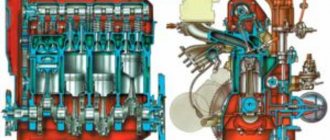
The cylinder block can without a doubt be called the heart of an internal combustion engine. And the most important element of the cylinder block is the so-called. head. It has another short and most commonly used name: cylinder head. Although the cylinder head is a kind of cover for the cylinder block, there are many features in its design. We can’t help but talk about the materials used. Let's figure out what a cylinder head is, what its purpose is, what elements it consists of, and what malfunctions it may have.
Purpose and device
The main functions of the cylinder head are:
- Location of parts of the gas distribution mechanism (GRM), as well as channels for supplying fuel and removing combustion products.
- Providing gas-dynamic parameters of a portion of air.
- Participation in the formation of the combustion chamber and its sealing.
- Supply and removal of oil for timing parts.
Important
A correctly calculated cylinder head plays an important role in ensuring that the machine complies with accepted standards for the amount of harmful substances emitted into the atmosphere.
The design of the cylinder head is determined by the operation of the internal combustion engine. The latter receives the energy of the burned fuel and converts it into rotation of the crankshaft. Therefore, the cylinder head must have:
- Places for injectors or spark plugs.
- The chamber in which the fuel will burn.
- Valve seats and valve guides.
- Installation locations for timing elements.
- Coolant jacket.
- Lubrication channels.
In addition to the elements listed above, depending on the design of the cylinder head, others are present. For example, a cover made of plastic or stamped metal, with a lubricant filler neck and a plug, protects against mechanical damage. The tightness of the internal volume is ensured by gaskets. Timing components: traverses, valves with springs and crackers, rocker arms with adjusting screws, hydraulic compensators. Mounting parts are also included.
In order for gasoline or diesel fuel to burn in the best possible way, thereby providing the fuel system with the specified gas dynamics parameters, the diameter of the intake valves is slightly larger compared to the exhaust valves.
A traverse is needed when in a 16-valve cylinder head it is necessary to open two valves simultaneously from one rod. The hydraulic compensator can come complete with a rocker arm. To return the open valve to its original position, springs are provided. Spark plugs are installed in engines that run on gas or gasoline, injectors in diesel engines.
Briefly about the types of cylinder heads
Depending on the overall design of the engine, cylinder head types are distinguished. There are four of them in total. They differ in design, as well as in the location of the combustion chambers, the type of timing belt and some other features. Regarding designs:
- One cylinder head in the so-called. in-line engines;
- Common heads for a number of cylinders in V-type (V-shaped) internal combustion engines;
- Separate cylinder heads in multi-cylinder in-line engines;
- Individual solutions: cylinder heads for single and multi-cylinder in-line internal combustion engines, V-shaped internal combustion engines and others.
Common 2-6 cylinder in-line engines use common heads. If the engine is V-shaped , then the cylinder head most likely covers one row of cylinders, although heads for each cylinder are also used, as in eight-cylinder engines . Individual cylinder heads can be seen in high-power diesel engines, as well as special power units, such as star and opposed two-cylinder units. If the engine is single-cylinder, then the head is strictly individual. The cylinder head is also classified according to the location of the combustion chambers. The following designs are possible:
- The camera is located directly in the head. With this design, the piston must have a flat bottom. There may be a displacer;
- The chamber is located both in the piston and in the cylinder head. Part of the combustion chamber is located at the bottom of the piston;
- The chamber is located directly in the piston. With this design, the cylinder head has a flat bottom surface, optionally with recesses for installing inclined valves.
But the classification does not end there either. Depending on the timing device and the presence of this mechanism in principle, the block heads may have different designs. For example:
- There is no timing belt. This is possible in single-cylinder, two-stroke, valveless, as well as multi-cylinder, lower-valve engines;
- Valves, rocker arms and other engine components are present. The camshaft is located at the bottom, the remaining engine components are mounted in the upper part of the cylinder head;
- Complete timing belt (camshaft, valves, drives, related elements). In this case, the parts are mounted in the upper part of the cylinder head.
The variety of timing belts is also determined by which engine they are designed for. There are heads for gasoline, gas, diesel units, for low-speed and forced engines, as well as air- or water-cooled . In general, the design of all heads is approximately the same, but in reality the heads are almost never interchangeable. Malfunctions of different types of heads are also similar.
Materials used
Quite stringent requirements are imposed on the materials used to manufacture the cylinder head. This is due to the fact that this unit contains a timing belt with inlet and outlet channels. Thus, the fuel mixture and hot gases pass through the cylinder head. This means that the metal works under conditions of high temperature and pressure, and is constantly in contact with a chemically aggressive liquid in the form of an aerosol. To solve these problems, the following is used for automotive engine cylinder heads:
- Aluminum. This metal is good because it is light, inexpensive and conducts heat well. Therefore, the thermal tension in the walls is always low, which is why detonations do not occur even in engines with very high compression. Engines in cylinder heads made of this material are distinguished by high power and efficiency. They are more convenient to manufacture and repair, because... easy to process.
- Cast iron. It can be alloyed or gray. In both cases, it is a material with significant specific density and, as a result, mass (Compared to aluminum, it is approximately twice as heavy). Another disadvantage is susceptibility to corrosion. Among the positive qualities, it should be noted greater strength and heat resistance. Most often, cylinder heads for diesel engines, especially for tractors, are made from this material. This is due to the fact that the detonation characteristics of diesel engines exceed the strength parameters of aluminum cylinder heads, which is why the latter quickly break.
Sometimes in air-cooled diesel engines the cylinder head is designed in such a way as to combine heat resistance with high thermal conductivity. Then the base of the head and exhaust valves is cast from cast iron. And everything else is filled with aluminum alloy. It turns out pretty good.
Despite the constant alternation of heating-cooling cycles, the cylinder head is deformed much less. And its heat dissipation is very good. On forced diesel engines, the operation of which is characterized by high thermal stress, special aluminum alloys are used.
Principle of operation
There are no difficulties with the operating principle in this case. The cylinder head forms a combustion chamber and fills it with a combustible mixture, after which it exhausts exhaust gases outside. In more detail it looks like this. In a carburetor engine, the cylinder head begins to work when the engine starts:
- The camshaft lobe pushes the rod through the lower end.
- The force is transmitted through the rod, the upper tip and the adjusting screw to the rocker arm through a hydraulic compensator.
- The rocker arm presses on the end surface of the valve. It lowers slightly into the chamber, which opens a circular slit. The fuel-air mixture is injected and ignited by the spark provided by the spark plug.
- The spring pushes the valve back. After the piston has made its downward stroke, when it goes up, it pushes out the exhaust gases. At a given point in time, the camshaft opens the exhaust valve. A similar gap is formed, through which the “smoke” escapes into the pipe and, through the exhaust pipe, into the atmosphere.
- This valve is placed back into the seat similar to the intake valve, with a spring
- The work cycle repeats.
In a diesel engine, the fuel is ignited by sudden compression rather than by a spark. Here, for normal operation of the engine, it is necessary to ensure precise adjustment of the high-pressure fuel pump (HPF) - the injection moment must be synchronized with the movement of the valve.
Gas joint seal
Order special equipment on our website: Special equipment rental in Russia
The tightness of the gas joint seal (i.e., the joint between the block and the head) is of great importance for any power unit. If this is not provided, the fuel mixture will not burn completely, power will drop and there will be problems with starting. In addition, the engine operation will be excessively noisy and its wear will accelerate. Achieving complete tightness is ensured by installing a gasket. Currently, three types of seals are used:
- Metal. They are made from sheet copper and steel. These are very strong and durable products. Loads are distributed evenly. If the cylinder block is specific, then the gasket contains additional sealing elements.
- Asbestos. In addition to the specified material, their structure also contains metal elements. Main advantages: high fire resistance and elasticity. Disadvantages: does not “like” temperature fluctuations and vibration. With prolonged use, it loses its properties.
- From composite materials, so-called. "non-asbestos". Made from rubber and synthetic fiber. These are elastic and resilient products with a long service life. They are not afraid of corrosion and sudden temperature changes. Good electrical insulators. Eco-friendly. Disadvantages: expensive, not always available in the periphery. Today they are considered the best.
Important
The service life of any gasket depends not only on its characteristics. It is important to follow the rules for installing the cylinder head, accurately adjust the power unit, fill it with high-quality fuel, ensure that there is no scale in the cooling system, as well as ensure that the pump and thermostat are operating correctly.
All pads are disposable. These products must not be reused, even if they appear undamaged. The reason is that complete tightness is not ensured at the specified tightening torque. The bolts are tightened from the central to the outer ones. The gasket must be changed in a clean environment so that chips, dust, etc. do not get into the combustion chamber. When purchasing such a part, you need to buy originals, preferably from well-known manufacturers.
If during engine repair it is planned to replace the cylinder head, then experts advise purchasing this unit assembled. As practice shows, installing parts from different manufacturers subsequently results in operational problems.
Conclusion
The cylinder head is a seemingly simple component of an internal combustion engine, in which there is simply nothing to break. Due to the complexity of modern engines and the fact that they are operated in harsh conditions, you cannot be sure that problems with the cylinder head will never arise during the entire period of operation of the vehicle. Of course, in most cases, only replacing the gasket is required, but it is important for the car enthusiast to remember that any change in the nature of the engine’s operation may indicate the appearance of far-reaching problems. Remember that abnormal engine operation, increased oil and fuel consumption, decreased acoustic comfort and strange behavior of the unit at different speeds indicate the need for diagnostics.
Common breakdowns
A cylinder head is an ingot of metal of complex shape. It has many functional parts. The main damage is cracks. In addition, troubles such as:
- The thread under the candle has been torn off.
- Loss of tightness due to gasket failure.
- The compensator, spring, valve, rocker breaks.
- The valve seat falls out.
- Due to the gap that appears at the bottom of the head, “smoke” enters the cooling system.
- The beds under the camshaft are worn out.
If cracks appear, there are options. If this is a gap between the combustion chamber and the cooling jacket, then it hardly makes sense to repair it. But in places outside the gas joint, the hole can be welded; it is not at all necessary to change the cylinder head. When the beds wear out, bronze bushings are installed.
If any defect is detected, the cylinder head must be repaired immediately. Otherwise, the unit quickly fails to such an extent that it becomes unrepairable. For example, if the valve does not close completely, the piston knocks on its plate. The valve is deformed, due to which it is no longer completely adjacent to the seat. Because of this, defects in the cylinder head and even the piston group occur. As a result, one of the piston groups fails. If you call for repairs at the initial stage, the problem can be solved relatively easily and quickly.
By the way, immediately after repair it is very useful to “listen” to the engine. If its operation is unstable, it is recommended to contact a specialist as soon as possible. Because if the repair was done by a mechanic of not very high qualifications (to put it mildly), then it will not be possible to solve the problem by grinding in the parts, no matter what this master says on this matter.
Regardless of whether the cylinder head repair was simple or complex, in conclusion the head must be properly polished, and optionally also milled. This is especially true for the mating plane. An experienced specialist is able to restore the cylinder head almost to its original condition. But this may take a lot of time.
Features of engine assembly after head repair
The necessary rigidity in the head is provided by the power frame. It consists of vertical bosses that have recesses for bolts and a main base plate located underneath.
During factory assembly, unacceptable deformation of the cylinder head is prevented by a strict sequence of tightening bolts or fastening studs with certain tightening torque standards. Therefore, following any cylinder head repair, it is important to follow these strict guidelines. Since any distortion breaks the tightness of the connection and leads to damage to the gasket or damage to the head itself, which subsequently has to be replaced.
If, when checking the engine after installing the cylinder head, leaks of oil or coolant are detected, this indicates improper tightening of the bolts and a violation of the tightness of the system.
In turn, the bolts are tightened using a torque wrench that controls this process.
Each stud and each bolt must be tightened in strict order and with tightness controlled. Moreover, the tightening torque may differ for different engine models. This data can rarely be found in the operating manual, but it will definitely be in the repair manual for a specific engine.