It’s probably no secret that motor oil plays a key role in the overall configuration of an internal combustion engine. The main function of the lubrication system and the fluid itself is to prevent dry friction of the contacting surfaces of various engine elements, eliminate waste products and contaminants, and cool parts.
Some components of the power unit are approached by oil under pressure, others are lubricated by splashing, and some engine components are even treated only due to the natural flow of liquid onto them.
The difference between a dry sump and a wet sump
The most popular is the wet sump lubrication system - in which the oil is constantly stored in a special sump. When the engine is running, the oil pump collects lubricant from the sump and supplies it under pressure to the appropriate channels.
This solution is considered quite reliable and has been tested for decades. But this system is not without its drawbacks and often simply does not cope with its functions in some conditions. It is in such situations that a dry sump comes to the rescue, the operating principle of which is slightly different from a wet unit.
This lubrication system is most often installed on racing cars, but is sometimes found on SUVs, agricultural machinery and sports cars. Among other things, today a dry sump can often be found even on motorcycles.
Engineering is not for everyone
What is the main purpose of a dry sump system?
By and large, it was invented in order to ensure an uninterrupted supply of oil to the power unit even in the most extreme conditions. For ordinary city cars driving no faster than 80 km/h on a flat surface, such a system is not needed; a classic wet one is sufficient.
A dry sump can be useful on vehicles used in less than ordinary conditions. In addition to real SUVs and all kinds of all-terrain vehicles that overcome various obstacles, it is often found in sports and racing cars, which, although they do not jump over bumps, due to high overloads, oil also actively splashes around their engine.
Purpose
So, a dry sump is one of the types of lubrication system of an internal combustion engine. Its popularity among sports and racing cars is explained very simply. When passing dangerous turns, intensive braking and acceleration, as well as on rapid descents and ascents, the car tilts, swaying longitudinally and transversely. At this time, the oil in the sump of a conventional wet sump splashes heavily throughout the entire system.
As a result, the fluid foams, the oil pump cannot take in the sloshing oil, which is why the engine does not receive the lubrication it needs. In this case, the pressure suddenly decreases, and the motor itself is subject to significant wear. It’s easy to guess that as a result, not only the engine’s service life is significantly reduced, but there is also a risk of it jamming, breaking and overheating.
But the operating principle of a dry sump implies a different device - the oil is not located inside it, but in a special tank. Thanks to this solution, the possibility of foaming of the liquid is eliminated. A pressure pump supplies lubricant to the parts rubbing inside the engine. Moreover, the liquid flowing into the pan is immediately pumped back into the tank using the appropriate pump. Thanks to this, oil does not accumulate in the pan, that is, it remains dry. This is how this system got its name.
For every “plus” there is a “minus”: do you need it?
Why not install a similar lubrication system on all cars? Indeed, the dry sump operating principle of which we are considering today has quite a few advantages.
In addition to the main advantage - uninterrupted oil supply under any conditions, there are several more. For example, in our case, large crankcases are not needed, so the engine can be made more compact.
Also, due to the fact that more lubricant circulates through the power unit, it is cooled better, which also has a good effect on its operation.
As always, there are several “BUTs” that have made dry sump the privilege of only select cars.
Firstly, the complexity of the design. Despite the fact that the engine itself can be made more compact, additional components appear around it (oil tank, radiators), due to which, in fact, the weight gain is not so noticeable. All this affects the cost and requires additional maintenance.
Secondly, such designs require more oil, and this is also an additional expense.
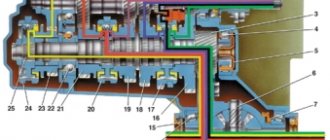
Dry sump engine design
The system is equipped with several main elements:
- Special tank for oil.
- Oil radiator.
- Pressure oil circuit.
- Lubricant pressure sensor.
- Thermostat.
- Bypass and pressure reducing valves.
- Bleeding pump.
- Temperature sensor.
- Oil filter.
The difference between two-stroke and four-stroke engines
To understand how the crankcases in two-stroke and four-stroke engines differ, you need to remember the differences between the units themselves.
In a two-stroke internal combustion engine, part of the body plays the role of an element of the fuel system. Inside it, air is mixed with fuel and supplied to the cylinders. In such a unit there is no separate crankcase that would have an oil pan. Engine oil is added to the fuel to provide lubrication.
A four-stroke engine has more parts that need lubrication. Moreover, most of them do not come into contact with fuel. For this reason, lubricant must be supplied in larger quantities.
Oil tank
The reservoir used in a dry sump system can have different shapes. Inside the tank is equipped with special partitions that prevent vibrations and foaming of the oil when the car is rocking.
In addition, the tank is equipped with ventilation. It is necessary to eliminate gases and air from the tank that get inside along with the lubricant from the pan.
In addition, the tank contains thermostats, pressure sensors and a dipstick for checking the fluid level. The tank itself is compact, which allows it to be installed in any suitable location.
By choosing the optimal zone, you can also successfully distribute weight, which is extremely important for racing cars in terms of handling. Also, the operating principle of a dry sump allows the tank to be placed in such a way as to improve its cooling and reduce the temperature of the lubricant.
Purpose of the crankcase gas exhaust system
When the air-fuel mixture burns, enormous pressure is created in the cylinder. Therefore, even on a working engine, some of the exhaust gases inevitably break through the piston rings into the crankcase. Also, diesel fuel and gasoline vapors enter the sump from the combustion chamber through the rings on the compression stroke and during incomplete combustion of the fuel injection pump.
During operation, a mixture of oil vapor, gasoline, exhaust gases and water vapor creates increased pressure in the crankcase space. If you do not remove this explosive mixture, the pressure will not only interfere with the removal of oil from the cylinder walls, but will also squeeze out the crankshaft and camshaft seals.
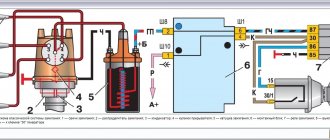
Pumps
The injection pump supplies oil to the system under pressure. In this case, the liquid passes through the oil filter. The pump is most often located just below the oil reservoir, which makes it possible to build the necessary pressure. By the way, bypass and pressure relief valves are responsible for its adjustment in a dry sump system.
The scavenge pump works by moving the oil trapped in the sump back into the oil reservoir. Its performance is much higher compared to a pressure pump. The design includes several sections, depending on the characteristics of the motor.
If the internal combustion engine is highly forced, there is one pump section in each crankcase fragment. V-shaped engines are also equipped with an additional section necessary for pumping out the oil supplied to the gas distribution element. The turbocharged engine is equipped with the same system to pump out the lubricant that processes the turbocharger.
Both the pumping and pumping pumps are of the gear type. They are located in the same housing and also have a common drive from the crankshaft. Systems with a camshaft are slightly less common. The drive can be either belt or chain.
The Importance of Lubrication
For any engine, good lubrication of all parts is critical. To do this, very efficient pumps are installed in the engines, whose task is to ensure oil circulation in the unit. This pump is located in the engine sump or crankcase; through a filter element, it takes oil from below and delivers it upward through the oil channels. If some kind of failure occurs in this process, for example, due to clogged oil channels, then this ends in overheating of the rubbing parts and even their jamming.
Oil radiator
In an internal combustion engine with a dry sump, this spare part is represented by a liquid cooling radiator. The part is located between the motor and the injection pump. There are also other options when the radiator is located between the sump pump and the tank.
Forced internal combustion engines can be equipped with additional oil radiators, which are air-cooling elements. This radiator is connected to the system via a thermostat.
Pros and cons of this lubrication system.
Pros:
1) The dry sump system allows for stable oil pressure under all vehicle driving conditions.
2) More efficient oil cooling.
3) Engine power is slightly higher.
4) A dry sump minimizes oil contact with exhaust crankcase gases. As a result, the oil does not oxidize and age as quickly.
Let's move on to the cons:
1) Maintenance of such a system is more expensive.
2) Availability of a number of additional elements leads to weight gain.
3) Such a system needs to be filled with more oil by volume.
Sources
- https://KrutiMotor.ru/sistema-smazki-dvigatelya-s-suhim-karterom-ustrojstvo/
- https://voditelauto.ru/sistema-smazki-s-suhim-karterom/
- https://auto-ru.ru/suhoj-karter.html
- https://auto-self.ru/sistema-smazki-s-suhim-karterom/
- https://labuda.blog/202455.html
- https://www.DriveNN.ru/journal/novosti/chto-takoe-dvigatel-s-suhim-karterom-i-gde-ego-ustanavlivayut-id31817
- https://7gear.ru/tuning/suhoj-karter.html
- https://EuroAutoUfa.ru/obsluzhivanie/sistema-smazki-s-suhim-karterom.html
- https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5d415450ddfef6219b4d8316/sistema-smazki-s-suhim-karterom-5d41dd36a2d6ed00ad6e5bd4
Advantages
As already mentioned, the operating principle of a dry sump makes it possible to achieve stable lubricant pressure under any circumstances and driving conditions of the machine. In addition, this system allows you to effectively cool the oil, which is extremely important for forced internal combustion engines, which are very sensitive to fluid temperature.
Regarding the specific configuration, the dry sump motor has a small sump, which significantly reduces the overall dimensions of the power unit. Thanks to this, such an engine can be mounted a little lower, moving the center of gravity and increasing the stability of the car. In addition, due to this, the aerodynamic properties also change positively, since the bottom of such cars is flatter.
By the way, this is why all modern motorcycles with forced engines are equipped with a dry sump. After all, it allows you to compactly place the lubrication system without compromising the technical characteristics of the device. So a dry sump for a motorcycle today is not a whim, but a necessity. At least for those that are designed for fast driving and have powerful forced internal combustion engines. It is this system that is presented in the most popular models: Honda Moto, Buell, EBR, KTM, BMW and other sports models.
The power of a dry sump motor is also slightly higher than that of its classic counterparts. Such engines start and spin up more easily, since the crankshaft does not have to rotate in oil and fight its resistance. In addition, it does not splash the liquid, due to which the oil density increases, it does not foam and, as a result, is consumed less.
Another advantage of a dry sump is the fact that it minimizes contact of the lubricant with the exhaust gases. Thanks to this, the oil oxidizes and ages more slowly. In addition, deposits and contaminants do not accumulate in the pan, due to which the lubrication system of the internal combustion engine remains cleaner for a long time.
The oil circuits are located outside the engine. This makes it possible, if necessary, to identify the cause of the breakdown much faster and repair the motor, without disassembling it. So we can say that dry sump lubrication systems are more reliable and easier to use.
Varieties
Engine sump protection Is engine sump protection necessary?
All crankcases that cars are equipped with can be divided into two categories depending on which power unit they are installed on.
Therefore, it is customary to separately consider designs for:
- two-stroke internal combustion engines;
- four-stroke power plants.
The difference in crankcase design is due to differences in the design of the internal combustion engines themselves. Pallets are either detachable or non-detachable. Often the pan acts as an integral element of the crankcase, and does not simply serve to collect lubricating oil.
Two-stroke engines
The peculiarity of F. Carter's invention for a two-stroke engine is that the crankcase and the motor are one whole. This is an integral element of the housing and one of the components of the power supply system of the power unit.
It is inside the crankcase that the process of preparing the air-fuel mixture takes place. After this, the mixture moves into the cylinders of the power unit. This is one of the differences in comparison with the four-stroke analogue.
Also, two-stroke engines differ in that here the oil comes into direct contact with the fuel. When preparing a mixture for cylinders, the crankcase allows you to power the engine, and also simultaneously lubricate the elements of the cylinder-piston group.
Two-stroke diesel engine
This design of the system leads to the fact that fuel and lubricating oil are mixed inside the power unit. This explains the increased smokiness and darker color of the smoke produced and exiting through the exhaust pipe. The exhaust has a bluish tint, which is a characteristic feature of motor vehicles. It is there that two-stroke engines continue to be used, unlike cars.
On two-stroke engines, the service life of spark plugs is significantly lower compared to a four-stroke competitor. Two-stroke internal combustion engines are practically no longer found on cars, and motorcycle manufacturers are also abandoning them.
Crankcase and four-stroke engine
In the case of four-stroke engines, the crankcase plays a secondary or auxiliary role. Most often, the crankcase is needed only as a container for collecting oil, nothing more.
It is not difficult to explain this decision. Modern four-stroke engines do not welcome oil entering the cylinders. Therefore, their exhaust has less smoke and a lighter color. The exhaust composition is cleaner and more environmentally friendly.
An important component of a four-stroke engine in terms of exhaust gas purification is the catalyst. Now it is installed on almost all modern cars with internal combustion engines.
Location and purpose
Having understood what a car crankcase is, you can pay a little attention to the issues of its placement and functionality. Let's start with where exactly the power plant crankcases are located.
They are located in the same place as the engine itself, since they are its integral and integral part.
Let's start with where exactly the crankcases of the power plants are located. They are located in the same place as the engine itself, since they are its integral and integral part.
The crankcase acts as the space between the sump and the engine crankshaft. It is inside this space that the crank mechanism is located and carries out its movement. In fact, such an element as the engine sump is located in the engine. That is, the question of where it is is not entirely correct.
Since the crankcase has a container (pan) located to collect oil, very often both elements are described by the same concept. But in reality, the pallet is an integral part of the structure in question.
Mounting the engine to the frame
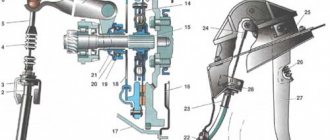
Despite the good balance of modern car engines, vibrations still occur during their operation, which should not be transmitted to the frame. Therefore, the engine mount (suspension) must be such as to reduce the transmission of vibrations to the car frame and prevent the appearance of stress in the cylinder block when the frame is distorted due to the car moving on an uneven road. Engines are attached to frames or semi-frames at three, four and five points.
The engine of the GAZ-24 Volga car is mounted at three points on rubber mounts. Two supports are located in the front of the cylinder block, on its sides, and one support is located at the rear, under the front of the transmission extension.
The ZIL-130 car engine is attached to the frame at three points: one support at the front and two at the rear (clutch housing feet). The engine of the GAZ-53A car is attached to the frame at four points: two supports in front and two in the back (flywheel housing and clutch feet). The KamAZ-5320 diesel engine is mounted at five points (Fig. 10): two front supports are installed on cylinder block 1 on its sides; two supports at the rear are reinforced on both sides of the flywheel housing 13; one support support is located on the gearbox housing 22.
The front supports consist of a bracket 4 connected to the cylinder block 1, and through a rubber cushion 7 and a coupler 6 - with a bracket 5. The latter is riveted to the rack 9, and the rack to the frame spar 10.
The rear supports consist of an engine bracket 12 mounted on the flywheel housing 13, and a rear support bracket 11 riveted to the frame spar 10. The bracket 11 with the cover 20 covers the shoe 16, installed between the brackets and connected by a bolt 15 to the bracket 12. The shoe is made of aluminum alloy and is located in a rubber cushion 14. Between the cover 20 and the bracket 11, adjusting shims 2L are placed. A steel sleeve 18, pressed into the shoe, prevents it from being crushed. .
The support support consists of a bracket 23 mounted on the gearbox housing 22. The bracket shelf is covered by a rectangular rubber cushion 27 located in the holder 25, connected through a lining 26 to a cross member 24. The latter is connected to brackets 28 riveted to the frame side members. Rubber cushions located under the supports reduce shock loads on the engine when driving
Flaws
As for the disadvantages, the dry sump system is considered more complex and expensive. The presence of many auxiliary parts leads to a natural increase in mass. In addition, more lubricant itself must be poured into such a system.
So internal combustion engines with such a lubrication system are several times more expensive, and the costs of their maintenance increase significantly, especially when it comes to repairing or replacing some elements. This is why a dry sump is not installed on most budget cars. After all, such machines, as a rule, are not intended for use in extreme conditions.
What is the dry sump system used for?
The dry sump lubrication method is used mainly on sports cars and specialized vehicles that have to operate under unusual conditions. The essence of this lubrication method is that the oil is not in the crankcase. Accordingly, it does not need to be pumped out from there with an oil pump.
The fact is that when the car is moving along a city highway, it is not difficult for the oil pump to pump oil out of the crankcase and circulate it to work. Whereas, for example, when driving off-road, on a slope, from a slope and in other difficult situations, this is much more difficult to do. Due to the inability to pump oil out of the crankcase with an oil pump, since it flows over the crankcase from side to side, there is a high risk of oil starvation of the engine, and at the same time associated problems - overheating, jamming, cracks in the cylinder block, and so on.