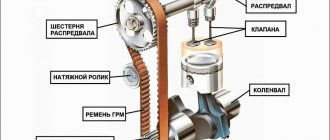
Signs and causes of an engine jam in a car
Contrary to the common misconception that a low-mileage engine in a new car cannot seize, alas, it is worth saying that a similar problem can happen to any engine and at almost any mileage. Engine “wedge” is a problem for which any motorist must be mentally and financially prepared.
Sometimes this happens suddenly, but sometimes the engine gives warning signals to the driver long before failure, and one of the main reasons for immediate failure in this case may be scuffing, deformation, destruction and soldering of parts.
What is a motor wedge?
Let's start with the fact that if the engine is operating in its nominal mode, that is, normally, then all moving and rubbing elements of this engine that interact with each other must be lubricated with lubricants that are appropriate and specific to the technical characteristics of the engine. For example, it is unacceptable for the piston ring to be in direct contact with the cylinder walls - between the elements there must be a thin layer of oil film, which reduces friction and, accordingly, can extend the trouble-free operation of the engine, not limited to several thousand kilometers, but several hundred thousand.
However, if this thin micron-thick layer of lubricant disappears from the honed surface of the cylinder and the metal elements come into contact with each other without lubrication, even microscopic irregularities will cause a rapid increase in friction, as a result of which most of the mechanical energy (up to 95%) is converted into heat . And the most dangerous thing for internal combustion engines will begin - dry friction.
The problem is that once such a process begins, over time (and quite quickly) it will only worsen, one problem will lead to another. The more the rubbing elements heat up, the more they will expand, increasing pressure and displacing the remaining oil film.
Even if the lack of lubrication was a temporary phenomenon, as the metal expands due to its heating, the gaps will decrease and the engine oil may simply cease to perform its function of reducing friction between the involved components, simply being forced out of critical places.
In extreme cases, so much heat can be generated that the engine will eventually stop abruptly, signaling a costly repair (at best) or the need to purchase a new motor.
Often, when the engine is starved of oil, the connecting rod bushings jam.
In this case, the bushing can rotate, and the pin can get jammed both in the upper head of the connecting rod and in the piston bosses, which can lead to the “hand of friendship”; the cylinder block can be pierced by the connecting rod without hope of subsequent restoration. see also
Ten signs that your car is seriously faulty
In other cases, the working parts simply actively “rub”, wearing out the mating surfaces at an accelerated pace or deforming them. Such a crippled engine may start after cooling, but it is unlikely to operate at its nominal value. It will knock, rattle and pull poorly, for example due to worn bushings, or smoke like hell due to worn rings.
We would like to tell you about the 10 most common causes of engine seizure. Perhaps, knowing them, you will be able to avoid expensive repairs or at least reduce their cost by noticing the problem in time.
AutoXS.ru - Auto Encyclopedia
What does an engine sound like when it seizes? There are specific signs that will tell you that a disaster is about to happen. However, a seized engine can also be identified by the characteristic sound it makes, which anticipates an impending problem. At the initial stage of the problem, you will hear a slight pipe tapping sound when moving. The noise will come from the engine. At the next stage, a deafening metallic knock will be heard. Also called "dead man's knock," it occurs when the piston rod hits the crankshaft. If you notice signs of engine seizure, you should send the car to a service center. Early diagnosis can save you thousands of dollars.
The photo shows traces of rubbing of the piston skirt on the walls of the cylinder block. If you do not open the engine in a timely manner, a meat grinder may occur, as in the first photo. Signs of a seized engine: how to determine that the engine is seized?
If there is a significant decrease in engine power, the low engine oil pressure indicator light comes on, or if there are strange noises coming from the engine compartment, you should have your vehicle's engine checked.
Pay attention to the symptoms of engine seizure:. Pipe Tapping As already discussed, a slight pipe tapping sound may indicate an engine stalling problem.
The noise occurs when the starter hits the flywheel.
Pipe Tapping As previously discussed, a slight pipe tapping sound may indicate an engine stalling problem. The noise occurs when the starter hits the flywheel.
Smoke Smoke or even an open flame coming from under the hood can be another sign of a seized engine. Since the starter in this state cannot crank the engine, the wiring overheats, which causes smoke or even fire.
Engine failure is a fairly obvious sign of problems with your car. But the engine should not be brought to this state. A complete engine failure means that the engine will not start under any conditions. Battery-powered lights, radios and other components can continue to operate.
Loosening of engine parts When a part of an internal combustion engine, the piston, becomes loose, it can pierce the cylinder head. You can find out about such a problem by performing periodic engine checks.
Lack of engine oil is the most common cause of seizure. Low oil levels lead to increased friction, overheating and other problems that cause the engine to seize. This problem can also be caused by water or rust accumulated inside the engine. Another possible cause is breakdown or failure of engine parts, but engine seizure is unlikely.
On the video collection you can watch real cases of engine wedges from life:
Source
Lack of engine oil
photo: freebie.photography
Every engine burns at least a small amount of oil, so if the driver does not check the oil level for a long time, the engine is at risk of seizing.
In the case of new engines that have not yet been run-in, or, conversely, in heavily worn old engines, oil consumption can even exceed 1 liter per 1000 km.
If the oil level approaches the minimum, the likelihood of failure increases. Just because there is sufficient oil pressure in the pan during normal driving with a minimum amount of oil in the pan does not mean that it will also remain so, for example, when driving fast on the highway or during long, tight turns, when centrifugal force pushes most of the oil into the pan, where the oil pump can no longer reach it.
The influence of gasoline on the technical condition of the power plant
The wear of the power plant largely depends on the quality of the combustible mixture: fractional composition, octane number, tendency to form deposits, anti-corrosion properties and other characteristics affecting the combustion process. Low grade fuel accelerates engine failure by 1.5 - 2 times.
Components of a low-quality fuel mixture:
- Difficult to evaporate fractions;
- High resin content;
- High sulfur content;
- Inconsistency of detonation resistance with the brand of gasoline;
- Rich mixture (lots of gasoline, not enough air);
- Lean mixture (lots of air, not enough gasoline).
- The fractional composition of gasoline depends on the distillation temperature:
- 10% evaporation: the starting qualities of the fuel and the tendency to form vapor locks are determined;
- 50% evaporation (working fraction): characterizes the ability to operate stably at low speeds, throttle response, and warming up of the unit;
- 90% evaporation (heavy fraction): affects the power, efficiency, and durability of the power plant.
A large number of resins leads to a heavier fractional composition.
Getting into the engine with the fuel, the resins settle on the valves, combustion chamber, pistons, spark plugs and form carbon deposits as a result of exposure to high temperatures. Valves hang, early detonation and ignition occur in the cylinders, and fuel supply becomes difficult. Normal resin content, 2-20 mg per 100 ml of fuel.
Sulfur, its compounds, acids, alkalis, and water affect the corrosive properties of gasoline.
Operating on fuel with a high sulfur content leads to increased wear as a result of high carbon formation and reduced detonation resistance.
Detonation resistance is increased by adding ethyl liquid (1-TC or R-9).
It contains a large amount of tetraethyl lead (58 or 54%). To remove lead from the engine, special additives are used that form volatile compounds with it and remove it with the exhaust gas. When such gasoline is stored for a long time, the additives lose their capabilities, and lead enters the engine without subsequent removal from it.
Wrong choice of engine oil
photo: en.wikipedia.org
Using an unsuitable lubricant, which results in a weak oil film and/or increases the rotation speed, causing the oil film to simply scatter to the sides without settling on the hone.
Warning! Modern liquid oils with low resistance (low viscosity) are more susceptible to this phenomenon than “non-ecological” thick oils with parameters such as 10W60.
Oil dilution with fuel
photo: carkeys.co.uk
This is a common problem with diesel engines equipped with particulate filters.
During the so-called forced regeneration of the diesel particulate filter (DPF), that is, the afterburning of soot by increasing the temperature in the filter, the injection system supplies additional doses of fuel to the engine. There can be so much of it that the unburned excess flows down the surfaces of the cylinder walls and penetrates into the oil. If the process goes correctly, there are no problems - the fuel evaporates under the influence of temperature and flows back into the combustion chambers through the crankcase ventilation.
It’s worse if, for example, the car drives very short distances or the engine stalls while burning soot - then the unburned fuel is concentrated in the oil, and over time it becomes so much that it will no longer evaporate, and the liquefaction process will begin with a subsequent deterioration in the quality of fuel and lubricants.
Due to the ingress of diesel fuel, the oil level may even rise above the maximum risk - there may be so much fuel in the crankcase.
Typically, components that are particularly sensitive to poor lubrication will begin to suffer first, such as turbocharger bearings or timing drive components.
The problem is difficult to detect, since on many cars the increase in oil level due to the admixture of fuel is compensated by the natural combustion of engine oil - the oil level remains practically unchanged, although its composition will obviously be different.
Ridiculous cases
If the engine seizes, signs of thickened oil may indicate sugar entering the system. Similar consequences occur when stirring a raw egg, which, when the motor is running, will certainly heat up and weld all the channels. How the latter substance enters the system is known only to the owner of the car.
Sugar can be poured into the fuel by ill-wishers through the refueling hatch. There are many substances that change the composition of the oil. It happens that a driver may mistakenly pour a mixture that is lethal to iron into the engine neck.
A malfunction where coolant penetrates into the oil can also lead to jamming of the rubbing metals. This can be noticed when measuring the level using the dipstick. The changed composition is noticeable to the eye and to the touch: by color, viscosity, and the presence of foam. A whitish tint indicates a loss of oil quality.
Engine oil in coolant
photo: drive2
There may be several reasons for this, including damage to the cylinder head or cylinder head gasket, corrosion of liners, and so on, including failure of the heat exchanger gasket.
If the oil mixes with the coolant, a mayonnaise-like emulsion will form, or if the coolant gets into the oil, whitish foreign flakes will be visible in it. The lubricating parameters of such a mixture are much worse than those of pure oil, and it can also clog oil channels.
In addition, the likelihood of such a unit jamming increases due to the fact that the more coolant is drained from the engine, the worse its cooling will be.
Warning! The problem of coolant in the oil affects not only engines, but also automatic transmissions. “Automatic machines” are often equipped with oil coolers connected to engine cooling. If the seals fail, antifreeze can leak into the transmission oil.
Meanwhile, minimal contamination of the transmission oil is enough for the gearbox to become unusable and simply break. The first sign of an impending problem is usually the transmission slipping, which can result in complete loss of drive.
Antifreeze reacts with friction lining materials. The linings peel off and get into the gearbox oil system, blocking the channels and accelerating wear of the elements.
If the gearbox is not working properly, before repairing it is worth contacting a mechanic with a request to inspect for the presence of coolant in the transmission oil; special reagents are used to identify it.
Belt break
A disastrous result is observed when the timing belt or chain breaks. Often the cylinder blocks even bend. At the moment of impact, the valve covers break. As a result, the engine has to be overhauled.
If repairs are insufficient, broken parts may remain in the crankcase; under some circumstances, they will again end up in the next engine wedge. A loose damper can also get caught under the timing belt or chain. Valves and cylinder blocks become deformed under incorrect operating conditions.
Scores appear that constantly touch the moving metal. At some point, when the wear becomes large enough, final wedging occurs and the crankshaft can no longer be turned.
Clogged/coked oil channels
photo: carmagazine.co.uk
The most common causes of this problem are the use of poor quality motor oils and excessive drain intervals, or both.
It's also worth knowing that using name brand oils will not always prevent problems. Firstly, some are not as good as they are portrayed in advertising (ask auto mechanics), and secondly, there are many fakes on the market.
Not only the brand of oil is important, but also its origin.
Often the mechanics themselves are also to blame for the breakdown because they were careless. It happens that, for example, after replacing a seized turbocharger or head gasket, they forget to flush the lubrication system of metal filings and other debris such as overheated engine oil. Sometimes the oil line becomes blocked, for example due to excessive use of silicone when sealing the cylinder head cover or oil pan.
Prevention
- Change the oil. To avoid the first or repeated engine seizure, check the condition of the oil and its level once a week, regularly change the oil filter and the oil itself. To check the oil for wear, a small part of it is taken out of the engine at operating temperatures, allowed to cool a little and see what condition it is in. If the oil does not emit an unnatural odor, it is transparent and slowly drains from the dipstick, then everything is in perfect order. But, if the oil becomes cloudy or has a dark brown color, this indicates the need for replacement soon.
- If you tap the motor, stop moving immediately. This can save you from more serious problems, such as a broken cylinder block wall. And this is a very major breakdown that cannot be solved on your own.
- Check the coolant level. To do this, you need to look under the hood and look at the amount of antifreeze in the expansion tank.
But this must be done according to special rules:
- Make sure the engine is cold. Because only in this state is all the antifreeze in the tank.
- Look at the indicators on the tank, they are usually labeled MAX and MIN. If they are absent, then if there is a sufficient quantity that does not require replenishment, the liquid level should not be below the middle of the container.
You will learn about the initial stage of repairing a jammed engine from this video:
Oil pump malfunction
photo: procarmechanics.com
In this regard, Volkswagen's two-liter TDI engines have gained notoriety in recent years. These engines used two extremely inefficient and low-quality versions of oil pumps - in one the pump chain drive constantly failed, in the other there was a very thin shaft driving the pump, which also often fails.
see also
The best gasoline engines of recent years (19 models)
The effect in both cases is the same - the oil pressure drops without any warning, and now seconds separate a normally operating engine from failure and seizure of an engine operating at high speeds.
Prevention
Engine wedging can be prevented by carefully maintaining the vehicle. Periodic inspections and constant monitoring of the performance of control and signaling units helps to avoid the situation when operation continues during malfunctions
It is important to notice the following conditions in time:
- visually low coolant level;
- visually low oil level in the crankcase;
- oil pressure sensor does not respond;
- deviations in economizer readings;
- change in engine thrust;
- extraneous sounds in the operation of the car: knocking, humming, ringing, grinding.
Immediate diagnostics in a car service center of suspiciously operating components will save you from expensive major repairs. It is recommended to stop operation if you are not sure about the serviceability of the engine.
Clogged oil filter
photo: mercedesbenzhiltonhead.com
This is a problem that can occur for various reasons. The most common is a low-quality filter with a small amount of filter material that clogs too quickly.
Branded filters usually have a “bypass” valve, which, if the filter is clogged, allows oil to pass through without cleaning it—dirty oil in the engine is better than dry operation.
The cheapest filters often don't have one and are more prone to clogging.
The second reason: extended oil change intervals.
Active driving immediately after starting the engine
photo: publicdomainpictures.net
It often takes a few seconds for motor oil to reach every nook and cranny of the engine, especially in cold weather.
If you start turning the engine at high speeds immediately after a cold start, some of its components may work for the first few seconds with virtually no lubrication. This won’t kill the engine right away, but it will definitely limit its service life.
Storage
The drug belongs to hazard class III. It is non-toxic, does not cause poisoning of insects and animals, and does not destroy the soil structure. Shelf life: 2 years.
It is recommended to store in a dry place at temperatures up to + 30 degrees. Does not lose its properties when dropped to – 30 degrees. After the expiration date, the drug must be disposed of. Make sure that the packaging is not damaged and keep it away from children and animals.
Watch the video material about the growth stimulator Bud.
Engine overheating
photo: assets.superstreetonline.com
At high temperatures, engine components expand, displacing the oil film from tight contact points.
Overheating can be the result of a malfunction in the cooling system (fan failure, stuck thermostat, coolant leak, pump failure), excessive thermal load on the unit, a broken water pump drive belt, and so on.
Warning! Overheating can be both a cause and a consequence of engine seizure.
Recycling of auto junk
Firstly, there is such a topic as recycling old cars. Workers of such services sometimes resort to cunning maneuvers for good purposes. They purposefully kill the diesel engine. The point is that there is a risk. Old cars that are running, even if they are damaged and awaiting their turn for recycling, can again end up on the “junk car” market . To prevent this, a way has been invented to kill the engine, the main driving force of the car.
This is done in this way: after completely draining the oil from the engine, so-called liquid glass (sodium silicate) is introduced into the system, then the car is started and left to idle until the engine stalls on its own, then they try to start it again.
The result will only be a broken motor. The entire “killing” process takes anywhere from 3 to 7 minutes. Thanks to this, recycling employees quite legally send junk cars to the press for melting.
Source
How to avoid engine seizure?
photo: unsplash.com / Evan Hein
The best way, the most logical and if not the only way to avoid engine seizure (that is, serious damage) is to regularly change the oil and filters and check the condition of the engine.
It doesn't hurt to carefully monitor the coolant temperature, although a sharp increase in temperature is often a signal that something has just happened to the engine.
You should also not ignore the oil pressure indicator light on your dashboard. Many drivers check the oil level only when the red light with an “oil can” starts flashing on the panel.
It's definitely too late because when this light comes on, it means that the engine oil pressure has dropped below normal, providing only minimal lubrication to the engine components.
see also
The principle of operation of the engine speed limiter and their types
Always pay attention to the “Check Engine” light, carry out timely maintenance, filling the engine only with high-quality motor oil and other fuels and lubricants.
Do not overheat the engine and, finally, do not trust engine repairs to incompetent mechanics.
AutoXS.ru - Auto Encyclopedia
The photo shows traces of rubbing of the piston skirt on the walls of the cylinder block. If you do not open the engine in a timely manner, a meat grinder may occur, as in the first photo. Signs of a seized engine: how to determine that the engine is seized?
If there is a significant decrease in engine power, the low engine oil pressure indicator light comes on, or if there are strange noises coming from the engine compartment, you should have your vehicle's engine checked.
Pay attention to the symptoms of engine seizure:. Pipe Tapping As discussed, a slight tapping sound may indicate a seizing problem. The noise occurs when the starter hits the flywheel.
The noise occurs when the starter hits the flywheel.
Pipe Tapping As discussed, a slight tapping sound may indicate a seizing problem. The noise occurs when the starter hits the flywheel.
SmokeSmoke or even an open flame coming from under the hood can be another sign of a seized engine. Since the starter in this state cannot crank the engine, the wiring overheats, which causes smoke or even fire.
Engine failure is a fairly obvious sign of problems with your car. But the engine should not be brought to this state. A complete engine failure means that the engine will not start under any conditions. Battery-powered lights, radios and other components can continue to operate.
Loosening of engine parts When the fastening of a part of an internal combustion engine, the piston, becomes loose, it can pierce the cylinder head. You can find out about such a problem by performing periodic engine checks.
Lack of engine oil is the most common cause of seizure. Low oil levels lead to increased friction, overheating and other problems that cause the engine to seize. This problem can also be caused by water or rust accumulated inside the engine. Another possible cause is breakdown or failure of engine parts, but engine seizure is unlikely.
On the video collection you can watch real cases of engine wedges from life:
Source