Timing valves are located directly in the combustion chamber and are designed for high temperature loads. However, if the normal operation of internal combustion engines is disrupted, even the heat-resistant material from which they are made is destroyed over time. How quickly the valves burn out depends on the nature of the problem. Typical signs that a valve in a cylinder has burned out are rough operation and difficulty starting the engine, as well as loss of power. However, these same symptoms can also occur with other problems. This article will help you understand what a “burnt valve” means, why this happened and learn about ways to diagnose the timing belt without removing the head.
How to understand that a valve has burned out: causes, signs and consequences
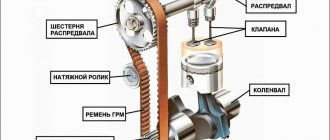
The valves of the gas distribution mechanism of automobile engines are used on four-stroke engines and are located in the cylinder head. Through them the working mixture is injected and exhaust gases are discharged. The valve plates have conical chamfers and are tightly ground to the seats, which is checked for leaks when assembling the motor. The slightest leak leads to gas leakage and loss of compression.
How to determine valve burnout
Exhaust valves usually burn out; when open, they are washed by a stream of hot exhaust gases, heating up to the point of loss of strength and rapid oxidation of the heat-resistant steel of their plates. In advanced cases, this is also accompanied by cracks in the metal.
The intake ones are rarely destroyed, since the amount of exhaust gases passing here is much smaller in volume, and moreover, a relatively cold flow of fresh mixture (air) passes through them in diesel engines and gasoline engines with direct fuel injection. This keeps the plates nicely cool in addition to dissipating heat through the socket.
From the point of view of the symptoms that appear after a burnout, there is no particular difference which valve has burned out. Compression, that is, the ability of the cylinder to compress the mixture before ignition, will disappear or decrease in any case.
Symptoms
Since valves rarely burn out simultaneously in all cylinders, the first sign will be “triple” of the engine. This term arose due to the predominant share of four-cylinder engines, when if one fails, the engine runs on the remaining three. This is what they began to call any cessation of ignition in the cylinder, regardless of their total number.
Compression, if it has not completely disappeared, is especially important at low speeds and during startup. In these modes, a burnt-out valve will manifest itself first. Removing the spark plug will show blackening of the insulator, and there may be a smell of gasoline if the engine ECU has not yet turned off the corresponding injector.
The summary list of symptoms is quite typical:
- misfire in one of the cylinders;
- rapid throwing of unburned hydrocarbons into the candle;
- shots are fired into the muffler, part of the fuel is thrown out to the outlet and ignites there;
- the smell of gasoline in the crankcase, unburned fuel flows down the cylinder walls and dissolves in the oil, after which it again passes through the ventilation and enriches the mixture in working cylinders;
- Compression drops dramatically, sometimes to zero.
It is the compression measurement that will give the signal to rebuild the engine. You should distinguish problems with piston rings from a burnt valve.
An additional check is usually carried out by pouring approximately 5 ml of engine oil through the spark plug hole. If the compression increases, the rings are to blame (so-called oil compression); if not, gases escape through the valves or a broken gasket, but you still have to remove the head, after which everything will become clear and visual.
The burnout of the valve is clearly visible from the condition of its chamfers.
Why do engine valves burn out (main reasons)
In normal mode, the valve remains in the seat for some time, being tightly pressed against the counter chamfer by the valve spring. At the same time, it is intensively cooled through the contact of the chamfer with the metal of the socket. The temperature difference here is large, so heat transfer occurs quickly.
The engine is calculated very accurately, so any reason for the valve plate temperature to increase will upset the balance of heat removal, and the average temperature will begin to rise. The metal will lose its properties, rapid oxidation and burnout will begin.
Detonation
Detonation occurs when abnormal combustion is activated by a spreading flame front. There are many reasons for this:
- poor anti-knock properties of gasoline (octane number is lower than that for which the engine is designed);
- compression ratio too high;
- over-poor mixture;
- high temperature in the combustion chamber;
- increased ignition timing.
During detonation, more energy is spent on impact destruction of parts and local overheating, which also applies to valves. The only question is which part will collapse first, after which the engine will stop.
Violation of the thermal gap
Valves, especially exhaust valves, become hotter during operation than the metal of a well-cooled cylinder head. Therefore, the geometric increase in their size due to thermal expansion requires compensation.
In engine designs, unwanted elongation of the valve stem is combated in two ways - by creating a thermal gap between the camshaft cam and the pusher, as well as by using various hydraulic compensators.
Thermal clearances require periodic adjustments using existing bolts or selecting the thickness of the pushers. If this operation has not been carried out for a long time, then due to the wear of the working chamfers of the plates and sockets, the gaps are reduced, the valve spends more and more time separated from the metal of the socket, where it should dump heat.
As the valve temperature rises, it lengthens even more. At some stage, the chamfers stop touching, the plates overheat and burn out. The compression disappears.
Why is there a problem?
The symptoms and signs of a burnt valve are very similar to other types of faults. Moreover, many drivers do not believe in this particular malfunction until the very end and waste time on unnecessary actions.
Valves perform an important function. They allow fuel to enter the combustion chamber. And they release the burnt gases after finishing their work. As is clear from the described valves, they are constantly in aggressive conditions. They are exposed to gases and high temperatures. This leads to the destruction of the metal that makes up the valve. Gradually it burns out.
This happens especially often with old cars whose valves were made of not very good materials. Also, many people make this problem themselves. They fill their car with fuel that is not intended for it. As a result, increased combustion temperature leads to damage to these elements of the cylinder head (cylinder head).
The main sign of burnt valves is engine tripping. That is, one or more cylinders are not working. With this malfunction, the tightness of the combustion chamber is compromised. A burnt-out valve allows gases to pass through during fuel combustion. As a result, they do not push the piston down, but simply go directly into the manifold. This causes one cylinder to miss.
The driver notices exactly this in the form of engine tripping. Another symptom of this problem is an increase in fuel consumption, which is not surprising, because part of it simply flies into the atmosphere.
Reasons for burning valves on a gasoline internal combustion engine
The main reason here is the deviation of the combustion mixture from the optimal mode. Both too lean and rich mixtures burn slowly. In any case, there will be an increase in the temperature of the valve disc with all the ensuing consequences.
With a lean mixture, the situation is aggravated by the presence of excess oxygen, which will create the same effect as with oxygen cutting of metals.
Gasoline that is too good, that is, with an octane rating higher than that for which the engine is designed, will also overheat the plate.
High-octane gasoline also burns more slowly, overheating exhaust system parts. This is well known to owners of old cars that run on gasoline, which have not been on sale for a long time. It is necessary to increase their compression ratio to prevent overheating.
Adviсe
Check the valve carefully when purchasing. Check the size standards and inspect the part for visible defects. Purchase spare parts only from certified points of sale from reputable manufacturers. The money saved on a cheap purchase will result in expensive repairs.
Check the valve clearances in the engine. Too short a distance is a common cause of overheating. Reduced clearance indicates wear of the valve seat. Install stiffer motor seats to prevent damage.
Why do valves start to burn out after installing HBO?
Gas has a very high octane number, which engines are not designed for. Even if the mixture is adjusted correctly, the temperature of the exhaust valves will be higher than when operating on standard gasoline. This results in increased wear of the seats and the need for frequent adjustment of thermal clearances.
If you skip this operation, the valve will “freeze”, that is, it will stop closing and quickly burn out. But even if there are hydraulic compensators, when working in conditions of constant overheating, the correct geometry of the working chamfers is distorted. Cooling deteriorates, and there is no longer any reserve for temperature resistance.
Often the HBO is not adjusted precisely enough. In an effort to save money, the mixture is over-lean, it burns very slowly, the temperature rises, and the power drops.
Along with the need to increase thermal clearances, this factor must be taken into account when installing LPG on engines not intended for this purpose.
Information for the consumer about preventing the valve grinding operation at the ZZA cylinder head.
When installing ZZA LLC cylinder heads on engines, it is forbidden to spill gasoline and grind the valves. Complete tightness of the combustion chamber is achieved during the running-in process by “tapping” the valves in the first minutes of engine operation.
The seat material used (heat-resistant powder material with a porous structure) and blade processing of the working chamfer with high precision in diameter, angle of inclination and roughness make it possible to eliminate the operation of grinding in the working chamfer of the valves.
During the running-in process, the valves are knocked against the seats and at the same time the tightness of the combustion chamber sharply increases compared to a new (unrun-in) cylinder head.
Carrying out valve lapping on new cylinder heads produced by ZZA LLC using lapping pastes with unknown characteristics does not improve, but rather worsens, the service life of the “valve sleeve-valve-seat” connection for the following reasons:
— the possible introduction of abrasive material into the porous structure of the seats and bushings leads to intensive wear of the surfaces of the valve and seat during operation;
— when lapping paste gets on the valve stem, the surface roughness of the valve stem inevitably deteriorates and the thin carbonitrated layer is destroyed, which is used to increase the hardness of the metal surface and reduce the coefficient of friction in order to increase wear resistance;
— in oil reflector caps the geometry of the working edge is violated, which requires 100% replacement of the caps;
— after the grinding operation, high-temperature washing with water under pressure with special detergent additives and subsequent drying is required, which is usually not used in a car service center.
Valve lapping is used in repair technologies for cast iron seats with high hardness (over 55 HRC), and for powder seats (hardness 35-40 HRC), it is necessary to use a special cutter based on the hole in the bushing for the valve stem.
Hi all! Let's talk today about such a holivar issue as grinding valves. The procedure in the vast expanses of Drive 2 is, to put it mildly, popular - I have not yet seen a single description of a major overhaul of an internal combustion engine that did not mention this “ritual”! Moreover, we will rather not even talk about the rubbing itself, but about those things that cause its need.
First, let's look at how the valve-seat assembly works in geometric terms:
We see a bunch of chamfers (and the saddle may not have a chamfer, but a radius)
Barik-CZ wrote a lot about the geometry of the seat and its influence on the operation of the internal combustion engine, but I want to draw attention to several key points for the life of the cylinder head: 1. The valve is pulled to the seat using a return spring
2. The ratio of the valve pressing force to the area of the chamfer on the seat gives the specific pressure of the valve on the seat. 3. The valve is cooled through the chamfer on the seat.
As you can see, all the key moments for the operation of the cylinder head rest on two chamfers - on the valve plate and on the seat.
What happens if the chamfer on the saddle is uneven? The specific pressure at different points of the seat will be different; in the zone with maximum pressure, wear will be significantly faster than in neighboring ones. As a consequence, a violation of the tightness, a breakthrough of hot gases with a simultaneous sharp increase in the temperature of the valve in the zone of gas breakthrough and almost zero cooling in it. The result is valve burnout.
Valve burnout on a diesel engine
There is no fundamental difference in the causes of burnout between diesel and gasoline engines; the differences come down to the characteristics of fuel equipment malfunctions. For diesel engines of the old and new schools, it is organized in different ways.
The only common problems are with the nozzles, which can cause deviations in the amount of cyclic flow due to overflow or, conversely, low productivity.
A feature of old engines may be disturbances in the operation of mechanical injection advance machines, which play approximately the same role as ignition advance in gasoline engines. With modern diesel engines this is monitored much more accurately and reliably. But at the same time, the most efficient heavy fuel engines are very critical to the composition of the mixture due to the use of turbocharging.
Excessively harsh operation is possible, changing the thermal regime and exposing the combustion chambers to abnormal shock loads.
Why is adjustment necessary?
The correct procedure depends on:
- uninterrupted operation of the LADA Kalina engine (operation with a reduced noise level in the timing belt, no errors in the camshaft sensor);
- reduction of fuel consumption to a level close to that regulated by the manufacturer;
- less wear on the camshaft cams and the pushers interacting with them.
- cleanliness of combustion chambers and valve plates due to the absence of carbon deposits.
Valve adjustment in a Lada Kalina car should be carried out with a periodic mileage of 20 thousand km or a little more.
It is not recommended to neglect this procedure, since the regulatory value of the gaps at the valves of the intake and exhaust circuits changes. This circumstance provokes a loose fit of the valve discs to the seat seats, which inevitably leads to the formation of carbon deposits, incomplete combustion of fuel, damage to the discs with subsequent burnout and other troubles in the timing belt in the LADA Kalina model. As you can see, in the absence of the required clearances, there is a violation of the correct functioning of the engine as a whole, and the only harmless point here is the owner’s acoustic discomfort due to the increased noise of the timing belt.
Note that adjustment of the valve mechanism requires 8 valve engines of Lada Kalina cars.
Consequences
The valve that begins to let gas through will gradually collapse. This can lead to damage to other parts, cylinder walls, piston, rings. Unburned gasoline will lead to damage to the catalyst, and once it gets into the oil, it will greatly change its properties, which can damage the liners and crankshaft.
The engine will vibrate, destroying the attachments and mountings of the power unit. Power will drop, consumption will increase.
Is it possible to drive
Driving with loss of compression is highly undesirable. Timely repairs minimize the consequences, preserving the engine as a whole.
All its parts and systems are firmly connected during operation; a violation of this balance will lead to an avalanche-like increase in destruction. Instead of replacing the valves and eliminating the cause of the burnout, a major engine overhaul will be required.
How much does it cost to fix the problem?
The price of a burnout repair service greatly depends on the make and model of the car, the cause of the failure, the consequences that have already occurred, as well as the general condition of the engine.
You will need to remove the block head and reassemble it, replacing the valves, possibly their seats and guides, oil seals and grinding the discs into the sockets. In simple cases, you can spend approximately 6,000 rubles, but this figure does not carry any useful information.
The fact is that when opening any engine, a lot of problems with very time-consuming solutions can be revealed. Weakened and torn threads, broken geometry of the joint between the head and the block, defective hydraulic compensators and much more.
How to avoid the problem?
The main reason for burnout is the operation of the part under increased loads. The operating temperature of the valve is about 600-650 degrees. To prevent overheating, the gaps should be checked. Due to the short distance, friction occurs and, as a result, overheating of the valve.
Signs may also indicate poor quality fuel. On carburetor cars, the mixture is adjusted manually
It is important not to allow too much The same applies to cars with LPG. There are two main generations:
- Second.
- Fourth.
In the first case, the mixture is adjusted mechanically by adjusting the “greed” tap. Adjusting it is very simple - turn the tap until the car starts to stall. Next, unscrew it 1-2 turns. This is the most optimal setting. In the case of fourth-generation HBO, the configuration is done programmatically by specialists.
If the valve is burnt out, pay attention to the quality of the product when purchasing. A defective item will not last long
A high-quality valve eliminates various risks, scuffs and other defects. The part itself is inexpensive, but installation will take a lot of work. After all, to replace it, it is necessary to “throw off” the block head and further grind the seats.
Signs of valve burnout
In the event of a burnout in the cylinder during the compression stroke, sufficient pressure does not develop, since part of the fuel-air mixture (FAM) leaks through the valve. Therefore, combustion in such a cylinder occurs incorrectly or is completely absent, which is naturally reflected in the operation of the engine.
Symptoms of valve burnout:
- uneven idle. In this case, the nature of the work will depend on the area of the hole formed between the valve chamfer and the cylinder head seat. This can be either a slight vibration and a slight twitching when changing the gas, or tripling, in which one of the cylinders does not work completely;
- loss of power;
- characteristic booming sound in the intake tract. Occurs if the intake valve on a car is burnt out;
- increased fuel consumption;
- difficult start.
On vehicles equipped with the self-diagnosis feature, the Check Engine light will illuminate on the instrument panel. Reading the diagnostic tool as a fault, you will most likely see misfire, lean/rich mixture errors. The first type of error is recorded due to uneven rotation of the crankshaft, which occurs when there is a malfunction in any of the cylinders. The second is associated with improper combustion in an idle cylinder, as a result of which part of the fuel injection fuel flies into the exhaust tract, confusing the oxygen sensor (lambda probe).
After identifying a fault code for a specific cylinder, you can safely unscrew the spark plug to measure compression. If there are no errors, you will have to resort to more sophisticated diagnostic methods.
Fault localization
The most common and effective method for determining a burnt-out valve is compression measurements. If the results show low compression, then this is clearly a sign of burnout. But here you need to take into account a small nuance - using compression measurements it will not be possible to exclude CPG defects. Low compression is not only due to burnout. Various other defects can reduce it - for example, it could be broken rings. Therefore, if all the signs of a burnt valve are observed on a VAZ-2109 or on any other car, you will have to additionally diagnose the car.
How to determine a bad cylinder?
The essence of the simplest test comes down to sequential shutdown of the cylinders. By simulating a malfunction, we observe changes in engine operation. After turning off the boiler in which the valve has burned out, changes in operation will be minimal. What are the best ways to do this?
- Remove the high-voltage wire from the spark plug. At this time, the coil will experience increased loads, so the duration of such a stress test should not exceed 2-3 seconds. To avoid the risk of electric shock through a cracked GDP, such a check should be done wearing rubberized gloves or using pliers with plastic/rubber handles.
- Physically disconnect the injector chip. If you have specialized diagnostic equipment, this can be done programmatically by connecting to the car via the OBD-II connector.
Video: Why valves burn
Compression check
Having identified a non-functioning cylinder, we must check the cylinder for leaks. There are several ways to do this:
- measuring compression in the engine. Even the cheapest compression meter with a suitable measurement scale will be suitable for these purposes. The main thing is that there is an adapter with a suitable thread available. Without trusting the accuracy of the device, focus not so much on the number shown, but on the difference between the cylinders. Compression when the valve burns out decreases by 3-6 atm. in comparison with neighboring pots;
When cranking the engine with the starter, the throttle valve must be fully open, the fuel supply to all cylinders must be turned off, and the battery must be fully charged.
- checking the cylinder for leaks using a tester. The device is a gearbox through which compressed air is supplied to the cylinders. A pressure gauge installed nearby measures the actual pressure after the reducer, converting air loss into a percentage leakage rating;
- relative compression measurement. You can’t do such a test yourself, but a diagnostic technician with an oscilloscope will check it in no more than 15 minutes. You can measure relative compression using the starter current or using the CSS script by Andrey Shulgin.
Burnt out valve or piston problems?
A burnt valve is far from the only reason for decreased compression in the cylinder. Therefore, the following steps will help us understand whether the valve is burned out or there are problems with the piston system.
The most primitive test is to pour several cubes of engine oil into the “squat” cylinder, and then repeat the measurement. If the compression has increased, then the reason is not in a burnt-out valve, but in the cylinder-piston group (CPG).
Pull the dipstick out and look at the amount of gas escaping from the hole. If the engine is breathing heavily, the reason is the piston. If the crankcase ventilation system copes with its task, the valve seat or the valve itself has burned out. In a more advanced diagnostic version, a special device measures the volume of crankcase gases.
Symptoms of a burnt valve
How can you tell if the valves are burnt out? The easiest way to establish this is by visual inspection, but to do this you would have to remove the cylinder head, which is quite labor-intensive and expensive. Therefore, to begin with, it is worth being guided by indirect signs. Knowing what happens when a valve burns out and how this affects the operation of the internal combustion engine, you can determine the breakdown without disassembling the engine.
How to determine that the valve has burned out, see the table, which shows the characteristic symptoms and main causes.
| Symptom | Causes | Why is this happening |
| Detonation (“knock fingers”) | The octane number does not correspond to that recommended by the manufacturer. Ignition set incorrectly | If gasoline is low-octane or does not ignite at the right time, then when the mixture is strongly compressed, instead of smooth combustion, an explosion occurs. Combustion chamber parts are subject to shock loads, valves overheat and may crack |
| Increased fuel consumption | Incorrect timing operation | The operating mode of the timing belt with a damaged valve is disrupted, power drops, and with it the efficiency of the engine, which can lead to increased consumption |
| Deterioration of traction and dynamics | Decrease in total engine power | A burnt-out valve prevents working compression from being achieved in the cylinder; as a result, the necessary force is not created to move the piston |
| Difficulty starting | The piston speed decreases | The piston is not able to create the necessary force to rotate the crankshaft |
| Shaking and rough idling, change in engine sound | Cylinder misfires | Normally, flashes in the cylinders of an internal combustion engine occur at even intervals (half a turn of the crankshaft for a 4-cylinder internal combustion engine) and with the same force, so the engine rotates evenly. If a valve burns out, the cylinder cannot do its job and the engine is subject to load changes, causing vibration and strong vibrations. |
| Silencer shots | Ignition of VTS in the exhaust manifold | In a leaking cylinder, the air-fuel mixture does not burn completely. As a result, remaining fuel enters the hot exhaust tract and ignites. |
| Popping sounds in the intake | The air-fuel mixture returns to the manifold and receiver | If the intake valve burns out and poisons, then during compression part of the mixture returns to the intake receiver, where it burns when a spark is applied |
The valve has burned out and can no longer provide a seal.
Based on the symptoms listed above, you can find out that the valves in the engine are burnt out. A combination of several signs indicates this with a higher probability. The seat, to which the valve must fit tightly when closing, can also burn out, although this is a less common failure.
If the symptoms indicate the presence of cracks in the valve or that the valve seats are burnt out, the cause of the failure can only be reliably determined through complete diagnostics and troubleshooting. To carry out repairs, in any case, you will have to remove the cylinder head and then replace the failed parts.
Cost to fix the problem
You can replace a valve on a domestic car with your own hands at minimal cost, spending about 1,000 rubles on the valve itself, a new cylinder head gasket, lapping paste, and antifreeze for topping up. But usually it doesn’t end with just one burnout: it may be necessary to mill or replace a cylinder head deformed due to overheating, as well as grooving the valve seats. A pinched valve causes the camshaft cam to wear out.
Service stations are reluctant to change one valve, and full maintenance and repair of the cylinder head starts from 5-10 thousand rubles for a VAZ - up to tens of thousands for modern foreign cars.
After replacing burnt valves and repairing the cylinder head, it is important to eliminate the root cause of the burnout. If this is not done, the part will soon fail again!
The combustion process of the mixture in a working engine
To better understand the causes of valve burnout, you need to know the basics of gas exchange processes in the engine and their sequence.
- Intake stroke. The intake valves are open, the piston moves down, creating a vacuum zone. At this moment, a mixture of fuel and air is sucked from the intake tract (gasoline engines with distributor injection into the intake or with a monoinjector) or a pure air charge (internal combustion engines of the Diesel cycle and gasoline engines with direct injection).
- Compression stroke. The piston begins to move upward, the intake and exhaust valves close. The mixture compresses, the temperature in the combustion chamber rises.
- Working stroke. A few degrees before the highest dead center (TDC) of the cylinder, the mixture is ignited by a spark (gasoline internal combustion engines) or self-ignites from contact with heated air (diesel engines). Under the influence of the force of expanding gases, the piston rushes down. The reciprocating movement of the piston through the connecting rod and crank mechanism is transmitted to the rotational movement of the crankshaft.
- Release stroke. The exhaust valves open. The piston moving towards TDC pushes the exhaust gases into the exhaust tract.
The phases of valve overlap and inertial filling are omitted intentionally, since they do not significantly affect the consideration of the issue of valve burnout.
Adjusting thermal clearances in the engine valve mechanism
We measure and adjust the gaps on a cold engine. Remove the engine screen. Disconnect the throttle drive cable from the throttle assembly sector (see “Replacing the throttle drive cable”). Having unscrewed the three fastening nuts, remove the throttle valve drive cable bracket and move the bracket with the cable to the side (see “Removing the receiver”).
Use a Phillips screwdriver to loosen the clamp on the lower crankcase ventilation hose... ...and remove the hose from the cylinder head cover pipe.
Using a Phillips screwdriver, loosen the clamp on the crankcase ventilation hose (main circuit)… …and remove the hose from the cylinder head cover pipe
Using a Phillips screwdriver, loosen the clamp on the crankcase ventilation hose (idle circuit)… …and disconnect the hose from the cylinder head cover pipe
Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the two nuts securing the cylinder head cover... ...and remove the washers.
Remove the two rubber bushings.
Remove the cylinder head cover. Remove the front timing belt cover (see “Checking the condition and replacing the timing belt”). The procedure for checking and adjusting clearances in the valve drive mechanism is as follows. We turn the crankshaft by the bolt securing the generator drive pulley clockwise until the installation marks on the camshaft pulley and the rear timing belt cover align (see “Checking the condition and replacing the timing belt”). Then turn the crankshaft clockwise another 40-50° (2.5-3 teeth on the camshaft pulley). In this position of the shafts, we check the gaps at the first one with a set of feeler gauges.
...and the third camshaft cam. The clearance between the camshaft cams and shims should be 0.20 mm for intake valves and 0.35 mm for exhaust valves. The clearance tolerance for all jaws is ±0.05 mm. If the clearance is different...
...then we install a device for adjusting the valves on the studs of the camshaft bearing housings.
We rotate the pusher so that the slot in its upper part faces forward (along the direction of the car).
We insert the “fang” of the device between the cam and the pusher (1 - device, 2 - pusher)
By pressing down on the lever of the device, we recess the pusher with the “fang”...
...and install a clamp between the edge of the pusher and the camshaft, which holds the pusher in the lower position.
Fixing valve tappets when replacing the adjusting washer
: 1 — latch; 2 - adjusting washer Move the device lever to the upper position
Use tweezers to pry the adjusting washer through the slot and remove it. If you do not have a device for adjusting the valves, you can use two screwdrivers. Using a powerful screwdriver, leaning on the cam, press the pusher down. Inserting the edge of another screwdriver (with a blade width of at least 10 mm) between the edge of the pusher and the camshaft, fix the pusher and remove the adjusting washer with tweezers. We adjust the gap by selecting an adjusting washer with the required thickness.
To do this, use a micrometer to measure the thickness of the removed washer. The thickness of the new adjusting washer is determined by the formula: H = B+(A-C), mm
, where “A” is the measured gap; “B” is the thickness of the removed washer; “C” - nominal gap; “H” is the thickness of the new washer. The thickness of the new washer is marked on its surface with an electrograph. We install the new washer in the pusher with the marking down and remove the lock. Check the gap again. When adjusted correctly, a 0.20 or 0.35 mm feeler gauge should fit into the gap with slight pinching. Consistently turning the crankshaft half a turn, we check and, if necessary, adjust the clearances of other valves in the sequence indicated in the table.
| Angle of rotation of the crankshaft from the alignment of the marks, degrees | Cam number (counting from the camshaft pulley) | |
| exhaust (gap 0.35 mm) | inlet (gap 0.20 mm) | |
| 40-50 | 1 | 3 |
| 220-230 | 5 | 2 |
| 400-410 | 8 | 6 |
| 580-590 | 4 | 7 |
We assemble the engine in the reverse order. Before installing the cylinder head cover...
...replace its sealing gasket with a new one.
The main causes of valve burnout
Detonation
Detonation is a process of improper combustion of TPVS, in which a shock wave occurs, propagating at supersonic speed.
Detonation combustion is one of the main causes of burnout of pistons and valves. Causes of detonation:
- discrepancy between the octane number of gasoline and the compression ratio. The burning rate of low-octane fuel is higher, and the auto-ignition temperature is lower. Therefore, the mixture detonates even before the spark is applied;
- low quality gasoline. In attempts to increase the octane number of gasoline using additives, unscrupulous gas stations sometimes confuse the proportions. In this case, a situation is possible when the declared octane number is both lower and higher than the actual one. In the second case, additives slow down the combustion rate of the mixture, which increases the thermochemical load on the exhaust valves;
- Spark plug heat rating is too low. The mixture spontaneously ignites from the hot parts of the candle;
- lean mixture. Due to an excess of oxidizer (oxygen), at the end of the compression stroke, near the hot areas of the combustion chamber, pre-flame reactions begin, developing into detonation combustion. The cause of a lean mixture may be air leaks, clogged injectors, or lack of fuel pressure.
2. Violation of the thermal gap
If the thermal clearance in the valve actuator is too small, the valve does not fit tightly to the seat, resulting in poor heat dissipation. Due to constant overheating, cracks appear in the valve head, and the most heat-loaded particles even break off.
Incorrect adjustment of the exhaust valves can also be one of the causes of detonation, since at high temperatures there is a risk of pre-flame reactions.
Effect of late and early ignition
If combustion does not start in a timely manner, the valve TPVS experience increased thermochemical loads. Thus, with early ignition, the mixture is ignited before the estimated time of the piston approaching TDC. Therefore, the peak pressure in the cylinder increases earlier than the ideal 10-15º after TDC. The piston, valves and combustion chamber walls experience excessive thermal and shock loads.
Ignition too late results in the mixture still actively burning when the exhaust valves begin to open. Again, increased thermal loads lead to burnout of the exhaust valves.
Auto Novichok - a blog for novice car enthusiasts
If you want to give another person the opportunity to use your car, it would be correct to formalize this decision. For this, various powers of attorney are used, of which the maximum powers are given by a general power of attorney for a car. It allows the person who is included in it to do very much with the vehicle [...] A car today, although it has ceased to be a luxury item, still continues to be classified as a very expensive purchase. It is not surprising that owners are worried about their property and want to protect themselves from unexpected expenses resulting from theft or damage to the vehicle. In this article we will tell […] The presence of toll roads still gives rise to controversy, but this does not change the situation. There are enough sections of roads in Russia where you have to pay to travel. Modern technologies can simplify this process. Like NFC chips in phones and smart watches, a small box is also installed in a car, which [...] Air conditioning in a car is not so much a luxury as a means of ensuring comfortable driving conditions. This is a system of several main components that regulates the temperature and humidity in the cabin. The operation of a car air conditioner is based on the same principles as the operation of a household air conditioner. Naturally, cars of various classes and […] The offset of an ET wheel rim is one of its main geometric characteristics, on which the very possibility of installing certain rims on a car depends. It reflects not only and not so much how much the wheel will protrude beyond the body, although this is how the meaning is understood [...] When a diesel engine operates, a large volume of substances harmful to humans and other living organisms is formed. This includes carbon monoxide, lead compounds, and many other compounds. Particularly dangerous is nitrogen dioxide, which is formed as a result of the reaction of oxygen and nitrogen in the air under conditions of extremely high temperatures. […] More and more car enthusiasts are looking at “mechanics” with contempt. Of course, the need to constantly pull the gearshift lever and periodically squeeze the clutch becomes tiresome over time. Therefore, the number of drivers switching to cars with automatic transmission is growing from year to year. However, this also has its own peculiarities of driving, now [...] Any design of an internal combustion engine requires the presence of spark plugs. They ignite the combustible mixture, thanks to which the engine sets the car in motion. But due to a number of factors, including the formation of soot, over time the candles gradually fail and cease to perform their functions. Let's look at [...] Vehicles include a large number of elements that ensure full operation. Needless to say, among such systems there are no insignificant ones. Especially when it comes to the braking system, which directly ensures driver safety. The main brake cylinder can easily be called a key part in the brake hydraulic drive circuit. That's why […]
Valve burnout on a diesel engine
The symptoms of a burnt valve on a diesel engine are similar to those on a gasoline engine. But the leading cause is faulty injectors. Due to overflowing injectors, the temperature in the combustion chamber increases and the combustion time of the mixture increases.
There is no concept of detonation in a diesel engine. But with early injection, no less dangerous severe combustion occurs when the pressure in the combustion chamber develops earlier than the calculated one. The walls of the combustion chamber at such moments experience increased shock and thermal loads.
Source