What is a gear ratio? Quite often you can hear the question “what is a gear ratio” from car owners. In this article I will try to briefly cover this topic. So, transmission mechanisms transmit the rotation of one shaft to another, i.e. force the second shaft to rotate through the rotation of the first. This question was explored by Leonardo da Vinci. Some of his inventions are still used today in the designs of bicycles and even cars.
Thus, based on his sketches of gears, globoid worm gears, bevel gears, spiral gears and roller chains, the current vehicle gearbox mechanisms were developed. The gear ratio is the ratio of the angular speeds of the drive to the driven gear (wheels, shafts) or the ratio of the radii of the driven to the drive gear. In particular, gear ratios of a gearbox are determined by the ratio of the number of teeth of the driven gear to the drive gear. If several pairs of gears are involved in the transmission, the total gear ratio is the product of the gear ratios of all pairs of gears participating in the transmission.
What is the gear ratio of the box and what depends on it
So, the gear ratio of a gearbox is the ratio between the number of teeth of the drive and driven gears. Let's try to explain it more clearly. If, for example, there are 60 teeth on the driven gear, and 30 on the drive gear, then this pair is characterized by a gear ratio that is 2. To understand this, you need to apply a simple formula: 60 divided by 30 and you get 2.
Important
The gearbox ratio, without exaggeration, is considered the most important indicator of gear or stepped transmissions, based on the transmission of torque from the motor to the drive of any other unit. One of the key functions of this mechanism is to reduce or increase the transmitted torque.
For example, if you correctly change the number of teeth on the gears, you can influence the torque transmitted to the so-called “consumer” - increase or decrease it according to needs. In conventional cars, the torque transmitted from the internal combustion engine to the drive wheels through the gearbox and drive axle gearbox increases. In powerful off-road SUVs, a low-range transfer case is additionally used for this purpose.
Answering the question of what the gear ratio of the transmission and gearbox affects, let us note, first of all, the dynamics of acceleration. The maximum speed that the vehicle can develop also depends on this indicator. Step boxes are equipped with several pairs, and the inverters of these pairs are different.
A higher number means higher traction that the corresponding gear can provide. The engine picks up speed more quickly, the car accelerates more actively, but the speed will be limited, and in order to increase it, you need to switch the gear to the one that is higher.
Most often, the torque supplied to the gearbox from the engine increases significantly at low speeds (from first to third). As for high gears (from fourth to sixth), while driving in them, the frequency converter decreases, so the car develops high speed. True, the intensity of acceleration in high gears is lower than in first, second or third.
Among other things, the acceleration dynamics also depend on the main gear ratio - if it is higher, it means better dynamics, regardless of the gear, and the lower the maximum driving speed.
Considering what was described above, we can conclude that the gear ratios of cars are selected depending on the power of the power unit, the torque, the purpose for which it is planned to be used, and many other factors. If the designers managed to choose the right gear ratios, then there will be no complaints about the dynamics of the car.
The balance between dynamics and efficiency also plays an important role, because fast cars that consume minimal fuel simply do not exist. If you need to achieve impressive dynamics, you shouldn't count on efficiency.
General definition
A clear example of changing the number of revolutions is most easily observed on a simple bicycle. A man pedals slowly. The wheel rotates much faster. The change in the number of revolutions occurs due to 2 sprockets connected in a chain. When the large one, which rotates with the pedals, makes one revolution, the small one, standing on the rear hub, rotates several times.
Torque transmissions
The mechanisms use several types of gears that change torque. They have their own characteristics, positive qualities and disadvantages. Most common transmissions:
Belt drive is the simplest to implement. It is used when creating homemade machines, in machine tools to change the speed of rotation of the working unit, in cars.
The belt is tensioned between 2 pulleys and transmits rotation from the driver to the driven. Performance is poor because the belt slides on a smooth surface. Thanks to this, the belt assembly is the safest way to transmit rotation. When overloaded, the belt slips and the driven shaft stops.
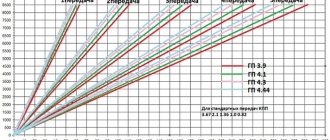
Gear ratios for each gear from first to fifth
To calculate gearbox ratios, you can use the following formula:
K = K1/K2
In this case, K1 is the number of teeth on the driven gear, while K2 is the number of them on the drive gear. To determine the gear ratio from the gearbox to the wheels, you need to find out the ratio of the differential driven gear and the gearbox secondary shaft gear.
In other words, it is necessary to calculate the main gear ratio. So, if there are 15 teeth on the gear of the secondary shaft of the box, and on the driven gear there are, for example, 51, by simple calculations we get the following: 51 divided by 15 = 3.4.
The gear ratio of a particular vehicle is indicated in its operating instructions. For example, on a VAZ 21083, gear ratios from 1st to 5th gear correspond to the following indicators:
- 1 – 3,4.
- 2 – 2,5.
- 3 – 2,0.
- 4 – 1,7.
- 5 – 1,4.
If the car is equipped with a 6-speed gearbox, then in sixth gear the gear ratio is 1.2.
Conclusion
Modern cars are quite complex mechanisms, where a large number of elements predominate, the operation and structure of which every motorist should know (at least basic knowledge). If you have this information, you can eliminate the possibility of getting into a difficult situation when there is simply no one to turn to for help, and nowhere. Of course, a car enthusiast will not be able to master all the aspects regarding the gear ratio. However, you should highlight the key aspects for yourself so that you will subsequently be able to make the most of your car’s lifespan, without causing structural elements to become overloaded and subsequently fail.
Tuning the gearbox by changing the gear ratio - is it necessary?
We already wrote above that optimal dynamic performance is observed at maximum torque; the characteristics of the motor here do not play as significant a role as it might seem. The greater the difference between the revolutions and the maximum torque, the more reluctant the car is to accelerate.
Typically, the gear ratio of each gear is selected in such a way that the driver can quickly accelerate the car in lower gears, and in high gears simply maintain a stable speed, while saving fuel. When it is necessary to increase dynamics, they resort to tuning - they narrow the range of frequencies developed by the engine at one speed (gear).
In other words, gears are made shorter using the so-called “closed row of gearboxes.” This allows the power plant to quickly reach maximum speed in low gears. Moreover, at the moment of switching to a higher speed, the engine speed does not decrease, as happens with standard gearboxes, they are maintained at a stable level, being in the range of the highest torque.
To achieve this goal, another pair of gearboxes with a changed gear ratio are installed on the car. If the same model is produced with several variants of power units (1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8 l), the main pair is taken from the version with a less powerful power unit. For example, together with a 1.6-liter engine, the main pair from a 1.2 or 1.4-liter engine is installed. This allows you to significantly reduce the overall gear ratio, improving dynamics, but entails an increase in fuel consumption.
However, it is important to remember that at high speeds, especially in 5th gear, the engine will gain maximum speed, this is fraught with discomfort - vibrations increase, shaking and extraneous sounds appear. Experts advise choosing the right number of gear ratios, taking into account the task and customer requirements, as well as many other factors that will enhance the dynamics without compromising traffic safety.
Gradual reduction ratios are the prerogative of racing drivers and provide better dynamic performance at high speeds. But this is true when driving on flat areas without turns. For normal driving, this solution is not relevant; it is better to use higher gear ratios.
Advantages and disadvantages
Worm final drive
Each type of gear connection has its pros and cons. Let's look at them:
- Cylindrical main gear. The maximum gear ratio is limited to 4.2. A further increase in the tooth ratio leads to a significant increase in the size of the mechanism, as well as an increase in the noise level.
- Hypoid main gear. This type is characterized by low tooth load and reduced noise level. In this case, due to the displacement in the meshing of the gears, sliding friction increases and efficiency decreases, but at the same time it becomes possible to lower the driveshaft as low as possible. Gear ratio for passenger cars – 3.5-4.5; for freight – 5-7;.
- Bevel main gear. Rarely used due to its large size and noise.
- Worm main gear. This type of gear connection is practically not used due to the complexity of manufacturing and the high cost of production.
The main gear is an integral part of the transmission, on which fuel consumption, maximum speed and acceleration time of the vehicle depend. That is why, when tuning a transmission, a pair of gears is often replaced with an improved version. This helps reduce the load on the gearbox and clutch, as well as improve acceleration dynamics.
Selecting gearbox ratios to increase power
The gear ratio in a gearbox clearly characterizes the gears. They are a rotating element that rotates the gears. The gearbox, in turn, distributes the power of the motor. Each gearbox has a gear ratio, what is this number, what does it affect and how to calculate it?
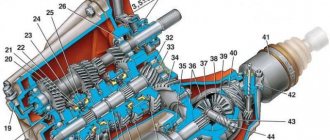
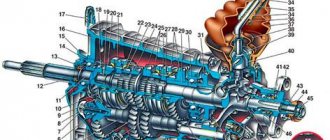
Any gearbox has the following elements:
- Carter. Has components and parts of the box itself. Attached to the clutch. During operation, the gears are subjected to heavy loads, so they need careful lubrication. Therefore, oil is filled to half its volume.
- Shafts with primary and secondary gears. These elements are located in bearings. All gears have a different number of teeth.
- Synchronizers. Provides quiet operation and smooth gear shifts. It is very important to shift gears smoothly so that the synchronizers have time to operate, otherwise the gearbox may fail and the car will have to be sent in for repairs or repaired yourself, which will require financial costs.
- Additional shafts for reverse. Similar to the input shafts. They rotate like primary and secondary, but in the opposite direction.
- Shift lever. Provides transmission of speeds if you have a manual transmission. If you are the owner of an automatic transmission, then the speed switches independently.
- Mechanism for switching the locking system and lock. Responsible for changing gears using a lever or automatically. The locking system does not allow activating multiple gears at once. The locking system prevents the gears from switching off on their own.
Basic faults
- failure of the differential bearing - in gearboxes, bearings are used to allow the differential to rotate. This is the most vulnerable part that operates under critical loads (speed, temperature changes). When the rollers or balls wear out, the bearing emits a hum, the volume of which increases in proportion to the speed of the vehicle. Neglecting timely replacement of the bearing threatens to jam the gears of the main pair, which subsequently leads to the replacement of the entire assembly, including satellites and axle shafts;
- activation of the GP teeth and satellites. The rubbing surfaces of parts are subject to wear; with every hundred thousand kilometers, the teeth of a pair wear out, and the gap between them increases, leading to increased vibration and hum. For this purpose, adjustment of the contact patch is provided by placing spacer washers;
- cutting off the teeth of the gearbox and satellites - occurs if you often drive away with slipping;
- licking of the splined part on the axle shafts and satellites - natural wear and tear according to the mileage of the car;
- turning the axle bushing leads to the fact that the car will stand still in any gear and the gearbox will rotate;
- oil leak - possibly as a result of increased pressure in the differential housing due to a clogged breather or due to a leak in the gearbox cover.
Specifics of operation of the rear axle gearbox
During vehicle operation, gears cling to each other with their teeth, however, even observing high metrological standards of production and adjustment, it is impossible to avoid their wear. Gears are made from high quality hardened steel. The gear housing is filled with special oil. Since the oil, being liquid, periodically tends to leak out of the cracks of the housing, to solve this problem, special gaskets called oil seals are used in the areas where the shafts exit. Unfortunately, the service life of the oil seals is significantly lower than the gears themselves, so when they wear out, the gear housing often contains oil smudges. If the oil completely leaks out (this happens if the seals are not replaced in a timely manner), the life of the gearbox is reduced significantly. In addition, dust and dirt tend to get through worn oil seals. To prevent such phenomena, it is recommended to check the gear housing from time to time using an inspection hole.
How does the service work?
Gearbox maintenance is rarely done; usually everything is limited to changing the oil. At a mileage of over 150,000 km, the bearing may need to be adjusted, as well as the contact patch between the driven and drive gears. When changing the oil, it is extremely important to clean the cavity from wear products (small chips), as well as dirt. It is not necessary to use flushes for the axle gearbox; it is enough to use 2 liters of diesel fuel and let the unit run at low speeds.
Tips on how to extend the performance of the GP and differential:
- change the oil in a timely manner, and if your driving style is more sporty, the car endures high loads (driving at high speed, transporting cargo);
- When changing the oil manufacturer or changing the viscosity, flush the gearbox;
- When driving over 200,000 km, it is recommended to use additives. Why is an additive needed? Molybdenum disulfide, contained in the additive, reduces friction of parts, as a result of which the temperature decreases, the oil retains its properties longer. Remember that if the main pair is heavily worn, there is no point in using an additive;
- Avoid starting with slipping.
What's the result?
As you can see, the gear ratio has a serious impact on the dynamic performance and characteristics of the car. As part of the design of a gearbox, engineers separately take into account engine power, the intended purpose of the vehicle, etc., based on which gear ratios are selected for the entire range of gears.
It is also possible to make changes only to the transmission, which in itself gives noticeable improvements. When tuning a transmission, it is necessary to take into account the feasibility of certain modifications, as well as take into account the modes in which a particular car will be operated.
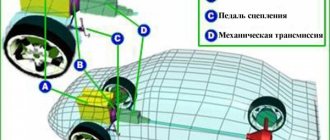
The design and principle of operation of a manual gearbox. Types of mechanical boxes (double-shaft, three-shaft), features, differences
Gearbox differential: what is it, differential design, types of differentials. How does a gearbox differential work in a car transmission?
Gears: types of gears, their distinctive features. Advantages and disadvantages of gears, manufacturing, maintenance of a gear pair.
Planetary gear (planetary mechanism) device. Where is planetary gear used in a car? Planetary gearbox, features.
“Manual” gearbox: the main pros and cons of this type of gearbox, the operating principle of a car’s manual transmission (manual transmission).
Power take-off (PTO): what it is intended for, how the PTO works, features, types and types. What you need to consider when using this box.
Types of spinning reels
Technically, the term “spinning reel” applies only to spinning reels—“meat grinders.” Inertial reels, although they can be installed on a spinning rod, are now almost never fished with archaic inertial reels like “Nevsky” ones, and for modern multiplier inertial reels there is a separate class of rods - casting rods, which have a special finger trigger and a special ring design. You can read more about them in this article.
Spinning reels
Most fishermen use the term “spinning reel” to mean spinning reels. Having appeared at the end of the 19th century, spinning reels gained enormous popularity, first in Europe, and then throughout the world, with the exception of the United States, where at that time a long-standing culture of using multipliers had already developed.
Inertia-free casters are easy to maintain and inexpensive, and their most outstanding quality is their long casting range and ease of casting, as well as effective work with small baits and thin tackle. Further in the article we will talk specifically about the choice of inertia-free coils.
You can read about other types of reels that you can install on a spinning rod at the end of the article.
We often hear the same question from people who are just starting to master fishing skills and are thinking about choosing a spinning reel: what gear ratio should the reel mechanism have and what size spool is suitable for certain fishing methods?
The size of the spool, as well as the gear ratio, is a fundamental characteristic of the reel. Different manufacturers have their own standards, but most often on Japanese reels there are markings 1000, 1500, 2500, and on European ones - the last digits of the article or markings 20, 25, 30. The larger the number, the heavier class the reel belongs to. The spool on the skirt also indicates its line capacity.
So, you need to choose a reel in accordance with the fishing method and the class of the rod. For the ultra-light and light class, reels up to size 2000 or size 20 are suitable; for average - 2500, 3000 or 25, 30; for heavy - 4000 or more. When choosing a reel, you should also take into account its weight so that all the gear is balanced. You shouldn’t put a 2000 reel on a heavy class rod, and a 4000 on a light spinning rod.
In my opinion, the more the better. In any case, there is a friction. the main thing is that there are more bearings.. and features in the size of the spool.. depending on what kind of fishing line you have.
if memory serves
The higher the ratio, the “stronger” the reel is, designed for catching large fish. That is, all other things being equal, the ratio 5:1 will be steeper than 5:2. And for herbal plants, almost any ratio will do, as long as it rotates. Moreover, as a rule, as the number of bearings increases, the price becomes more expensive. Therefore, it seems to me that we should be guided by the possibility of a pocket.
on the contrary, the lower, the stronger.
that's right, I remembered it the other way around
In general, everything is simple here, I try to take reels that have 2 spools, because it is convenient. We wind a braided cord on one spool and a monofilament line on the other. And if necessary, we use one or the other on our fishing trips. But this criterion is not strict, so if you find a cool reel, but with one spool, do at your own discretion.
A very important thing, since it affects the operation of the entire gear as a whole. If the reel is poorly laid, then problems may appear during fishing, such as loops, “beards”, etc. This affects casting and line coming off the spool. There are several ways to find out what type of coil is laid:
Diawa + Shimano = perfect fit. Why? I wrote about this in the first paragraph.
The presence of an endless screw in the coil. This is a technology that allows you to lay the line perfectly. You should ask the seller about its presence in the reel.
Search the Internet and read reviews. Moreover, I would relate this point to the entire article as a whole, since now is the 21st century and on thematic forums you can find a lot of information on specific models.
That's all that is important to consider when choosing the right reel for your feeder
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that feeder reels, as a rule, are not marked feeder, although everything is changing. As a rule, manufacturers make coils for specific tasks, but there is a wide variety of coils
Therefore, do not be shy about the various inscriptions on the boxes, look at the coil through the prism of the technical characteristics that we discussed above, read thematic forums, and you will not miss when choosing a feeder coil.
Master of Sports in Feeder
Selecting gearbox ratios to increase power
The gear ratio in a gearbox clearly characterizes the gears. They are a rotating element that rotates the gears. The gearbox, in turn, distributes the power of the motor. Each gearbox has a gear ratio, what is this number, what does it affect and how to calculate it?
Any gearbox has the following elements:
- Carter. Has components and parts of the box itself. Attached to the clutch. During operation, the gears are subjected to heavy loads, so they need careful lubrication. Therefore, oil is filled to half its volume.
- Shafts with primary and secondary gears. These elements are located in bearings. All gears have a different number of teeth.
- Synchronizers. Provides quiet operation and smooth gear shifts. It is very important to shift gears smoothly so that the synchronizers have time to operate, otherwise the gearbox may fail and the car will have to be sent in for repairs or repaired yourself, which will require financial costs.
- Additional shafts for reverse. Similar to the input shafts. They rotate like primary and secondary, but in the opposite direction.
- Shift lever. Provides transmission of speeds if you have a manual transmission. If you are the owner of an automatic transmission, then the speed switches independently.
- Mechanism for switching the locking system and lock. Responsible for changing gears using a lever or automatically. The locking system does not allow activating multiple gears at once. The locking system prevents the gears from switching off on their own.