Car brake system: what does a motorist need to know?
Before you get behind the wheel or get a driver's license, in addition to the rules of the road, you need to study all the internal systems of the car.
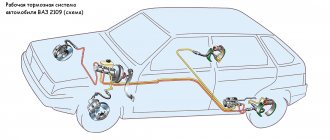
First of all, the safety of the driver and passengers depends on this. Serviceable brakes are a guarantee of a calm and confident ride on the road. To understand all possible situations or problems with the braking system, you need to understand how it works. On most cars, the braking process involves:
- brake discs (in some cases drums);
- pads
- brake fluid.
Each component plays a separate role in the process of mechanical deceleration of the car. When you press the pedal, a piston moves in the main brake cylinder, which releases the brake fluid. The latter, in turn, passes through the highways and actuates the brake cylinders on the wheels, and the pads are pressed against the drums or discs.
In modern cars, an anti-lock braking system (ABS) may be involved in the braking process. It allows you to avoid complete blocking of the vehicle's wheels during braking, thereby preventing the car from going into an uncontrolled skid.
Additionally, an expansion tank for brake fluid and a vacuum booster are involved in the process. The latter serves to reduce pressure on the brake pedal.
Reasons for replacement
There are several characteristic malfunctions that must necessarily entail the replacement of the TJ.
- The presence of leaks from the brake cylinders, which lead to the loss of a large amount of fluid.
- The appearance of air pockets in the pipeline and hose system. They arise due to a leak in the brake system elements.
- Scuffs or deformation of flexible hoses installed on wheels. They also require replacement of the hoses themselves.
- Violation of the integrity of the sealing rings in the main brake cylinder, which leads to leakage of the working substance.
- Fluid leaking through the sealing ring of the pusher on the rear wheels.
- Violation of the tightness of the system circuit. This can be felt by a partially collapsed brake pedal.
- Mechanical failure of one of the elements of the braking system. In addition to repairing or replacing them, you will definitely have to change the TZ.
Choice of TZ
IMPORTANT! To ensure normal functionality of the braking system, the brake fluid must be selected correctly. Modern compositions such as "Rosa" consist of 93-98 percent polyglycols. The remaining percentages are additives that help combat oxidation and corrosion on the metal components of the vehicle.
To choose the best option for a brake substance, you should take into account the main parameters of its selection so that it meets the requirements of the VAZ 2114 model. After all, this is the car we are talking about.
| Index | Requirement |
| Boiling point | It must be high so that steam bubbles do not form inside the system and block the flow of liquid |
| Viscosity | Good viscosity ensures efficient pumping of fluid through the system |
| Hygroscopicity | This criterion is responsible for the ability of a substance to absorb water |
| Lubrication | The thermal fluid should not only promote braking, but also prevent overheating of the internal surfaces due to the lubricating effect |
| Neutral to rubber | The composition should not have a destructive effect on the rubber elements used in the system |
| Corrosion resistance | The liquid should protect metal elements from corrosion and rust. |
| TZh class | You should choose the DOT 3 marking |
Having chosen the vehicle that is suitable for your car, you should replace it. It’s entirely possible to do the work yourself, but you should first read the instruction manual, consult with specialists, or watch visual video lessons.
Draining and bleeding process
Why does the brake system need to be bled?
The main reason for the need to bleed the brakes is the presence of air in the system. The entry of even small bubbles disrupts the operation of the brakes. Due to the uneven distribution of fluid, the compression process of the brake pads works asynchronously. If the intensity of the brakes on each wheel is different, the braking process becomes unpredictable (to varying degrees) and the driver may lose control at an unexpected moment.
It is worth noting that bleeding the system is, for the most part, a mandatory procedure after replacing the brake fluid.
Knowing when it's time to bleed the brakes is easy:
- An experienced driver who knows his car will immediately feel problems with the brake pedal. This may be an increase in the working stroke or excessive softness when pressed.
- Scheduled brake fluid replacement. Replacements must be made after reading the vehicle's operating manual.
- During a sudden stop, the car goes into a skid or a slight roll is felt in one direction or another.
On average, brake fluid is replaced every 2 years or every 50–60 thousand kilometers. However, during scheduled maintenance it is better to check the condition of the fluid using a special tester.
After any manipulations with the system, it is necessary to check the serviceability of the brakes and, in case of deficiencies in operation, carry out preventive maintenance to avoid problems while driving. The cause may be repair work on the master cylinder or vacuum booster.
Types and types of ABS anti-lock systems
Based on the number of control circuits, there are three types of anti-lock braking systems:
- single-channel - when one wheel is blocked, all four are released;
- two-channel - triggering occurs based on data from the best (high-threshold) or worst (low-threshold) wheel;
- four-channel - each wheel is adjusted separately, which ensures maximum braking efficiency.
Important! Modern cars are equipped with four-channel systems.
Depending on the location of components and maintenance features, there are three types of ABS:
- with components (hydraulic module, valves, accumulator and pump) located in a single unit;
- with components spaced in the form of different units;
- with optional SBC and ESP systems.
Despite the complicated design, it is quite possible to replace ABS brake fluid yourself.
Air in the system: how does it manifest itself and how to get rid of it?
It should be noted that, due to its structure, brake fluid is always in contact with air, thanks to the hole for the float rod - through the reservoir cap of the master cylinder. However, if the system depressurizes, you should not immediately blame the gas turbine cover, since the mechanism is designed in such a way that air cannot enter the working circuits.
However, to eliminate this source of the problem, it is worth pressing the brake pedal successively and leaving it pressed for several minutes. If the pedal slowly lowers, we can talk about a violation of the tightness of the system.
An additional cause of depressurization may be worn hoses or incorrect brake bleeding procedures. Already at the first action of air, while driving, the brake will work too softly and periodically fall into the floor, and the process of braking the vehicle will work unevenly and slowly.
Rear wheel brake
Rear wheel brake on VAZ 2114
- Hub nut
- Hub flange. The brake drum is attached to it
- Lower tension spring
- Left pad
- Thrust spring
- Cylinder
- Upper tension spring
- Guide bar
- Eccentric
- Right pad
- Pad cover
Tip: when driving through deep puddles or fording a river, the brakes get wet. This dramatically reduces braking efficiency. Immediately after overcoming a water obstacle on a straight section and at low speed, brake several times. The pad linings, discs and drums will become hot and dry. The system's efficiency will be restored.
In general, the braking system of the VAZ-2114 is simple and reliable. For a person who has experience driving cars of other brands, servicing it on a “fourteen” will not be a problem. But even those drivers who got behind the wheel of a car for the first time can easily understand the operating principle and operating features of the VAZ-2114 brake system. But remember: it is better to service the brake system at warranty service stations from experienced technicians.
The necessary set of tools for work
When you notice the first symptoms of a problem with the brakes, you need to decide whether it is possible to contact a service center. Our specialists have the necessary experience and skills to carry out work quickly and safely. Equipment plays a special role in solving the problem.
If in specialized places they use unique devices with universal adapters for any car, then when bleeding the brakes with your own hands, improvised means are sufficient. To carry out this, you need to acquire a set of appropriate keys, a container for brake fluid and several hoses. The diameter of the holes must completely match the bleeder fittings.
General rules for bleeding brakes
Before proceeding with actual bleeding, it is worth preparing clean brake fluid. Be sure to use only the liquid that was previously poured into the car.
If it is not possible to find out the exact brand of the substance, it is better to use the liquid that is provided in the car’s operating instructions.
It is better to pump the brakes with a partner. The main task of the assistant will be to consistently press the brake pedal at a signal, but the work of the chief mechanic will fall on your shoulders.
- The first step to successful and high-quality work will be a preliminary check of each circuit and drive unit for leaks.
- Most often, problems arise with the master brake cylinder - the most inaccessible portion of air is localized in it. It may need to be pumped several times by loosening the threaded valve.
- Each car has its own unique brake bleeding sequence. You must read it in the vehicle's operating manual before starting the procedure. For most vehicles, the sequence starts with the rear wheels and is represented as "right rear wheel - left rear wheel - right front wheel - left front wheel".
Important points
Before you start pumping, you should remember a number of important rules that will help you avoid additional problems.
- Before work, inspect the main components for leaks. If the seal is broken somewhere, bleeding the brakes will be a waste of time and effort.
- Always monitor the brake fluid level in the expansion tank. If it becomes empty during operation, the system will become even more airy.
- Never use an open-end wrench to unscrew fittings - the edges are easily torn off.
- Be sure to clean the fittings from dirt; before pumping, it’s a good idea to spray them with WD-40 and wait 10-15 minutes. Often the fitting becomes tightly “stuck” to the brake cylinder and breaks off when you try to unscrew it. If the fitting does not budge, try gently heating and cooling it several times.
- On vehicles equipped with a brake force regulator (sorcerer), the rear of the vehicle must be loaded before bleeding. You can simulate loading by slipping a screwdriver between the regulator rod and the pressure plate.
- If there are no special instructions from the manufacturer regarding the bleeding order, the following scheme is recommended: rear right wheel, rear left, front right and front left.
Procedure
Success and high-quality pumping of the brake system lies in following the entire technology of action:
- The first step is to replace the fluid in the GTZ tank or check its quantity and, if necessary, top it up to the maximum level.
- For more comfortable work, it is necessary to clean all air release valves on each wheel from dirt, dust and deposits.
- According to the correct sequence provided in the instructions, it is necessary to unscrew the fitting plug on the desired wheel and attach the prepared hose over the valve.
- The second end of the tube is placed in a previously prepared container with brake fluid.
- The partner progressively presses the brake pedal from 3 to 5 times and at the last movement fixes the pedal in the pressed position.
- At this time, you need to unscrew the air valve halfway. After opening the valve, liquid along with air bubbles will begin to flow through the tube into the container. When the pressure of the liquid escaping into the container disappears, the valve can be screwed back firmly, and your partner can release the brake pedal.
- The process may have to be repeated several times on each node. The main thing is to maintain the wheel sequence and control the amount of fluid in the master cylinder reservoir.
After pumping is completed, you need to make sure that the fitting plugs are tight and that the brakes are operating. After the test, if successful, the brake operation will return to normal. If the driver still feels problems in operation, then perhaps attempts to bleed the brakes with their own hands were unsuccessful, or there is a problem with the wear of the pads or discs.
Front brake mechanism
The design of the front brake mechanism on the VAZ 2114
The front brake mechanism consists of the following components:
- Brake disk. Directly connected to the wheel hub and rotates with it. Slowing down the rotation and stopping the disk leads to the slowing down and stopping of the wheel.
- Pad guide. Serves as a holder for the pads and a base for the guide pins.
- Caliper. It combines the pads, cylinder, and piston into a single unit and ensures uniform transmission of force from both pads to the disc.
- Brake pads. They directly act on the disc, squeezing it on both sides and slowing down the movement.
- Cylinder. A sealed cavity in which the piston moves.
- Piston. Under the influence of hydraulic fluid pressure, the pad is pressed against the disc. Thanks to the “floating clamp” system, the second block is pressed simultaneously. This ensures uniform wear of their linings and discs and guarantees effective braking.
- Seal ring. Prevents fluid leakage and ensures system tightness
- A cover to protect the guide pin from dirt, allowing for unhindered movement of the pads.
- Guide finger. Allows the pads to move evenly and adhere to the disc with their entire plane.
- Protective cover. Protects the disc from road dirt.
The front wheels are equipped with disc brakes. They automatically adjust the clearance from the pad to the disc. The caliper and cylinder form a floating caliper, which creates the same even force on both pads. This ensures uniform wear of the linings. To monitor their wear, there is an indicator on the inner block.
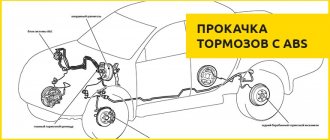
Differences and specifics of bleeding brakes with ABS
The anti-lock braking system allows you to control the vehicle's handling when braking. After pressing the pedal, the central control panel receives a response signal from sensors installed on the front and rear wheels. Thanks to the control system, the wheels slow down at the same speed as the car itself. In other words, thanks to ABS, the car cannot skid.
Regardless of the manufacturer, most devices have common characteristics:
- Electronic speed sensors on the hubs;
- Pressure controllers for main brake fluid lines;
- Electronic unit for signal processing.
Unlike most cars with simple braking systems, bleeding anti-lock brakes is difficult. For the procedure to be successful, it is necessary to familiarize yourself in detail with the theory of ABS operation. However, if the hydraulic accumulator, valves and pump are located nearby due to the design solution, the pumping technology will be very similar to the standard one.
Before starting work, in addition to standard tools, you must acquire a scanner to read information from the electronic unit. However, if the car has additional sensors, it is better to take the vehicle to a specialized salon. Any improper intervention calls into question the safety of road users.
Usually, for successful bleeding with the ABS system, it is enough to monitor the pressure in the hydraulic system. The standard value is 180 atm, but to work with the brakes it must be reduced - turn off the ignition and apply the brake 20 times. Only after this, some of the liquid will splash out and the pressure will drop significantly. After reducing the pressure, you can begin to turn off the ignition and disconnect the connectors and controllers on the GTZ tank for further manipulations.
Brake fluid selection
In theory, even plain water will do - since, being a liquid, water cannot be compressed. However, it is important to remember that the main function of the braking system is to convert kinetic energy into thermal energy through friction. And the reality of this process is that some parts of the brake system will be exposed to very high temperatures. In fact, it is not uncommon for the rotor temperature to reach 600ºC while the vehicle is in motion, which can raise the temperature of the brake fluid to 150ºC. Since the boiling point of water is 100ºC, it is obvious that the water in the brake system can easily boil - and therefore release gases into the brake pipes - reducing the effectiveness of the system.
ATTENTION! Water is also a big problem in cold weather if it freezes to ice!
The "obvious" solution to this problem is to use a fluid that is less sensitive to extreme temperatures. Hence the development of “brake fluid”. However, unfortunately, there is no “ideal” brake fluid. And like most things in the world, adding certain useful features usually comes with trade-offs in other areas. With brake fluid, we typically must balance the fluid's sensitivity to temperature, its cost, and its effect on other components in the system.
Simply put, you can reduce the sensitivity of a liquid to temperature by varying its ingredients. However, certain combinations of ingredients can significantly increase the cost of the fluid and can react with original materials, damaging seals and causing corrosion of the entire brake system.