The vehicle engine is the most important module responsible for the quality of movement, as well as the performance of the entire unit. Its condition, as well as the quality of interacting elements, directly affects the safety of the driver and passengers during vehicle operation. That is why timely diagnosis and troubleshooting is a top priority for every driver.
The efficiency of the engine is largely determined by the characteristics of the functioning of auxiliary devices, including equipment that ensures fuel injection into the cylinders. The volume of fluid it supports depends on the following factors: injector operating time, pressure level inside the fuel rail, and the functioning of the intake manifold.
In order to take into account all the factors mentioned, as well as to ensure more accurate fuel supply, many car manufacturers use pressure regulators in their engines. They allow you to maintain the recirculation of flammable liquid at the proper level.
Design and principle of operation of RTD
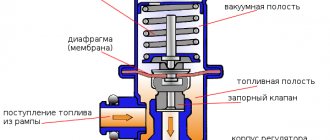
The RTD is designed in the form of a diaphragm valve, to which a fuel supply hose is connected on one side, and a spring mechanism of the intake manifold on the other. This device provides the necessary pressure difference between air and flammable liquid at the nozzle, as well as in the intake manifold. Taking this into account, excess gasoline or diesel will be sent to the tank via the return line.
The device for adjusting fuel pressure is designed in the form of two chambers: fuel and diaphragm. After fuel enters the first tank using the inlet fitting, it is supplied to the diaphragm sector using a special inlet pipeline. If the pressure level in the lower chamber exceeds the total created by the spring in the diaphragm, the latter moves in such a way that the remainder of the fuel mixture is returned to the gas tank through the return line. In this way, a constant pressure drop in the system is maintained within 2.5 bar.
Vehicles with diesel engines include a check valve in the fuel system, which has a slightly different structure. Its constituent elements are a solenoid and a rod that rests on the ball to block the return flow. In this way, the engine is protected from rapid wear, which is associated with a decrease in hydraulic vibrations. Maintenance and restoration of the fuel pressure regulator on a diesel engine is carried out similarly to its gasoline counterpart.
Regulator design
The design of the mechanical fuel pressure regulator is simple. It consists of a body, which is internally divided by a membrane into two chambers. One of them is called the fuel chamber, the second is called the vacuum chamber (or simply vacuum). Each of the chambers is connected to the system components by fittings and channels. The fuel chamber is connected through channels to the fuel rail, and a fitting for the line for draining excess gasoline (“return”) also comes from it. The vacuum chamber also has a fitting, which is designed to connect to the intake manifold.
A needle valve is fixed to the membrane, the seat for which is the channel of the drain line fitting. This valve is constantly in the closed position, and a spring installed in the vacuum chamber presses it to the seat.
Location of the RTD in the fuel rail of the vehicle
The use of a special regulator for the fuel system is associated with the need to reduce or increase the pressure of fuel supply to the engine when it operates at different speeds. For example, idling requires a very small amount of fuel, while as the speed increases, the intensity of its injection should increase.
In order to equalize this difference on all injectors, the device is installed at the end of the fuel rail. As standard, it is mounted in the fuel rail. Very often, its location can be changed - for example, the RTD is placed in a return hose or even in a tank.
Placement in the gas tank makes it possible to avoid the need to install additional fuel lines, and the check valve blocks excess fuel from entering the system. Regardless of the location, the RTD performs the same function, which is to support the fuel pressure required and safe for the vehicle engine.
This is interesting: How to get a medical certificate for a driver’s license in 2022 (detailed instructions)?
For systems without fuel recirculation, the RTD is located in the fuel tank and is designed to maintain the same fluid pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. The specificity of this arrangement is that the differences between the fuel pressures in the tank and in the intake manifold will not be constant, which is ultimately taken into account in the duration of injection of the working fluid.
Preparatory work
- Take a tire pressure gauge and wrap flax or fum tape around the tip, this will prevent fuel spills and air leakage.
- Prepare a hose with a maximum internal diameter of 9 millimeters, and you will also need clamps for fastening. It is necessary to fix the hose on the pressure gauge and tighten everything with clamps.
- Place the prepared tool on the engine so that the hose and pressure gauge fixed on it do not roll off the surface. This will avoid fuel spilling on the engine.
- We unscrew the nipple spool on the ramp (fuel splashing is possible due to residual pressure).
- We put a hose with a pressure gauge on the ramp connections and secure everything with a clamp.
- Homemade pressure gauge for measuring pressure in the rail assembly.
Possible causes of malfunction in the operation of the RTD
The design of the fuel pressure regulator is designed in such a way that the fuel pressure in the system remains stable while the engine is stopped. However, this is not always possible to achieve. This is due to wear and tear on the valve, which over time loses its ability to hold fuel. In this regard, in order to start the engine, the driver has to turn the starter for a long time.
The most common problems with the fuel control device are the following nuances.
- The valve in the device does not hold pressure completely. The main reason for such a breakdown is the subsidence of the spring, which has lost the ability to create the necessary resistance. In this case, gasoline will return back to the tank without entering the engine injectors.
- Difficult fuel movement due to clogged pressure regulator. This leads to the fact that it is unlikely that the engine can be started with half a turn.
- There is a jamming of the device associated with an uneven change in pressure level. With this malfunction, problems arise with the acceleration of the vehicle, and the dynamics are also reduced, affecting the safety of the driver and passengers.
It is worth noting that the fuel pressure regulator most often fails due to wear. Such a breakdown occurs after 100-200 thousand kilometers. In this case, thinning or drying out of the membrane is observed. At the same time, the spring weakens, and the valve gradually wedges. If problems with the valve are observed before this point, the cause of the breakdown is poor-quality assembly or a defective part.
Another cause of valve malfunction may be poor fuel quality. In this situation, foreign impurities that enter the working fluid clog the RDT. Unlike the first option, when you can replace the membrane yourself, you will have to contact a service center to install a new device, since cleaning the valve is not provided.
Replacing the check valve
Removing the fuel pressure regulator
When checking the fuel pressure regulator shows a malfunction, it is recommended to replace it immediately to avoid rapid wear of engine parts.
We replace the fuel pressure regulator:
- Reduce pressure in the fuel line;
- Carefully pull off the vacuum hose from the RTD;
- Unscrew the fastening nut from the fuel drain tube (it is attached to the hose);
- We unscrew the bolts that secure the check valve to the fuel rail;
- Now you can remove the fitting from the hole;
- Next, you need to remove the check valve from the fuel drain pipe (pay attention to the O-ring, which will be useful for installing a new part);
- We install the new RTD in the reverse order.
The failed part has been replaced, and then its operation must be checked using the method indicated above. The main thing to remember: timely diagnosis of a malfunction of the fuel pressure sensor will allow you to avoid serious consequences
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm valve. Fuel presses against it at one end, and the intake manifold spring presses against it at the other. At lower speeds, the valve opens, accompanied by the draining of residual fuel from the engine into the tank. The next time fuel is supplied, the pump starts, drawing the liquid through the filter. There is a special stabilizer on the fuel rail, whose task is to maintain optimal pressure in the system.
Signs of RTD malfunction
There are a number of signs of vehicle engine operation that can be used to determine that the RTD is out of order. The most common among them are:
- unstable operation of the power unit (it stalls), in which the fuel fluid pressure level is stable and the other systems are working normally;
- there is a decrease in motor sensitivity;
- there are jerks and failures in the operation of the power unit, which is especially noticeable in motion;
- the level of harmfulness (presence of CH and CO) of exhaust gases increases;
- fuel consumption increases;
- There are difficulties starting the engine.
Also, if malfunctions occur in the RTD, there may be an increase in fuel consumption and leaks of working fluid on the system hoses, which cannot be solved by installing new clamps and replacing tubes. If the symptoms of malfunction described above appear, it is useful for each driver to be able to check the fuel pressure regulator.
This is interesting: What is a car chassis? 2 modern design types
Diagnostics of the presented equipment is carried out as follows.
Step 1. Unscrew the plug of the fitting that supplies fuel fluid to the first chamber and inspect the o-ring. In the event that it has lost its integrity or obvious defects are observed, it is necessary to replace it.
Step 2. Remove the spool from the fitting, which is done in the same way as with a similar device in the tire. After this, you need to fix the tire pressure gauge using a special clamp on the latter and measure the pressure while the power unit is operating. After checking the parameters with those specified by the manufacturer, we can draw conclusions about the malfunction of the device. It is worth considering that when you disconnect the vacuum hose, the pressure level should increase slightly. When this does not happen, a complete replacement of the device is inevitable.
Without using a pressure gauge, you can also check the pressure in the fuel rail. In this case, it is necessary to pinch the flammable liquid return hose while the engine is running. When this is done, the engine with the universal fuel pressure regulator inoperative begins to gain power and all cylinders begin to operate.
Despite the effectiveness of this method, it is not always possible to clamp the return hose for the engines of modern types of vehicles, since they have metal tubes or hoses of insufficient length. If you want to check the RTD on the injector, you can use only one method, which involves using a pressure gauge.
Checking the fuel pressure regulator
Testing the functionality of the fuel pressure regulator will depend on whether it is mechanical or electrical. the old regulator of a gasoline engine . You need to act according to the following algorithm:
- find the fuel return hose in the engine compartment;
- start the engine and let it run for about one minute, so that it is no longer cold, but also not hot enough;
- using pliers (carefully so as not to damage it!!!) pinch the above fuel return hose;
- If the engine was previously “troubling” and running poorly, but after pinching the hose it started working well, it means that the fuel pressure regulator has failed.
It is impossible to pinch rubber fuel hoses for a long time, since in such conditions an additional load is created on the fuel pump, which can damage it in the long run!
How to determine the performance of an injector
In modern injection gasoline engines, firstly, instead of rubber fuel hoses, metal tubes are installed (due to high fuel pressure and for reliability and durability), and secondly, electrical sensors based on strain gauges are installed.
Accordingly, checking the fuel pressure sensor comes down to checking the output voltage from the sensor when the supplied fuel pressure changes, in other words, increasing/decreasing engine speed. This will make it clear whether the fuel pressure regulator has failed or not.
Another method of checking is with a pressure gauge. So, a pressure gauge is connected between the fuel hose and the fitting. Before doing this, be sure to disconnect the vacuum hose. You also first need to find out what normal fuel pressure should be in the engine (it will be different for carburetor, injection and diesel engines). Typically, for injection engines, the corresponding value is in the range of approximately 2.5...3.0 atmospheres.
You need to start the engine and check the readings on the pressure gauge that the pressure is normal. Next you need to give it a little gas. In this case, the pressure drops slightly (by tenths of an atmosphere). After which the pressure is restored. Next, you need to use the same pliers to pinch the return fuel hose, as a result of which the pressure will increase to approximately 2.5...3.5 atmospheres. If this does not happen, the regulator has failed. Remember that you cannot pinch the hoses for a long time!
How to check on a diesel engine
Checking the fuel pressure regulator on modern Common Rail diesel systems is limited only to measuring the internal electrical resistance of the sensor control inductive coil. In most cases, the corresponding value is around 8 ohms (the exact value must be clarified in additional sources - manuals). If the resistance value is obviously too low or too high, it means the regulator has failed. More detailed diagnostics are only possible in a car service center at specialized stands, where not only sensors are checked, but also the entire common rail fuel system control system.
Repair and replacement of RTD
If your vehicle exhibits any number of symptoms of fuel regulator malfunction, diagnosing the fuel regulator is the only step toward returning it to proper operating parameters. In the event that a check indicates that the device is out of order, the following must be done.
Step 1. Remove the fitting plug to be able to control the pressure of the flammable liquid at its end.
Step 2. Using a special metal protective cap, carefully remove the spool from the inner cavity of the fitting.
Step 3. Reduce the pressure in the power system, and then carefully remove the vacuum hose from the device.
Step 4. Remove the nut used to secure the fuel supply tube.
Step 5. After the two bolts that secure the module to the fuel frame are unscrewed, you need to smoothly remove the fitting from their holes.
Step 6. Carefully remove the RTD.
As a rule, the removed device cannot be repaired, and it is replaced with a new, more functional one. You can purchase a module with delivery either in any specialized store or via the Internet.
Failure options
The regulator is a simple device from a technical point of view, so there are few breakdowns that can happen to it. In almost all cases it is recommended to replace the RTD.
What can break:
- Spring. This is the main failure in the RDT. Due to the weakening of the spring, the engine becomes “starved”, there is not enough fuel at high speeds, when the clutch is pressed and during transient conditions.
- Pollution. When clogged, the ability to pass fuel is lost. The engine stops in any operating mode. If the RTD is heavily contaminated, the pressure in the vehicle rises sharply and fuel leaks through the sealing material. The problem is solved by pumping a large amount of fuel into the fuel pump.
- Jammed. The RTD in the ramp may periodically jam. The car twitches.
How to repair an RTD?
As part of component repair, the following work must be performed:
- Look under the hood of the car where there is a fitting plug designed to control fuel pressure. Unscrew it, then using a special protective metal cap, carefully unscrew the spool inside the fitting.
- Connect the hose with the pressure gauge and secure it to the fitting using a clamp. After starting the engine, check that the pressure reading on the measuring device does not exceed 3.25 Bar.
- Disconnect the vacuum hose from the RTD. This operation should be accompanied by an increase in pressure. If nothing happens, repairing the fuel pressure regulator is useless; you will have to replace the element with a new one.
If the part cannot be repaired, we proceed to install a new device.
- Disconnect the vacuum hose. The pressure will begin to increase. Having reduced the pressure in the power system, proceed to remove the vacuum hose. You will need to unscrew the securing nut on the fuel drain pipe, where diesel or gasoline flows through the fuel filter to the RTD.
- After unscrewing the two bolts securing the device to the fuel rail, you can safely remove the regulator from the fuel discharge tube itself. The ring remaining in the ramp can be easily removed by hand and placed on the regulator before installation.
- Install a new regulator and perform all previous steps in reverse order. Make sure the new device is in working order, only then proceed with complete assembly. Upon completion of installation, perform a control check of the operation and serviceability of the device.