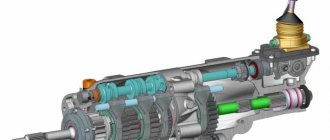
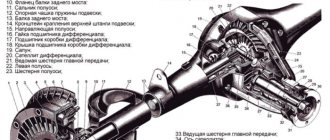
A car's transmission is a whole complex of mechanisms that ensures the functioning of all its driving mechanisms and transfers the energy of the internal combustion engine to them. Literally, the word “transmission” from English into Russian can be translated as follows: “transfer”, “transfer”, “translation”. In fact, even a simple chain drive on a bicycle is already a transmission. But when applied to bicycles, the word “transmission” did not catch on. It is customary to say “transfer”. But in the field of mechanical engineering and transport technologies, the concept of “transmission” is applied both to the mechanisms connecting the internal combustion engine with moving elements, and to the systems that ensure the functioning of such mechanisms. Although, if we are already talking about a bicycle, then using its example it is easiest to clearly explain the essence of the transmission as such. To move quickly on a bicycle, you need a high rotation speed of the rear drive wheel. A chain drive ideally allows you to solve this problem without changing the diameter of the wheel. True, if we consider the structure of cars, then the engine already appears, and the design becomes more complicated, as does the range of its “responsibilities”. For example, when driving an internal combustion engine, you constantly need to expend energy to overcome all kinds of resistance, including overcoming the inertia of the car itself. Fuel consumption, safety and comfort of the driver and passengers of the vehicle, and the efficiency of performing certain tasks depend on the quality of transmission mechanisms (MT). For example, MT forklifts provide the operator with comfortable interaction with the forklift, freely drive up to the racks and carefully unload it. The smoothness of the transfer of actions from the internal combustion engine to the mechanisms of the reaping part depends on the MT of the combine. The MT of a mining dump truck determines whether it can provide an effective start after the body is fully loaded or whether it can move uphill at high speed.
Purpose and transmission diagrams
The direct purpose of the car transmission is to step by step regulate the torque from the flywheel and distribute it over the drive wheels.
MTs make it possible to coordinate the operation of the internal combustion engine with the resistance to vehicle movement, expanding the traction force on the drive wheels and the range of speed changes.
The transmission scheme of a car depends on whether the car in front of us is front-wheel drive or rear-wheel drive.
In a vehicle with rear wheel drive, the transmission most often includes a clutch, gearbox, cardan mechanism, and rear drive axle assembly. This option is very popular with commercial vehicles (including trucks, buses).
In vehicles with front-wheel drive (the most common option for passenger cars), the transmission most often includes: clutch, transaxle, cardan drive to the front drive wheels and constant velocity joints.
The clarification “most often” when describing the design was made for the reason that some elements can “migrate”. For example, transaxle can be found in the design of some cars with rear-wheel drive. This design solution was used more than once in the production of some Chevrolet and Nissan Alfa Romeo models. The solution is especially popular with sports cars with independent suspension. Transexl can be connected to the internal combustion engine using various shafts (cardan shafts, with rubber couplings).
The transmission design of all manual all-wheel drive vehicles and a number of vehicles with additional equipment (for example, municipal vehicles) also includes a transfer case.
Separately, it is worth paying attention to the hydromechanical schemes. They do not have a clutch, but each gearbox stage is equipped with an autonomous shift element.
Dependence of transmission on drive type
The design of the transmission differs from the type of drive with which the vehicle is equipped. Today there are the following variations:
- front;
- rear;
- full.
Front-wheel drive cars use a classic chain. Rotation from the power unit is transmitted only to the front axle through the gearbox. A car with a 4WD system must have a center differential. Torque is transmitted simultaneously to the front and rear axles, and the transfer case distributes rotation to the axle shaft. The rear-wheel drive box contains all the same elements as the front-wheel drive box. The only difference is the drive axle. Also, the torque element in such cars is transmitted using a driveshaft.
What is included in a car's transmission?
Vehicle transmission components:
- Clutch, clutch or friction clutch (the latter option is often found on agricultural machinery, such as tractors). Disconnects the engine from the transmission and smoothly connects them when changing gears, when starting to move. The basis of most clutches is a friction disc or discs pressed against the flywheel or pressed together. The clutch can be controlled mechanically (pedal), hydraulically or electrically.
- Gearbox (gearbox). The main function of any gearbox is changing the relationship between angular speeds, shaft torques, angular and linear movements (that is, changing the gear ratio). The unit allows you to change the torque, speed and direction of movement of the vehicle, as well as disconnect the engine from the transmission. The design of the unit depends on the type of gearbox.
- Transexl - drive axle in a block with a gearbox.
- The cardan is a mechanism that transmits torque between the shafts in front-wheel drive cars and from the gearbox to the rear wheels in rear-wheel drive cars.
- Carter. The casing in which the main gear, axle shafts for attaching the hubs of the drive rings and the differential are located.
- Main gear. Increases torque and transmits it to the axle shafts of the drive wheels, adapts engine power to operating conditions.
- Differential. Distributes torque between drive shafts and allows the wheels to rotate at different angular speeds. Driving safety when turning on a dry, smooth road depends on the differential. The differential can be made in the form of a clutch (viscous or frictional) or worm semi-axial gears (Thorsen differential) with automatic self-locking of the mechanism at the moment of the difference in torque on the drive shaft and the housing.
- Half shafts Transmits torque from the differential gear directly to the wheel (via the hub).
- Angular velocity joints. They transmit torque from the differential to the drive wheels. CV joints, unlike transmissions, are able to operate unhindered at significant angles of rotation (up to 70 degrees).
- Transfer case (“transfer case”). A device aimed at distributing engine force over the drive wheels. The transfer case helps increase torque when driving on bad roads, off-road, and distribute torque between the drive axles of the vehicle.
To increase functionality, ergonomics, and competitiveness, the vehicle transmission structure is constantly being improved. Let's consider the popular all-wheel drive MT 4Matic, xDrive, 4Motion, Quattro.
Features of popular transmissions 4Matic, xDrive, 4Motion, Quattro
- 4Matic all-wheel drive systems (installed on numerous Mercedes-Benz passenger models) with permanent all-wheel drive include freewheel and center differentials that allow the engine torque to be divided into two axles. Each axle, thanks to free differentials, can rotate freely at different speeds. In addition, the 4Matic provides driving control through a stability control system (traction control, anti-lock brakes and traction control are provided).
- xDrive all-wheel drive transmissions (developed by BMW) are distinguished by the presence of a friction multi-plate clutch. It acts as a differential. Also, one of the main features of the solution is that the system provides the ability to redistribute the interaxle torque in the widest possible range (0 to 100%).
- Quattro system (Audi). A distinctive feature is that the MT and ICE are located longitudinally. Most Quattro transmissions have an electronically locking differential. Thanks to it, the problem of slipping of the drive wheels when accelerating on a slippery road surface automatically disappears.
- 4 Motion (popular MT Volkswagen). The peculiarity of the scheme is that the torque of the internal combustion engine is distributed among the axes depending on the situation on the road.
Most Quattro and 4Motion transmissions have an electronically locking differential. Thanks to it, the problem of slipping of the drive wheels when accelerating on a slippery road surface automatically disappears.
Drive types
Depending on the number of driving wheels involved, different torque transmission systems are possible. A car's transmission consists of mechanisms that implement these circuits.
- Rear drive. The engine is located in front of the car or in the center of the body within the wheelbase, or at the rear above the axle, or in the rear overhang. The gearbox for organizing better weight distribution can be in a block with the engine or with a final drive to the rear wheels.
- Front-wheel drive. It is used in mass-produced cars, although it is sometimes used in more expensive classes, as well as in light trucks. The difference can only be in the transverse location of the power unit or longitudinal. The first scheme is more compact and easier to implement.
- Plug-in all-wheel drive. There are many options possible, but two are most often used. On utilitarian SUVs, the driver manually engages the front axle in difficult areas while keeping the rear axle constant. Crossovers use an electronic or viscous coupling that connects the rear axle; in this case, the front axle is always used.
- Permanent all-wheel drive. All wheels in the car are always used to create traction. Various mechanical and electronic devices can change the torque ratio between axles or even wheels.
Classification
Transmissions are usually classified depending on the method of energy transmission (type of torque converter, vehicle drive, used gearbox.
Depending on the method of energy transmission, the following types of vehicle transmission are distinguished:
- Mechanical. Energy is transmitted through mechanical friction in the clutch, the interaction of hinges, and gears.
- Hydromechanical. Torque occurs due to mechanical friction and hydraulic work. TMs work here thanks to a fluid coupling, a torque converter.
- Hydraulic. Rotation is due to the injection of oil to the hydraulic turbine under high pressure. That is, energy transfer is carried out through liquid.
Depending on the drive, there are front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive transmissions.
How they differ can be judged based on the features of the device diagram given at the beginning of our material. Depending on the gearbox, the transmission is:
1. Mechanical. 2. Automatic. 3. Robotic. 4. Variable (stepless) - with a variator.
Read more about transmissions with different types of gearboxes in our material “Gearbox”.
And as a little advertisement
This project was carried out mostly by MPEI graduates.
If you want to learn more about electric drives, hybrid transmissions, electric drive control systems and all auxiliary equipment, to study the microprocessor tools used in the industry, then we inform you that the Department of Automated Electric Drive (AED) of the National Research University "MPEI" is recruiting for a master's degree in the direction of 04/13/02 " Electrical power engineering and electrical engineering”, training program – “Electric drive and automation”. More details - under the spoiler
You can enroll in a master's program in this specialty on a competitive basis using a budget-funded form of education or on a paid basis without competition. Nonresidents are provided with a hostel. The training program of the Department of Electrical Engineering can be found on the website of the National Research University MPEI. More information about the admission rules, deadlines for submitting documents and conducting entrance tests can be found on the website of the admissions committee of the National Research University MPEI.
The Department of Automated Electric Drive of the National Research University "MPEI" is the leading department in this specialty in Russia, has more than 20 million rubles. annual volume of research work, publishes more than 20 articles per year in publications indexed by the scientometric databases Web of Science and Scopus, the department is taught by employees of NPF VECTOR LLC and NPP CICL+ LLC - one of the leading enterprises in areas of development of electric drives and hybrid electric transmissions.
More details here: www.aep-mpei.ru
Mechanical transmission
Power transmission is carried out through mechanical transmissions of rotational motion.
Pros:
- Low cost.
- High efficiency.
- Small dimensions.
Mechanical systems have the highest efficiency among others, the smallest weight, and are the easiest to manufacture.
Important!
There is no need to confuse the mechanical method of energy transmission and the manual transmission. Yes, most often solutions with a manual transmission are precisely solutions with mechanical energy transmission. And that’s what everyone calls a car’s manual transmission. But this is not an axiom. Among tracked vehicles, there are solutions where energy is transmitted through mechanical transmissions, and the boxes are by no means mechanical.
How difficult and how long does it take to make such a feasibility study?
From scratch, without experience, of course it’s unrealistic.
We took on this because we have already made similar solutions, we already have experience in designing converters, motors, we have mastered software for control controllers, etc. Those. for us, in fact, this was another option for assembling what we already know how to do. But since the design is new in one way or another, during the testing and commissioning process a myriad of problems still emerged that required all sorts of improvements, both hardware and software. But this will be discussed in more detail in the next article. Development took approximately two years. From the moment we started talking about the project until the dump truck rolled out of the workshop under its own power. This is actually a very fast pace. However, traveling is, of course, not enough. The most important thing is how the machine performs in operation. What kind of “childhood” diseases will there be, what kind of “adult” ones, what will be the service life of the equipment: only time will tell. Now the car has covered about 20,000 km and continues to be used.
Hydromechanical transmission
The unit is characterized by the presence of a hydromechanical gearbox (the design combines a mechanical gearbox + a hydrodynamic torque converter).
The greatest efficiency of the system is observed when it has automatic control. A torque converter with wheels with curved blades, which is a mandatory element of such a unit, automatically changes the torque transmitted from the engine.
The process of transmitting torque is subject to changes in the load on the gearbox output shaft.
- The freewheel starts the process of rotation of the reactor wheel in only one direction. It coincides with the rotation path of the pump wheel.
- The working area is filled with oil under pressure.
- The pump wheel rotates.
- The pump vanes capture the oil.
- Under the influence of centrifugal force, the oil ends up on the turbine wheel.
- Oil enters the reactor.
- The direction of fluid flow changes.
- The oil flows back into the pump wheel.
Thus, there is a closed circulation of oil on the face.
Pros and cons of hydromechanical solutions Hydromechanical solutions are valued for their wide range of adjustment of gear ratios, the ability to provide stepless changes in energy flow parameters, reversal, and quick response to changes in operating conditions and the situation on the road. It is possible to automate the process of switching speeds and establish full control over the filtering of torsional vibrations. Hydromechanical MTs are very popular with agricultural, municipal vehicles, and heavy-duty road trains. The solution is perfect for transferring power flow from the internal combustion engine to the drive of the drive axles. The installation of such units is also common on mining dump trucks. It is possible to eliminate dynamic loads on shafts and excess disk friction.
The most popular and efficient are hydromechanical automatic transmissions.
True, with many advantages, they also have disadvantages:
- The ratio of the torque on the driven link to the torque on the driving link (that is, the transformation ratio) is quite low (does not exceed 3).
- There are difficulties with increasing braking force (this problem is acutely felt when entering the internal combustion engine braking mode.
- High material consumption.
What does KTEO look like?
The set of traction electrical equipment (KTEO) includes two traction motors installed in the wheels of the dump truck, a power generator connected to the diesel engine, and a control cabinet in which, in fact, there are transistor converters. Another option may include a cooling system, a separate top-level controller, some kind of display panel for the driver, software for the technician’s laptop to diagnose all this equipment. This is what it all looks like:
On the top left is a generator, on the bottom is one of the traction motors, on the bottom on the right is a cabinet with converters, and above it is a radiator for the cooling system. On the top right is a high-level controller with a small diagnostic console.
All this junk must have the dimensions and connecting connectors required by BelAZ in order to be inserted into the existing current design of the dump truck.
Dry technical characteristics of our kit
— Rated power of the traction generator, kW: 750 — Rated power of the traction electric motor, kW: 320 — Rated power of the braking resistive installation, kW: 2x600 — Rated rotation speed of the traction generator, rpm: 1900 — Maximum torque on the traction motor shaft: 8490 — Nominal efficiency of the traction generator, %: 95 — Nominal efficiency of the traction electric motor, %: 94 — Cooling of KTEO units: air Generator GST-850 is a classic synchronous generator, with two three-phase stator windings, power 850 kW (mode S6), rated – 750 kW (mode S1). In the GTS-850 there is no third harmonic winding, since the field winding (OW) is powered using an field winding converter (FW) directly from the direct current link (DCL).
DVIT-320 – switched reluctance motor with independent excitation, with three three-phase stator windings, power 320 kW (mode S1), operation with maximum torque in the rotation speed range 0...286 rpm, operation with constant power on the shaft - 380... 4050 rpm
The SHU B-90 control cabinet is structurally composed of three monoblocks housed in one housing.
Braking resistors can also be included in the kit, although they are usually the same type for all manufacturers. They look like this:
The orange section is the resistors themselves (insulators and a high-temperature tape stretched between them), and the round barrel is a motor with a fan. So the braking resistor is like a big hair dryer. In this case, the fan motor is DC, and it is connected in parallel with the braking resistor. It turns out that as the voltage across the resistor increases, the fan speed also increases, which is very convenient. The air flow from such a resistor with a power of 1 MW does not burn at all, but is very pleasant, especially in cold weather. Only the fan at full power is extremely noisy.
So the braking resistor is like a big hair dryer. In this case, the fan motor is DC, and it is connected in parallel with the braking resistor. It turns out that as the voltage across the resistor increases, the fan speed also increases, which is very convenient. The air flow from such a resistor with a power of 1 MW does not burn at all, but is very pleasant, especially in cold weather. Only the fan at full power is extremely noisy.
Hydraulic transmission
Instead of dry friction of mechanical MTs, a torque converter is used. Planetary gears are used to transmit torque, helping to create ideal conditions for implementing a wide range of gear ratios. In particular, such solutions are not afraid of strong vibration loading.
Huge advantages of the solution:
- There is no interruption in the power flow when changing gears.
- The solution provides excellent transmission of torque.
- There is no need to apply impact forces to operate the gears smoothly.
But in order to get the most out of a unit with a torque converter, you have to take care of installing your own fluid coupling for each gear.
Hydrostatic transmission
The GST transfers rotational energy from the internal combustion engine to the wheel or auger through a pump by directing the working fluid to the hydraulic motor.
The solution is most often installed on vehicles if it is important to provide a large gear ratio. The main objects where MTs of this type are installed are grain harvesters, road construction machines, and bulldozers.
GST does not prevent vehicles from slipping on viscous soils, and when moving back and forth it is easy to ensure straightness of movement. Even if the bulldozer blade is released as much as possible, the vehicle does not stall when moving slowly forward. This is especially valuable when working with a bulldozer.
GTS does not have a high level of efficiency, but the internal combustion engine of such TMs operates more economically when compared with a mechanical transmission.
Everything has already been invented before us and has been working for a long time. Why do more?
BelAZ - (Belarusian Automobile Plant) produces dump trucks, but it often purchases components such as diesel and electric transmission from other organizations.
It is beneficial for BelAZ to have several equipment suppliers in order to stimulate competition, try new design solutions and have insurance in case of supply failure from one of the manufacturers. Nowadays, electric transmissions for BelAZ vehicles are already manufactured by many companies, such as Siemens (Germany), General Motors (USA), a branch of OJSC Power Machines (Russia), such companies (Belarus), Ruselprom (Russia) and ... “we” are trying their hand.
We are an association of several companies, in this project led by ZAO PTFC ZTEO, a transport equipment plant located in Naberezhnye Chelny. At this plant, electric motors and a generator for our transmission are manufactured and tested, power converters and software are made by Moscow and NPF VECTOR, and the design of traction motors is carried out at MPEI University.
Since we have experience in developing electric transmissions for other vehicles, a decision was made and agreements were established to make an electric transmission for BelAZ. The agreement with the dump truck manufacturer was simple: make your own transmission for one vehicle. If it works and doesn’t break down during operation, they will buy more from us. If not, then they won’t even pay for the development and production of this equipment. We decided what to do.
This is how a dump truck with our set of traction electrical equipment (KTEO) was born. At the same time, the first version of our equipment was installed on a used dump truck as part of its overhaul. The old electric transmission was removed from it “for spare parts”, and our new one was installed there. All replacement and installation of wiring, docking to the existing equipment of the dump truck and modification of the software to suit the nuances of a particular machine are at the expense of the contractor.
Electromechanical transmission
An electromechanical transmission is a solution with a traction generator, a traction motor (or several motors).
Installation objects:
- heavy-duty dump trucks,
- large capacity buses,
- off-road vehicles (all-terrain vehicles, harvesting and transport vehicles),
- crawler tractors,
- multi-unit high-capacity trains,
- mining dump trucks
The main feature is that the energy is transferred to the generator and can be reused if necessary.
Braking occurs with energy return. If a battery system is installed, you can drive in slow motion with the engine turned off. The entire power of the internal combustion engine can be converted into electricity. Among the disadvantages are impressive dimensions, high cost, and efficiency lower than that of mechanical systems.
Common breakdowns
If we talk about this type of machine, such as passenger cars, the transmission in them most often fails due to the following breakdowns:
- CV joint A malfunction of this mechanism is indicated by the appearance of uncharacteristic sounds. It cannot be repaired and requires replacement.
- Clutch. Most often it fails due to aggressive driving. The component requires timely adjustment.
- Automatic transmission parts. They wear out due to lack of maintenance.
It is worth noting that the transmission of a truck is subject to heavy loads and therefore requires more frequent maintenance.
The most common transmission breakdowns
- A loud noise when the clutch is engaged is a “symptom” of wear of the springs (fork, damper) or the appearance of a gap in the spline joint. Most often, the solution to the problem is to replace the driven disc or springs, but sometimes it is enough to simply secure the fork spring more thoroughly.
- An increase in noise when the clutch is disengaged is a signal of wear and damage to the gearbox shaft bearings. As a rule, the problem is solved by replacing the bearing.
- “Lubricated” gear shifting. It occurs as a response to the wear of many parts. A detailed diagnosis and replacement of one or more parts is important - retainer springs, balls, “crackers”, gears, clutches, gear selector levers, synchronizer locking rings.
- Oil is leaking from the gearbox. Most often the problem is wear of the oil seals or gaskets, and they need to be replaced. But the problem may also be a loosening of the crankcase or its covers. In this case, adjustment of the fasteners (nuts) is required.
- The gearbox makes a hum and noise. This often happens when the oil level in the box is insufficient. And here it is important to understand the cause of the oil leak, eliminate it, and then restore the oil level to the required standards. In addition, the problem may be related to wear of synchronizers, bearings, and gears. In this case, they need to be replaced.
- When the vehicle goes uphill, slippage begins. Downshifting begins prematurely. Here, as in the previous case, the reason is most often a drop in the oil level. But simultaneous wear of the piston cuffs and clutch discs cannot be ruled out. This may be a direct incentive to replace them.
- Engine knocking at idle. This is evidence of the end of the life of the friction clutch discs. The problem can only be solved by replacing them.
Interactive training!
Based on LCMS ELECTUDE, a special training course and test system for testing knowledge of “Car Transmission” are available. 29 training modules are excellent opportunities to study the structure and operating principle of different transmissions. Great attention is paid to the device and service.
Mechanism operation
All motorists know that the gearbox has several speeds: low, high, and additional intermediate ones. If the driver selects the lowest setting, the vehicle's transmission will have little effect on the engine. The car will move slowly, and this will increase its acceleration at the moments when you need to get underway and continue moving.
When the gearbox is set to high settings, the rotational force will be reduced and the speed will increase. At the same time, the transmission allows you to determine the optimal operating mode of the power unit for maximum optimization of fuel consumption. As the speed of the machine increases, its power will decrease. To overcome obstacles on the way, it is recommended to reduce the speed of the vehicle. You should also remember that when driving fast, it is not advisable to transport heavy loads, since in such cases the vehicle will not have enough power.
Modern cars with manual transmission most often have several intermediate speeds. This allows drivers to easily cope with various obstacles while driving.