The answer to this question will be incorrect, since the Niva has a permanent all-wheel drive . Many people confuse the function of the transfer case lever, believing that it turns the front axle on/off, while its function is to lock/unlock the center differential.
Therefore, the function of enabling/disabling all-wheel drive on a Niva can only be implemented by interfering with the vehicle’s design. More details about this in the article.
The Niva driver does not have the ability to disable the drive to the front or rear wheels, as is implemented in modern all-wheel drive vehicles of other brands, but he must know how to use the transfer case.
Is it possible to disable all-wheel drive on a field?
The Chevrolet Niva SUV comes from the factory with all-wheel drive on all four wheels. The lever located under the dashboard is responsible for controlling the differential in the transfer case. ... To be able to disable the drive in order to save on fuel, it is necessary to install a shutdown unit and lock the differential.
Interesting materials:
How to record Google Translator voice on Android? How to record music via iTunes on iPhone? How to burn to CD? How to enroll a child in school in the Moscow region? How to write the system to a flash drive? How to record Stories with Android music? How to sign up for a traffic police test without a driving school? How to schedule an interview at the us embassy in Kazakhstan? How to power a light bulb from a potato? How to fill dates in Excel?
Design and principle of operation of the Niva 2121 transfer case
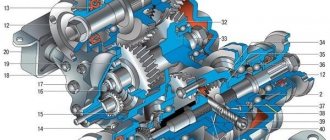
The transfer case mechanism includes more than 60 independent parts, which is confirmed by the presented drawing. Therefore, it is quite prudent to name the main elements and their purpose:
- frame;
- differential housing;
- shafts;
- couplings;
- oil seals;
- satellites;
- gears;
- flanges;
- levers.
Photo No. 1
A pair of gears are tightly seated on the drive shaft, one of them (large) is intended for high gear, the second (small) is responsible for low gear. They have serrations with straight and oblique profiles. The first ones are in contact with the coupling, the second ones - with the intermediate shaft. The inclusion of one or another row causes the coupling to move along the hub in the horizontal direction, after which it is connected to the gear on the transfer case drive shaft.
The intermediate position turns off the gearbox (the gearbox is open), and the vehicle cannot be moved in this mode. The front helical gear on the intermediate shaft is used to control the differential.
The locking is engaged, or the rigid coupling of the drive shafts of both axles, is carried out through a clutch. The design is typical for modifications 21213 and 21214, and the latter is additionally equipped with a speed sensor drive.
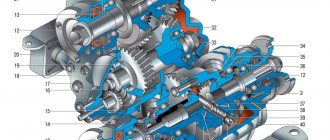
Photo No. 2
In the operating state (with the transfer case reduction gear connected), the gear ratio in the first stage changes from 4.4 to 7.83, the second - from 2.52 to 4.58, the third - from 1.63 to 2.9, in the fourth - from 1.2 to 2.14, fifth - from 0.98 to 1.75, which is expressed in an increase in traction on the wheels.
Possible problems
Harsh operation and insufficient attention to how to use the transfer case on the Niva 2121 lead to the appearance of:
- vibrations in the body while moving;
- vibrations at start;
- hum;
- noise when maneuvering;
- tight switching modes.
Experience shows that the culprits are: insufficient oil level, incorrect centering of the steering wheel, loosening of the support fastenings and damage to the rubber bands. An additional influence is exerted by the condition of the cardan and the engine itself.
Tips for operating Lada 4×4 and Chevrolet Niva
Beginners do not immediately remember at what position of the handle the differential is locked. But this is indicated by a warning indicator on the dashboard. If it lights up, the differential is locked. The front handle of the transfer case is responsible for locking the differential. If it is in the forward position, the differential is unlocked, in the rear it is locked.
The rear handle allows you to engage a lower gear. This must be done before getting into difficult road conditions. Since the box does not have synchronizers, switching must be done when the car is stationary. In this case, you need to depress the clutch. If the switch does not occur, you need to slowly move away, shaking the steering wheel.
When driving on a flat road, the rear transfer case handle should be in the rear position, and the front handle should be in the forward position.
What to do if the front and rear wheels are hanging out? As mentioned above, even locking the differential will not help solve this problem; the car will not move. To set the car in motion, you can pour soil under one of the hanging wheels. If there are passengers in the car, you can move them to the rear or front of the car by loading one of the axles.
Advantages of Lada 4×4 and Chevrolet Niva cars
Why have these inconspicuously designed cars remained so popular over the years? The secret is the relatively low cost, which is combined with good maneuverability, reliability and simplicity of design. Many people appreciated this vehicle during trips to hunting, fishing, and off-road travel.
Of course, Lada4×4 and Chevrolet Niva have many disadvantages. They are inferior in many respects to modern SUVs, which are distinguished by increased comfort and the presence of many additional options, but for those who are looking for an inexpensive, easy-to-repair car with high cross-country capability, the Niva is a pretty good option.
Lada 4×4
Chevrolet Niva
Location of levers on Lada 4×4
Transmission units
Differential locations
edit this post
The relatively complex scheme for distributing torque from the internal combustion engine to the wheels is explained by the universal purpose of the Niva 2121 - if used correctly, it can be used comfortably in the city and along muddy country roads. Such properties are ensured by the presence of a transfer case with a center differential lock, complementing a 4- or 5-speed manual transmission, depending on the year of manufacture. The lever, located closer to the dashboard , is responsible for turning off/on the center differential, the second “small” lever controls the range multiplier and has 3 positions: high and low rows, as well as neutral.
Features of differential operation
The moment is distributed in such a way that it is transferred to where the load is less. This can be confirmed by the usual picture - the car has three wheels on the asphalt, and one on the ice. She fails to move. The friction force of rubber on ice is much less than that of rubber on asphalt, which means that the load on a wheel standing on ice is less than on others.
And the differential transmits all the torque towards the minimum load. As a result, one wheel rotates at breakneck speed, while the rest stand still and the car does not move. The situation is approximately the same when a car cannot climb a mountain on an icy road. In this case, one wheel caught on ice spins, but the car stops.
Work that no one needs is being done. The wheel “grinds” the road surface (ice). Getting rid of such useless work is blocking both on the Niva and on any other car adapted to difficult roads. But usually the devices described are not available on all machines.
Main problems with the range multiplier
The main function of the range multiplier has the properties of a gearbox divider; it turns them on or off the gear speed.
Most transfer case breakdowns are purely mechanical in nature (for example, a cut shaft between the gearbox and the transfer case). This is provoked by inattention to fuel and lubricant levels, wear of rubber bands, incorrect location (alignment) of the unit, and the condition of adjacent components. The first indicator of problems with the transfer case is characteristic noise and vibration in the body.
Vibration when driving on Niva
The first reason is that at a speed of more than 70 km per hour, it’s all about the cardan shaft; only the original one must be installed. Next, replace the crosspiece on the cardan shaft, after which you must drag the shaft to a stand and balance it, otherwise the vibration will resume.
Important: The shaft itself on the Niva lasts two years, then it must be replaced. It is better to order from the manufacturer, this is not difficult to do on the Internet.. The second reason for vibration is the intermediate shaft, it must also be original, otherwise it will quickly fail
We take only the original AvtoVAZ one from the factory, otherwise vibration and breakdowns cannot be avoided
The second reason for vibration is the intermediate shaft, it must also be original, otherwise it will quickly fail. We take only the original AvtoVAZ one from the factory, otherwise vibration and breakdowns cannot be avoided.
The third reason for vibration is the breakdown of the gearbox flange bearings. To eliminate the problem, place additional support on the gearbox.
How to overcome noise when maneuvering in a transfer case
You can buy new handles for the levers. We change it ourselves, prying up the support with a screwdriver, take out the lever axis and get rid of the old handles. We remove the old lever springs and install new ones. Insert the lever axis and secure it with a corkscrew nut. Now, when driving with the new handles, there is no characteristic noise in the cabin. The handles can be easily changed without leaving the salon.
Stiff switching of the lock lever
This issue can be easily solved in the following way: when driving, just turn the steering wheel slightly and the lock will immediately turn on without any problems.
There are also: jamming of the pneumatic cylinder, sticking in the neutral position, or the rod is sitting tightly. Burnt gear and shift fork.
Transfer case for Niva, signs of breakdowns:
- problematic engagement of the front axle;
- overheating of the range multiplier;
- leakage or excessive consumption of oil during operation of the transfer case;
- self-switching of the front axle.
Repairing the transfer case in Niva 21213 with your own hands is quite possible in case of minor breakdowns. The owner of a Chevy Niva will only need the basic skills of a car mechanic. It is more difficult to correctly install and center the Niva transfer case. Here it is still recommended to contact a car service. A diagram of the unit itself is presented in the vehicle documentation.
Gear Modes
Let's take a closer look at how to use the transfer case on a Chevrolet Niva. It serves to switch to a lower gear and also blocks the center differential; this can be done at the same time. In order to engage a lower gear, you need to shift the lever to the right and up; to lock the lever, you need to pull it to the left all the way. The handle has the following designation:
- Low(L) - decrease;
- N-neutral;
- High(H) - normal, increased.
Low gear is engaged at a speed of no more than 5 kilometers per hour, or after a complete stop. In order to overcome a steep climb, or when driving where there is soft ground, so that the vehicle speed is minimal and at the same time stable, a lower gear must be engaged in advance. For example, if you are driving on a flat road in second or third gear, and a bad section of road appears in front of you, you need to stop and shift to a lower gear.
It is not recommended to turn on the center differential at high speed, since the car may skid strongly at the moment of switching. It is advisable to block where there is a slippery surface and the wheels begin to slip.
These include:
- Switching the transfer case should only be done when the car is not moving.
- You can also engage the differential while the vehicle is moving.
- You can switch to a lower gear while the car is moving.
- To ensure long-term and uninterrupted operation of the differential, it is necessary to periodically turn it on, especially in winter. This should be done once every 7 days.
Among domestic car enthusiasts, the Chevrolet Niva is a fairly popular SUV that appeals not only to fans of extreme driving, but also to fans of measured driving outside the city. Many people know that one of the features of a car of this brand is the presence of a transfer case in it.
Using this unit, you can enable downshifting, locking, or two functions at the same time, depending on the conditions. The question of how the Niva Chevrolet transfer case should be used correctly is of interest to many happy owners of such a vehicle and those who only intend to purchase it.
It should be immediately noted that you can engage both the lock and the transmission at the same time using the Chevrolet lever that changes gears. So, the lever shifts to the right, and then immediately up to engage a lower gear. To switch back to higher, the lever should simply be moved back.
Using a Niva Chevrolet transfer case, in addition to the above, neutral gear is also engaged, while the car will remain reliably in one place. The lock can be engaged at any time - in normal gear, in low gear - just switch the Chevrolet lever to the left.
This mechanism can operate in five modes:
- Neutral is on.
- The differential is unlocked when the "lowering" is turned off. In this case, the torque is distributed in a ratio of one to two.
- The differential is locked when overdrive is engaged. Here, torque distribution is carried out automatically, depending on the quality of wheel grip on the road.
- Downshift is engaged and the differential lock is disabled. The transfer of forces occurs in the same ratio as in the first case.
- The differential is locked and the gearbox is engaged. In this case, all axles are rigidly locked together, including the axle shafts. Torque is produced unevenly, depending on the type of road surface (dirt, sand, etc.). In this mode of operation, the best cross-country ability of the vehicle is achieved. But driving with a constantly engaged downshift and with locks will not work. This increases the load on the transfer case bearings. The Chevrolet Niva will soon require serious intervention in the transmission. Fuel consumption also increases significantly, which greatly eats up the tires.
Features and malfunctions of the transfer case
The Chevrolet Niva transfer case not only moved back by 250 mm, but also changed the installation angle by 4 degrees. Chevrolet engineers calculated that this angle would be optimal for the operation of driveshaft joints. The design of the transfer case uses small-module, low-noise gears, so the howling of the transfer case, as on the old Niva, is now completely eliminated.
Another common malfunction of the transfer case on old Nivas was vibration. On Chevrolet, this issue has been practically resolved by installing new pillows and the appearance of a third attachment point. This will eliminate not only operational vibrations and noise, but also the likelihood of incorrect installation of the transfer case after repair, prevention or troubleshooting.
There is another malfunction that few people think about, however, this problem is related to the resource and endurance of constant velocity joints. The fact is that a cermet valve is installed directly under the CV joint boot mounting clamp. Its task is to compensate for excess pressure inside the cover, thereby protecting it from rupture, and the CV joint itself from water and dirt. If you monitor the performance of the cermet valve during repairs or replacement of hinges, the boot will last a long time and will reliably protect the CV joint.
Even such a complex system as the Chevrolet Niva transmission can be succinctly described in an accessible way. Each owner is required to know the basic principles of operation of the systems of his car.