Why do you need a VSM system?
The VSM Integrated Management System is a system that can give the driver more control over his car while ensuring vehicle stability on the road.
.
In addition, the use of this system in a car helps solve several other equally important tasks for the motorist:
- Thanks to the system, parking and maneuvering at low speeds becomes easier and more convenient, because you need to put less effort on the steering wheel.
- Wheel torque increases at high speed.
- The reactive force of the wheels increases significantly when they return to the middle position.
- When driving at an angle, this system helps to correct the position of the front wheels. This is also true in difficult weather conditions, when driving is difficult due to strong wind, rain or even ice.
The main difference
The difference between this system and similar solutions for the car is the way it affects the car. VSM does this by directing force to the front wheel, while its control-improving counterparts primarily focus on the braking system.
If you constantly use a car without using this system, you may encounter the fact that in any situation on the road you will have to make great efforts to control the car. It is also worth noting that using the system offers the user many benefits.
Safety of the chassis, which is ensured by reducing the load on its elements during difficult maneuvering and parking
This is a great advantage that helps keep the car in good condition and save money on replacing this important automotive component.
Improved driver maneuverability. This advantage is provided by high-quality hardware, a system that helps remove most of the load from the motorist and transfer it to mechanical means.
This is the best solution for novice motorists who still find it difficult to cope with all the difficulties associated with driving
VSM along with an automatic transmission will help solve the issue of automating all driving processes, so it is a very simple and convenient solution.
The system shows its highest efficiency when the vehicle is moving on different surfaces on different wheels. This means that if one wheel moves on ice and the second on normal asphalt, then the first wheel will not skid in the direction of travel. Thanks to this, it will be possible to preserve the chassis for a long time; while driving, there will be no imbalance or other unpleasant moments that are the consequences of such driving.
High efficiency with fast maneuvering. In such cases, the system also manages to show its best side and achieve high results for users. It's no wonder that customers are choosing to install it more and more often.
This system is increasingly being used in the creation of new cars along with other control systems, but its main difference, thanks to which it can be distinguished, is its focus on the front wheels.
The remaining options on the market and introduced into modern cars affect the brakes,
This ensures a smoother ride for the car. In contrast, this system allows the user to gain not only control over his car, but also a high level of controllability with easy steering movement.
This effect is achieved due to the high-quality redistribution of load between the functional parts of the chassis.
Due to the large number of advantages, relatively low cost
, the ability to prevent skids even before they occur - this system has gained high popularity among developers.
In some cars it completely replaces all other stabilization systems
, but more often it is used together with other solutions to make driving easier. Since it is integrated, it outputs important signals to the driver's control panel so that he receives up-to-date information about the current state of things instantly.
Conditions under which you need to turn off the ESP stabilization system
Scientifically, ESP is an electronic vehicle dynamic stabilization system - Electronic Stability Program. Different manufacturers call it differently: Volkswagen, Audi, MercedesBenz call it ESP, Hyundai - VSM, Honda - VSA, and BMW, Jaguar, Land Rover - DSC.
The dynamic stabilization system or vehicle stability control system developed on the basis of the ABS anti-lock braking system, the ASR anti-skid system, the TCS traction control system and other various systems that have different names, but use the same principles of wheel traction control.
When the vehicle is moving, the ABS/ESP control unit (computer) analyzes the position of the vehicle using various sensors placed on the car.
Using this data, the ESP system can adjust the braking force between the wheels, applying the brakes to a specific wheel if necessary to level the vehicle, thereby preventing the vehicle from lateral movement or skidding.
As a result, the ESP system provides the car with good dynamic balance.
According to the US Transportation Security Administration (unfortunately, there are no similar studies in our country), the ESP system can reduce passenger car accidents by more than 30%, and SUV and crossover accidents by 50%.
But since this system is so useful and directly affects road safety, why did automakers provide the ability to disable the vehicle stabilization system? So, why the ESP system is useful and when it should really be turned off is in our review.
1) Drift, quick start
If you are a racing driver, like to drift your car, or don't want the stability control system to interfere with your car's handling, you should turn off ESP. Otherwise, the system will prevent you from drifting when the car's wheels begin to lose traction. If you do not turn off ESP, the system will limit wheel slip not only by braking the wheels, but also reduce the transmission of torque to them.
2) Driving on sand or mud
When going outdoors or driving through mud, we advise you to also turn off the ESP system so that the electronics do not brake some wheels that begin to slip on a road that runs through rough terrain. Also, off-road driving requires power, which will be limited by the dynamic stabilization system, as a result of which the car may get stuck. If you are already stuck, then you also need to turn off ESP, as it will prevent you from leaving.
3) Rain and snow, slippery roads: when driving uphill
We know that in rainy and snowy weather, the ESP system is excellent at helping drivers keep their car on slippery roads. Thanks to this, we feel more confident behind the wheel in bad weather.
And all due to the operation of electronics, which perfectly regulates the stability of the machine even in difficult weather conditions. But if you are driving uphill on wet or slippery roads, it is better to turn off the ESP system. This is necessary so that the car climbs smoothly uphill.
Otherwise, the ESP system may, on the contrary, contribute to the car skidding when going uphill.
4) The vehicle is equipped with snow chains
If your car is equipped with snow chains, in this case we would also advise you to disable the ESP system. Otherwise, the ESP system will transmit incorrect data to the stabilization system control unit, as a result of which the car will not align on the road as desired. Ultimately, this will affect driving safety. In this case, it is better to disable ESP.
How does disabling the ESP system work on different cars?
All cars, as we know, are created differently. The algorithm of the ESP system is also different. Especially when disconnected. For example, in some cars, pressing the ESP OFF button once only turns off the ABS system first. This is how, in particular, disabling ESP works in the Hyundai Creta crossover. If you then press the button again within a few seconds, the stabilization system will turn off completely.
Source: https://1gai.ru/publ/522162-pochemu-sistemu-stabilizacii-esp-mozhno-vyklyuchit-vot-kogda-nuzhno-otklyuchat-esp.html
SRS system in a car
The abbreviation SRS stands for Supplementary Restraint System, and it refers to the vehicle's active safety system. It is she who is responsible for the condition of all the elements that should provide protection for the driver and passengers of the vehicle in the event of various emergency situations.
The SRS system includes the following components:
- Airbags (front and side);
- Touch sensors that monitor in real time the position of people inside the car;
- Acceleration and impact sensors;
- Seat belt pretensioners;
- Control modules;
- SRS main module;
- Active head restraints.
In addition, the design elements of the SRS system also include connecting cables, autonomous power supplies and connectors.
Frontal airbags are located directly in front of the driver (in the steering wheel) and front passenger (in the dashboard), and side airbags are located on the sides, in the seat backs and side body elements. Their design includes special squibs filled with dry gas and triggered by electrical impulses.
Touch sensors (pressure sensor and backrest position sensor) are located in the seats, and the acceleration sensor (often also called an overload sensor) is located in the front of the car, directly behind the radiator grille. It is designed on the principle of a pendulum, and if its position changes sharply as a result of a collision, it closes the electrical circuit, thus generating a control signal transmitted to the main SRS module.
In most cases, it is located in the tunnel channel (or rather, in the front part of it), and its most important function is to control such elements of the SRS system as airbag modules and seat belt pretensioners. The latter, just like the touch sensors, are located in the front seats and are equipped with squib pistons: when triggered, they are set in motion and very quickly tension the belt. It goes without saying that active head restraints are also located on the seats, being mounted in the upper parts of the backrests.
Features of new Hyundai/Kia cars: fuel-efficient engines and start/stop systems
Hyundai-Kia Group's first in-house direct injection engine, the 2.4 L GDI, was used first in the Sonata and then in the Hyundai Grandeur, Veloster, Accent and Kia Optima. A 2.0-liter Turbo GDI, combining direct injection and turbocharging technologies, is available on the new Sonata. Both engines help reduce emissions.
On the powertrain front, the new Veloster is the first Hyundai to feature a dual-clutch transmission.
Highly available driving stability features include VSM (Vehicle Stability Assist), which provides coordinated control of the ESC and power steering, and Hill Start Assist. In terms of crash safety, rear-seat side airbags and driver knee airbags are increasingly available, especially on high-end models.
In terms of driving and parking assistance, high-end Grandeur cars have advanced intelligent cruise control, intelligent parking assist and other advanced features. The start/stop system, which contributes to better fuel efficiency, is available on a growing number of European and other models. Visibility features include an auto-dimming rearview mirror and rain-sensing front wipers.
In terms of ride comfort and convenience, dual automatic air conditioning is becoming increasingly available, providing separate climate conditions for the driver and front seat passenger. Hyundai has started using the Blue Link telematics system in the US.
Advanced systems available on new Hyundai and Kia models, as well as fully upgraded models
| Hyundai | Kia | ||
| Motion stability | Vehicle Stability Control (VSM) | Grandeur, Veloster, Elantra, Accent | Sportage, Picanto |
| Hill Assist Control (HAC) | ix20, Accent | Optima, Sportage, Picanto | |
| Crash Safety | Rear side airbag | Grandeur, Sonata | Cadence |
| Driver knee airbag | Greatness | ||
| Front active head restraints | Sonata, ix20, Accent | Optima, Sportage, Rio | |
| Driving and parking assistance system | Emergency stop signal | Greatness | Sportage, Rio, Picanto |
| Advanced Intelligent Cruise Control | Greatness | ||
| Smart Parking Assist | Greatness | ||
| Intelligent Stop and Go (ISG) | ix20 | Sportage, Rio | |
| Visibility | Auto-dimming rearview mirror | Sonata | Optima, Sportage |
| Front wipers with rain sensor | Cadenza, Sportage | ||
| Comfort and convenience | Dual automatic air conditioning | Sonata | Cadenza, Optima, Sportage |
| Start button | Sonata | Cadence, Optima, Elantra | |
| Telematics system | Grandeur, Veloster | ||
| Eco-Shift indicator | ix20 | Sportage, Rio | |
,
How and when the VSM system is activated
This system is used as an add-on over other traffic stabilization aids, and automakers usually define it in their descriptions as an addition to their list. Existing indicators can be used to signal activation, for example, ESC and EPS activation in Hyundai Accent or Creta.
Active Steering mode is switched off when driving in reverse or on a slope. Speed limits for inclusion are speeds above 15 km/h on a road with turns and above 20 km/h when braking. You can disable or enable this mode manually by pressing the ESC OFF button. The activation of the equipment is felt by ear and by a slight pulsating movement of the brake pedal.
Using the methodology
Systematization of the value stream is carried out on different scales - from simple administrative procedures to large-scale production for the global market. The method helps identify steps that do not add value and need to be eliminated, as well as weak points where the process can be improved: speed up, reduce costs and provide safer working conditions.
Creating Value Stream Mapping is divided into three blocks:
- A production or process flow
is a traditional flowchart in which, from left to right, the path of value creation is recorded, starting with the purchase of raw materials and ending with the shipment of products. If, in addition to the main process, there are additional or auxiliary ones, they are applied under the main one. In this way, the main tasks are separated from the secondary ones. - Information or communication flow
- at the top of the value stream map, arrows depict information flows that occur in parallel with production. Both formal and informal data exchange are taken into account. Information flows are plotted on the map in free form, as they flow in reality. - Timeline and distances
are lines that are drawn at the bottom of the map. The time line is divided into upper and lower parts. The lead time is displayed at the top - the waiting time. The cycle duration is shown below. Below the time line there may be another line, at the very bottom, showing the distances along which the product or personnel move within the process.
Parts of a value stream map
Value Stream Mapping effect
Value stream mapping is useful for a company of any size.
Using Value Stream Mapping brings results:
- provides a consumer perspective
- uses a common language for all employees to monitor the flow of value
- provides a holistic view of product creation
- helps to identify weak points in production at a glance
- helps employees deeply understand the work process
- A powerful tool for improving production workflows
How to create Value Stream Mapping
The application of the CPSC consists of three blocks: creating a map of the current state, creating a map of the future state and drawing up a plan for implementing improvement measures. It is not enough to simply visualize the production process - without planning, implementing and analyzing improvements, the Value Stream Mapping methodology is meaningless.
Current state maps provide a starting point for creating a lean future state. It allows the organization to find losses, their sources and causes: if at this point we are experiencing losses, then why is the process designed this way and how can it be improved?
A future state map is a definition of the future ideal state of production. This may include creating a continuous flow, using FIFO or supermarket material flow methods where continuous flow is not possible, and production levelling. Finally, the future state map identifies improvements to be implemented.
FIFO - first in, first out, the first part that enters the process is the first to leave it. The parts move strictly in order, and the number of parts in the line is limited. When the line is full, the previous process stops.
Supermarket (supermarket) - several parallel FIFO lines on which various parts and products move. The basic idea of the supermarket is that when one part or unit of product is taken out of the process, it is immediately replaced (similar to a regular supermarket when we take an item off the shelf)
It is important to maintain a supply of all parts, but avoid overproduction
Production levelling is a method of organizing a production process in which intermediate goods are produced at a constant rate so that further processing can also be carried out at a constant and predictable rate.
The most important part of value stream mapping is the improvement plan. It identifies each activity needed to achieve the future state, the responsible team or employee, and the deadline. Plan activities typically refer to Kaizen events or Six Sigma projects. In order not to miss any of the activities to improve the plan, it is better to register them in the company’s task manager.
⇡#Hi-Tech
Almost all the high technologies that were previously the prerogative of more expensive models are now available for the updated Toyota crossover. The fully loaded RAV4 now offers the same hi-tech capabilities as the new Land Cruiser (which was also recently redesigned) and some of its competitors. True, the test car was deprived of most of the options, and therefore I can only guess about ease of use, such as navigation and voice control. In this regard, I will limit myself to a brief listing of all the “goodies” that a buyer of a Japanese crossover can theoretically receive.
The 2022 model may be equipped with an interesting option - a panoramic viewing system, which in the USA is beautifully called Bird's Eye View. It works like this: wide-angle cameras are installed on four sides of the car, the image from which is combined into a single picture of a circular seamless panorama and then displayed on the display of the Toyota Touch 2 multimedia system. Moreover, you can view the car’s surroundings both statically and on the move - for example, when overcoming obstacles or when driving in particularly tight conditions.
The Toyota Safety Sense package includes several active safety systems. There is a system for automatically switching high beams to low beams (and vice versa), which constantly assesses the level of road illumination and takes into account the headlights of oncoming cars, as well as the taillights of passing cars.
Lane Departure Warning recognizes road markings and alerts the driver if he has crossed the line but has not activated the turn signal, both visually and audibly. If the driver continues to violate the traffic lane and generally behave, according to the computer, inappropriately, the system for monitoring and informing about driver fatigue will prompt the tired pilot to stop and rest.
RAV4 can also warn about the threat of a frontal collision: if the distance to the vehicle in front decreases too quickly, the system will warn the driver about the threat, and, if necessary, perform emergency braking.
In cruise control mode, the RAV4 is able to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front, automatically slowing down if it detects a vehicle moving slower than a set speed value.
The RAV4 is trained to recognize road signs and then display them on the 4.2-inch on-board computer display. Moreover, if the driver does not comply with the requirements of the signs (for example, exceeds the speed limit), the car will use sound signals to remind the reckless driver of the importance of traffic rules.
Of all the high technologies that the test crossover had, there was only the Toyota Touch 2 multimedia system (and then with reduced functionality, since it was deprived of navigation and voice control), plus an on-board computer with a 4.2-inch display on the dashboard. Touch 2 is not a new device, but is well known from other Toyota cars. In the basic version, the system’s capabilities are typical and limited to the simplest functions: radio, playing music from external storage media, communication with a mobile phone via Bluetooth (receiving and sending calls, working with SMS messages, synchronization with the contact book.), as well as displaying information about trips with calculation of average fuel consumption. Using the Touch 2 center is quite convenient - in addition to the 6.1-inch resistive touch screen, there are also several large physical keys located on the sides of the display to control the system. The system menu itself is organized simply and does not feature overly deep catalogs, in which you can get lost if you are unaccustomed to it, as, for example, in the system of BMW cars.
Automobile accidents claim millions of lives every year. The shocking figure is directly related to the number of cars in the world, which has already reached some astronomical levels. That is why engineers, when developing modern cars, place the safety of the driver and passengers at the forefront. One of the latest inventions of modern engineers today is the integrated vsm system. In fact, this is exactly what will help the driver even in the most difficult and extreme road situations with the help of active vehicle control.
However, you can understand its principle of operation only by understanding the operating principles of the most famous security systems, which are familiar to many today.
Main goals
The vsm control system, according to the developers, is capable of performing at least 5 important tasks, including:
- Significantly facilitates steering column movement when parking or maneuvering at very slow speeds.
- The steering torque at high speed is significantly increased thanks to the system.
- The reactive force of the wheels increases at the moment when they return to the middle position.
- The system adjusts the position of the front wheels when driving on a slope, if there is a crosswind or if the tire pressure varies.
- Exchange rate stability is significantly improved.
Thus, it turns out that most often vsm at the time of its operation refers to the electric power steering and through it has a significant impact on the behavior of the car and the operation of all safety systems. That is, in fact, vsm combines the impact of car safety services on the steering wheel and brakes.
In practice, the system proves its relevance and necessity at the moment of sudden acceleration or braking. Especially in situations where one of the wheels is in unsatisfactory driving conditions in water or, for example, stands on an uneven surface, and the other, opposite, is on dry and smooth asphalt. In this situation, the car can easily begin to pull to the side and an uncontrolled skid is possible. It is at this moment that vsm intervenes, which does everything to keep the car on the road and prevent it from skidding.
In practice, the system's operation is completely invisible. Only experienced drivers will be able to see or feel it in action. Beginners will most likely ignore the actions of the invisible assistant and will only feel the difference when they change to another car.
Every day the road may present new challenges, but you will always maintain control of the car on difficult surfaces, hills, winding roads and unexpected maneuvers of other drivers thanks to the advanced electronic control system.
Feel completely protected in the Sorento Prime. The rigid power structure of the body is created using high-strength steels, and six airbags are included as standard equipment. The highest level of safety is confirmed not only by laboratory crash tests, but also by simulations of real collisions.
360° surround function
The system makes parking and maneuvering in tight spaces easier. Thanks to four cameras, the display shows a view of the car from above, which helps the driver check the situation from his own angle in any direction while parking or making maneuvers.
※ Operating conditions: ignition on, transmission lever in D/R/N positions, speed up to 20 km/h.
ESC (Exchange Stability Control)
controls the speed and direction of the vehicle.
At the same time, the system constantly compares the received parameters from the sensors (ABS sensor, yaw rate, acceleration, steering wheel turn) with the actions of the driver and works out the loss of vehicle traction, due to which a skid may occur.
When the system (ESC) detects a loss of control, it instantly applies individual braking force to each wheel.
Anti-lock braking system (ABS)
ensures that when braking there is no loss of friction between the car's wheels and the road surface. When a driver suddenly presses the brake pedal, there is a chance that the car will spin out of control and skid down the road. The main task of the anti-lock braking system is to prevent such a situation from occurring.
Lift Assist System
needed in cases where the car starts to move on an uneven road. The system ensures that the machine does not roll back on steep inclines and has a number of significant advantages. Firstly, with its help, a car on an uphill slope is more willing to move away, which relieves the driver of the need to use the parking brake. Secondly, the safety of both the driver and pedestrians is increased.
How the system works
This is - when the driver stops pressing the brake pedal, the decrease in pressure in the brake system begins to gradually slow down. The hill assist system will come into action when several factors coincide: the road rise exceeds 5%, the car is started, and the driver presses the brake pedal.
The KIA Sorento Prime is equipped with front and side airbags that protect the driver and front passenger, as well as two curtain airbags that protect everyone in the cabin.
Emergency braking system
I am needed so that in a dangerous situation on the road the car’s braking mechanism operates with maximum efficiency. According to statistics, when the emergency braking system is in operation, the braking distance is reduced by 15-20%. This is sometimes enough to avoid a serious collision, accident or accident.
System
BAS - based on the speed at which the driver presses the brake pedal, determines whether an emergency braking situation has arisen on the road. Data on the speed of pressing the pedal is transmitted to the electronic control unit from the speed sensor of the vacuum booster rod. In the event that the signal value goes beyond the set norm level, the rod drive electromagnet is activated. The vacuum brake booster begins to act on the brake pedal - this is how the emergency braking process starts. It takes effect earlier than the ABS system.
Emergency Belt Pretensioner (EFD)
The seat belts on the front seats of the KIA Sorento Prime are equipped with special EFD pretensioners. In an emergency, the seat belts are pre-tensioned, keeping the driver and front passenger firmly in their seats, providing additional protection in the event of a collision.
Emergency communication system ERA-GLONASS
In unexpected cases, the system will connect you with an operator to clarify whether everything is in order, or call emergency services.
LED headlights with dynamic low beam function
The headlights can additionally illuminate corners, providing better visibility at night. In addition, the rotating optics adapt to the steering angle, weight and speed of the vehicle.
In active head restraints
a special movable lever is built in, which is located in the back of the chair. When the car hits an obstacle, the inertia forces the driver into the seat and his weight presses on this lever. In this case, the counteraction mechanism immediately begins to work - even before the driver’s head tilts back, the active head restraints move towards it and soften the force of the impact. After this, they return to their original position. It is worth noting that for the most effective operation, the head restraints must be pre-adjusted.
Active head restraints are activated when the car encounters an obstacle at low or medium speed, and also in some cases of a rear-end collision. It is in these situations that the likelihood of injury increases due to the “whiplash” effect.
Integrated Active Management System (VSM)
Helps the vehicle maintain a stable position while braking and cornering, especially on wet, slippery or uneven surfaces, by working together with the stability control system and the electric power steering. Based on the information collected by the sensors, the stability control system and the electric power steering take effect as soon as the vehicle starts to move. sliding and return it to a safe trajectory.
High Strength Steel (AHSS)
The KIA Sorento Prime uses more than 52.7% high-strength steel in its construction. This unique grade of steel is used to strengthen the front, rear and sides of the vehicle, as well as in areas of the body that experience maximum stress.
Rear subframe
A rigid rear subframe ensures high road stability.
Vertical rear shock absorbers
The vertical arrangement of the rear shock absorbers helps smooth out the negative effect of driving on uneven roads and provides even greater comfort in the cabin.
Intelligent automatic parking system SPAS
This system is designed to help you with both parallel and perpendicular parking. It automatically recognizes a suitable parking space, turns the steering wheel and estimates the distance to other cars. All you have to do is step on the gas, brake, and shift your Sorento Prime.
Blind Spot Monitoring (BSD)
Blind Spot Monitoring uses sensors that scan the sides and rear of the vehicle for dangerous proximity to other vehicles in the blind spot zone. If an object is detected, the driver will be notified by a visual signal on the side mirrors and the central display. If the driver turns on the turn signal and another vehicle is detected in the blind spot on that side, a warning sound will sound.
One of the main problems facing automakers is increasing vehicle safety, including while driving. To achieve this, cars are equipped with various devices that help the driver cope with control in the most difficult situations. One of them is the integrated active control system VSM.
How does AWD work?
A typical All-wheel drive operating scenario is as follows. Imagine that you are driving along a normal road, even with bumps and puddles, but still far from off-road. It is clear that in such conditions all-wheel drive is useless, because it causes increased fuel consumption. Front-wheel drive is quite sufficient - it is both economical and provides good handling.
It's a different story when you pull onto a dirt road, especially if it's recently rained and the dirt has turned to mud. On two driving wheels you can thoroughly “sit down” in some hole or puddle. Therefore, the AWD on-board computer automatically connects the rear wheels, transferring part of the engine power to them. The car becomes all-wheel drive. But here there are some differences from traditional all-wheel drive vehicles.
Traditional all-wheel drive technology, 4WD, typically distributes power equally between the axles and wheels. In the case of AWD, the front axle almost always gets the most power, accounting for 60 to 90 percent of the engine's power and torque. Only a few manufacturers like Audi and Subaru provide the usual equal (50/50) distribution between the axles.
Another difference from 4WD is the absence of low gears and the possibility of differential locks. Many off-road enthusiasts do not like this lack of “adult” options, and their indignation is well founded. After all, a lower gear significantly increases the power supplied to the wheels, and differential locks prevent wheel slipping. Without these functions, attacking serious off-road conditions is quite reckless.
When driving off a paved road in an AWD vehicle, remember that the success of your trip depends mainly not on your driving skills, but on the quality of the on-board computer program. Some manufacturers bring elements of traditional 4WD to All-wheel drive by providing manual control, but this is rare. In general, AWD is perfect for driving on light off-road conditions, but not in remote, deep swamps.
Working with What-if Scenarios
There are many ways to identify and handle problems with your value stream. Many Lean experts will start with current state data and look for hot spots, bottlenecks, or problems that can be easily solved. This method tends to achieve some quick wins and prioritizes the process accordingly.
Others will start from the end. For example, starting from a goal state, if they know they need to have takt time below a certain threshold, they will start there and work their way back from the goal state to the current state, compressing the process until they reach their goal.
Taking a look at an example of the current state of VSM, shown below in Figure 3, we can see that there are a number of hot spots that can be addressed with the VSM team to make improvements. Here are some examples:
Figure 3
Example #1 : Notice that in the Information Flow section, the U/I development and development teams use SharePoint, while Excel is used by the test and build teams.
Possible Solution: After discussion, the VSM team decides that a unified communication solution will increase the speed of product transition from one team to another and increase visibility into the product pipeline. Note that isolated information silos (unintegrated information storage and processing facilities) such as those shown here can cause process inefficiencies, promote bottlenecks, and contribute to poor communication between teams and specialists.
Example No. 2. In the Time Ladder section, we see that each request to add a new feature to the software will take an average of three days to process before it is processed by the U/I development team. This has already created a backlog of 18 requests that are ready and waiting to be worked on. This would be a great place to start process improvement discussions with the VSM team.
Possible Solution: The VSM team decides they can temporarily reassign one of their team members to help overcome the accumulated three-day backlog to help catch up. This temporary assignment can be reapplied as needed if someone on the U/I team is unavailable for work.
Example #3: In the Product Flow section, we see that the testing team spends an average of 45 minutes in test preparation for each feature tested and has a backlog of 12 features that need to be tested. During the VSM team's discussion, it turns out that this is caused by the need to manually reconfigure the test environment each time.
Possible solution: The VSM team discusses this and decides that an automated solution for managing test environments will solve this problem and also help reduce the two-day lag shown in the time slot between the development team and the testing team.
Finally, the VSM team develops a future state VSM, shown in Figure 4, and determines that by implementing these three changes, production lead time is reduced from 12.5 days to 8 days, which is within the desired range.
Figure 4
Algorithm for VSM operation on Hyundai Creta
Activation of this complex on the SUV occurs automatically when the following conditions occur:
- The driver of the Creta drives along a winding road at a speed of over 15 km/h;
- The dynamic stabilization complex – ESC is activated;
- When braking on uneven surfaces, the Creta's speed exceeds 20 km/h.
However, it is worth remembering cases when the VSM system will not work:
- Driving in reverse;
- Moving with the ESC complex turned off - in this case the ESC OFF indicator lights up;
- During descent or ascent;
- If the electric power steering indicator light comes on or flashes - EPS.
It is also necessary to take into account that during the operation of the VSM complex a specific sound may be heard. The brake pedal is also pulsating. These are signs of correct operation of the system and do not indicate a malfunction.
The benefits of the VSM complex are obvious.
Kia Optima: VSM (Vehicle Stability Management) - Driving
This system further improves vehicle stability and steering response. when the vehicle is moving on a slippery road or the vehicle has detected changes in the coefficient of friction between the right and left wheels when braking.
VSM operation
When VSM is running, the ESC indicator light () flashes.
When vehicle stability control is working properly, you may feel a slight pulsation in the vehicle and/or abnormal steering (EPS) response. This is only an effect of the brake and EPS steering and does not indicate anything unusual.
VSM does not work when:
- Driving on the side of the road, such as on a slope or slope
- Moving backwards
- The ESC OFF () indicator light remains on the instrument cluster
- The EPS warning light remains on the instrument cluster
VSM disabled
If you press the ESC OFF button to turn off the ESC, the VSM will also cancel and the ESC OFF () indicator will light up.
To turn on VSM, press the button again. The ESC OFF indicator is on. out.
Fault indicator
VSM can be disabled even if you do not cancel the VSM operation by pressing the ESC OFF button. Indicates that a malfunction has been detected somewhere in the electric power steering system or VSM system. If the ESC indicator () or EPS warning light remains illuminated, take your vehicle to an authorized Kia dealer and have the system checked.
✽ NOTICE
- VSM is designed to operate at speeds greater than 15 km/h (9 mph) on curves.
- VSM is designed to operate at speeds above 30 km/h (18 mph) when the vehicle is braking on a split road. A split road consists of surfaces that have different friction forces.
WARNING
- Vehicle Stability Control does not replace safe driving practices, but is only an auxiliary function. It is the driver's responsibility to always check the speed and distance of the vehicle in front. Always hold the steering wheel firmly while driving.
- Your vehicle is designed to activate as intended by drivers, even with VSM installed. Always use all normal driving precautions. at a safe speed for conditions such as driving in inclement weather and on slippery roads.
- Driving with tires or wheels of a different size may cause the VSM system to malfunction. When replacing tires, make sure they are the same size as your original tires.
HAC (Help Assist Control)
Hill start assist is a comfort feature. The main purpose is to prevent the vehicle from rolling back when driving uphill on an inclined surface. HAC keeps brake pressure bu...
Good braking practice
WARNING Always set the parking brake whenever you leave or park your vehicle. As far as possible and fully engage the vehicle's transmission in the P (park) position. If the parking brake...
See also:
Inspection 1. Check points for headlight failure (HID) (1) Check the battery voltage. (The low beam will be turned on when the battery voltage is above 9V.) (2) ...
Component and Component Locations Component Locations 1. Windshield Defroster Relay (built-in relay box in engine compartment) 2. Windshield Defroster Switch 3. Windshield Defroster. 4. Deicer connector...
Installation 1. Installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal. When installing, apply ATF or white Vaseline...
,
How does ASR work?
As mentioned above, ASR is a variant of ABS with enhanced functionality. Therefore, in addition to the sensors, modulators and control unit, which are the main components of the anti-lock braking system, it also includes:
- Return pump;
- Solenoid valves;
- Signal generation module for engine control unit.
The return pump is used to create additional pressure in the brake system, and when it is turned on, it begins to function as the brake master cylinder. Solenoid valves are responsible for connecting this pump and, when the moment comes, releasing the excess pressure. As for the signal generation module for the engine control unit, its purpose is quite clear from the name itself. It is used in cases where ASR operates in the power unit torque reduction mode.
The design of modern traction control systems provides a function of informing about their operation: at this moment, a special light comes on in the car interior, on the dashboard. It should be noted that drivers have the opportunity to disable the ASR installed in their vehicles, however, experts do not recommend doing so, since this traction control system does provide increased safety and its use in cars has a number of important advantages.
Stability control (ESP, DSC, ESC, VSC)
The exchange rate stability system (another name is the dynamic stabilization system ) is designed to maintain vehicle stability and controllability by identifying and eliminating a critical situation in advance.
Depending on the manufacturer, the system has the following names:
- Electronic Stability Program, ESP ;
- Electronic Stability Control, ESC ;
- Vehicle Stability Assist, VSA ;
- Vehicle Stability Control, VSC ;
- Vehicle Dynamic Control, VDC ;
- Dynamic Stability Control, DSC ;
- Dynamic Stability Management, DSM ;
- Dynamic Stability Traction Control, DTSC .
THIS IS INTERESTING: How to reset the Starline alarm to factory settings
The design and principle of operation of the exchange rate stability system are discussed using the example of the most common ESP system.
Stability control system
Stability control is a higher level of active safety system.
The ESP system includes the following systems:
- anti-lock braking system (ABS),
- brake force distribution system (EBD),
- electronic differential lock (EDS),
- anti-traction system (ASR).
The directional stability system has the following device:
- Control block;
- hydraulic block;
- wheel speed sensors;
- brake pressure sensor;
- acceleration sensor;
- rotation speed sensor;
- steering angle sensor.
Using sensors, the dynamic stabilization system evaluates the driver's actions and vehicle movement parameters.
How the stability control system works
The occurrence of an emergency is determined by comparing the driver’s actions and the vehicle’s movement parameters. If the driver's actions differ from the actual driving parameters of the vehicle, the ESP system is activated.
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the electronic stability system activates the relevant safety systems and controls their operation.
Source: https://www.infocar.ua/term_stability.html
Features of work
The active control system integrated into the car is a highly specialized unit. In practice, it is used relatively recently, and the device is found only on relatively new cars, naturally only on foreign cars - VAZ engineers have not yet invented anything like this. In fact, it only works as a set with the above security systems and coordinates their work. In addition, vsm can affect the electric steering column. As the developers say, this control system in an emergency can even block incorrect actions by the driver. In practice, it looks like this: if the driver starts turning the steering wheel in the wrong direction. At that very moment of maneuver, significant efforts will be required from him than during normal driving.
The difference will be felt immediately and sharply, so that the driver’s attention is guaranteed.
Precautionary measures
The presence of a mass of electronic systems in a car can also play a cruel joke on the owner. The negative side is that the owner of the Creta begins to rely too much on electronics, neglecting safety precautions while driving.
IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER
– electronic systems
are NOT an
unconditional guarantee of safety.
However, you definitely shouldn’t rely on electronics alone.
This means that the presence of the VSM complex in the SUV package does not mean that you can drive recklessly with impunity. The VSM system itself cannot prevent an accident. Therefore, it is always necessary to maintain a distance from the car driving in front and not exceed the speed allowed by the rules. This is especially true in bad weather, on uneven, wet or slippery roads.
Separately, it is worth noting the moment associated with the wheels of the Hyundai Creta. They should be the same. If the tires or wheels of the crossover are different in size, the VSM system may not work correctly. Therefore, driving with wheels of different sizes is highly not recommended, especially if we are talking about a long trip.
Over the past couple of decades, industry leaders in automotive design and manufacturing have been confronted with the serious problem of low driver readiness to operate a vehicle in high-risk environments. Many facts and police statistics say that the ability to drive a complex, heavy and powerful passenger car without killing yourself and others is no longer enough for the average driver.
The first, focused on a comprehensive solution to the problem, was the integrated active control system VSM. In essence, a new computer unit was combined with a system of sensors and control modules for anti-lock brakes and a directional stability system.
What functions are assigned to the integrated active control system VSM:
- obtaining from all available vehicle sensors the most reliable information about the current state of the vehicle;
- comparison of the objectivity of the ABS and ESP control commands with the tendencies of the driver’s actions and comparing them with the optimal possible options stored in memory;
- indirect VSM intervention in the operation of the steering wheel, engine, brake system and gearbox.
Important! VSM differs from many intelligent assistant options in that it helps the driver act beyond information or recommendations.
Is it possible to fully automate the control system?
Sometimes it is easier and much cheaper to teach the necessary skills to a system that already exists than to purchase a new one. The specialist who will manage the inventory must submit timely reports on reserves. Moreover, there are always several classes:
- the main one is both the worker and the one who remains in case of delays and sales growth;
- temporary - one who rises or falls during the season, defects and illiquid products.
This will have to be monitored taking into account all changes
It is important to be able to analyze multiple factors. In addition, the unstable volume cannot be predicted; here the expert will have to work based on his experience and instinct
As for the defective product, it is necessary to take action against it and find out the reasons for its occurrence, as well as assess the scale of the disaster.
Who benefits from using VSM?
The value stream mapping exercise can be used to achieve a variety of goals. For example, it can solve tactical problems when applied at the practitioner/specialist level. On the other hand, it can generate high-level strategic understanding when VSM is applied by management.
When creating a map, it is important to know from the beginning what your main goals are and who needs to be present during the mapping sessions to achieve the desired outcome. If the goal is strategic change, the session should include people with the appropriate authority who can directly influence the flow and make the necessary strategic changes. Likewise, if your goal is more mundane, you will need appropriate team members who can execute these types of tactical changes.
While there are a number of benefits that will be perceived by team members, stakeholders, executives and even shareholders, the real benefit from VSM is the end customer. He will receive a better product that will be delivered faster and will better meet his needs and expectations.
Problems that VSM solves
If we try to generalize what problems such an integrated system solves, we can note the following:
- Reducing steering effort when parking and maneuvering at low speeds;
- increase in steering wheel torque at high speed;
- an increase in the reactive force of the wheels when they return to the middle position;
- adjusting the position of the front wheels when driving on a road with a slope, side winds, or differences in tire pressure;
- increasing stability (course rate).
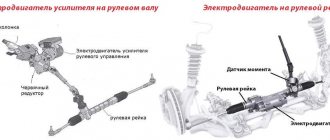
Thus, the VSM system is engaged in stabilizing the position of the car on the road while driving in the same way as ESP, ABS and other devices with similar purposes. The difference between them will be that VSM, through the electromechanical booster, acts on the steering wheel and not on the brakes
. In other words, the effect on the steering wheel and brakes is combined.
This is especially true when acceleration or braking occurs on different surfaces (one wheel on ice, water or other surface, the other on asphalt). As a rule, the car begins to pull to the side as a result. To correct the situation, control signals are sent to the steering mechanism, correcting the position of the car. In principle, the situation considered is typical for the operation of such a control system. The possibility of skidding may occur again during sharp maneuvering, in which case VSM will also help keep the car from skidding.
It should be noted that such a device is not included in the standard equipment of the car.
An active control system such as VSM primarily ensures vehicle stability on course when driving on different surfaces under different wheels. In this case, not only signals are generated to brake an individual wheel, but also to the steering, thanks to which the car continues to move along a given course and it is possible to avoid skidding.
The author is kind, but I can also be evil!
asked a question in the section Choosing a car, motorcycle
What is an integrated active control system in a car and is it worth overpaying for it when buying a car? and got the best answer
Answer from F Vehicle Dynamics Integrated Management (VDIM) VDIM is an electronic vehicle stability control system that integrates all known active safety systems, power steering and engine management. Having complete information about the current state obtained from sensors located throughout the vehicle, VDIM not only optimizes the operation of the anti-lock brake system, brake force distribution system, anti-skid and traction control systems, but also improves the basic dynamic characteristics of the vehicle. VDIM simultaneously controls the powertrain, transmission and braking system according to driving conditions, and also stabilizes the vehicle's behavior on low-traction road surfaces. The new Dynamics Control system is less intrusive than conventional stability control systems, but is much more effective: while conventional safety systems are activated just after the vehicle's performance limit has been reached, VDIM is activated long before this point occurs. As a result, the scope of operation of active safety systems is expanded, and due to this, softer and more predictable vehicle behavior is ensured, since these systems operate more accurately, more gently and flexibly
Reading time: 4 minutes.
integrated active control system vsm. The article describes the main purpose of the system, the principles of its operation and interaction with other car security services.
Automobile accidents claim millions of lives every year. The shocking figure is directly related to the number of cars in the world, which has already reached some astronomical levels. That is why engineers, when developing modern cars, place the safety of the driver and passengers at the forefront. One of the latest inventions of modern engineers today is the integrated vsm system. In fact, this is exactly what will help the driver even in the most difficult and extreme road situations with the help of active vehicle control.
However, you can understand its principle of operation only by understanding the operating principles of the most famous security systems, which are familiar to many today.
About forces and moments
The torque developed by the motor goes to the wheels, and the car begins to move. This is a very simplified way to describe the process of moving it. However, when starting to move, maneuvering and braking, a wide variety of forces act on the car, and the nature of their influence depends on the speed, road condition and driver actions.
Sometimes these actions are erroneous and incorrect, which can result in an accident. To avoid this, developers have come up with more than one electronic device that assists the driver in difficult conditions. Without touching on them all, it is enough to mention the most famous and well-known ones:
- ABS – anti-lock braking system;
- ESP - exchange rate stability system (different manufacturers have different names - ESC, DSC, DTSC, etc. In the following text the most common abbreviation ESP will be used);
- TCP - traction control system.
The operation of any of these active control devices is based on constant monitoring of signals from sensors. Based on them, the controller determines the discrepancy between the actual driving mode of the car and what it should be, and it also takes the necessary measures, for example, it reduces the speed, slows down or unlocks the wheel, and changes the engine operating mode.
ECO PRO mode
When ECO PRO mode is selected, the driving dynamics control switch is located on the control panel of the center console.
ECO PRO mode provides a fuel-optimized driving style. Nevertheless, there is enough driving dynamics. The driver's driving behavior with optimized fuel consumption is supported primarily by the display (see operating instructions). Intelligent power management and the air conditioning system form the basis for ECO PRO mode. In practice, consumption reductions of up to 10% can be achieved.
ECO PRO consists of four 4 components:
- Quiet ride
This selects a different characteristic curve for the accelerator pedal and selects different shift points for the automatic transmission. For manual transmissions, a different shift point indicator is installed. If the automatic engine start/stop system is deactivated, activating the ECO PRO mode reactivates the automatic engine start/stop system.
- Adjusting the air conditioning system
The air conditioning system is configured more efficiently. The air conditioning system performs reduced air drying and reduced air cooling. The load on the refrigerant circuit is reduced. Thus, less mechanical drive power is required. Refusal to operate an internal combustion engine with increased heat transfer. The PTC auxiliary heater (diesel engine) operates with less heating power. The air conditioning compressor turns off if the required temperature can be reached even without creating cold. Increases accessibility for the automatic engine starting and stopping system. In this case, you may have to give up some comfort functions.
The car saves these settings for later recall of ECO PRO mode
- Reducing the number of electrical consumers
The heated exterior mirrors are turned off (saving up to 100 W). The maximum seat heating temperature does not exceed approx. 37.5 °C (otherwise approx. 42 °C). The power of the rear window heating is also limited.
- Display in the instrument cluster and additionally on the central information display
Display example
| Designation | Explanation | Designation | Explanation |
| 1 | Increased range | 2 | Charging the battery |
| 3 | Switch point indicator | 4 | ECO PRO mode |
| 5 | Tips for ECO PRO in the central information display |
Upgrading the ECO PRO module implements additional functions:
Hierarchy in Value Stream Maps
The VSM map is generated based on a standard template. But, like any process modeling diagram, it can be detailed. This creates a hierarchy of steps inside the map, where you can use drop-down/collapse descriptions of processes without having to flicker all the objects on one field at once. In addition, detailing is convenient for identifying objects of greater or lesser significance, removing into the layers of detailed diagrams those “little things” that should not distract from assessing the overall picture of the process.
Let’s add an “Assembly” object and enter its properties by double-clicking on it. When selecting the data mode - “Rollup Data”. Well, or in simple terms - “with detail”.
Now we have the opportunity to create other VSM cards within the existing one, or even create a new one.
Click on “New” and get a dialog where, as the name of the card, enter “VSM Assemblies” and click “OK”. The new map's timeline properties will be set to their default values. Click “OK” on the properties dialog and we see that the “Assembly” object now has a shadow - a sign that it has its own detail map.
ground level sensor;
Depending on the optional equipment, a maximum of 4 ride height sensors are connected to the ignition control unit (2 on the front axle, 2 on the rear axle). On vehicles with EHC, the rear sensors have 2 channels: 1 connection to the ICM ECU and 1 connection to the EHC ECU.
The two-channel ride height sensor has not been installed since 09/2010 (bus message from the ICM control unit).
The ride height sensor is a non-contact sensor. The ride height sensor converts the distance traveled proportionally through the steering angle into an analogue voltage signal. The sensor can rotate around its own axis by 360°. The measuring range is 70° (depending on installation position, see also characteristic curve). The signals are analog voltage signals.