The presence of an on-board computer on the fourteenth VAZ model greatly simplifies the process of diagnosing some faults. Displaying error codes on the BC panel allows you to pinpoint the location of the malfunction. The functions of the built-in device include a self-diagnosis function that allows you to determine the entire list of problems in the machine systems. Often during such diagnostics, error 14 of the VAZ 2114 is displayed. To understand the method for eliminating the problem, it is worth knowing the decoding of the fault number “14”.
Useful video:
Cause of error 14 on VAZ 2114
In addition to built-in on-board computers, models 2114 and 2115 with an injector have an error detection function through the dashboard. By holding down the odometer button and turning the ignition to the first position, the self-diagnosis process begins. The functionality of the fuel gauge, tachometer, speedometer and coolant temperature needles will be checked.
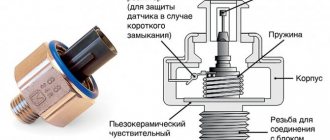
Common error 14 on the VAZ 2114 means a high signal from the antifreeze temperature sensor (the so-called DTOZH).
The reason for the appearance of code “14” lies in the following points:
- The temperature sensor is faulty;
- There is a break in the DTOZh connection circuit;
- The error codes were summed up and displayed on the panel as the sum “14” (options for other faults should be selected);
- The insulation of the sensor is broken, as a result of which it no longer transmits correct readings.
Useful : Where is the DTOZH located on the VAZ 2114?
As soon as error code 14 appears on the instrument panel of the VAZ 2114, you should replace it or check the reliability of the wiring connection to the DTOZH. In the VAZ 2114 model (injector, 8 valves), this element plays a rather important role in the formation of the correct air-fuel mixture and is responsible for the timely activation of the cooling fan.
VAZ (LADA) errors via OBDII protocol
Fuel system and air supply
P0000-P0099, P0100-P0199, P0200-P0299
P0030 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the oxygen sensor heater
P0031 - Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage
P0032 - Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage
P0100 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the mass air flow sensor (MAF)
P0101 - Incorrect operation of the mass air flow sensor (MAF)
P0102 - Low signal level of the mass air flow sensor (MAF)
P0103 - High signal level of the mass air flow sensor (MAF)
P0112 - Intake air temperature sensor signal low
P0113 - Intake air temperature sensor signal high
P0114 - Insufficient contact of the electrical circuit of the intake air temperature sensor
P0115 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the coolant temperature sensor
P0116 - Incorrect operation of the coolant temperature sensor
P0117 - Low signal level from the coolant temperature sensor
P0118 - High signal level from the coolant temperature sensor
P0119 - Insufficient contact of the electrical circuit of the coolant temperature sensor
P0120 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the throttle position sensor
P0121 - Incorrect operation of the throttle position sensor
P0122 - Low signal level from the throttle position sensor
P0123 - High signal level from the throttle position sensor
P0130 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the oxygen sensor
P0131 - Oxygen sensor voltage low
P0132 - Oxygen Sensor Voltage High
P0133 - Low speed oxygen sensor
P0134 - No response from oxygen sensor
P0135 - Heated Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction
P0171/171 – Air/fuel mixture too lean
P0201 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector 1
P0202 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector 2
P0203 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector 3
P0204 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector 4
P0222 - Throttle Position Sensor 2 Low
Ignition system
P0300-P0399
P0300/300 – Multiple misfires (ignition)
P0301 / 301 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder No. 1
P0302 / 302 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder No. 2
P0303 / 303 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder No. 3
P0304 / 304 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder No. 4
P0326 - Incorrect operation of the knock sensor
P0327/327 – Knock sensor signal low
P0328/328 – Knock sensor signal high
P0335 / 335 - Malfunction in the crankshaft position sensor electrical circuit
P0336 - Incorrect operation of the crankshaft position sensor
P0337 - Low signal level from the crankshaft position sensor
P0338 - High signal level from the crankshaft position sensor
P0343/343 – Camshaft Position Sensor High Signal
P0351 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the ignition coil "A"
P0352 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the ignition coil "B"
P0363 - Misfire (ignition) - lack of fuel supply
Emission control
P0400-P0499
P0422 / 422 - Low catalyst performance
P0441/441 - Evaporative Emission System - Flow Incorrect
P0442 - Evaporative Emission System - Minor Leak
P0443 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the evaporative emission solenoid valve
P0444 - Evaporative Emission Solenoid Valve Circuit Open
P0480 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the engine cooling fan
P0485 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the engine cooling fan
Speed and idle control
P0500-P0599
P0500 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the vehicle speed sensor
P0501/501 – Vehicle Speed Sensor Malfunction
P0504 / 504 - Incorrect brake pedal position sensor signal
P0505 - Malfunction in the idle speed control system
P0506 - Engine idle speed below acceptable values
P0507 - Engine idle speed is higher than permissible values
P0511 - Idle Air Bypass Control Circuit Malfunction
P0560 - System voltage (on-board network) - malfunction
P0562 - Low voltage in the system (on-board network)
P0563 - High voltage in the system (on-board network)
Electronic control unit (ECU) and its subsystems
P0600-P0699
P0601 - Electronic Engine Control Module - Memory Checksum Error
P0603/603 – Engine control module external RAM module error
P0615 - Starter relay circuit malfunction
P0628 - Fuel Pump Control - Low Signal
P0650 - Malfunction indicator circuit malfunction
Transmission
P0700-P0799, P0800-P0899, P0900-P0999
P0830 / 830 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the clutch pedal position sensor
Other errors
P1135 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the oxygen sensor heater
P1140 - Measured engine load differs from calculated load
P1141 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the oxygen sensor heater installed after the converter
P1301 - Cylinder 1 - Converter critical misfire detected
P1302 - Cylinder 2 - Converter critical misfire detected
P1303 - Cylinder 3 - Converter critical misfire detected
P1304 - Cylinder 4 - Converter critical misfire detected
P1335 - Throttle Actuator Control Monitoring - Position Out of Range
P1336 - Controller type does not match standard
P1425 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the canister purge control valve
P1426 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the canister purge valve
P1513 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the idle speed sensor
P1514 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the idle speed sensor
P1541 - Fuel pump relay control circuit malfunction
P1545 - Throttle position is out of operating range
P1570 - Immobilizer control circuit malfunction
P1578 - Invalidity of throttle valve relearning results
P1600 - No communication with immobilizer
P1602 - Interruption of on-board network voltage
P1603 - Malfunction of the internal microprocessor memory module
P1612 - Electronic control unit processor memory reset error
P1617 - High signal level from rough road sensor
P1620 - Incorrect operation of the internal memory module of the control unit
P1621 - Incorrect operation of the control unit RAM module
P2020 - Incorrect operation of the drive position sensor of the intake manifold geometry changing system
P2122 - Low signal level from the gas pedal position sensor
P2127 - Low signal level from the gas pedal position sensor
P2135 - Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor - Voltage Correlation
P2138 - Accelerator pedal sensor voltage correlation
P2187 - Air/fuel mixture too lean at idle
P2188 - Air/fuel mixture too rich at idle
P2302 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the ignition coil "A"
P2305 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the ignition coil "B"
How to resolve error 14?
Before starting work, you must make sure that the reason for the error display on the panel is the result of a sensor failure. If your car has problems with detonation, loss of engine power and increased consumption, you need to check the condition of the sensor. The cost of this element is low, so it is worth replacing it as a preventative measure. Incorrect readings from the DTOZ complicate the work of the car’s “brain”, because Accurate temperature readings are required to form the correct mixture. In general, DTOZH is considered one of the reliable elements in the control system, but it is worth replacing it periodically. The best way to resolve the error is to replace the sensor. If there is a wire break, then it is enough to restore the connection. We will describe the step-by-step process of replacing a faulty element below:
- Cool the engine and drain the antifreeze from the radiator and engine block. Unscrew the cap of the expansion tank.
- Find the desired sensor near the thermostat housing and mark its current position.
- Unscrew the sensor from its seat using a 21 key.
- Next, install the new element in accordance with the marked marks. Use a small amount of high temperature resistant sealant and apply it to the threads of the DTOZH.
- Pour new antifreeze or antifreeze into the system.
When diagnostics are running, a similar code, P2114, may be displayed. It means the TPS is malfunctioning. The problem is solved by replacing it completely.
Is it possible to drive with error 14?
On domestic cars, on-board computer errors are displayed quite often during testing. You should not ignore the readings, because... Some malfunctions seriously affect the normal operation of the engine and other systems. It is acceptable to move with error “14”, but this is fraught with the following disadvantages:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- The engine operates in a changed temperature range;
- Antifreeze may boil in the expansion tank.
Malfunctions that arise in the engine cooling system should be corrected promptly, because Operating at elevated temperatures increases the likelihood of overheating. Please note that the error code may be displayed even after the problem has been resolved, because Data is still stored in the BC memory. Next, we’ll look at ways to reset data without using third-party devices.
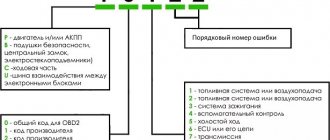
Basic error codes for VAZ 2114 injector: decoding
Note!
The table is also relevant for version 2115.
Exhaust system – 0000
- 30 – open circuit of the oxygen sensor heater to the catalytic converter;
- 31 – also with a short circuit to the car body;
- 32 – similar with a short circuit to 12V;
- 36-38 – the same value as 30 only for the output sensor.
Air line defects – 0100
- 102/103 – Mass air flow sensor open circuit or signal violation;
- 112/113 – sensor lines t˚ overboard, impulse violation;
- 116 – engine overheating;
- 117/118 – damage to the DTOZH circuit;
- 122/123 – TPS line, short circuit or insulation failure;
- 130 – failure of the oxygen sensor in front of the catalyst;
- 131/132 – similar element, signal level violation;
- 133 – slow response of DK1 to commands;
- 134 – break in the power cable DK1;
- 136 – DK2 is broken;
- 137/138 – short circuit or violation of wiring DK2;
- 140 – fuse DK2 burned out;
- 141 – the heater of the same device is broken or damaged;
- 171/172 – excessively lean or enriched fuel mixture.
Error codes VAZ 2114 1.6 liters related to fuel supply - 0200
- 201/204 – break in the injector control line for all injectors in series;
- 217 – motor overheating;
- 230 – the fuel pump has failed or the corresponding relay has burned out;
- 261/264/267/270 – short circuit of the injector control circuit at +12 V, respectively, for each insert;
- 263/266/269/272 – failure or defect of the injector driver for each in series;
- 262/265/268/271 – Short circuit of highways to the car body.
Error codes on the VAZ 2114 on-board computer indicating a breakdown in the ignition system - 0300
- 300 – there are misfires;
- 301-304 – similarly for each cylinder, respectively;
- 326-328 – DDS is broken or there is no signal;
- 335-338 – failure, short circuit or interruption of the DPKV wiring;
- 342/343/346 – malfunction of the phase distribution sensor;
- 351-354 – open circuit for all pistons in series;
- 363 – the mixture in the cylinders does not ignite, emergency fuel supply cut-off.
Additional attachment that does not have a direct effect on the motor – 0400
- 422 – the catalyst may have clogged or the exhaust gas flow rate has dropped critically;
- 441 – failure of power supply to the adsorber purge valve;
- 444 – power failure above the specified element;
- 445 – short circuit of the gearbox to the car body;
- 480 – power wires to the main radiator cooler are damaged;
- 481 – failure of the coolant fan control circuit No. 2.
Failure, malfunctions in the SU speed control system – 0500
- 500 – speedometer sensor is broken;
- 506/507 – low or high speed of the vehicle;
- 511 – XX regulator – lines from the relay and ECU are interrupted;
- 560 – the battery is low or the power cable is broken.
- 562/563 – Short circuit on on-board wiring.
On-board network of auxiliary or main equipment – 0600
- 601 – ECM, ROM error;
- 615 – secondary starter relay, wiring damage;
- 616/617 – also with short circuit to ground or 12V;
- 627 – fuel pump control relay, possible line break;
- 628/629 – similar with a short circuit to the body or on-board system;
- 645-647 – compressor clutch, damage to the wiring with contact with the housing or other cables;
- 650 – the “Check Engine” lamp is broken, check the engine, there may be damage to the wiring;
- 654 – tachometer failed;
- 685-687 – malfunction of the main engine control relay, complete replacement of the part is required;
- 691/692 – problems with the main cooling fan relay.
Auxiliary systems – 1000
- 102 – breakdown of heater DK1;
- 115 – failure or malfunction of the above device;
- 123/124 – violation, too rich/lean mixture at idle;
- 127/128 – similar, only for partial load on the internal combustion engine;
- 135 – rupture of heating line DK1;
- 136/137 – incorrect fuel supply at low engine load, the throttle drive may be malfunctioning;
- 140 – discrepancy between measured and actual load;
- 141 – failure of heater DK2;
- 171/172 – incorrect information comes from the potentiometer;
- 301-304 – the ignition in the cylinder does not work correctly, consistently for all combustion chambers;
- 386 – incorrect sequence of testing the detonation channel;
- 410/425/426 – wiring of the canister purge flap, short circuit or line damage;
- 500 – the fuel pump relay line is damaged;
- 501/502 – similarly with a short circuit to the body or wiring;
- 509/513/514 – control center of the XX regulator, open or short circuit on board or 12V;
- 541 – damage to the wire of the BN relay, possible oxidation of the terminal;
- 570 – break in immobilizer control cables;
- 602 – no power to the ECM, oxidation of the pads is allowed;
- 606 – the bump sensor is broken, the part needs to be replaced;
- 616/617 – similarly with a change in signal level, there may be a short circuit inside the device;
- 2301/2303/2305/2307 - the ignition coils are shorted to 12 volts, in series for each piston.
Important!
Only the most popular error codes for the dashboard of the VAZ 2114 and similar models are listed here. There are other indices, but due to their low prevalence they are not mentioned.
How to reset errors on a VAZ 2114?
The procedure for resetting old problems without the presence of devices is extremely simple. The corrected error 14 on the dashboard is stored in the car's computer memory until the battery is disconnected. It is enough to remove the negative terminal from the battery for a few seconds and when checking again, the BC will not display any codes.
If “14” is still lit on the dashboard, check the car for other breakdowns, because Diagnostics in VAZ works on the principle of adding two error indicators into one sum.