in our VKontakte group
DIAGNOSE YOUR CAR YOURSELF!
When the ignition is turned on, the malfunction indicator lamp lights up continuously. When the engine starts cold, the warning lamp turns off and blinks once. If there is any malfunction in the system, the warning lamp lights up.
Conditions for the DTC to Occur
The ignition switch is in the on position.
Conditions for setting the DTC.
The ECM detects a persistent short to ground or an open in the signal circuit.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The malfunction indicator lamp lights up. The controller records the operating conditions at the time the fault is detected. This information is stored in a status record buffer and fault logs. An archive of diagnostic trouble codes is saved.
Conditions for Clearing DTC/Malfunction Indication
The malfunction indicator lamp turns off after three consecutive test cycles have completed without failure. The historical DTC clears after 40 heat cycles without failure. The DTC can be cleared by a scan tool.
Diagnostic guidelines
An intermittent fault may be caused by a loose connection, chafed insulation, or broken wiring under the insulation. Any circuit suspected of causing an intermittent fault should be carefully tested for the following conditions. Removed terminals Terminal connections Faulty locks Deformed Damaged terminals Loose connection between terminals and wires Physical damage to wiring harnesses
Good day! The check light is on, error 0650 VAZ 2114 Error 0650, lamp circuit malfunction, has anyone had this? what did you do? Error 0650.
Similar articles
One comment on “Error 0650. Check light Error 0650 VAZ 2114 Error 0650 lamp circuit malfunction”
I got a check because of a light bulb. Try changing the light bulb
I figured out the errors, maybe it will be useful for someone (the symptoms were the following - waste of fuel, about 23 l/100 km in winter, 2.0 L engine). After diagnosing elm, the following came out:
P0650: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (ML) Control Circuit
P0038: HO2S Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
(the second lambda as it turned out)
I’ll tell you right away the decoding of all this, and more specifically, what to change and adjust I searched for a long time and with little success, and the benzene oil went on as usual. finally found this: “The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) operating range is 350 to 850°C (662 to 1562°F). By using a HO2S sensor heater, the time required to activate the fuel control is significantly reduced. The current through the heater is controlled by the PCM via a pulse width modulation control circuit. The cold HO2S sensor circuit has low resistance and carries high current. On the other hand, as the temperature of the sensor resistor increases, the current gradually decreases.”
What does this mean? as explained by friends comrades + their thoughts = 1. P0038: HO2S Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 1 Sensor 2) P0038 HO2S heater control circuit high short circuit to positive electrical heating circuit
— bank 1 sensor 2 is the 2nd lambda (clean, wash, didn’t, bought a new one) spare part code
39210 23750.
2.
P0650: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (ML) Control Circuit P0650 Malfunction in the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) circuit;
the malfunction was due to a malfunction lambdas, voltage was supplied to the lambda, the voltage was silent, the voltage became stronger (by the way, there is such a feature that wires can come off and short-circuit to the body, so check the wiring before replacing the lambda). Well, that’s all, I’m moving on to testing it in practice))) photo of the new lambda 2, located after the catalyst, otherwise some services can make a complex replacement, the replacement is simple and inexpensive; you don’t need to unscrew anything too much. Good luck to everyone!
Causes of error P0650
The most common causes of the P0650 code are:
- Short circuit or break in electrical wires related to the CAN bus, or damage to the corresponding connectors
- Control module ground wire loose or damaged
- Malfunction of the malfunction indicator light bulb or LED
- Malfunction indicator lamp control circuit malfunction
- CAN bus fault
- In rare cases, a faulty powertrain control module (PCM)
Description and meaning of error P0560
This generic powertrain/engine diagnostic trouble code typically applies to all 1996-newer vehicles, including but not limited to Hyundai, Toyota, Saab, Kia, Honda, Dodge, Ford and Jaguar vehicles. The PCM controls the charging system to a certain extent on these vehicles. The PCM can control the charging system by monitoring the power or ground circuit to the voltage regulator inside the alternator. The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the ignition circuit to determine whether the charging system is operating. If the voltage is too high or too low, a fault code will be set. If voltage is not present when it should be, a fault code will be set. This is strictly an electrical issue. Troubleshooting steps may vary depending on the manufacturer, type of charging management system, and wire color.
What are the symptoms of a P0650 code?
The main symptoms of this error are:
- Storing P0650 Code in Computer Memory
- The Check Engine light illuminates, indicating a malfunction, on the vehicle's dashboard
- The Check Engine light comes on in the absence of any faults
- The Check Engine light does not light up when there is a malfunction
- Absence of any symptoms other than the P0650 error code being stored in the computer's memory
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0560 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light). It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in memory as a malfunction).
- The red battery charging indicator is on.
- The engine stalls or has trouble starting.
- Frequent or unpredictable engine stalling.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Harsh, erratic or unpredictable shifting of automatic transmissions.
- Incorrect instrument readings.
- Constant battery drain.
The P0560 code is quite serious because it can cause problems with the battery, starting system, or charging system. This may also affect the functioning of other vehicle systems. Therefore, if a malfunction is detected, it is recommended to eliminate the error as soon as possible.
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0650 code?
When diagnosing this error, the mechanic will do the following:
- Check for P0650 with an Advanced OBD-II Scanner
- Start the vehicle and check to see if the malfunction indicator light comes on for a few seconds and goes off shortly thereafter
- Determines whether the malfunction indicator light has burned out
- Checks whether the malfunction indicator lamp is properly connected
- Visually inspect electrical wires and connectors for shorts, looseness, and damage.
- If necessary, repair or replace all shorted, broken, damaged or corroded components.
- Determines whether the malfunction indicator lamp fuse has blown
- If no problem is found, check the powertrain control module (PCM).
Diagnosis and problem solving
First of all, you need to check whether the light comes on at the right time. It should light up for a few seconds when the ignition is turned on. If the light turns on for a few seconds and then goes out, then everything is fine. The working light is also indicated by the fact that it remains on.
If the malfunction indicator lamp does not light up at all, you need to determine the cause of the problem.
Check if it is burnt out, replace if necessary. Also inspect whether the lamp is installed correctly and whether there is a good electrical connection. Visually inspect all wiring and connectors leading from the MIL to the PCM.
Inspect the wires for frayed insulation. Disconnect all connectors as necessary to check for bent pins, corrosion, and broken terminals. If problems are found, clean or repair as necessary.
Check that other parts of the instrument cluster and other warning lights are working properly. Please note that you may need to remove the unit during diagnostic steps.
If your vehicle is equipped with a PCM or MIL fuse, check it and replace it if necessary. Use a digital voltmeter to check the corresponding wires in the circuit at the lamp end and the PCM end. Check for short to ground or open circuit.
If everything is within manufacturer's specifications but P0650 remains, replace the PCM; it may be an internal fault. Replacing the PCM is a last resort and requires the use of specialized hardware to program it.
What repairs can fix the P0650 code?
To resolve the P0650 code, you may need to:
- Replacing the malfunction indicator light bulb or LED
- Proper connection of the malfunction indicator light
- Repair or replacement of electrical wires or connectors
- Replacing fuses
- Properly connecting or replacing the control module ground wire
- In rare cases, replacing the powertrain control module (PCM)
- Clearing present trouble codes from the computer's memory and test driving the vehicle to see if the P0650 code appears again and determine if the problem is resolved
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0650 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Chery
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Cruz, Lacetti, Silverado)
- Chrysler
- Daewoo (Daewoo Matiz, Nexia)
- Ford (Ford Transit)
- GMC Sierra
- Hyundai (Hyundai Grand Starex, Santa Fe, Solaris, Sonata, Starex, Tucson)
- Isuzu
- Iveco
- Kia (Kia Rio, Sid, Sorento, Sportage)
- Nissan
- Opel (Opel Astra, Vectra, Zafira, Corsa)
- Pontiac (Pontiac Grand Prix)
- Renault (Renault Duster)
- Rover
- Saab 9-3
- Volvo
- VAZ 2114, 2115
- Volga Chrysler
- Gazelle Business, Sable, ZMZ 405
- Lada Priora
- UAZ Bukhanka, Iveco, Patriot
You can sometimes encounter other errors with fault code P0650. The most common are the following: P0172, P0340, P1258, P1516, P1518.
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0650
It should be noted that in some vehicles the Check Engine light may not come on immediately, but only after detecting the error multiple times. For more detailed information, please refer to the vehicle's owner's manual.
Diagnosing and repairing the P0650 code can take a lot of time and effort, so if you encounter this code, it is recommended that you seek help from a qualified technician who has the necessary diagnostic equipment.
Need help with error code P0650?
The company - CarChek, offers a service - on-site computer diagnostics; specialists from our company will come to your home or office to diagnose and identify problems with your car. Find out the cost and sign up for on-site computer diagnostics or contact a consultant by phone
Error codes
Each error has its own identification number. For the convenience of users, errors are sorted into the following groups:
Group 01
01 series codes occur due to problems with the main sensors. For example:
The most common error in this group is p0106. It indicates problems with the pressure sensor inside the intake manifold. Its main reasons are:
After eliminating the code, you must reset and restart the engine with diagnostics. If necessary, carry out thorough cleaning.
Group 03
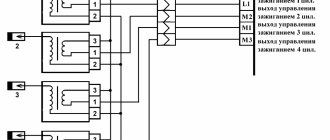
Errors occur when there is a problem in the ignition system. Common ones are:
Malfunction indicator lamp, circuit low voltage
- The ignition switch is in the on position.
- The ECM detects a persistent short to ground or an open in the signal circuit.
- The malfunction indicator lamp lights up.
- The controller records the operating conditions at the time the fault is detected. This information is stored in a status record buffer and fault logs.
- An archive of diagnostic trouble codes is saved.
- The malfunction indicator lamp turns off after three consecutive test cycles have completed without failure.
- The historical DTC clears after 40 heat cycles without failure.
- The DTC can be cleared by a scan tool.
Fault code P0560, how to find the cause?
Before starting troubleshooting, you need to check the voltage in the vehicle's on-board system and at the battery terminals. It should not be lower than 11.5 V. If the car starts, check the voltage supplied by the generator with the high beam headlights on, which should be within 13.5 - 14.5 V.
If the voltage is not normal, then it is necessary to check the tension of the drive belt or remove and repair the generator.
If the on-board network voltage corresponds to the norm, it is necessary to find the cause of the low voltage on the ECU.
To find out the reasons for the appearance, it is necessary to check the condition of the controller's power circuit and its connection to ground. To speed up the process and reduce labor costs, it is advisable to divide the chain into two parts. First, you should check the voltage value at terminal 87 of the main relay block. The voltage should not differ from the battery voltage by more than 0.5 V.
If the voltage is not normal, you need to find the place of bad contact by checking the circuit from the battery to the relay, according to the connection diagram.
If the voltage at terminal 87 of the main relay is normal, with the ignition on, check for a voltage drop at terminal 30 of the same relay and terminal 37 of the controller block. If the voltage at pin 30 is low, change the relay or eliminate bad contact in the relay block.
If there is a voltage drop at pin 37 of the controller block, it is necessary to eliminate an open or broken contact in the circuit from the main relay to the controller, according to the connection diagram.
When, after performing all the checks and work, the P0560 fault code remains active, there may be a weak contact in the plug connection of the controller or a malfunction of the controller itself.
VAZ (LADA) errors via OBDI protocol. Self-diagnosis.
1 — Malfunction of the engine control unit.
2 — The voltage in the on-board network is too high.
3 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the fuel level sensor.
4 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the antifreeze controller.
5 — Error in external temperature controller.
6 — Overheating of the engine (power unit)
7 — Emergency oil pressure in the engine.
8 — The voltage in the vehicle's electrical network is too low.
9 — Low battery level (battery is discharged)
12 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the malfunction indicator located on the instrument panel.
13 — No data (loss of communication) from the oxygen sensor (lambda probe)
14 — High signal level of the coolant temperature sensor (antifreeze).
15 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the coolant temperature controller.
16 — Increased voltage in the vehicle’s electrical network
17 — Low voltage in the on-board network
19 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the crankshaft position sensor.
21 — Malfunction in the throttle position regulator.
22 — Low signal level of the throttle position sensor
23 — High signal level of the intake air temperature sensor
24 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the vehicle speed sensor.
25 — Low signal level of the intake air temperature sensor
27 — Incorrect signal from the exhaust gas system sensor
28 — Incorrect signal from the exhaust gas system sensor
33 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the air flow meter
34 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the air flow meter
35 — The ECU has detected a deviation in idle speed
41 — Incorrect signal coming from the phase regulator
42 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the electronic ignition system
43 — Incorrect signal coming from the knock sensor
44 — The mixture in the engine cylinders is too lean or rich
45 — The mixture in the engine cylinders is too lean or rich
49 — Vacuum leak
51 — Malfunction of one of the memory modules of the control unit - RAM or PROM
52 — Malfunction of one of the memory modules of the control unit - RAM or PROM
53 — Incorrect signal coming from the exhaust gas sensor
54 — No signal from the octane corrector regulator
55 — Poor air-fuel mixture at low load on the car engine
61 — Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the oxygen sensor (lambda probe)
E - Determining an error in a data packet stored in EEPROM
How to fix the problem
After diagnosis, the problem should be repaired. When reading a signal, it is necessary to check the circuit and devices following it. The most accurate method is to replace the damaged part with a known good one (new). This will eliminate the possibility of incorrect repairs. If the device is in working condition, the lines are checked; usually a primitive test is sufficient. However, if the control unit or relay fails, you will need a special tester and the ability to use it.
Separately, it is necessary to take into account that factory terminals and blocks become loose and oxidize over time. If the contact on the hitch deteriorates, the on-board computer or laptop program will say that the part is damaged, even if it is not.
You can prevent this from happening in the following way.
- Check the condition of the connectors once every 5000 km. The pads should sit in place tightly, without play. If necessary, elements must be replaced with new ones.
- Check plug connectors two to three times a year for oxidation. Oxides reduce the flow of electricity through on-board wiring, which leads to incorrect display of information.
- Experts recommend purchasing and using oil for electrical terminals. The liquid is similar in composition to transformer lubricants. The formula prevents water and oxygen from reaching metals, which prevents them from rusting.
Important!
You can diagnose VAZ 2114 error codes on the instrument panel and ECU yourself, only if you understand the essence of the process. If you don’t have confidence in your own abilities, it is recommended to contact a qualified technician.