The fuel pump is one of the most important components of the engine power system. A pump malfunction leads to interruptions in the operation of the internal combustion engine, failures when pressing the gas, or even problems with starting. Let's look at the design and operating principle of fuel pumps for injection and carburetor engines; Let's talk about breakdowns and diagnostic methods.
According to their operating principle, fuel pumps (FP) of gasoline internal combustion engines are divided into 2 types:
- electrical;
- mechanical.
During engine operation, the fuel pump is used to pump fuel from the tank to the carburetor or fuel rail with injectors. On cars with direct injection and a high-pressure fuel pump (HPF), the fuel pump is used as a booster section.
Where is the fuel pump located, the purpose of the device
The location of the device responsible for the uninterrupted delivery of energy in operating mode depends on its type.
Mechanical ones are used on cars with carburetors, and also as an auxiliary system for diesel vehicles. To create an active and at the same time effective vacuum, the function of controlling the fuel pumping mode is transferred to the engine camshaft. Even car owners who do not have special knowledge will always accurately tell you where the mechanical fuel pump is located. When troubleshooting or replacing this unit, look for this unit in the area where the engine is located. Electrically driven fuel delivery systems are driven directly from the battery or generator. This removes the restriction on the location of this element. Depending on the designer’s design, superchargers can be located in the fuel tank area or in the engine compartment. The design of the fuel pump depends on a number of factors. These include the assigned functions, expected dynamics and engine power.
Connection diagram
The mechanical fuel pump is mounted very simply - in the provided mounting location. After installation, all that remains is to connect the fuel supply line hose to the inlet and outlet ports, after which the unit is completely ready for operation.
As for electric pumps, two connection schemes are practiced on modern cars: Long fuel supply ring - return of unused fuel from the injectors back to the tank. Short ring – return of unused fuel to the tank directly from the fuel pump.
How does a diesel engine fuel injection pump work?
Thanks to the use of proprietary Common Rail injection equipment, diesel fuel under pressure is supplied at a given moment to the spraying devices - nozzles. The process is controlled automatically. The main work of the fuel injection pump of a diesel engine is reduced solely to creating ultra-high pressure of diesel fuel. Complete combustion of fuel in the working cylinders of the engine ensures maximum power from a diesel engine that runs on diesel fuel.
The main requirement for injection pumps is the supply of diesel fuel under a pressure force of at least 150 megapascals (Mpa). The material used to manufacture the pump casing is high-quality aluminum alloy AL9. The fuel pump uses a so-called plunger pair - a set of parts consisting of a small cylinder of small diameter and a corresponding rod. The material used to manufacture these elements is high-strength steel 25Х5МА. In order to ensure maximum efficiency of the diesel engine, the production of these parts meets the requirement for ultra-high precision.
The volume of fuel supplied and the time it enters the combustion chamber are determined by the crankshaft rotation speed. When the driver presses on the gas, increasing the load, a calculated portion of diesel fuel is supplied to the engine, sufficient for the smooth functioning of the engine. The efficiency of the power unit depends on the serviceability of the high-pressure fuel pump, which means that the responsibility of the car owner includes timely maintenance and regular analysis of the condition and possible failures of all its elements, including the injection pump.
Features of work
The distinctive properties of energy supply systems depend on the structural assembly. The drive unit contains rotary and gear pumps. Centrifugal devices typical for foreign cars should be looked for in the gas tank. The classification often uses a division into remote mechanisms that are mounted directly on the car body. Submersible structures are used inside tanks. With this design of the fuel pump, cooling of the moving parts is ensured and cases of idling are prevented. Additionally, the design of the supercharger includes sensors responsible for monitoring the level of gasoline and pressure in the supply system.
Unlike mechanical ones, electric models receive a signal to operate not from the camshaft, but from the engine control unit. A special relay is responsible for turning it on, which works synchronously with the ignition system. The pressure in the injection system can reach 0.4 MPa for gasoline and 0.7 MPa for diesel engines.
Main pump.
This type of pump is used in the well-known CR engine system. In this design of a diesel engine, the compressor responds to supplying the required amount of fuel mixture to the diesel fuel conductors. Unlike analogues, main devices allow achieving the highest pressure in the fuel line of a diesel engine. As the working pistons move as part of the fuel injection pump, the pressure in the ramp constantly increases. At the moment when the pressure becomes optimal, the intake valve opens and the fuel mixture enters the line.
Repair and maintenance of each compressor may have its own characteristics, so before starting repairs, familiarize yourself with the characteristics of your engine
.
If a faulty fuel injection pump is detected, it is worth promptly starting to repair the pump to preserve the service life of the internal combustion engine.
Good luck!
Mechanical and electric fuel pump
The fuel pump is the most important element of the fuel system. Its main task is to deliver fuel from the fuel tank at the rear of the car to the metered supply system in the engine compartment. Such a system is considered to be a carburetor or injector. The fuel pump can be represented by either a mechanical design or an electric fuel pump.
Mechanical fuel pumps have found their application in cars with a carburetor and provide fuel supply under low pressure. Electric fuel pumps are used in cars with fuel injection, as they are responsible for supplying fuel at high pressure and maintaining operating pressure in the system.
A mechanical fuel pump is mounted outside the fuel tank or near the carburetor, since there is no need to create high pressure in the fuel supply system. The electric fuel pump must be located inside the fuel line or fuel tank.
There is also a scheme for installing two fuel pumps at once. One fuel pump is installed in the tank and works with large volumes of fuel, pumping it under low pressure. Another fuel pump operates with a small volume of fuel and creates high pressure in front of the injection system. This pump is called a high pressure fuel pump. It is often located in the engine compartment near the power plant or directly on it.
It is worth noting that carburetor engines are considered obsolete, having long given way to more productive, economical and environmentally friendly fuel injection engines. There are a number of models where the electric pump is controlled by the ECU. The system takes into account the position of the throttle valve, the quality of the fuel-air mixture and the composition of the exhaust, thereby simultaneously adjusting the operation of the fuel pump.
Electric fuel pumps of the most modern type, while maintaining high pressure, exhibit excessive noise during operation and tend to heat up quickly. This determined their location in the fuel tank. The fuel is cooled by the gas pump itself, and the walls of the gas tank significantly absorb noise from the operation of the device.
How to repair TNND
If the efficiency of the unit has decreased, the low pressure fuel pump of the diesel engine must be dismantled and inspected. Often, productivity increases again after washing and cleaning the working cavities and elements of the device.
Knowing how the low-pressure fuel pump of a diesel engine works and the operating principle of the device, you can easily repair it or replace it.
High pressure fuel pump (HFP) of a diesel engine
is one of the most complex components of the fuel supply system of diesel engines.
Mechanical design
A mechanical fuel pump consists of:
- covers;
- mesh filter;
- upper part of the body;
- top plates;
- working diaphragms;
- spacers;
- safety diaphragm;
- bottom plates;
- rod;
- return spring;
- lower part of the body;
- lever for manual pumping;
This design forms a chamber that has inlet and outlet valves. These valves are located in the upper part of the mechanical fuel pump housing. Such valves are textolite washers, which are pressed by small springs to brass valve seats.
Operating principle
The special drive lever of a mechanical fuel pump moves up and down all the time, but the diaphragm is moved downwards by the lever only when the fuel pump chamber needs to be filled. The diaphragm is pushed back up using a return spring. This is how the process of supplying fuel to the carburetor occurs.
If you look at the operation of a mechanical fuel pump more closely, you should take into account the slight difference between rear-wheel drive vehicles and front-wheel drive models. A car with rear drive wheels has an eccentric located on the drive shaft. This element exerts an impact on the pusher. Front-wheel drive models have a similar eccentric, but it is already located on the engine camshaft.
The pusher presses the lever, and the lever already presses the balancer. This balancer is located at the bottom of the fuel pump housing. The balancer overcomes the resistance of the spring and pulls down the rod with the diaphragms of the fuel pump. In this way, vacuum is achieved. Fuel passes through the inlet fitting, and the inlet valve allows fuel into the cavity above the diaphragms.
Next, the eccentric jumps off the pusher. The lever, balancer and rod with diaphragms are released. The pressure spring forces the rod with the diaphragms to move upward, thereby creating pressure in the working chamber of the fuel pump. Under the resulting pressure, the intake valve closes and the exhaust valve opens. Through this valve, fuel enters the outlet fitting, then continues to move along the connecting hose and penetrates the carburetor float chamber. More information about the carburetor can be found in the article on fuel supply devices.
If you manually pump fuel on a mechanical fuel pump, then the pumping lever on the pump body through the cam immediately affects the balancer and the rod with the diaphragms. The pusher is not used in this case.
When the float chamber in the carburetor is completely filled, then the needle valve will no longer allow fuel to pass there, and the pump will operate in standby mode. The point is that the pressure from the movement of the diaphragms in the pump body is still not able to overcome the resistance of the needle valve.
Fuel pump drive
The VAZ 2107 fuel pump operates from a pusher (rod) and an eccentric located on the shaft of auxiliary devices (“piglet”, intermediate shaft), which is driven by the timing mechanism through a gear. Auxiliary devices include distributor, oil and fuel pumps.
Operating principle
The drive works as follows:
- the intermediate shaft rotates via a timing chain;
- the eccentric acts on the rod and pushes it;
- the rod presses the fuel pump lever, ensuring its operation.
Fuel pump drive malfunctions
As the fuel supply unit wears out, problems may occur that affect the performance of the latter.
Rod wear
The main sign of a worn-out rod is that the car does not reach the required speed. If the car accelerates, but, having gained speed to a certain value, does not develop it anymore, the reason is precisely the wear of the rod. Recently, the pusher has been made from such low-quality metal that it leads to wear out literally after 500–1000 km. The edge of the rod on the eccentric side is simply flattened, which indicates the need to replace the part.
Rod wear directly affects the performance of the fuel pump
The fuel pump rod should be 82.5 mm long.
Electrical device
The electric fuel pump is structurally similar in some parts to a mechanical one in a number of elements. Such a pump operates thanks to a special core, which is pulled into the solenoid valve until the contacts for supplying electric current are disconnected.
Turning the key in the ignition before starting is a signal to the car's on-board computer. At this stage, electric current is already supplied to the fuel pump. The engine has not yet been started, but in a couple of seconds the electric motor inside the fuel pump already raises the pressure in the fuel system to operating pressure. This is why it is recommended to wait 2-3 seconds before turning the starter and starting the engine.
If the ECU does not receive a signal that the engine has been started successfully, then the fuel pump is turned off automatically. This is done for security purposes. Some cars are designed so that the fuel pump starts when the driver's door is opened.
An electric fuel pump is capable of creating fuel pressure at around 0.3-0.4 MPa, and in engines with a direct injection system this figure reaches 0.7 MPa. In this article we will not talk in detail about the high-pressure fuel pump (HPF) for diesel and gasoline engines with direct injection. Read about such a system in the corresponding section of the site.
A special feature of the gasoline electric pump is the use of a modular system in its design. This is due to its direct contact with the fuel. Key elements of the pump also include a fuel intake, a fuel filter and a sensor that indicates fuel consumption.
An electric pump has a diaphragm that moves up and down. The result is that a vacuum is created above the diaphragm on the downward stroke. This allows the suction valve of the electric pump to open. Through such a valve, gasoline passes through the filter and ends up in the chamber above the diaphragm. When the diaphragm moves upward, the resulting pressure closes the inlet valve and opens the discharge valve, which pushes the fuel further into the system.
Essential elements
The electric fuel pump consists of:
- cameras;
- intake and exhaust valve;
- diaphragms;
- return spring;
- solenoid valve;
- core;
- electrical contacts;
The check valve is responsible for shutting off the fuel system when the engine is stopped. The pressure reducing valve maintains high operating pressure in the fuel system.
Main faults and service life
The average service life of key system elements is 200,000 kilometers. The resource can be compared with the overhaul interval of a gasoline engine with a fuel injection pump, when the car requires complex intervention. The main malfunctions of pumps for supplying and maintaining pressure in the system can be classified in two areas:
- Violations in the control unit. The unit receives incorrect signals, which directly affects the responsiveness of the car when driving;
- Mechanical wear of individual parts. Due to the rather complex circuit of the fuel pump, it is unsuitable for restoration (disassembly and diagnostics will be expensive). It’s easier and cheaper to buy a new part for later replacement.
Diagram and general view of the VE distribution pump
The VE distribution pump diagram is shown in the first figure, and its general view is shown in the following.
The main functional blocks of the VE fuel pump are:
- low pressure rotary vane fuel pump with control bypass valve
- high pressure unit with distribution head and dosing coupling
- automatic speed controller with a system of levers and springs
- solenoid shut-off valve that shuts off the fuel supply
- automatic device (automatic) for changing the fuel injection advance angle
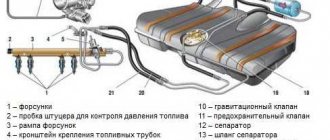
Rice. Fuel pump diagram - Bosch VE: 1 – pump drive shaft; 2 – bypass valve for regulating internal pressure; 3 – fuel supply control lever; 4 – regulator weights; 5 – fuel drain jet; 6 – full load adjustment screw 7 – regulator transfer lever; 8 – engine stop solenoid valve; 9 – plunger 10 – central plug; 11 – discharge valve; 12 – dosing coupling; 13 – cam disk; 14 – automatic fuel injection advance; 15 – roller; 16 – coupling; 17 – low pressure fuel priming pump
Rice. General view of the distribution injection pump VE: a – injection pump; b – high-pressure block with a distribution head and a dosing coupling. The positions correspond to the positions in the previous figure.
Types of fuel pumps
There are three main types of electric fuel pumps - gear, centrifugal and roller.
Gear
In a gear pump, fuel is supplied by a rotor (inner gear, movable), which is located eccentrically relative to the stator (outer gear, stationary). As the rotor rotates, the sides of its teeth form small chambers that change size depending on where the stator passes.
At the inlet, the chambers have a maximum size and suck in fuel due to the discharge into themselves. As it rotates relative to the stator, the chamber decreases in size, thereby ensuring the supply and injection of fuel at the outlet of the pump.
Roller
A similar principle is used in a roller pump, in which the fuel supply is also carried out due to the eccentric arrangement of a rotating rotor with movable rollers and a stationary stator. The rollers move in special recesses in the rotor. The space that appears between the rotor and the roller is completely filled with fuel at the moment when the roller, under the influence of centrifugal force, strives to break out of the rotor as much as possible.
Continuing to rotate, the rotor moves the rollers relative to the stator, the shape of which changes, forcing the rollers to be pressed against the center of the rotor's axis of rotation and thereby compressing the fuel. At the outlet, an additional condition is created in which the outlet port opens and high pressure fuel is removed from the pump.
Centrifugal
In a centrifugal pump, fuel supply is ensured using an impeller, which is equipped with special blades around the entire perimeter. The rotation of the impeller occurs inside a cavity equipped with two channels - suction and discharge. The rotational movements of the blades provide a vortex flow of fuel, thereby achieving an increase in pressure.
If, due to their design features, gear and roller pumps are mounted directly into the fuel line, then the centrifugal pump is located in the fuel tank. In modern fuel systems, preference is given to a centrifugal pump, which is much less noisy and provides a smoother (without pulsations) flow of supplied fuel, although it has limitations in performance and pressure created.
The operation of the electric heat pump is controlled by the internal combustion engine control unit. The fuel pump begins its work in parallel with the ignition being turned on, however, there are cars in which the pump is activated when the driver's door is opened (even before the ignition key is inserted or the start button is pressed).
The electric pump is capable of maintaining a rather narrow, but sufficient for normal engine operation, operating pressure range, which is regulated by changing the voltage and using a safety valve that limits the maximum permissible pressure in the system.
Vacuum
The operation of the vacuum pump is based on a conventional fuel pump of a carburetor engine. The only difference is in the drive, but the mechanical part itself is almost identical.
There is a membrane dividing the working module into two chambers. In one of these chambers there are two valves - inlet (connected by a channel to the tank) and outlet (leading to the fuel line, which supplies fuel further into the system).
This membrane, when moving forward, creates a vacuum in the chamber with valves, which leads to the opening of the inlet element and the pumping of gasoline into it. During reverse movement, the intake valve closes, but the exhaust valve opens and the fuel is simply pushed into the line. In general, everything is simple.
As for the electrical part, it works on the principle of a pull-in relay. That is, there is a core and a winding. When voltage is applied to the winding, the magnetic field that arises in it draws in the core connected to the membrane (its translational movement occurs). As soon as the voltage disappears, the return spring returns the membrane to its original position (return movement). The supply of impulses to the electrical part is controlled by the electronic injector control unit.
Fuel pump design
What is a low-pressure fuel pump, its design, operating principle and purpose.
Depending on the type of drive, fuel supply pumps are divided into two large groups: mechanical and electrical. The former are used only in carburetor engines, and also as booster pumps in diesel engines. The latter are used for both gasoline and diesel engines.
Mechanical fuel pumps
Mechanical fuel pump design
The mechanical pump is located on the engine and driven by a special eccentric. Structurally, it consists of the following elements:
- frame;
- diaphragm;
- pusher;
- stock;
- return spring;
- valves on the suction and discharge channels;
- filter;
- eccentric.
In cars equipped with rear-wheel drive, the eccentric is located on the drive shaft, and in cars with front-wheel drive it is located on the engine camshaft. The movement of the diaphragm in such a pump ensures the movement of fuel. When the diaphragm is at its lowest point, a vacuum occurs in the working chamber, and the latter is filled with liquid. When the diaphragm moves to the upper position, fuel is pushed into the discharge pipe. The valves prevent the fuel from flowing back.
For diesel engines, such systems are often used as low pressure pumps. They perform the function of pumping fuel and are located next to the high pressure pumps (). On the practical side, this allows you to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the filtration system and create a stable excess pressure.
Electrically Driven Fuel Pumps
Roller fuel pump. 1 – check valve; 2 – safety valve; 3 – electrical connector; 4 – electric motor; 5 – impeller
Electric pumps are installed on engines with distributed and direct injection. They are driven electrically by a battery or. According to their design, electric pumps are divided into the following groups:
- Vacuum. Such a pump has a similar design to a mechanical one, but the eccentric that drives the working units is replaced with an electric drive.
- Roller. In such a device, fuel moves due to the rotation of the rotor (movement of the rollers). At the moment when the distance between the roller and the rotor increases, a vacuum occurs, the suction valve opens, and the fuel is sucked in until it is completely filled. At the next moment, the rotation of the rotor ensures that the distance decreases, and fuel is supplied to the engine through the opened injection valve.
- Geared. Suction and injection of fuel is realized through the rotation of the rotor gear. It is located eccentrically with respect to the stator gear. The teeth of the gears form chambers through which the fuel passes. During rotation, the volumes of the chambers constantly change, which ensures the required pressure.
- Centrifugal. Such a pump has an impeller equipped with blades that move fuel from the suction to the discharge channel. Pressure is created due to the turbulence that occurs when the blades act on the working fluid.
- Plunger Gasoline pumps of this design are rare. Such systems are mainly used in diesel vehicles as injection pumps. They have pairs of plungers driven by a cam shaft. As the plunger moves upward, the outlet and inlet holes are closed sequentially. This forms the pressure necessary to open the discharge valve and subsequently supply fuel to the engine.
Why is an electric pump better than a mechanical one?
ATTENTION! A completely simple way to reduce fuel consumption has been found! Don't believe me? An auto mechanic with 15 years of experience also didn’t believe it until he tried it. And now he saves 35,000 rubles a year on gasoline! Read more". The efficiency of an electric pump is clearly visible on diesel cars, where diesel fuel is supplied under high pressure, and on gasoline cars with a direct injection system.
Fuel is injected directly into the cylinders of the power unit. And in this case, a conventional mechanical pump simply will not be able to provide the required level of pressure
The efficiency of an electric pump is clearly visible on diesel cars, where diesel fuel is supplied under high pressure, and on gasoline cars with a direct injection system. Fuel is injected directly into the cylinders of the power unit. And in this case, a conventional mechanical pump simply will not be able to provide the required level of pressure.
Direct injection injectors use two pumps. The electric one is installed in the fuel tank, from where it pumps gasoline, and the second pump is the injection pump. The latter’s task is to increase the pressure of gasoline before it is directly supplied to the injectors.
The electric pump is capable of pumping an average of 1-2 l/min. Crazy efficiency, which is only possible at a pressure of 3-4 atm. To equalize the operating pressure to the desired performance level, a special regulator is used in the fuel rail. It's called RDD.
Types of pumps
Today, two types of gasoline pumps are used, which differ in design and installation location. However, the principle of operation for all models is the same - pump fuel under pressure, ensuring its normal supply to the cylinders of the power unit.
So, according to design features and design, it is customary to divide pumps into:
- standard, with a mechanical operating principle;
- high-performance or electric.
Mechanical fuel supercharger
Mechanical fuel pump
The first type of pump is used on cars equipped with carbs. In most cases, it is located on the cylinder head of the engine. Thus, designers achieve direct and short drive with a camshaft. Fuel is pumped through the vacuum created by the pump diaphragm.
The diaphragm or membrane is located inside the pump housing. It is spring-loaded at the bottom, and fixed to the rod in the middle, which, in turn, is integrated with the drive. There are two valves at the top: one admits fuel, the second releases it. The device is also provided with fittings, there are also two of them. One draws in fuel, the second pumps out. The working area of any mechanical pump is considered to be the cavity located above the diaphragm.
The operating principle is based on driving an eccentric cam. It is located on the camshaft. When the latter rotates, the cam transmits movement to the pump through the drive.
Pump diagram
In more detail it looks like this.
- After starting the engine, the camshaft begins to rotate, thereby activating the pushing element.
- The latter triggers the lever.
- It, in turn, pulls the axis with the diaphragm, overcoming the spring pressure.
- A vacuum is created in the space above the diaphragm or in the working cavity.
- Due to the vacuum effect, the inlet valve opens and fuel is pumped inside.
- After turning the camshaft one turn, the pusher returns to its place due to the action of the spring.
- At the same time, the drive lever and the diaphragm with the axis return to their initial positions.
- Because of this, the pressure in the sinuses increases, the inlet closes, the outlet opens.
- The pressure pushes the fuel out of the cavity and into the carburetor.
It turns out that all actions of a standard pump are based on changing pressure properties. However, this does not mean that the carb necessarily requires high pressure, such as the injection systems of diesel engines. No, just a mechanical pump should create it in small quantities. The pressure should be enough to inlet and outlet fuel, that's all.
Thus, the mechanical type gasoline pump works constantly while the engine is turning. As the camshaft begins to rotate, a vacuum occurs in the pump; at the final revolution of the shaft, the fluid pressure increases. Thus, there is an alternation of decrease and increase in pressure, which is the principle of operation of a mechanical pump.
Obviously, after stopping the engine, the fuel pump no longer works. But it has a manual mode. For example, in winter it is recommended to first pump a little fuel into the carburetor, and only then start the engine with the starter.
Interesting point. In the carburetor, engineers have provided spare chambers in which fuel is collected in reserve when the engine is running. It is used at the moment of discharge, when the exhaust valve is still closed. A smart and effective device solution.
Electric pump
Electric fuel pump
Used on injection units, in which fuel enters the engine not through the carburetor, but through injection. In such a system, a mechanical pump is not needed, since it will not be able to provide the required pressure.
Injection a priori implies the presence of strong liquid pressure. Let us remember that the injector migrated to gasoline systems from diesel engines. And they are simply not able to work without high pressure.
The electric fuel pump is located in two places: in the fuel line or inside the tank. The last option is much more common. And this is caused by several goals. Firstly, while inside the tank, the pump is washed by liquid, which ensures its cooling and protection from overheating. Secondly, here it is securely hidden, and the risk of mechanical damage is reduced significantly.
As you know, direct injection gasoline systems have become widespread today. This is the same diesel device, only on gasoline, where injection occurs directly into the cylinders under high pressure. A conventional electric pump cannot cope here, so the designers provided a high-pressure fuel pump. This supercharger works in tandem with an electric pump.
The division of responsibilities between them is as follows:
- a submersible electric pump (the one in the tank) creates all the conditions for the normal flow of fuel into the system;
- The fuel injection pump provides significant liquid pressure before it flows directly to the injectors.
Gasoline pump with gears
There are quite a few models of electric pumps today. However, only three varieties are widely used. These are devices that operate using gears, rollers and a turbine.
Let's start with a gear-type pump. Its operation is based on the movement of an eccentric. Such a unit is installed in the fuel line. Two internal gears, placed one inside the other, perform the main functions of pumping fuel. The drive is an internal gear, which is directly connected to the electric motor of the pump. It is offset relative to the second gear and has a direct effect on it.
A roller pump or rotary-roller pump is installed in the same way - in the fuel line. Its design also includes an electric motor. Instead of gears, a disk with rollers works. It is mounted directly onto the rotor, and the whole thing is housed in a supercharger housing. Like the drive gear, the rotor is slightly offset in relation to the supercharger, thereby providing an eccentric location. The supercharger, in turn, is equipped with two outputs: through the first, fuel enters, through the second, it is pushed out.
The operating principle of such a pump is simple. The rotor speed creates a vacuum, and gasoline is pumped in. The rollers carry the fuel liquid further to the exit zone, but first it is provided with pressure due to the eccentric design. In other words, because of this, gasoline is compressed, which creates its pressure.
Main electric fuel pump
Finally, the turbine or centrifugal pump, which is more common today, is the submersible variety. It is placed inside the tank, and hoses and tubes are connected directly to the outlets of the unit. Gasoline is supplied to such a pump via an impeller. The latter has many blades and is protected by a special camera. During rotation, turbulence is created that sucks in fuel and compresses it, providing the necessary pressure before delivery.
Above are simplified diagrams of the operation of electric pumps. In reality, everything is much more complicated; you have to take into account the contact system connected to the on-board network, the design of the valves themselves, and much more. An electric fuel pump is necessarily controlled by the control unit and is put into operation only until the starter device is activated, and its power supply is protected by fuses and relays.
How to find out which fuel pump is on your car
Any more or less experienced driver is, of course, well aware of what type of gas pump his car is equipped with. As mentioned above, carburetor engines are equipped with mechanical fuel pumps installed in a specific location. However, sometimes carburetor engines are also equipped with electric pumps - this point needs to be clarified when buying a car, especially “hands-on”.
On cars with a fuel injection system, as well as with a direct injection system, exclusively electric fuel pumps are installed, which are located directly in the fuel tank.
Is it possible to repair a fuel pump yourself?
Mechanical fuel pumps, due to their simple design, are subject to repair - in fact, there is nothing special about them that can break. Most often the membrane fails, sometimes the rod. All this can be replaced, although most car enthusiasts prefer not to bother and buy a new pump - it is inexpensive and can be replaced in literally 10 minutes.
As for the electric fuel pump, it is not recommended to repair it, especially on your own. Theoretically, the electric fuel pump cannot be repaired - this is provided by the manufacturer. In practice, some craftsmen open the case and try to repair or replace damaged or failed parts. Such amateur activity is fraught with serious damage to the fuel system, so there is no point in experimenting, and it is better to purchase a new pump.
Signs of a fuel pump malfunction
In a mechanical fuel pump, malfunctions most often occur due to wear of the sealing gaskets and the formation of leaks between parts of the housing. As a result, the tightness of the structure is broken, air gets in, fuel stops getting into the carburetor and the engine stalls. A similar consequence is caused by membrane rupture and valve failure. At the same time, the car begins to move jerkily until the fuel supply stops completely.
On cars with mechanical and electronic injection, the signs of a fuel pump malfunction are slightly different, but they can be classified into certain groups:
- The engine does not start. Rotation of the starter with dry spark plugs does not cause flashes in the cylinders. There is no pressure in the fuel line, or it is extremely low; the buzzing of the pump is not heard when the ignition is turned on or the starter is operating.
- The engine does not start, although occasional flashes occur in the cylinders. There is pressure in the fuel line, but without a pressure gauge its value cannot be determined. The candles are dry.
- The engine starts and idles normally, but pressing the accelerator causes it to stop. If you want, it is possible to raise the speed to medium, but attempts to start lead to the engine stalling. There is a black coating on the spark plugs, the operation of the fuel pump is characterized by a changing sound.
- The engine starts, holds idle speed normally, and picks it up easily at neutral speed. When driving at medium and high speeds, a “twitching” is observed. It happens that after a certain mark on the tachometer the speed does not pick up, and the engine stops producing the required power under load. At the same time, the spark plugs are white, and by their appearance it seems that the car is ignited too early or has a lean mixture.
It is worth noting that the above symptoms of fuel pump malfunctions are also typical for other engine breakdowns, and they cannot be used to unambiguously diagnose a fuel pump malfunction. For example, speed also fluctuates if there is a problem with the air sensor, throttle valve, clogged injectors or poor quality fuel.
Types of fuel pumps
Current models are equipped with both mechanical and electrical fuel pumps. Mechanical pump
found in carburetor cars,
electric fuel
injection pump, where fuel enters the car engine under pressure.
The mechanical gasoline pump is located outside the gas tank, but the electric one, on the contrary, is located inside it. There are cars in everyday use that have 2 fuel pumps installed. The mechanical unit operates under low-frequency pressure because the carburetor and fuel pump are located close to each other.
Possible causes of fuel pump malfunction
A mechanical fuel pump may fail for the following reasons:
- If the integrity of the diaphragm is damaged.
- After dirt accumulates under the valves.
- When the filter is clogged.
- When the spring loses its elasticity.
- If the seal of the housing is broken.
- Due to natural wear and tear of parts during operation.
The electric fuel pump of a modern car is quite reliable. Malfunctions in it arise only due to the influence of certain factors, among which the most common are the following:
1. Faulty wiring in the form of dirty, rusty, melted or damaged wires in the fuel complex interferes with the operation of the device and also limits the required current parameters, making it difficult to pump fuel.
2. Debris and foreign impurities in the fuel tank in the form of rust, dirt, water, mechanical particles that penetrate the fuel pump and cause its breakdown.
3. A clogged fuel filter with debris from the tank contributes to a sharp decrease in the pressure created by the pump and a deterioration in its operating parameters.
4. Driving a car for a long time with a small amount of fuel, during which the pump is not immersed, experiences significant overheating, quickly consumes internal lubricant and fails.
5. Natural wear of the rubbing parts of the pump.
Injection pump maintenance
Routine care measures for the node include:
- The oil level in the injection pump housing is checked every 60 hours of operation.
- Oil changes are carried out at intervals of 240 working hours.
- Every 960 hours the pump is checked on a special stand.
During the fuel injection pump diagnostics process, the following parameters are checked:
- pressure generated by an individual section
- performance of a separate section
- uniformity of fuel supply by sections
- section performance in correction mode
- regulator operating modes
If a discrepancy is detected in the technical parameters issued by the unit during the inspection process, the unit is adjusted or, if necessary, repaired with the replacement of failed parts. To carry out repairs, as well as to correctly configure the unit, an appropriate material base and an appropriately qualified specialist are required.
How to check the fuel pump?
If the fuel pump does not start when the ignition is turned on, the check begins by looking for electrical problems:
- Checking the fuse. To do this, find the fuse box, find out which one is responsible for the fuel pump (check the diagram) and inspect it for burns. It’s even better to immediately replace it with a known working one with the same characteristics and see if it works;
- Checking the fuel pump control relay. It can be installed near the fuse box, injection control unit or other places. To check the pump relay, you need to remove and measure the winding resistance with an ohmmeter. If the indicator tends to infinity, then there is a cliff;
- Check current supply. To do this, you need to get the fuel pump itself without disconnecting it from the power supply. Turn on the ignition and measure the voltage at the terminals; normally it should be 12-12.5 V. If the motor does not work, it will have to be replaced;
- You can ring the fuel pump motor itself. Measure the resistance of the stator winding with an ohmmeter, first at the motor contacts for a break, then between the contact and the housing. If there is conductivity, it means that the stator winding is short-circuited to the housing;
- If everything is normal, evaluate the condition of the mesh filter. Perhaps it is clogged to such an extent that it does not allow the required amount of gasoline to pass through, in which case it must be cleaned and used further;
- Check the check valve, which prevents gasoline from returning back from the fuel line. Either test with a pressure gauge (the indicator should be no more than 0.3 MPa), or clean the valve and see how the engine operation changes;
- And finally, check the gasoline pressure in the system. To do this, connect a pressure gauge to the fuel rail and measure the pressure with the engine off, idling and while driving. When the engine is turned on, the pressure gauge reading should be between 3-3.7 atm.
If the check shows that the fuel pump is faulty, it is not repaired, but replaced. All the elements are adjusted too finely to try to repair something without special equipment.
When buying a gas pump, it is better to give preference to good, well-known brands rather than a suspiciously cheap “confiscated” product. Then there is a chance that the new pump will last at least 100 thousand km and will not create problems.
Design and principle of operation of a diaphragm fuel pump
Such a pump is widely used in carburetor cars and is mounted on the engine.
The diaphragm fuel pump is driven by the camshaft eccentric, most often by means of a pusher.
1 - rod; 2 — washer; 3 — clip; 4 - diaphragm; 5 — internal spacer; 6 — external spacer; 7 - nut.
The main element of the fuel pump is the diaphragm, which is sandwiched between two parts of the housing. It is she who pumps gasoline from the tank to the carburetor. In the event of a rupture, a special drain hole is provided, which prevents fuel from entering the engine crankcase with oil. A special mesh filter is installed in front of the valves to prevent the entry of small particles. A manual pumping lever is usually installed at the bottom, making it easier to start the engine.
After starting the engine, the eccentric moves the pusher, which, using a lever mechanism, lowers the rod and diaphragm. The return spring is compressed, and a vacuum is created above the diaphragm, which opens the valve and pumps gasoline from the tank.
During the next rotation, the eccentric releases the pusher and lever mechanism. The spring expands and the diaphragm rises. The valve closes and gasoline enters the carburetor.
During operation, the fuel pump tends to heat up from the heat of the engine, especially in hot weather. For this purpose, a cooling system for the fuel pump is provided, which is provided by the gasoline itself. It is a system of circulation and further draining of gasoline back into the tank. This eliminates the possibility of boiling and evaporation of gasoline, as well as various interruptions in engine operation. If the fuel pump overheats, the gasoline supply stops and the pump does not work, even if a manual drive is used to pump gasoline from the tank.
Overheating of the fuel pump is one of the main disadvantages of the diaphragm system. Drivers used various cooling methods, including placing a wet rag over the fuel pump. This problem was completely eliminated in a more modern analogue, which was developed in the era of injection engines - an electric fuel pump, which gradually replaced the mechanical fuel supply system.
How to change a gasoline pump on carburetor engines
The procedure for replacing a fuel pump on carburetor cars is not complicated. First, you need to turn off the engine and let it cool to make repairs more comfortable. Then perform simple manipulations:
- Remove the hoses from the inlet and outlet of the fuel pump.
- Unscrew the two nuts that secure the pump housing to the motor.
- Carefully remove the housing.
- Remove the pump rod and remove the old gaskets.
Reassemble in the reverse order, change the rod if necessary and install a sufficient number of gaskets. It is important that the rod protrudes no more than 1.2 mm above the surface.
Filter and mesh of the electric fuel pump, why they are needed and how often they are changed
Fuel from the gas station usually needs additional cleaning. The injection system is especially sensitive to fuel quality. Fuel filters are used for additional cleaning. The cleaning process is carried out in two stages: first, rough cleaning - through the fuel pump mesh.
Large particles of rust and debris are filtered out here. The second stage is fine cleaning, which is performed by the fuel filter. In different car models, fine filters are installed in different places. Most often it can be found under the hood of a car.
The injection system requires very thorough cleaning of the fuel - from 5 micrometers. The pressure in such a system is quite high, so fuel filters are made of durable material or stainless steel.
replacing the fuel filter
The engine owner's manual should indicate how often the fuel filter needs to be changed. Most often, this procedure is carried out once every two years or after a certain mileage of the car. However, given the quality of fuel at domestic gas stations, it is recommended to change the filter at least once a year. During intensive use of the car, it is recommended to periodically check the fuel filter and, if necessary, change it immediately.
You can replace the filter at a service station or yourself - the procedure is simple. Before changing the fuel filter, it is necessary to relieve the pressure in the rail.
For this:
• Disconnect the minus terminal. • Remove the fuel pump relay. • Connect the terminals to the battery. • Start the engine and wait until it stalls.
Now you can remove the fuel filter. We pinch the latches on both sides of the filter with our fingers and carefully remove it. Remember - approximately 100 grams of fuel remains inside the filter and it can leak out. Next, we perform the steps in reverse order - install a new filter, disconnect the terminals, replace the relay, connect the terminals, start the engine. We check for leaks at the connection between the filter and the fuel hoses.
We recommend: Purpose and principle of operation of the main automatic transmission sensors
It is very important to be able to determine when the filter is clogged. First of all, this can be signaled by poor engine starting; traction drops significantly; during sharp acceleration, the engine “chokes” and may stall. At idle, the engine runs unevenly; while driving, the engine lacks fuel if the speed exceeds 100 km/h.
How to check the fuel pump on an injector
Owners of fuel-injected cars know that when the ignition is turned on, the fuel pump motor turns on, pumping fuel from the gas tank to the engine begins, and a peculiar sound similar to a buzzing is heard.
If you suddenly notice that when you turn the ignition key, the fuel pump does not activate, then you will have to look for the causes of the malfunction. This could be electrical wiring, the pump itself, a relay, or a motor. It is better to look for the cause of problems in a certain sequence. First, check whether power is supplied to the fuel pump and so on, along the chain.
The principle of operation of the fuel pump
Schematic diagram of a fuel pump
The main function of a fuel pump is to transfer fuel from the tank to the engine. In injection engines, the fuel pump is connected to the fuel rail, and in carburetor engines - to the carburetor. In this case, it is necessary not only to pump fuel, but also to provide a certain pressure. Too high pressure leads to increased richness of the mixture and high fuel consumption. Too low pressure leads to a lean mixture and a drop in power. Both the first and second cases negatively affect the engine life. That is, the fact that the gas pump pumps fuel does not indicate its full serviceability.
How to check the pressure in the fuel rail?
You will need a pressure gauge that measures pressure in the range from 7 to 10 atmospheres. If you choose a pressure gauge with a large margin, you risk getting less accurate measurement results. Specialized stores sell a kit for measuring pressure, but you can also design your own device.
If you want to assemble the device yourself, you will also need a hose with an internal diameter of 9 millimeters. You will also need plumbing tow, with which you can seal the connection between the pressure gauge and the tube. All parts are connected and tightened using a clamp. You will also need a car spool. Next you need to perform a series of actions:
- Place the car on a level surface that is prevented from rolling, turn off the ignition and open the hood.
- Check that the injection nozzles have access to the fuel rail.
- Find the fuel pressure plug and remove it. Then you should unscrew the nipple using the spool.
- Prepare an empty container (a regular bucket will do) and a clean rag. This is necessary to collect residual fuel, which under pressure can splash out in different directions. Therefore, take care of the safety of your skin (especially your face and eyes).
- Connect the device to the fitting and begin checking the mechanism.
Checking the pressure in the fuel rail should occur in four operating modes of the power unit:
- when the ignition is on;
- at idle engine speed;
- code the fuel pressure regulator tube is reset;
- when the drain tube is compressed.
Why does the fuel pump pressure drop, possible reasons
One of the most common reasons is lack of power supply to the fuel pump. The fuel pump pressure may also drop while driving, when the power supply suddenly stops and the engine simply stalls. An equally important indicator is the amount of fuel supply. That is, the fuel pump may hum (there is power), but not supply the required amount of fuel and not create the required pressure in the rail. The pressure gradually accumulates in the ramp and should be about 300 kPa. To check the pressure in the fuel rail, use a pressure gauge. Pressure indicators must correspond to the specific brand of car. For example, for injection models of VAZs, when the ignition is turned on, the norm is 3 atmospheres, at idle speed - 2.5, when the gas pedal is pressed - 2.5-3 atmospheres.
Using a pressure gauge, you can most likely determine the nature of the malfunction: failure of the rail pressure regulator, breakdown of the fuel pump, decrease in its performance as a result of exhaustion, contamination of the filters (fuel filter, fuel pump mesh). For example, if the filter is dirty, the pressure will increase very slowly or abruptly.
When the fuel pump pressure drops below normal, the engine may not start at all, or may start with difficulty, jerk, trip, operate unstably, with dips, etc. If the reason lies in the fuel pump and not in the fuel filter, then most likely the pump mesh is simply clogged. In this case, it will be enough to clean or replace it.
If there is a suspicion that the fuel pump is broken, this can be checked very simply. Just turn the ignition key and listen carefully to see if you can hear the hum of the pump. If you do not hear the characteristic humming sound of the unit running, there may be a problem with the power supply or wiring. It should be noted that in expensive brands of cars, for example, premium ones, it is impossible to hear the sound of a running pump due to high-quality sound insulation.
The list of possible reasons for a non-working fuel pump, and, accordingly, a drop in pressure, includes:
• Broken fuse. • Failure of the fuel pump relay. • Failure of the pump electric motor. • Oxidation of contacts, etc.
Electric fuel pumps
Here the system is more complex, because there are two types: submersible devices placed in the tank, and remote ones, fixed separately. Both are powered by an electric motor located directly in the pump. How to check the fuel pump?
Voltage
Take a regular tester, or if you don’t have one, a car light bulb with the wires attached. Now you need to detect your device. If the fuel pump is remote, it is located somewhere near the tank. If submersible, look for the output terminals (usually they are under the rear seat). Further:
- turn on the ignition;
- touch the voltmeter probes or wires from the lamp to the contacts;
- if the device readings correspond to 12-12.5 volts or the light comes on, it means that voltage is supplied to the pump.
Wiring
Assessing its condition is easy: take a pair of long wires and connect directly to the pump. If it “squeals”, consider that the cause of the malfunction has been found. And if not? Go ahead.
Fuse
Everything is clear here: you need to find where it is and replace it, or insert a bug. If the fuse blows, the problem is most likely related to the positive wire going to the fuel pump, which shorts to ground.
To find it, read the labels on the fuse box cover. Pull the part out of the socket. Just in case, you need to check the serviceability of the relay with the battery terminals removed. Wind a wire onto its plus and connect it to two points of the relay: “85” and “30”. Connect the negative electrode to the light bulb contact and the relay terminal “86”. The second wire from the lamp must be connected to pin “87”. If the lamp lights up, the relay is working properly. If you have a multimeter, connect its probes to terminals “85” and “86”. An infinitely high resistance indicates a winding burnout. But what to do when you find that the relay’s performance is zero, and there is nowhere to purchase the part? Just bridge its contacts “87” and “30”.
How to check fuel pump pressure
It happens that the device works, but the engine does not start. In this case, you need to check the pressure, which should be from 2.5 to 3.2 kg/sq.m. cm (check the operating instructions for your machine). When you press the accelerator, it rises by an average of 0.5 kg/sq.m. see. If this is not possible, try inspecting the coarse filter. To remove it, if the pump is a submersible type, remove the hatch by unscrewing the bolts. Next, check the fuel pipes for fuel leaks. Finally, replace the fine filter.
Mechanical fuel pumps
They are installed on carburetor power units and are characterized by a simple design; the operation of the devices does not depend on the power supply. The functioning of the pump is ensured by a drive that moves a diaphragm, which contracts and pumps gasoline. How to check the fuel pump? There are two main methods.
No removal or disassembly
Disconnect the hose attached to the carburetor fitting and place it in a suitable bottle. Feel for the pump lever on the device and sharply press it several times. A relatively strong stream of gasoline will come out of the hose with a minimal amount of air (almost no bubbles).
There is a small nuance here that inexperienced drivers fall for. If the device pusher rests against the eccentric, the pumping will not work. In such a situation, simply crank the crankshaft slightly with the starter. You can do it easier if you have an assistant. Ask him to “turn” the starter and look at the stream of fuel. If it is weak, the spare part will have to be dismantled and inspected.
With disassembly
Look at the top cover of the pump for any leaks. If they are:
- Disassemble the device and replace a couple of gaskets;
- The following objects of inspection are diaphragms: cracks and ruptures are not allowed.
- Clean the filter mesh, intake and exhaust valves: the parts must be free of dirt and deposits.
- If new gaskets are installed and gasoline is still leaking, place the top cover on the body without them and point it at the light. It is quite possible that after a strong tightening the planes do not fit tightly together. The problem can be solved with sandpaper.
As for imported gasoline pumps, some of them are non-separable. You can try to drill out the rivets, but if there are worn parts inside, you will have to buy them somewhere or make them yourself.
Car won't start after replacement
Car won't start after replacing fuel pump? This phenomenon is not uncommon. In many cases, this is not a problem. The car cannot start immediately because the pump takes time to pump up the pressure that was previously reduced. To bring the pressure to the optimal level, you need to turn on the ignition for 5 seconds so that the instrument panel lights up. Next, turn the engine with the starter. If it doesn't work on the first try, you should wait about a minute and try again.
If cranking the starter does not help start the engine, then one of the following reasons may be occurring:
- errors were made when assembling or connecting the BN;
- the new fuel module is faulty;
- the car's security system has gone down or a blockage has occurred;
When installing and connecting a new pump, failures of various types are possible: from malfunction of the valves on the fuel pump to breakage of contacts, terminals or connectors.
It is important to identify the exact nature of the problem and determine its type - electrical or mechanical. The simplest breakdown relates to the power supply to the fuel pump; it either exists or it doesn’t. If we are talking about an immobilizer or alarm system, then the anti-theft system can turn off the power supply to the BN, preventing the car from starting. Don't forget about filter clogging either. If the valves are stuck, the device can operate and produce characteristic sounds, but at idle.
The listed malfunctions prevent fuel from entering the ramp, so the engine cannot start. To clearly determine the cause, it is important to make sure that there is no gasoline in the rail. Next, it is recommended to dismantle and connect the BN from the dimensions or batteries directly. This method is considered the fastest for checking the device.
Preventing fuel pump breakdowns
The best prevention for long-term operation of the fuel pump is its careful and proper operation, as well as compliance with the following rules:
- All scheduled vehicle repairs must be accompanied by the replacement of all fuel filters.
- It is necessary to monitor and ensure the cleanliness of the fuel tank and filters, as well as monitor the quality of the fuel being refilled (the absence of water, sand and other impurities in it).
- Eliminate the possibility of water getting into the fuel tank.
- Protect the fuel pump housing from mechanical stress that causes dents and cracks that contribute to the development of corrosion processes.
Submersible fuel pump.
Gazelle fuel pump operating principle
The submersible fuel pump is a rotary vane type, installed directly in the fuel tank. Recently, these pumps have been widely used. When installed, the pump is part of the fuel module, which also includes a filter, indicator sensors and fuel reserve lamps, as well as damping devices, a fuel line and wires.
Like a remote pump, a submersible pump consists of an electric motor and a pump and has a check valve and pressure relief valve.
For normal operation of the pump, its centrifugal part must have small clearances, and ideally its parts should be in contact. At the same time, these parts rub against each other. Gasoline, when passing through the pump, lubricates these parts, so operating a pump without gasoline is detrimental to it, especially a submersible one.
Fuel pump service life
The service life of a fuel pump depends on its design and the materials from which it is made. Depending on the model of the device, the fuel pump will work without interruption for a period of 100 to 200 thousand kilometers of the car.
The pump fails for two main reasons:
- untimely replacement of fuel filters. Moreover, some pay attention only to the fine cleaning element, but the cleanliness of the mesh, which is installed directly on the pump itself, deserves no less attention. When the pump tries to create pressure through a dirty filter, it gets hotter. Timely maintenance will extend the life of the pump;
- The fuel level in the gas tank is often low. Because of this, the device does not receive proper cooling, so the risk of overheating increases significantly.
Also pay attention to the video on how to restore some pumps:
Symptoms of malfunction
If the fuel pump is completely faulty, the car will not be able to start. When such a breakdown occurs while driving, the engine will stall and the car will stop. If a technical problem is just beginning to appear, then at this stage you can judge the malfunction of this particular part by the following symptoms:
- The engine begins to operate intermittently (this symptom is especially pronounced at high crankshaft speeds).
- Jerking when trying to quickly gain speed.
- Unstable engine operation at idle speed.
- Unstable operation when driving on a long climb.
If the fuel pump is faulty, there may be some extraneous noise. If you use carburetor car models in which the fuel pump is installed on the engine, then a decrease in engine oil pressure is possible due to fuel getting into it due to a rupture of the supercharger membrane.