wheel toe | Camber | Custer | Total wheel toe | |||
| Linear, mm | Angular | Linear, mm | Angular | |||||
| "Lada Granta" 2190, 2191, 2192, 2194 | 0°±30’ | 1 about 40'±30' | 1.5 ±1 | 0,15°±10’ | 0°20’±30’ | 1°15’±30’ | 1.5±1 | 0°15’±10’ |
| "Lada Granta" cross | 0°15’±30’ | 3°00’±30′ | 0.5 ±1 | 0,05°±10’ | 0°35’±30’ | 2°20’±30’ | 1.5±1 | 0°15’±10’ |
When measuring, you should take into account the different values of the wheel alignment angles on the Lada Granta liftback and models with an electric steering system (indicated in the second line in the table) and without it.
| Car make | Vehicle rear wheel alignment angles | |
| Camber | Convergence | |
| "Lada Granta" | -1 about 00'±12' | +0 o 20'±20' |
| "Lada Granta" cross | -1 about 00'±12' | +0 o 36'±20' |
The different toe-in figures for the camber of the Granta's rear wheels are due to the use of different types of levers. The Lada Granta has a liftback and the camber of the rear wheels is the same as that of a regular sedan.
Wheel alignment parameters "Grants"
The angles of the Granta sport wheels are slightly different from the standard models.
| Car make | Angles of the vehicle's front wheels under load (in degrees) | |||
| Sport 219259, 219059 | Camber | Custer | Total toe | |
| Linear | Angular | |||
| -0,30’±30’ | 3 o3 0'±30' | -1.5 ±1 | -0°15’±10’ | |
Cost of inspection at a car service center
WATCH THE VIDEO
Many car enthusiasts adjust the parameters of the wheels, including the rear ones, on their own in a garage with a pit or on an overpass. All distances are measured using a ruler or tape measure and a plumb line. Since driving safety depends on these parameters and their adjustment, it is better to have this work carried out by specialists in a specialized workshop.
In addition, wheel alignment is not very expensive - from 800 rubles. However, the technician will inspect the car and conduct a full diagnostic. The driver is given a printout indicating the value of each angle.
How to adjust the wheel alignment of a Lada Granta car at a service station
Adjustment of suspension parameters at a service station is carried out according to the regulations, after first making sure that the car meets the following requirements:
After making sure that the car is ready for adjustments, connect the equipment.
Special reflectors are attached to the disks (they must be undamaged), the light from which is recorded by cameras, and the processor processes the received information. It is displayed on the screen and the wizard makes adjustments, the results of which are displayed in real time on the screen. After completion of the work, a document is issued reflecting the input data on the wheel alignment angles on the Lada Grant and the results after adjustment.
Conservatism or modern approach, which is better?
But such a conservative approach is more suitable for old Ladas, Muscovites, Volgas, Cossacks, as well as ancient foreign cars.
On modern cars, it is, of course, better to carry out such work at a service station, where, with the help of modern laser and computer equipment, everything will be done at a high level without any errors. And we all know that even a small error in this matter can lead to rapid tire wear.
A service station is certainly good, they will do everything quickly and accurately. But there is always a BUT. Firstly , no matter what modern equipment is in a car service center, without a good specialist it is a pile of scrap metal. And here problems can arise:
1. How much do you trust this specialist;
2. How accurately will the work be carried out (when the equipment was checked for compliance with metrological standards) and whether such accuracy is worth the money;
Self-adjustment of wheel toe
Having decided to check and adjust the angles of the Granta wheels with your own hands, you should prepare the car as follows:
Self-adjustment of wheel alignment
Once you are satisfied that these requirements are met, you can begin to work.
Preparing the site
To carry out toe-in installation work, a flat horizontal platform is required, equipped with a pit and having a reserve space for moving the car horizontally.
Tools
The required set is as follows:
You will also need wheel chocks.
Procedure
When starting to check and correct the suspension parameters, it is necessary to strictly follow the sequence of actions, first adjusting the caster, then the camber, and after installing them, proceed to the toe-in.
Checking camber, toe and castor
A vehicle installed on a prepared horizontal surface with its wheels aligned to move straight is ready for inspection.
You can check the camber using an ordinary plumb line by measuring the distance from it to the top and bottom points of the disc rim. If the difference between the upper and lower distances is negative, then the camber is positive and vice versa. Its correctness is checked in accordance with the wheel installation table.
The negative camber of the Granta rear wheels, set by the factory, has a value of 1°, therefore, the difference between the distances from the top and bottom points of the disk to the plumb line will be approximately 5 millimeters. If a discrepancy is detected, an adjustment is made.
To check the toe-in, you will need a telescopic ruler or, in extreme cases, a flat wooden strip or metal profile to measure the distance between the extreme front and rear points of the rim of the front wheels. The steering wheel spoke is fixed in a horizontal position. The measurement accuracy must be very high. According to the table, the total toe-in value of the front wheels (the result of subtracting the distance between the extreme front points of the rim of the discs from the distance between the rear extreme points between the rims) is 1.5 millimeters with a tolerance of 1 millimeter.
It is not possible to accurately measure the caster angle yourself in a garage environment. An indirect indicator can be the presence of washers on the suspension braces, each of which, if removed or added, changes the caster angle by 19 minutes.
The measured values of the angle parameters are checked against the table and adjusted if necessary.
Diagnostics of other suspension components, chassis, steering and braking systems
Before adjustment, you should fix the steering wheel spoke horizontally and make sure there are no plays in the suspension, bearings, steering rod joints and supports.
Toe adjustment
The correct alignment of the Granta wheels is established by rotating the adjusting threaded bushing between the steering rod and its tip.
What to do if the locknuts do not unscrew
The lack of regular camber adjustment leads to the fact that the locknuts, being exposed to the environment for a long time, undergo corrosion and “stick” to the tightening planes. In this case, they must be thoroughly cleaned with a wire brush, spilled with anti-corrosion liquid such as WD-40 and, after waiting for some time, loosened.
What to do if there is not enough adjustment
If the factory technological reserve is insufficient to set the required toe angle values, then this is a sign of a violation of the straightness of the wheel orientation or a malfunction in the suspension mechanism. A violation of the body geometry is also possible.
Adjusting camber and castor
To adjust the caster, change the number of washers at the ends of the suspension extension. In this case, you cannot exceed the limit of 2 pucks in front and 4 behind. If adjustment cannot be made, the reason is a violation of the body geometry or a defect in the suspension parts. Sometimes the factory caster settings do not automatically maintain straightness when driving.
On Lada Granta cars, the camber of the front wheels is adjusted using the upper bolt of the pair that secures the steering knuckle to the shock absorber strut. Having loosened them, rotate the upper one to achieve the required camber angle, then tighten it.
Security measures
To adjust the front wheels, their decoupling from the surface must be ensured. Therefore, to keep the car stationary on a pit or overpass, it is necessary to block the rear wheel chocks.
What tool will you need?
To carry out the correct wheel alignment procedure with your own hands, you will need a place with a flat surface. It is desirable to have an inspection hole, but you can get by with a regular jack. Tools you will need:
- Chalk;
- Regular ruler;
- Rope with a metal object as a plumb line;
- Standard set of keys. Hexagons, caps;
- Telescopic ruler.
This set does not include expensive special devices. All tools can be found freely available on the market. An overpass is suitable as a workplace. However, it is worth remembering that at a service station, manipulations are performed using digital equipment, which gives greater accuracy in calculations.
Possible nuances
All of the above can also be applied to cars with other types of suspension. However, depending on the design features of a number of elements, there may be significant differences. For example:
- Cars where a gearbox and steering linkage are installed instead of a rack and pinion drive require special attention to the condition of the bushings and the pendulum hinge. Their wear affects the adjustment, and it can often be detected only with a certain position of the parts.
- On machines with a pivot suspension, when adjusting the camber produced by rotating the eccentric, the caster also changes. It will also have to be controlled.
- Some car models provide toe adjustment not only for the front, but also for the rear wheels. In most cases, this parameter changes when the coupling mounted on the transverse link connecting the rear wheels is rotated.
- If the car has all-wheel drive and a continuous front axle is installed, then the design does not provide for camber adjustment.
You can do the job efficiently only if you know all these features.
The master's work is afraid
Of course, your task will be greatly simplified if you decide to invest in professional equipment. It is not necessary to purchase a complex stand with laser sensors and a computer terminal that processes information, connected to a database that contains all the necessary parameters for hundreds of machine models.
A relatively inexpensive optical stand is quite sufficient. The domestic version of such a device, SKO-1M, can be found in stores for a very reasonable price, around 60,000 rubles. , price. For a used one they ask for even less.
It’s not easy to do a wheel alignment yourself. What looks easy in words, in practice requires serious expenditure of physical and nervous strength. You shouldn’t expect that everything will work out the first time. You'll have to be patient. Remember that the most advanced wheel alignment equipment will not make you an experienced specialist. But in the hands of a master, even an ordinary PSK-LG line can work wonders!
Source