The ignition module on injection VAZ 2109 is deservedly considered one of the most complex electrical components. If the injectors have a module, then the carburetors have the simplest coil.
The actual, but incredibly important task of the module is the generation of high voltage current, which can reach 30 thousand watts. The current follows high-voltage wires to the spark plugs, which create a spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
The classic ignition coil is one of the components of the module, so the system works on a much more complex principle than on carburetors.
The procedure for connecting high-voltage wires on a VAZ 2109 (carburetor, injector)
The ignition module on injection VAZ 2109 is deservedly considered one of the most complex electrical components.
If the injectors have a module, then the carburetors have the simplest coil. The actual, but incredibly important task of the module is the generation of high voltage current, which can reach 30 thousand watts. The current follows high-voltage wires to the spark plugs, which create a spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
The classic ignition coil is one of the components of the module, so the system works on a much more complex principle than on carburetors.
The principle of operation of a four-stroke power plant
You can understand why it is important to connect high-voltage wires correctly if you study the principle of operation of the power plant. The VAZ-2109 carburetor or injector operate on approximately the same principle, since both power plants are four-stroke
- First, the cylinder volume is filled with the fuel mixture and exhaust gases. This process is called "inlet".
- The engine then goes into compression. With it, the valves are closed, and the crankshaft and connecting rod move the piston upward. The mixture of fuel and air is transferred to the combustion chamber.
- During the expansion stage, the ignition is switched on and a spark appears. It ignites the fuel mixture, resulting in the formation of gases. They put pressure on the piston, causing it to move down. This force is transmitted through the connecting rod to the crankshaft.
- The process is completed by the “release” of exhaust gases through the exhaust system.
How to check the ignition on an injector
First you need
o will conduct a full computer diagnostic of the system. If problems are found, the on-board computer ( ] - “computer”) is a device or system capable of performing a given, clearly defined, changeable sequence of operations
) will indicate them by way (
place, direction or the process of movement (or change); up to the scientific abstractions of this concept: Path - a system of communication along which passage or travel is carried out, along which
) red indication (
methods and techniques of observation, recording, control, characterization and assessment of the state and stages of development of various processes, objects and research systems to establish and control dependencies on
) “Check”.
Pushcha ( forest (indigenous forest, primary forest, primeval forest, pushcha) - a forest that has not been changed by human activity and natural disasters
) the whole reason for the breakdown (
toponym in Russia
) is not the electronic ignition module, but problems with the damper (
technique - a device for shutting off openings and pipelines: Damper - a valve for closing a chimney or ventilation duct Damper - a cover for closing the inlet of a furnace or
) throttle assembly (
a method of connecting and protecting linear material, for example, rope, by tying and weaving
).
Here you will need a multimeter with which you need to measure voltage ( Electrical voltage between points A and B - the ratio of the work of the electric field when transferring a test charge from point A to B to the value of this test charge
) in a system ( a set of elements that are in relationships and connections with each other, which forms a certain integrity, unity
).
After ( high-ranking diplomatic representative of his state in a foreign state (in several states concurrently) and in an international organization; official representative
) turning the key in the ignition system, indications (
testimonies are information expressed in oral responses of witnesses about circumstances relevant for consideration and resolution of the court case
) of the device must be the following:
- total voltage of the on-board circuit is 12 V;
- The throttle valve sensor readings are 0.5 V, while the throttle valve is open only 1%.
How to set the ignition
In order to correctly adjust and set the ignition on a UAZ, you must follow the sequence of actions that are given in the user's repair manual.
Before you begin adjusting the ignition system, you must place the vehicle on an inspection pit or a special platform for repair work and apply the hand brake. The wheel mechanisms of the vehicle must be secured with a stopper or stop. The power unit must be turned off.
After this, you can begin installing the ignition. To do this, it is necessary to fix the piston of the first cylindrical element in the position of the highest dead center. In this case, you need to check that the hole on the crankshaft pulley coincides with the pin on the cover of the timing gear block. It is necessary to slightly lower the mounting bolt located on the plate to the distribution equipment sensor housing.
Then remove the cover from the distributor and rotate the crankshaft 180°. The octane corrector must be in the zero position. Then it is necessary to tighten the pointer to the housing of the distribution mechanism sensor with a bolt so that its position coincides with the octane corrector mark.
After this, we adjust the slider by rotating it counterclockwise. This will help eliminate gaps in the drive. When the tip on the stator coincides with the red mark, you can fix the plate with a bolt.
Then you need to replace the switchgear sensor cover and check that the ignition leads are installed correctly according to the operating order of the cylindrical mechanisms (1-2-4-3). You need to count in a counterclockwise direction. The ignition setup on the UAZ is completed.
Now it is recommended to start the power unit and warm it up to operating temperature (about +80°C). Then you need to sharply press the accelerator at a speed of 40 km/h on a straight section of the road.
In case of severe detonation, it is recommended to turn the distributor sensor 0.5-1 turn on the octane corrector scale in a counterclockwise direction.
If there is no detonation, you need to increase the advance angle by turning the sensor clockwise.
Lada 2109 › Logbook › Dual-circuit ignition on the VAZ 2109
I suffered several times in the winter with starting the engine. Even when it’s not cold, but at 0 degrees, you come to start it and the car is silent. You unscrew the damp spark plugs and the battery eventually dies! With a good battery, it starts normally. As it turned out in the end, I had a contact ignition coil B- 117 from the classics. I immediately changed it to a coil from BSZ. And the car started to start and drive much better, but I didn’t stop there and decided to make a dual-circuit ignition with 2 hall sensors, 2 switches and 2 coils from the Volga ZMZ- 406
To begin with, I started assembling the distributor because it is the most basic and thinnest part of the system. I took the distributor from OKI as a basis, or an ordinary nine-wheel one. I just had it from the window lying in the garage. I completely disassembled it and started installing the second one. hall sensor directly to the standard platform at an angle of 90 degrees. Marked the approximate position of the 2nd sensor. On the platform there are risks of the approximate position of the middle of the sensor:
Drilled and tapped the threads for the bolts:
Then I carefully cut the hall sensors themselves with a metal cloth so that they do not interfere with each other. It looks something like this:
Then I modified the shaft, replaced the ignition angle advance weights with nine-shaft ones. They are smaller and lighter than those of the Oka, the photo shows Okushinsky weights! And accordingly, I also replaced the springs. The curtain remained the standard Okushinsky one, I didn’t touch it. If you make it from a nine-shaft shaft, then the curtain must also be modified sawing off two opposite ones so that it looks like in the photo:
That's all for the shaft! Next, I cut out a small piece from the distributor body itself to attach the fork of the 2nd hall sensor, drilled a hole and cut a thread for the bolt
Then I put the whole thing together. Here’s what happened:
Note: during assembly it turned out that the platform on which the hall sensors are attached from the Oka is larger than from the 2109 and it turned out to be easier to mount the sensor, so another one +, It is advisable to buy the same sensors themselves in the same store from the same batch as they are slightly different! That's all for now with the distributor!
Then I bought the rest of the necessary parts: 2 coils from the Volga ZMZ-406, a wiring harness for the BSZ 2108, an “Astro” switch, as I already had the same one
I connected the wiring according to the diagram:
Note: when connecting according to scheme 1, the tachometer will show half the revolutions. If you want to make a normal tachometer, then there is also scheme 2, you will need to solder in 2 KD213A diodes. But I did not do this and did it according to scheme 1. And don’t try to connect wires without diodes according to scheme 2; thereby you parallel both coils and it turns out that all 4 spark plugs spark at the same time when both hall sensors are triggered! Tested personally)
I made a metal mount for the coils, but it didn’t turn out very well:
And now about the most important thing: for the system to work well, you need to adjust the synchronization of the hall sensors so that the spark on all cylinders is the same advance. To do this, you need to make the opposite mark on the flywheel, this will be the TDC of the 2nd cylinder. You need to count 64 teeth along the crown from the standard mark. And Using a strobe light, align both marks from the 1st and 2nd cylinders, moving the 2nd hall sensor up and down or both sensors in the direction of the white arrows. To do this, I drilled holes with a thin drill in the sensors to move.
Members of the resistance - magazine Behind the Wheel
It starts poorly, jerks, does not pull... Very often, such engine ailments are treated by simply replacing high-voltage wires. The nature of the phenomenon is clear - we have written about it more than once. As is known, the spark energy depends on many parameters, including the power of the high-voltage pulse that reaches the electrodes of the spark plug. In other words, from losses in the ignition line. In a carburetor engine, the “science”, in general, ends there, but in an injection engine the influence of the control system is added. Indeed, if the combustion intensity is insufficient or if flares are missed, the feedback will work through the control system, increasing the fuel supply - to compensate for the supposedly excess oxygen. This will affect both gasoline consumption and especially the toxicity of exhaust gases. And if so, then each high-voltage wire actually becomes part of the engine control system!
Hence the purpose of our examination: analysis of the influence of various high-voltage wires on the main indicators of a real VAZ-2112 engine. As usual, everything was purchased from large metropolitan auto stores. We took two sets of wires from ten different companies - domestic and foreign. They took two for a reason - in order to prevent possible accusations of bias. Like, you can’t judge by one example! Let's not argue - it's better to change the verification procedure.
A laboratory ohmmeter was used to determine the resistance of each wire - all 80 of them. Then they measured the length of the wires, divided one by the other and got the linear resistance - in kilo-ohms per meter. Logically, for the same sets there should not be a large spread - the cable is cut from the same reel. But…
This happened in all sets from eight companies. But at Caesar in two wires it jumped almost an order of magnitude compared to the other six. Master Sport repeated the same picture, albeit for one wire. Little things? Maybe. But so that they do not distort the overall picture, we selected test kits for these brands so that the wires had approximately equal linear resistance, not without reason assuming that they would be quite standard. To compensate for the trouble, they allowed themselves to mutter that the manufacturer should have taken care of this.
From brand to brand, resistance varies by almost three orders of magnitude - from tens of ohms (for the Pro.Sport kit) to almost ten kOhms (for the Master Sport kit). Is this important for the motor? Let's find out.
For testing, we took spark plugs with a minimum resistance of the noise suppression resistor - we settled on Bosch Platin FR7DPX. At the same time, out of twenty candles, four were chosen with almost the same resistance - 3.2 kOhm. The spark plugs, of course, are in good working order - they were rechecked beforehand.
With each set of wires, the engine had to work out the so-called universal test cycle - with driving both in the city and on the highway. Its power, instantaneous fuel consumption and exhaust gas toxicity were measured. And out of love for art, they organized another test - they checked the uniform operation of individual cylinders. To do this, having brought the engine to a certain mode, the fuel supply to the cylinders was turned off one by one. Then, by simple subtraction, the indicator torque of each cylinder was determined and compared.
How to check high voltage ignition wires?
Checking high-voltage ignition wires for breakdown is carried out in one of three ways.
Visual inspection is the easiest way to check and detect damage to the insulating layer of high-voltage wiring. During this check, you need to make sure that there are no cracks, cuts or noticeable abrasions on the insulation surface. A breakdown can be visually determined by sparking. To do this, in the dark, just open the hood of the car, start the engine and turn off the lights. An insulation breakdown will be noticeable to the naked eye by sparks running through the wiring.
It is often impossible to visually determine that the high-voltage ignition wire is faulty. In such cases, the old proven method is used, which consists of the following steps. The engine is started and left to idle. Next, the contacts are removed one by one from the spark plugs and then put back on. All operations must be performed with rubber gloves, without touching the car body with your body. The conductor is faulty if, when it is disconnected from the spark plug, engine operation does not change.
The next method is to use a piece of wire stripped at both ends. The check is carried out at night with the engine running. One end of the segment is connected to the car body (“ground”), the other end must be driven along the high-voltage ignition wiring. If a spark appears when carrying out insulation, there is a breakdown in this place. This way, not only the insulation is checked, but also the plastic protective caps.
Checking high-voltage ignition wires with a multimeter
Car owners usually measure voltage with a multimeter, but the same device can also determine resistance, which is very useful when checking. To measure, high-voltage ignition wires are first disconnected or completely removed. The multimeter needs to be switched to resistance measurement mode, then the probes of the device need to touch the two ends of one wire. The device will show the measured value.
If, as a result of the test, one conductor turns out to be faulty, the rest will soon fail. Therefore, replacing the high-voltage ignition wiring is done as a set, rather than as separate wires. These products most likely will not be sold to you separately.
3 Tips for Selecting High Voltage Ignition Wires
Tip #1.
Carefully study the information about the product (manufacturer, terms of use, etc.) - it should be available both on the packaging and on the product itself.
Often, on fakes, the English word “silicone” is misspelled. This phenomenon is so widespread that it was even found in one authoritative print media on automotive topics. The authors mistakenly and without verification used the word “silicon,” which actually translates as “silicon.”
Tip #2.
Evaluate the quality of caps on high-voltage electrics.
The caps are made of silicone rubber; they are necessary to protect the wiring contacts and ensure the tightness of the connections. The minimum wall thickness of the cap is 3 mm. As inspection often shows, the electrical circuit is broken precisely at the junction of the conductor terminal with the contacts of the ignition system elements. This usually happens when the wiring is removed inaccurately or when there is a poor connection with parts of the ignition system due to poor fit, oxidation processes, etc.
Tip #3.
Evaluate the quality of the highest voltage ignition wiring.
Silicone products are of the best quality today. There are several simple ways to check their quality. For example, you can expose the cable to open fire. If the insulation is of high quality, it will not be easy to melt or even ignite it. Another way to check is to twist the wire tightly. If displacement or sliding of the core relative to the cable sheath is felt, and a characteristic crunching sound occurs, it means that the adhesion of the sheath to the insulation is poor. Also try moving the insulation layer along the conductor. There should be no displacements during testing; the cable must be solid. Otherwise, when installing or dismantling the wiring, the protection may be impaired.
Useful materials about cars
here!
Source
How to connect the ignition switch
Replacing the ignition switch involves dismantling the old one and installing a new mechanism with its subsequent connection. To remove the old lock you will need a Phillips and flathead screwdriver.
The procedure for dismantling the old vehicle ignition system lock:
- Remove the fasteners from the lower trim panel of the steering column.
- Insert the key into the lock and set it to the zero position, at which the steering mechanism will be locked.
- Remove the steering column.
- Unscrew the ignition switch mounting bolts.
- Insert a flat-head screwdriver into the small technological hole and press the latch that holds the lock.
- Push the lock out of its seat.
- Disconnect all system wires.
- Install a new lock, connect the wires and reassemble the mechanism, performing all the steps in reverse order.
All wires are connected in a clockwise direction.
To terminal number 50 you need to connect a red wire, which is responsible for the stable operation of the starter device.
To terminal number 15 you must connect a blue wire with a black stripe, which is responsible for heating the vehicle interior.
A pink wire is connected to pin number 30, and a brown wire is connected to 30/1.
The black wire must be connected to the INT connector, which is responsible for the operation of the side lights and headlights.
After all the wires are connected, you need to connect the battery terminal. A black wire should be connected to the top of the terminal. Then you need to start the engine and check the serviceability and functionality of the entire ignition system. First, it is recommended to check the operation of electrical devices, and then the serviceability of the starter mechanism.
If all wires are connected correctly, then when the ignition system key is in the zero position, all elements of electrical equipment will be disconnected from power. When the key is turned to the first position, the system is activated, which controls the internal combustion engine, generator set, headlights and brake lights, as well as washers and windshield wipers. When the key is moved to the second position, the starter is activated, the anti-theft system rod extends and retracts when the key position is changed.
If this does not happen, it means the wires are connected incorrectly. It is necessary to disassemble the mechanism and repeat the connection procedure.
What can multiple misfires lead to?
Single misfires are only a signal to the owner of a VAZ 2114 about problems with the engine.
Numerous incidents entail the following consequences:
- As a result of misfires, unburnt fuel will enter the catalytic reduction system. Because of this, the converter will overheat and fail.
- With repeated misfires, some of the gasoline will enter the lubrication system through the walls of the idle cylinder. Oil diluted with gasoline will lose its properties and will not be able to provide high-quality lubrication of loaded engine elements.
- All these factors can lead to engine failure and the need for expensive repairs.
The operating order of the VAZ 2106 cylinders: diagram, photo, video instructions
Much depends on the operation of the cylinders, so this unit must always be in working condition. Especially when it comes to old VAZ 2106 cars. In this article you can find out what is the operating order of the VAZ 2106 cylinders and for what reasons they may not work.
Work distribution
It may be necessary if it is necessary to identify a malfunction in the operation of the motor. Such breakdowns consist of unstable engine operation, that is, its tripping. It is necessary to diagnose the unit in cases where the engine power is too low, and the internal combustion engine itself regularly trips.
It should be added that the internal combustion engine throttles not only when driving at speed, but also in neutral gear. In addition to tripping and reduced power, fuel consumption in the vehicle increases. This sign is initial. In practice, interruptions in the operation of the power unit are observed when the carburetor is incorrectly adjusted, the spark plugs are broken, or one of the cylinders fails. In addition, air may leak into one of the cylinders.
But in order to accurately identify the malfunction, you need to know the operation of the cylinders in the vehicle. In a VAZ 2106 car it is as follows: 1-3-4-2. Accordingly, the numbers directly indicate the numbers of the cylinders themselves. The number “1” on the distributor cap is marked on the first cylinder. If you look at its cover from the side of the wires leading to the spark plugs, the cylinder operating mode will be 1-3-4-2.
Signs of malfunction of high-voltage ignition wires
Evidence that the ignition cables have become unusable are the following signs:
- difficulty starting the engine, especially in wet weather;
- At medium and high speeds, unstable engine operation is noted;
- the engine does not develop full power;
- increased fuel consumption is observed.
As a rule, when there is severe wear on the wire insulation, many microcracks appear, due to which current leakage occurs. As a result, the wire is not able to transmit to the spark plug a current that is sufficient in magnitude for its normal operation. This significantly increases the spark generation time and interferes with the correct operation of the engine cylinders.
Quite often there are cases when wires are damaged as a result of contact with any engine elements. Situations of loss of cap tightness are also possible, and as a result - oxidation of contacts and current leakage. Regular cleaning of contacts is a mandatory procedure, especially when operating a vehicle in difficult climatic conditions.
How can a car owner check the wires for leaks? In fact, everything is very simple: in a dark garage, open the hood and start the engine. Leak areas will glow quite brightly in blue. There is a slightly different method: instead of a spark plug, a spark gap is installed (two electrodes in one housing) and the energy supplied to the spark plug is controlled using it.
In order to increase the durability of the insulation, it is recommended to monitor and constantly keep it clean. The contacts between the spark plugs and each wire are also subject to constant checking and cleaning.
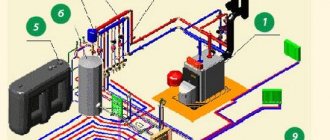
High voltage wires
Features of the ignition module
Now let's talk about a more complex issue - the ignition module and its design features.
The design includes several components, each of which has its own nuances.
Component
Peculiarities
There are always two coils on a VAZ 2109. This mechanism is responsible for generating current
Switch keys also work together. Through them, the current goes to the spark plugs, plus the controller regulates the time the current is turned on, which is calculated by receiving information from the crankshaft sensor
Electronic control unit
Responsible for distributing information in the form of electronic impulses
High-strength plastic is used for its manufacture, which largely ensures the durability and reliability of the device.
Ignition coil
Location
Any work related to repair, testing, and maintenance of the ignition module will be impossible to perform if you do not know basic things - the location of the device.
You can find the ignition module (ignition module) in the engine compartment. Find the high voltage wires that go to the spark plugs. One end is connected to them, and the other goes to the module. The MZ is small in size and enclosed in a plastic housing.
Device location
Principle of operation
Initially, on carburetor cars, the system worked due to the presence of an ignition coil. With injectors everything is somewhat different.
- Initially, the ignition coil is turned on, generating a high voltage current. The coil operates on the principle of magnetic induction;
- Then the electronic control unit MZ is connected to the work, performing the functions of control, transmitting commands, and ensuring the flow of current required by the characteristics to the spark plugs;
- Next, the spark plugs activate the spark, ignition occurs, and so on.
MH malfunctions
The ignition module often shows the most basic sign of failure - lack of spark. But this is not the only indicator of a malfunction. These also include:
- Lack of dynamics when accelerating the car. Trying to quickly pick up speed, you can clearly feel failures in engine operation;
- The engine does not produce the usual power; in some cases, the engine is not able to pull the car uphill;
- The idle speed fluctuates;
- One of the pairs of engine cylinders refuses to work. Here, most likely, there is no current that should come from the ignition coil.
To eliminate problems with the MH, the first thing you need to do is check the spark plugs, and then make sure the other elements are working.
Features of connecting high-voltage wires to the VAZ 2114
High-voltage ignition wires of the VAZ 2114 are part of the ignition system, through which an electrical impulse is transmitted from the module to the spark plugs. When the current hits the spark plugs, the fuel mixture ignites in the combustion cylinders, which gives rise to a new stroke of the engine.
BB wires must be of high quality
The design of the GDP, unlike conventional wires, is quite complex. In addition to the conductive core (which is made of copper) and protective insulation, they have metal tips and plastic protective caps.
Metal tips act as contacts; they fit into the sockets on the spark plugs and the ignition module. The durability of the GDP directly depends on how well the tips are made. When purchasing, be sure to check the strength of their attachment to the wire.
Finding the ignition moment in the ignition
On engine 402, ignition adjustment occurs according to the following algorithm and order:
- The crankshaft occupies a spatial position corresponding to 5 degrees of advance in ignition of the fuel mixture;
- This position can be easily achieved by aligning the mark on the pulley with the recess on the motor block;
- The coincidence means that the power plant has marked the end of a full piston stroke.
With the distribution sensor removed, adjustments are made as follows:
- I remove the spark plug from the head of the combustion chamber of the cylinder, which is listed as No. 1 in the order of fuel ignition;
- I cover it with a sheet of paper and turn the engine crankshaft;
- The air pushed out by the piston blows off the sheet, which indicates that it has reached the vertical maximum, from which the stroke begins;
- Then, using the keys, I set the octane corrector scale to 0.
Wiring replacement process
Before the VAZ 2114 armored wires are replaced, it is necessary to remove the old cables. To do this, you should: 1. Turn off the engine ignition. 2. Open the car hood. 3. Remove the old wiring leading to the engine and ignition unit. To maintain the order of connecting high-voltage wires of the VAZ 2114, you must be guided by the following diagram:
Cylinders are numbered from left to right. In the module, the internal ignition cylinder 1 is located on the lower left side. The second and third cylinders are located in the left and right compartments, respectively. The output of the fourth cylinder is located at the bottom in the right compartment.
What are the dangers of ignition malfunctions?
The optimal operation of the entire AP depends on the performance of all its elements, as well as the set torque. In practice, carburetor internal combustion engines require more precise adjustment.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the problems in more detail:
- The power unit detonates. When the driver presses on the gas, ringing sounds begin to be heard from under the hood. In practice, such problems appear in vehicles due to the timing being set too early. As a result, this causes the internal combustion engine to malfunction, and this can subsequently lead to deformation of the piston rings.
- When the engine starts, black smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe. Such problems usually indicate that the advance angle is set incorrectly, the timing is too late. Of course, correct adjustment will allow you to get rid of this problem.
- When idling, the power unit oscillates and operates unevenly.
- The internal combustion engine operates intermittently, when the driver presses the gas, dips appear. That is, the driver presses on the gas, but the car does not accelerate.
- The power of the power unit has decreased, that is, it takes much more time to gain speed. This problem may be due to the fact that the fuel-air mixture does not completely burn in the cylinders of the internal combustion engine.
When such problems occur, the car owner should start diagnosing the SZ, and if necessary, adjust the torque. In practice, most malfunctions are associated with this. But before you start making adjustments, you need to make sure that all components are working correctly. It is necessary to diagnose the spark plugs, the condition of the high-voltage wires, the coil and the distributor. Only if all these elements are intact, you need to start adjusting.
How to check high voltage wires
Finding high-voltage wires under the hood is not difficult, and diagnosing them is not fraught with any difficulties. There are three ways to check high-voltage wires, each of which allows you to determine whether there is a breakdown in them.
Visual diagnostics
The easiest way to check spark plug wires for insulation damage is to visually inspect them. It is necessary to carefully check that there are no cracks, cuts or severe abrasions across the insulation area.
Another way to visually check spark plug wires is to observe their operation at night. It is necessary to open the hood of the car at night, start the engine, turn off the headlights and watch the high-voltage wires. If they have strong insulation breakdowns, in the dark the “crickets” will be visible to the naked eye.
This is interesting: Reasons why there is no spark on a 4T scooter
Wire check
To check the spark plug wires, an ordinary wire with stripped ends on both sides can be used. In the dark, with the engine running, it is necessary to short-circuit one part of the wire to ground (car body), and run the other part along high-voltage wires in search of a place where the stripped tip will begin to produce a spark.
It is important to check not only the insulating material around the conductor, but also the plastic caps
Diagnostics with a multimeter
A multimeter in automotive diagnostics is most often used as a voltmeter, but it also has another useful function - the ability to measure resistance. To take measurements, you must completely remove the high-voltage wires (or disconnect one wire on both sides). Next, with the probes of the device set to ohmmeter mode, you should touch both sides of the wire, as a result of which the multimeter will display information about the resistance.
The resistance of serviceable high-voltage wires is up to 10 kOhm. At the same time, it can vary practically from zero. This depends on the type of wires themselves, the insulation used in them, the length, the presence of microdamages, and so on.
Checking for correct installation
If the order is followed without errors in the ignition of the 402 engine, then the next task will be to check the power plant while the car is moving:
- We go out onto the highway and, when driving 60 km/h, turn on fourth gear. We are accelerating. The appearance of short-term detonation knocks indicates that the ignition is installed correctly.
- Prolonged detonation knocks are confirmation of incorrect setting of the advance angle.
In this case, you should reduce it with an octane corrector, moving it to one notch. If detonation cannot be heard at all, then the advanced ignition angle of the fuel mixture should be increased. And check again for correct installation by accelerating the car to 60 km/h and shifting to fourth gear.
OPERATIONAL CHECK
To accurately determine whether it is time to change the high-voltage wires of the VAZ, you need to check their performance with a multimeter.
This operation will take you no more than 15 minutes:
- Turn off the ignition;
- We remove the wires: disconnect the first end from the ignition module, the second from the cylinder;
- We switch the tester to ohmmeter mode and connect the multimeter probes to the wire contacts.
If the high-voltage wires on the VAZ 2114 are in normal technical condition, the multimeter will show a resistance within the value indicated on the wire insulation; if the readings are different, the armored wires on the VAZ 2114 need to be replaced. The process must be repeated on each wire in turn.
If the test shows disappointing results, there is a possibility that the problem of increased resistance lies in oxidized contacts. In this case, you can try to revive the VVP by wiping the contacts with VD-40 or carburetor cleaning fluid.
Typical electrical wiring faults
Malfunctions, as a rule, boil down to the fact that electric current either does not flow to the spark plug at all, or if it does, it is in limited quantities. And this happens for the following reasons:
- When the current-carrying conductor through which the impulse passes breaks
- If there is a current leak, this means that the insulation is damaged, there is a breakdown of current on the side
- The resistance value exceeds the permissible value
- There are problems with the contacts (either with the spark plug, or with the distributor and ignition coil).
If a current-carrying wire breaks, then an internal spark occurs, in other words, a spark discharge is formed between the ends of the broken wire, which greatly reduces the voltage and also causes a parasitic electromagnetic pulse to occur. So:
- The resulting impulse, of course, negatively affects the correct operation of the vehicle’s electrical sensors
- Just one such defective high-voltage electrical wire often causes vibration and interruptions in the operation of the motor.
- In addition, a damaged high-voltage electrical wire leads to ignition in the cylinder with some delay or even every other time, then the synchronization of the operation of the cylinders and the engine as a whole is disrupted
Checking electrical wires
Anyone can check the wires, and do it with their own hands; this does not require electrical knowledge, or special hard-to-find tools or assistants, only the knowledge of what to do and in what order:
- First, you need to check the spark plug wires on the VAZ 21093 visually for visible damage (for example, cracks, kinks, etc.).
- Then you should make sure that there is no breakdown, this can be done even in the absence of any measuring instruments, it will be enough to look under the hood, with the engine running, when it gets dark, if there is a breakdown, then a spark will be visible while the engine is running on the broken electrical wire
- You can also check high-voltage electrical wires using a wire; you just need to take a piece of wire at night and strip the ends on both sides. Then you need to close one end of the wires to ground (this is the body of the machine), and take the other end with your hands and move along the entire length of each electrical wire, not missing joints and caps, etc. A spark will occur at the breakdown points
You can also measure the resistance of high-voltage electrical wires; for this we need a tester (multimeter):
- Turn on ohmmeter mode
- We remove the wire from the spark plug of the first cylinder, disconnect it from the distributor (see The device of the VAZ 2109 distributor: the difference between contact and non-contact ignition systems and adjusting the ignition timing)
- We connect the multimeter electrodes to both ends of the wire and check the readings
For serviceable electrical wires, the resistance varies from 3.5 to 10 kiloohms, it all depends on the type of electrical wires themselves. The resistance value is usually indicated on the insulation of armored electrical wires. When checking each wire, the spread between the values cannot exceed 2-4 kiloohms. If greater variation is detected, the wires should be replaced. By the way, the replacement is made as a set, that is, all together at once; the price here is not a reason to save money all together. In conclusion, we present to your attention the resistance readings for the most popular armored electrical wires:
- Tesla brands have a resistance of 6 kOhm
- Brands Slon (Elephant) with a range from 4 kiloOhm to 7 kiloOhm (where 4 kiloOhm goes to the 1st cylinder and so on up to 7 kiloOhm on the last cylinder)
- ProSport brands have almost zero resistance
- Brands Cargen (Kargen) with a resistance of 0.9 kiloOhm
Arrangement of high-voltage ignition wires
High-voltage wires consist of a conductive core, a protective layer (also called insulation), special metal contacts and caps. There are several types of high-voltage wires. The usual (cheap) type of wire is one that consists of stranded wire with thick insulation. The resistance of such high-voltage wires is zero, which does not properly affect the operation of the ignition coil.
The second expensive type of high-voltage wires consists of a thread placed in the center covered with ferroplast on top, which is wound with iron-nickel wire. This type of high voltage wire has sufficient resistance, which greatly reduces radio interference and is suitable for the normal operation of the ignition coil. To further reduce radio interference, increased insulation is used. It should be noted that the correct order of connecting high-voltage wires plays an important role in the normal operation of the engine ignition system.
Insulation of high-voltage wires is designed to prevent electrical leakage and isolate the conductor from moisture and other contaminants. Insulation can be single-layer or multi-layer.
Metal contacts of high-voltage wires (tips) are used to establish a connection between the wire cores and the spark plug sockets and distributor.
Requirements for high-voltage wire lugs:
- Ensuring reliable contact with the wire veins;
- Reliable and durable fastenings;
- Sufficient corrosion resistance and high-quality insulation.
Caps for high-voltage wires ensure tightness of contact connections, protecting the connection points from moisture and current leakage.
The procedure for connecting high-voltage wires: checking and replacing high-voltage wires
To check the wire, you will need a multimeter tester, with the help of which you can measure the resistance of the wires - which should be no more than 20 kOhm (usually the wire of 1 cylinder has a resistance of up to 10 kOhm). If the wire resistance is higher than 20 Kom, it must be replaced. Carefully inspect the wires for wear. When installing wires, do not allow kinks, distortions or tension on the wires.
Malfunctions of high-voltage wires
The main malfunctions of high-voltage wires include electrical circuit breakage and current leakage.
Causes of the malfunction: careless removal of the wire, poor connection, oxidation and subsequent destruction of the high voltage wire core. Current leakage occurs due to moisture entering the connection. At sub-zero temperatures, the insulation of high-voltage wires becomes rigid and the risk of damage to the wires increases. The service life also affects the wear of high-voltage wires. After all, when the engine is running, vibration occurs, which affects all connections, simply loosening them. The connections are also affected by the increased temperature that comes from the engine.
Recommendations for caring for high-voltage wires:
Periodically check high-voltage wires for damage. Check the reliability of connections between the tip and the elements of the ignition system;
Carry out all manipulations to remove and install high-voltage wires carefully and carefully, without tugging at the insulation.
Car ignition installation procedure
Construction machines and equipment, reference book
Category:
Car device
The ignition is installed to ensure normal operation and obtain the greatest power and efficiency of the engine. It is carried out if the ignition distributor is removed from the engine or if the ignition timing is not set correctly.
Installing the ignition on a GAZ-66 car in case of removing the ignition distributor is carried out in the following order: 1. Set the piston of the first cylinder to a position 4° before TDC on the compression stroke according to the marks on the flywheel and the arrow in the flywheel housing window. To determine the compression stroke, it is necessary to unscrew the first cylinder.2. Set the octane corrector to “O”, check the condition of the breaker contacts and the gap between them, and adjust if necessary.3. Insert the ignition distributor so that the vacuum regulator is directed upward, and by turning the drive shaft, insert the shank into the groove of the drive shaft.4. Using a screw, secure the fixed octane corrector plate to the drive housing and connect the wire to the distributor terminal.5. Loosen the nut securing the drive housing holder and turn the distributor housing to set the breaker contacts to the beginning of opening. It is better to determine the beginning of the opening of the contacts by the control light, for which connect it between the breaker terminal and ground (on cars with a contact-transistor ignition system, connect it between the unmarked terminal of the ignition coil and ground). Then turn on the ignition and, if the control lamp lights up, turn the distributor housing clockwise until the lamp goes out, and then slowly turn the distributor housing counterclockwise until the lamp lights up. In this case, the ignition distributor rotor must be located against the electrode with the number “1”.6. Tighten the nut securing the drive housing holder.7. Replace the distributor cap and connect the wire from the side electrode of the cap with the number “1” to the spark plug of the first cylinder. Connect the remaining wires to the spark plugs in the order of engine operation (1-5-4-2-6-3-7-8), following from electrode I clockwise.8. Connect the tube to the vacuum regulator.9. Check the correct installation of the ignition with the mileage of the loaded vehicle. To do this, on a flat road with a vehicle speed in direct gear of about 30 km/h, sharply press the throttle pedal all the way and hold it in this position until the vehicle speed reaches 60 km/h.
Rice. 1. Determination of TDC and setting the ignition on the ZIL-130 (ZIL-131) engine: 1 - crankshaft pulley; 2 — ignition installation indicator; I, II - ignition advance by 0° and 9°
If the ignition is installed correctly, during acceleration of the car, a slight detonation will be heard, which disappears when a speed of 40-50 jcm/h is reached. In case of strong detonation, it is necessary to move the index arrow of the upper plate of the octane corrector towards the “—” sign, and in the absence of light detonation, the index arrow must be moved towards the “+” sign. After adjusting the ignition timing, check the engine operation again using the vehicle's mileage.
The ignition installation on ZIL-131 and Ural-375D vehicles has features, the main ones of which are the following: 1. The piston of the first cylinder is installed in the compression stroke 9° before TDC with a contact ignition system and 6° before TDC with a transistor ignition system. Marks for setting the ignition are made on the engine crankshaft pulley (hole) and on the ignition setting scale.2. With a transistor ignition system, instead of installing contacts at the beginning of opening, it is necessary to rotate the distributor body to align the installation (red) marks on the rotor and stator of the pulse sensor and tighten the bolt securing the octane corrector plate to the distributor body.3. The spark plug wires are numbered, which makes it easier to distribute them among the cover sockets.4. On the Ural-375D vehicle, the ignition installation is not checked by mileage.
Read more: Main malfunctions of the ignition system and methods for detecting the causes of malfunctions
Category: – Car structure
How does a distributor work?
The distributor design is based on a rotating shaft (the so-called roller), driven by the engine camshaft. Devices and elements of the distributor are mounted on the shaft, which operate from the rotation of the shaft.
Operating principle of the distributor (ignition sensor-distributor) VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099
The operating principle of the distributor includes the operation of all its elements.
The rotor (runner) rotates and distributes the spark over the side contacts in the distributor cover. Then it goes through high-voltage wires to the spark plugs. The spark is supplied to the slider itself from the ignition coil through a movable central contact in the cover.
The Hall sensor has a gap through which a rotating screen with four teeth and four slots passes. When a screen slot passes through the gap of the sensor, a pulse is sent to the ignition system switch, which is a signal to supply a spark.
The centrifugal ignition timing regulator increases the ignition timing when the distributor shaft rotation speed increases due to the divergence of its weights and the impact on the Hall sensor screen, which allows the fuel mixture to burn in a timely manner and with maximum efficiency.
Operating principle of a centrifugal regulator
The vacuum ignition timing regulator, due to the vacuum transmitted to its housing, also affects the Hall sensor screen and increases the ignition timing angle when the load on the engine increases (the greater the load, the greater the vacuum, the greater the angle).
Vacuum ignition timing regulator for VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
By changing the position of the distributor relative to the scale on the housing of the auxiliary units, you can manually adjust the ignition timing up or down.
Adjusting the angle with a distributor, VAZ 2108 car
Notes and additions
— Two different ignition distributors (distributors) with different covers were installed on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars. For engines 2108 and 21083 this is distributor 40.3706, for 21081 – 40.3706-01. They are structurally identical, but differ in the characteristics of the vacuum and centrifugal ignition timing regulators. The distributor cover 40.3706-01, for engine 21081, is marked with yellow paint, the distributor 40.3706 is red. There are no differences between them, they are interchangeable.
Purpose of the distributor cover
The design of the ignition distributor cap (aka distributor) has remained and remains virtually unchanged throughout the entire history of the use of this device as part of the ignition system of gasoline engines:
- On most ignition caps, the contacts for the spark plug wires are marked with numbers that correspond to the serial numbers of the corresponding cylinders
- In addition to protecting the distributor mechanism itself from moisture and dirt, it also serves the purpose of alternating the supply of high-voltage current from the ignition coil winding through high-voltage wires to the spark plugs
- It is because of this narrow specialization that the distributor cap has undergone almost minimal changes along the evolution of all car systems
Let's look at the design and operating principle of this much-needed part.
The distributor cap is a molded part made of non-electrically conductive material (insulator) that has the following device:
- Metal contacts are pressed into this part - these are the side and central electrodes
- The number of side electrodes strictly corresponds to the number of engine spark plugs (but not cylinders, do not forget that there are engines in which there is more than one spark plug for each individual cylinder); the distributor cover on the VAZ 2109 in our case has four side electrodes
- A high-voltage (armor) wire coming from the ignition coil is connected to the central electrode from the outside
- To the side electrodes - high-voltage (armor) wires going to the spark plugs
- Inside the cover itself there is a central contact equipped with a terminal that has a spring-loaded contact element (“carbon”), which transmits voltage to the central (main) contact of the distributor rotor (ignition distributor)
VAZ 2114 engine repair
During the operation of the internal combustion engine on a car, various failures and malfunctions may occur, which can be eliminated by self-repair or with the involvement of specialists. The need for a major overhaul of the power propulsion system, with its proper operation, arises when the mileage reaches 150,000 km. In this case, a VAZ 2114 engine overhaul is needed.
Before you begin disassembling the engine, you need to drain the oil and coolant, and then wash the entire unit. Be sure to remove all attachments so as not to damage them during reassembly. Disconnect all pipes through which gasoline is supplied. Remove all systems and components related to the air supply, remove the air supply and exhaust hoses and pipes. Remove the cooling system pipes and crankcase breather. Don't forget to disconnect the throttle pipe. Remove the receiver, as well as the pipeline mounting bracket and the fuel rail, remove the injectors with regulators. Remove the wires with the ignition module and knock sensor. Unscrew the spark plugs. After this, unscrew all sensors. Remove the generator by first removing the tension belt. With the generator, remove all brackets and strips necessary for its installation and adjustment. Block the flywheel and remove the generator pulley. Remove the camshaft drive with the cover, tension mechanism and pulley. Unscrew the pump, remove the exhaust manifold and thermostat. Disconnect the oil filter and oil sump, then remove the oil pump. In order to remove the piston group, you need to unscrew the nuts from the connecting rod bolts and remove the cover. Since the flywheel is blocked, you need to unscrew its fastenings with the flange and remove the flywheel disk. Remove the caps from the main bearings along with the lower bearings. Carefully pull out the crankshaft
It must be handled very carefully to prevent damage and scratches. Remove the upper liners and thrust half-rings.
Many motorists, especially beginners who have just purchased a VAZ-2114, have wondered how the 8-valve injection engine that is installed on this car works. This article will discuss the design of the motor, its main characteristics, as well as dismantling and repair features. This information will be very useful for beginners and those who do not know how the main power unit works.
Video about the VAZ-2114 engine
The order of operation of all cylinders in the VAZ 2109 engine description, photo and video
Modern cars are mostly equipped with an internal combustion engine. In order to cope with various unforeseen situations on the road, you need to know the structure of the machine. The article describes the operating procedure of the VAZ 2109 cylinders, as well as possible malfunctions in the operation of the power unit.
Operating procedure
Often when repairing an engine, it becomes necessary to disconnect high-voltage wires. Some drivers, after disconnecting the wires, do not remember the order in which they were installed. As a result, there may be confusion with the wires, and if they are connected incorrectly, the car will not start. To avoid an unpleasant situation, you need to know how the internal combustion engine operates.
The principle of operation of the power unit is based on such a property of gases as the ability to expand when heated. A standard four-cylinder engine operates in 4 strokes:
- During the first stroke, the air-fuel mixture and part of the exhaust gases are “injected”. This mixture completely occupies the volume of the cylinder.
- In the second cycle, the “compression” process occurs. In this case, the valves are closed, and the piston moves upward due to the movement of the crankshaft and connecting rod. The working mixture fills the combustion chamber.
- On the third stroke, called “expansion,” a spark appears thanks to the spark plugs, which ignites the working mixture. The expanding gases exert pressure on the piston and force it to move downward. Then, thanks to the connecting rod, the crankshaft begins to move.
- On the fourth stroke, the process of “release” of exhaust gases is carried out. Through the exhaust valves they enter the exhaust system of the VAZ 2109.
In order for the operation of a multi-cylinder engine to be smooth and the crankshaft not to experience uneven loads, it is necessary that the work processes be carried out in a certain order.
There are different schemes that determine in what sequence the cylinders will function. The VAZ 2109 uses the following scheme: 1-3-4-2. The cylinders are numbered starting from the front cover of the power unit.
If we imagine the working process of the engine through the cylinders, then the order of operation is as follows:
- In the first cylinder, an upward movement occurs, the working process takes place: the air-fuel mixture burns, the gases expand.
- In the third, a “compression” process is carried out, in which the piston moves upward.
- The fourth receives the working mixture as the piston moves downwards, thus carrying out the “injection” process.
- In the second, the piston moves upward, while the exhaust gases exit through the exhaust valves.
Possible causes of failure
During the operation of the internal combustion engine, various malfunctions are possible. To detect them, you should perform the following sequence of actions:
- First you need to start the car. The engine should idle. At this time, you should listen to what sounds are coming from the exhaust pipe. If you hear regular popping noises, then one of the cylinders is faulty. The cause may be faulty spark plugs and lack of spark. The malfunction can also be caused by a large amount of incoming air or insufficient compression in the cylinder.
- It is necessary to inspect the candles. If there is carbon deposits, moisture or oxidation, you need to clean it. Check the gap between the electrodes, which should be 0.8 - 0.9 mm.
- Replace all spark plugs, regardless of their appearance and vehicle mileage.
- If there are irregular emissions, you need to inspect the high-voltage wires.
There should be no traces of oxidation on their tips, and the insulation should not be damaged. If defects are found, the wire should be replaced. Wires connecting to the coil - The gas distributor cap should be inspected. There should be no soot or cracks on it. The carbon contact should be checked for damage and wear.
- The rotor needs to be inspected. It must be solid and have no signs of burnout. All parts with defects must be replaced.
- The pressure in the cylinders is allowed to be no lower than 1.1 MPa, and the compression difference should not exceed 0.1 MPa. If the indicators do not correspond, engine repair is necessary.
CONNECTION FEATURES
The order of connecting high-voltage wires must be strictly sequential, since each cylinder of the engine corresponds to a specific socket on the ignition module. Considering that there is a numbering of the sockets on the ignition module body, the risk of confusing anything is minimal.
The procedure for connecting high-voltage wires of the VAZ 2114 injection type depends on the year of manufacture of your car. Fourteeners before 2004 had 4-pin ignition modules installed, and cars after 2004 had 3-pin coils.
The connection diagram for VAZ 2114 high-voltage wires to the ignition module (until 2004) is as follows:
Connection diagram for VAZ-2114 with ignition coils (after 2004):
In the pictures you can see the numbers of the landing slots. Each number must have a corresponding cylinder connected to it (cylinder numbering is counted from left to right).
To correctly install high-voltage wires on the VAZ 2114, follow the following algorithm of actions:
- Turn off the ignition. Open the hood and remove the power terminals from the battery;
- We remove the old GDPs from the mounting sockets on the module and cylinders;
- We remember the location of the high-voltage wires of the VAZ 2114 and connect new GDPs according to the diagram. Before replacing, it would not be amiss to draw this very diagram by hand on paper so as not to confuse anything;
- We connect power to the battery and, to check whether we did everything correctly, start the engine.
When installing the wiring, do not try to connect individual air intakes to each other with plastic clamps; to do this, you must use the comb holder that comes with them. A thin clamp can easily wear through the insulating coating. Also make sure that the GDP does not bend.
Connecting armored wires on VAZ 2115 and 2113 is carried out in a similar way.
Operating procedure for an inline 4 cylinder engine
The operating order of a 4-cylinder engine is designated as X―X―X―X where X is the cylinder numbers. This designation shows the sequence of alternating cycle strokes in the cylinders.
The order of operation of the cylinders depends on the angles between the crankshaft cranks, on the design of the gas distribution mechanism, and the ignition system of the gasoline power unit. In a diesel engine, the fuel injection pump takes the place of the ignition system in this sequence.
Of course, you don’t need to know this to drive a car.
It is necessary to know the operating order of the cylinders when adjusting valve clearances, changing the timing belt or setting the ignition. And when replacing high voltage wires, the concept of the order of operating cycles will not be superfluous.
Duty cycle
Depending on the number of strokes that make up the operating cycle, internal combustion engines are divided into two-stroke and four-stroke. Two-stroke engines are not used in modern cars; they are used only on motorcycles and as starters for tractor power units. The cycle of a four-stroke gasoline internal combustion engine includes the following strokes:
- Intake - the exhaust valve is closed, the intake valve is open, the piston moves downward, and the air-fuel mixture is sucked in.
- Compression - all valves are closed and the piston moves upward, compressing the air-fuel mixture.
- Working stroke - the valves remain closed; at the end of the previous stroke, a spark ignites the compressed mixture. The piston, under the influence of gas pressure from the burnt mixture, goes down, rotating the crankshaft.
- Exhaust - at the end of the previous stroke, the exhaust valve opens. The piston, pushed by the crankshaft, moves upward and displaces combustion products into the exhaust manifold.
The diesel cycle is different in that during intake only air is sucked in. Fuel is injected under pressure after air compression, and ignition occurs from contact of the diesel engine with air heated by compression.
Numbering
The cylinder numbering of an in-line engine starts with the one furthest from the gearbox. In other words, from the timing belt or chain side.
Sequence of work
On the crankshaft of an in-line 4-cylinder internal combustion engine, the cranks of the first and last cylinder are located at an angle of 180° to each other. And at an angle of 90° to the cranks of the middle cylinders. Therefore, to ensure the optimal angle of application of driving forces to the cranks of such a crankshaft, the order of operation of the cylinders is 1-3-4-2, as in VAZ and Moskvich internal combustion engines, or 1-2-4-3, as in GAZ engines.
Alternation of measures 1-3-4-2
It is impossible to guess the order of operation of the engine cylinders by external signs. You should read about this in the manufacturer's manuals. The easiest way to find out the operating order of the engine cylinders is in the repair manual for your car.
crank mechanism
- The flywheel maintains the inertia of the crankshaft to move the pistons from the upper or lower extreme positions, as well as to rotate it more evenly.
- The crankshaft converts the linear movement of the pistons into rotation and transmits it through the clutch mechanism to the gearbox input shaft.
- The connecting rod transmits the force applied by the piston to the crankshaft.
- The piston pin creates a hinge connection between the connecting rod and the piston. Manufactured from alloyed high carbon steel with surface hardening. Essentially it is a thick-walled tube with a polished outer surface. There are two types: floating or fixed. The floaters move freely in the piston bosses and in the bushing pressed into the connecting rod head. The finger does not fall out of this design thanks to the locking rings installed in the grooves of the bosses. The fixed ones are held in the connecting rod head due to a shrink fit, and rotate freely in the bosses.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=ilZyCD-QlJg
They break through armored wires, what does it affect?
Basic malfunctions of ignition wires
The main faults of the wires include electrical circuit breakage and current leakage.
An electrical circuit break usually occurs at the point where the metal contact of the wire is connected to the conductor, as well as to other elements of the ignition system. This happens when the wire is removed, when the wire is destroyed or oxidized, as well as when there is poor contact with the terminals of the elements in the ignition system. The place where the connections are broken heats up and sparks, which aggravates the situation and causes the core or metal contacts to burn out. Electricity leaks through contaminated wires, ignition coil, distributor cap, spark plugs, caps and damaged insulation, which contributes to the deterioration of their dielectric properties during operation.
Low temperatures increase the rigidity of high-voltage wires, which increases the possibility of damage to their insulating layer and caps. Constant vibrations from a running engine loosen the contact points, which leads to their deterioration. Rising temperatures have the greatest impact on the spark plug caps, as they are located closest to the heated engine parts. In addition, very often they become unusable when removed. Over time, dirt, dust, moisture, and secretions of fuels and lubricants, which serve as current conductors, collect on the elements of the ignition system. Leaks become even more noticeable when the insulation is damaged and in humid weather. In addition, dirt and moisture increase microcracks.
How to choose high-voltage wires - what to look for
When choosing high-voltage wires, you need to focus on the recommendations of their manufacturer, as well as the engine manufacturer. First of all, you need to study everything that is written on the package. It would be good if it indicated in Russian the models of cars or engines for which the wires were intended.
Do not rush to buy them if the packaging does not contain the manufacturer’s “coordinates” and instructions for their use. Spelling errors in captions are also a warning. There is a very common mistake in the word silicon. It should be taken into account that the international standard ISO 3808 applies to wires for cars, so all inscriptions are determined by the manufacturer.
Wire resistance is measured using a tester. But this method is not acceptable for wires with a current-carrying core wrapped around them, since due to their design features, the resistance value on the motor changes.
The level of interference from the vehicle's electrical equipment and from high-voltage wires is assessed using a car radio. The verification procedure can be seen in the diagram.
The insulation of the wires should not allow breakdown, therefore, when choosing it, take into account the maximum voltage that can be in the ignition system. The insulation and caps must be made of a material that retains its properties over large temperature differences, for example, silicone.
Many car enthusiasts consider car wires to be of secondary importance, and specialized publications do not pay due attention to them. The sellers also cannot say anything intelligible. Nevertheless, this detail is important and deserves attention, both when choosing and operating a car.
How to connect wires correctly
When replacing high-voltage conductors, they are first connected to the ignition distributor. The distributor cover is convenient in that it is always installed in one position. There is a special mark on it, thanks to which it will not be difficult to place the part in place. Before connecting the wires, inspect the cover. It must be intact, since if cracks appear, the performance of this unit is not guaranteed.
The mark on the distributor cover is located next to the wire socket of the first cylinder. The firing order of the cylinders is slightly out of order (1-3-4-2) due to the ignition slider. It moves around the circle (distributor) counterclockwise. It is precisely by this principle of movement of the slider that it is easy to remember the order of the wires. They need to be connected to carburetor and injection VAZ-2109 according to the same principle. On the distributor cover, connect the wires according to the principle of movement of the slider, this is the only way you can set the ignition correctly:
- the socket of the first cylinder is located at the mark;
- the third one is connected at the very bottom;
- on the same line with the socket of the first, there is a place for the wire to the 4th cylinder;
- at the top point the second cylinder is connected.
On the engine itself, the cylinder numbering goes from the location of the timing belt to the starter, that is, from left to right. The fourth cylinder is closest to the starter, and the first is closest to the timing belt. When connecting, it is important to look at which socket of the distributor cover the wire comes from, if you confuse their location, the car will not start.
If you have connected the wires correctly, but the car still does not start, then the problem may be in them. Check high-voltage conductors for integrity. If you haven't changed them in a while, it's worth buying a new set. The peculiarity of these wires is that over time microcracks can form on their surface. They lead to a lack of spark when the ignition distribution system is working. Moisture and dust get into these cracks, which damages the wire from the inside, although it appears intact from the outside.
Symptoms indicating a malfunction
Among the main and frequent breakdowns, several can be identified:
- So, the slider may burn out, and this may cause problems with starting the engine. The engine may start, but will immediately stall.
- If the fastening of the distributor is loosened, the OZ could be damaged. This can lead to difficulty starting, loss of power, and unstable engine idling. This is also one of the reasons for increased fuel consumption. To fix it, tighten the fastening with a 10 mm wrench - rotate two nuts, as well as one bolt.
- Another popular cause of malfunction is the distributor wires (VAZ-2109). They may be connected incorrectly or the order may be out of order. The engine may not start at all, or it will start, but at the same time it will “sneeze”.
- Oxidation or destruction of contacts in the cover is a common problem that occurs with ignition distributors for VAZ. If the contacts are oxidized, you can try to restore them with white spirit. This is one of the reasons why the engine troits.
- In addition, the distributor cover may be broken. VAZ-2109 quite often worries its owner about this. You can see the breakdown location very easily. It is clearly visible. A failed cover can cause current leaks, causing various interruptions in the operation of the motor.
- Another problem with the lid is the contact carbon in the lid breaking or wearing off. In this case, the engine will not start. To eliminate the cause, replace the coal separately or the entire lid. If the Hall sensor is malfunctioning, the engine will not be able to start. If the wires from the sensor are broken, the result will be the same.
If the vacuum corrector is faulty, the power unit will not pull up. The power and throttle response of the engine will decrease. The vacuum regulator sets the angle under load a little earlier. One of the possible reasons is a lack of tightness in the regulator body or a leak in the hose from the carburetor. Or the rotary plate of the corrector may be stuck. You can try to fix the leak. But often a complete replacement of the distributor on a VAZ-2109 is required. The asking price is up to five hundred rubles.
It is not difficult to determine that a VAZ-2109 distributor with a carburetor is broken. The car will jerk when driving. However, there are no other reasons for this behavior. If the tank is filled with high-quality gasoline, the fuel pump and carburetor are working properly, then the distributor is to blame for the vibrations. When the car picks up speed, the engine will rev.
Malfunctions can also be judged by an engine that refuses to start. When you press the accelerator pedal and increase speed, detonation occurs. This also indicates a non-working distributor. If the dynamics have deteriorated significantly, then the distributor should be checked. When the fuel rises, the first thing you need to do is find out if the breaker is working, and only then turn the carburetor.