A car with a faulty fuel injection pump loses power, increases fuel consumption, has problems starting the engine, increases smoke from the exhaust system, etc. There can be many reasons leading to pump malfunctions, from the appearance of moisture in the plunger pair to problems in the electronics. The best way to check the fuel injection pump is at a stand at a service station, but some faults can be determined independently in your garage. To learn how to do this, you should be able to identify the signs, and for this you need to know the reasons leading to this.
Checking the diesel fuel injection pump at home
A car with a faulty fuel injection pump loses power, increases fuel consumption, has problems starting the engine, increases smoke from the exhaust system, etc. There can be many reasons leading to pump malfunctions, from the appearance of moisture in the plunger pair to problems in the electronics. The best way to check the fuel injection pump is at a stand at a service station, but some faults can be determined independently in your garage. To learn how to do this, you should be able to identify the signs, and for this you need to know the reasons leading to this.
Repair of plunger mechanism
Next, you should move on to disassembling and inspecting the plunger supercharger. Disconnect the distribution head of the pump from the housing, and then place it with the pulley down so that the insides do not spill out. Before removing the cams, drive gear and centrifugal governor clutch, you need to check whether these parts do not jam when moving, and then, carefully supporting them with your fingers, remove them from the housing.
It is advisable to mark the rollers, washers, and axles of the cam clutch with a marker, because all mating surfaces have already rubbed into each other, and it will be better if they remain that way after assembly. After disassembly, you need to carefully inspect the parts for chips or wear. Heavily worn elements should be replaced with new ones.
The degree of wear of the plunger pair can only be estimated approximately. The performance of the precision interface is checked after the pump is assembled by measuring its operating pressure. Finally, you need to blow out all the filter elements (mesh) with compressed air, after which you can reassemble the pump in reverse order.
Types of fuel pumps
First, you should understand the types of fuel injection pumps for diesel cars, since each of them has its own typical features and breakdowns. However, all pumps, regardless of variety, have one main unit, namely plunger pairs (pistons and cylinders).
Injection pumps are divided into types according to the principle of injection:
- direct action with a mechanical plunger drive;
- battery injection.
In addition, high-pressure pumps are also divided into classes according to their design:
- In-line - the working segments are installed in a row, diesel fuel is injected in turn into all cylinders.
- Distribution - fuel from one section is supplied to several cylinders. They come in both single-plunger and double-plunger types.
- Multi-section - better known as a V-shaped or hydraulic accumulator. Installed on engines with high power but low speed.
On a direct injection injection pump, injection and delivery occur simultaneously through a mechanical plunger drive. On battery types, fuel is supplied in separate cycles - first it is pumped into the pump accumulator, and then into the injectors. With modern models, the entire process is controlled electronically.
Injection pumps are also installed on gasoline vehicles. Used on engines with direct injection. The pump is necessary to supply fuel to the cylinder chamber under high pressure, and a combustible mixture is formed in it, which is ignited by the spark plug.
Operating principle of fuel injection pump
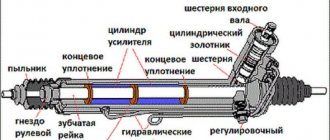
Despite the abundance of different types of pumps, all injection pumps operate on a similar principle and ensure the supply of portions of diesel fuel into the cylinders of a car engine under high pressure at strictly designated times. The size of the supplied fuel portions is determined by the load of the cylinders to the crankshaft. The basis of any type of injection pump is a plunger pair, consisting of a plunger (piston) and a sleeve (cylinder).
There are 2 main types of injection pumps based on their operating principle:
- Direct acting injection pump with mechanical plunger drive;
- Injection pump with battery injection.
The design also distinguishes several types of fuel injection pumps:
- in-line - pump sections are arranged in a row and supply fuel to a specific engine cylinder;
- distribution - one pump section can supply fuel to several different cylinders;
- multi-section (V-shaped) - for high-speed diesel engines.
In turn, distribution injection pumps can be single-plunger or double-plunger.
All direct injection injection pumps operate on the same principle:
- mechanical plunger drive;
- simultaneous pumping and injection processes;
- the pressure for fuel injection is created by the movement of the plunger.
Injection pumps with accumulator injection provide fuel supply in separate cycles: first, the fuel is pumped into the pump accumulator, then it enters the fuel injectors. Pumps with electronically controlled injectors are called the Common rail system.
Briefly, the operating principle of a high pressure fuel pump looks like this.
- Fuel from the tank enters the injection pump thanks to the booster pump. The fuel pressure at the inlet to the pump section of the injection pump is maintained by a pressure reducing valve.
- The movement of the plunger that supplies fuel to the engine cylinders is ensured by the cam shaft, which in turn is driven by the car’s crankshaft.
- The rotation of the cam shaft causes the plunger to move, which moves up the bushing. In this case, the outlet and inlet ports open sequentially.
- The pressure created by the movement of the plunger opens the discharge valve, after which the fuel flows to the fuel injector of the diesel engine cylinder.
- Excess fuel is drained from the plunger into the tank through a drain, screw, radial and axial channels through a drain fitting.
Signs of a high pressure pump malfunction
Most of the symptoms of fuel pump malfunctions are the same or very similar for most types and types. These include the following symptoms:
- a sharp increase in fuel consumption;
- engine operation becomes unstable, especially at low speeds;
- problems when starting the engine, extremely sensitive during cold periods of the year;
- reduction in car power;
- increased smoke from the exhaust pipe;
- leakage of diesel fuel from the injection pump;
- increase in noise when the engine is running.
Car owners with extensive experience note another clear sign of problems with the pump plunger - at idle, a “hot” engine can stall for no apparent reason. It cannot be started until the pump has cooled to normal temperature. A “cold” engine starts normally.
Why should you contact us?
Experience in the diesel engine maintenance and repair market shows that the fuel pump is one of the most vulnerable and sensitive elements of the engine design. It is important not only to monitor suspicious symptoms from the power unit, but also to pay due attention to the maintenance of the injection pump. Such serious work can only be entrusted to experienced and trusted specialists. Our technicians have been specializing in the repair and maintenance of diesel engines for many years. We are well aware of the design and maintenance features of units of different years of production. We have high-precision diagnostic equipment that will help you quickly identify the problem. Here are a few more arguments in favor of service at Diesel-Master:
- Repair within 1 day.
- Convenient location.
- Guarantees for all types of work.
- Use of certified equipment and original spare parts.
To become our client, fill out an application on our website or call us at +7 (921) 932-25-54,, 8 and choose a convenient time for your visit. If you have any questions regarding our work, you can ask them directly on the website - our specialists will contact you in a short time and provide all the necessary information.
Causes of fuel injection pump breakdowns
There are several most important reasons why a high pressure pump fails. This is usually due to the breakdown of the following parts:
- Plunger. The most common cause is contamination of the plunger pair. There are two main factors here. The first is the nature of the design (for example, the gap is too small). The second is poor fuel quality (presence of undesirable impurities clogging the device). In addition, contamination can also come from the engine - soot, dirt, etc. The operation is also affected by the wear of the plunger pair, which leads to severe overheating of the bearings.
- Presence of water in fuel. Moisture can wash away the fuel layer that protects the surfaces of precision parts of the high-pressure pump, which leads to a decrease in its service life and even possible jamming.
- Fuel filter is dirty. This leads to possible dirt getting into the plunger pair, and the pump also wears out.
- Irregularities in fuel supply and distribution. Another common reason for this is a malfunction of the plunger pair, namely wear of the drivers, teeth on the rack, discharge valves and contamination of the nozzles.
- Defective parts. Quite rare, but still found on cheap pumps. This may include cracks and chips of the housing, damaged bearings, jamming of plunger bushings, and the like.
- Bearing wear. More often caused by aging or defective parts. This leads to malfunctions of the pump, and the bearing itself and nearby parts overheat, which reduces its service life.
- Jamming of pistons and bushings. Leads to failure of the rack, cam shaft, gear, governor and keys. More often caused by moisture entering the cavity between the piston and bushing.
- Wear of injection pump components. Occurs as a result of aging or after water penetrates inside, which leads to corrosion of pump parts.
- Corrosion of the plunger pair. Appears when there is a large amount of water in the fuel.
- Problems in the cooling system. In other words, with prolonged use or heavy loads, the pump simply overheats. Cooling malfunction can be caused by insufficient antifreeze, blockages, breakdown of individual parts, etc.
If you suspect a faulty operation of the injection pump rack or related elements, you must check the following components for serviceability:
- detaching the rack from the regulator parts;
- check the clamps of the plunger leads;
- jamming of the gear rim screws.
The most dangerous cause of failure is a malfunction in the mobility of the fuel supply rack. If it is wedged at maximum fuel supply so that the regulator cannot return it to the reverse position, then the crankshaft speed in the engine sharply increases. This leads to the engine starting to work at the limit, and this is fraught with consequences. If the rack wedge is in the off position, the engine will not start.
When operating a car in low temperature conditions, there are cases of freezing of fuel injection pump parts and components. To prevent such situations, you should use fuel and oil that correspond to the temperature conditions.
In battery injection systems (or Common Rail), there are cases of control valve failure. Most often it is immediately replaced with a new one. Sometimes it is rebuilt and some parts are replaced.
Operating principle of fuel injection pump
Depending on the engine design and vehicle model, they may use different types of fuel injection pumps. Despite this, the operating principle remains the same: the unit is responsible for supplying diesel fuel under high pressure to the combustion chambers. The amount of diesel fuel can vary greatly, depending on the operating mode of the power unit and the load on it.
The main structural elements of the injection pump are the plunger and the cylinder bushing. Depending on the operating principle of these elements, all fuel pumps can be divided into two categories: battery-type injection pumps and direct-acting pumps.
Direct acting fuel pumps operate on the following principle:
- The plunger is driven by mechanical traction.
- Injection and forcing of fuel into the combustion chambers are carried out simultaneously.
- The plunger is responsible for creating the pressure necessary to supply the required amount of fuel.
Battery fuel injection pumps are otherwise called separate-action pumps. Diesel fuel is first pumped into a special accumulator, after which it enters the injectors, and then into the combustion chamber.
Manufacturers of fuel pumps use the following classification:
- In-line pumps. In them, each cylinder is directly connected to a specific pumping section, which is responsible for its power supply.
- Distribution pumps. Each section provides fuel to one or more cylinders.
- Multi-section models. Installed only on high-speed power units.
Based on the design of the injection pump, we can describe the principle of its operation in stages:
- A special pump pumps diesel fuel and supplies it to the fuel injection pump. The required operating pressure is ensured by the presence of a pressure reducing valve.
- The cam shaft connected to the crankshaft is responsible for driving the plunger, which supplies fuel to the cylinders.
- Under the influence of the shaft, the plunger moves upward in the cavity of the sleeve. At this moment, the fuel exhaust and intake valves open.
- When moving, the plunger creates the pressure necessary to open the discharge valve. Through it, the fuel is directed to the spray nozzles.
- Excess fuel is removed through special channels and returned to the tank using a drain fitting.
Experts note that coordinated and correct operation of the injection pump is possible only if all stages are coordinated. The pump is very sensitive to the operating mode and fuel quality, so if you ignore at least one of the points, this can lead to serious problems.
Determining faults in fuel injection pump
It is worth remembering that the most reliable data on the condition of the fuel pump can only be obtained after checking it at a special stand in a car repair shop. Naturally, such diagnostics at home is impossible without special equipment. But it is still possible to check some elements and the correctness of their operation.
Water in plungers
To do this, you will need to remove the belt from the timing mechanism and carefully rotate the pulley. When rotating with variable forces, there is no water. If you have to apply significant force when rotating or you can’t turn it at all, then there is moisture.
The presence of moisture in the fuel injection pump is extremely harmful both for it and for the entire engine. This leads to rapid wear of parts and a reduction in their service life, and can also cause corrosion and even a complete wedge of the unit.
Pressure in the plunger pair
You can check it using a special tester - KI-4802 or TAD-01A. If there is none, then a regular pressure gauge with a large measurement range will do.
The device is screwed in instead of the fuel pipe or fixed in the central hole of the injection pump head. Then the engine is started and readings are taken. Under normal conditions, the value should be close to 300 kg/cm2. This is a conditional value and depends on many factors, the main thing is that during testing the figure is as close as possible to the specified one. If the system pressure is significantly lower than 300 kg, the parts of the plunger pair are severely worn out and repair or replacement is necessary.
If you have confidence in your abilities
If you have any of the above symptoms, you should consider repairing your fuel injector. Below we discuss how to fix some malfunctions of a distribution-type axial injection pump with your own hands.
It should be noted that before taking on this work, you should study the structure of the unit being repaired, find out what tools may be needed, because in some cases you cannot do without special equipment, a puller, for example.
You should also prepare a camera to record each stage of disassembly. Otherwise, you may forget where certain parts were located. For disassembly, you need to prepare a suitable table and cover it with a clean cloth or at least a sheet of white paper. There should be no debris on the floor, otherwise an accidentally dropped part may not be found.
So, what can a car enthusiast without special qualifications do on his own?
- eliminate fuel leakage from the pump housing;
- check the serviceability of the solenoid valve;
- check the plunger fuel supply mechanism;
- check the automatic speed controller;
- clean the filter meshes;
- check the pressure developed by the device;
- adjust the automatic injection advance.
Prevention of fuel injection pump breakdowns
Timely implementation of the necessary preventive measures is the best repair. This will reduce financial waste due to unexpected breakdowns and extend the life of the fuel pump and the entire engine. Such measures include:
- regular flushing of the entire fuel system at least once a year;
- timely replacement of the fuel filter (cleaning is a bad option, fine dirt will still remain on the filter);
- fill the car only with high-quality fuel (gas stations have the appropriate documentation indicating the dates of delivery, composition, tolerances, seasonality and other important information; they must provide it to you upon request);
- during cold periods, use winter diesel fuel; in extreme cases, you can use a special composition to increase the fluidity of diesel fuel - anti-gel;
- if the car has to be parked for a long time, especially in winter, then it is better to fill the tank full - due to temperature changes, condensation settles on the walls of the tank, which will subsequently get into the fuel and into the injection system;
- maintaining normal fuel levels;
- in cold periods, before starting to drive, warm up the engine and all systems well, relying on the instrument readings on the panel;
- If you suspect poor quality diesel fuel, use special additives for diesel fuel.
By observing the listed preventive measures, you can extend the service life of all parts and components of the car, as well as reduce repair costs. The high-pressure fuel pump is the most important mechanism in the fuel supply system in diesel cars, so maintaining its normal operation is one of the most important points.
Prevention methods
As you know, it is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it later. In the case of engines, a similar principle works. It is important to understand that the fuel pump is a very complex and expensive unit, so listen to the prevention recommendations prepared by our company’s specialists:
- Flush the fuel system at least once a year, and clean or change the clogged fuel filter.
- Drain any remaining fuel that has settled in the tank. They may contain large amounts of impurities and combustion products, which automatically leads to filter clogging and other problems.
- Leave your car in the parking lot only with a full tank. Condensation can form on the bare walls of the fuel tank, which then enters the fuel and through it into the injectors.
- Monitor the fuel level in the tank, do not drive at a critical level.
The key factor is the correct choice of fuel in autumn and winter. It is important to understand that summer diesel fuel, even with a slight drop in temperature, rapidly loses its fluidity. If cooling continues, chemical reactions begin, causing the fuel to become waxy. Reaction products clog both filters and fuel pump channels. If during a sudden cold snap you did not have time to replace summer diesel fuel with winter fuel, at least warm up the car with a heater before starting the engine.
Another myth is the effectiveness of mixing summer diesel fuel and gasoline. This does not lead to adaptation of the engine to cold weather, but on the contrary can lead to catastrophic consequences for the fuel system. Substances have different physical characteristics - density, ignition temperature, nature of combustion, explosion hazard. It is for this reason that you should not trust refueling your car at unverified gas stations. Check the quality of the fuel and its warranties. Don't try to save money by going to cheap gas stations. Very soon, the imaginary savings will turn into serious repairs.
Fuel injection pump malfunctions
Malfunctions of diesel injection pumps lead to loss of power, increased fuel consumption, difficult starting, increased exhaust smoke, and others. Typical breakdowns of a high-pressure fuel pump in a diesel car include water getting into the plunger pairs, a drop in pressure in the plunger pair, damage to the integrity of the sealing rings, sensor or wiring malfunctions (in electronically controlled diesel engines).
Ideally, the injection pump should be checked at a special stand in a car service center, but simple checks of the fuel pump can be done in a garage.
Checking the injection pump
Symptoms of a pump failure are similar to engine component failures, and may also be similar to a vehicle cooling system failure. Therefore, to diagnose a breakdown of the injection pump itself, it is necessary to check and ensure the serviceability of the pump parts.
Ideally, fuel injection pump diagnostics and troubleshooting can only be carried out on a stand - a device that allows you to simulate the operation of a high-pressure fuel pump in operating ranges. However, since the cost of the stand is comparable to the price of the car, and for diagnostics it is necessary to remove the fuel injection pump from the car, such operations are carried out only in car services.
Types of fuel pumps
First, let's look at the types of fuel pumps for diesel cars, since each of them has its own characteristics and typical fuel injection pump malfunctions. So, knowing what type of pump it is, you can better understand the principle of operation and the immediate cause of the breakdown. Regardless of the type of high-pressure pump, you need to understand that the main unit is the so-called plunger pair - a piston (plunger) and a cylinder (bushing).
There are two main types of injection pumps:
- with direct action and mechanical action of the plunger;
- with battery injection.
However, high-pressure fuel pumps are still divided into classes according to their design. In particular:
- Rows . As the name implies, their working sections are arranged in one row, and fuel is supplied to each cylinder in turn.
- Distribution . With such pumps, one section can supply fuel to several different cylinders. Such devices can be single- or double-plunger.
- Multi-sectional . Another name for them is V-shaped or hydraulic accumulators. They are used for highly powerful, but low-speed engines. They are quite rare.
With direct injection fuel pumps, pumping and injection occur simultaneously. The mechanical drive of the plunger is responsible for this. With battery pumps, fuel is supplied in separate cycles, first it enters the pump accumulator, and only then into the injectors. The most modern systems are controlled electronically and are called Common Rail. They work based on information from numerous sensors located in different parts of the car.
Another injection system is a pump injector. In this case, they are combined into one mechanism. This system simplifies pressure control and also increases reliability, because if one injector fails, the engine will continue to operate, albeit with less power.
High-pressure fuel pumps were also invented for gasoline engines. They are used in engines with direct fuel injection. The pump's job is to supply gasoline under high pressure into the cylinders, where the fuel is directly mixed with the air mass, forming a mixture that is ignited by the spark plug.
Removing the injection pump from the engine
Removing the fuel injection pump may be necessary not only to find and repair faulty parts, but also to check the injectors and adjust the gas distribution mechanism. Removing the fuel injection pump is a rather labor-intensive task that not every car owner can handle. At a minimum, to carry out such an operation you must have considerable experience in independently repairing a car.
Removal of the injection pump is carried out in several stages. Depending on the type of pump, there may be differences in the sequence and some details of the process. To remove the injection pump, in addition to standard keys, you will need special devices - gears for cranking the crankshaft, clamps, stocks, drive gear pullers, spline keys and special tools for dismantling. Therefore, when removing the pump, it is advisable to use a set of tools for repairing the injection pump.
- First, you should drain all the coolant in the car.
- Next, the negative terminal of the battery is disconnected.
- The fan and fan casing are removed, complicating access to the injection pump housing.
- Then the cylinder head cover is removed.
- Next, remove the timing belt cover.
- Then the intake manifold is dismantled.
- Next, the first cylinder of the engine must be set to the top dead center position (the maximum distance between the cylinder and the crankshaft). To lock the cylinder in this position, use special tool 11 2 300.
- Then it is necessary to remove the timing belt from the camshaft pulleys and the injection pump shaft.
- Next, you need to disconnect the fuel line and drain wire from the pump. The oil drain hose is also disconnected.
- Next, you need to disconnect the distribution lines from the cylinder injectors using tool 13 5 020.
- Next, the electrical wiring parts are disconnected.
- Then you need to remove the fuel injection pump fasteners. To remove the central nut of the injection pump, first remove the cap nut, and then unscrew the central nut with an 18-mm open-end wrench.
- Next, the bolts on the fuel injection pump housing are turned out.
- To disconnect the injection pump from the sprocket, use the ejector screw and fixture 13 5 120, which is first screwed into place of the central nut. When removing the injection pump, the device must remain on the central pulley until the pump is installed back to avoid the sprocket falling.
Once the injection pump is separated from the center pulley and sprocket, it can be carefully removed. Further disassembly to search for faulty parts can also be carried out using a specialized kit for repairing high-pressure fuel pumps.
Signs of fuel injection pump malfunction
Despite the fact that high-pressure pumps belong to different types, the signs of their partial failure are typical and in many ways common to all. So, symptoms of a fuel injection pump malfunction include:
- increased fuel consumption in all engine operating modes;
- unstable engine operation, the car jerks while moving, especially at low speeds;
- difficulty starting the engine, most often in the cold season;
- drop in engine power and dynamic characteristics of the machine as a whole;
- increase in engine exhaust smoke;
- fuel leak from the high pressure pump;
- the appearance of an oil emulsion in the engine coolant;
- increased engine noise.
Experienced car enthusiasts identify another sign of a faulty high-pressure pump plunger. It lies in the fact that when the engine is hot, it may stall when idling. And at the same time, it will be almost impossible to start it until the pump itself cools down. “When cold,” the engine starts without problems.
Causes of malfunctions
Here are some popular reasons that cause damage to fuel pump elements:
- Natural mechanical wear of individual components. Each part has a limited service life and, even with careful operation of the car, wears out over time. If you use fuel of insufficient quality, the process speeds up significantly.
- Dust, dirt, and water getting into the fuel system. Even a minimal amount of sand or water can lead to complete failure of the injection pump.
- Fuel filter clogged. If the flow capacity is impaired, the pump is unable to provide the pressure necessary to pump fuel.
- Depressurization. The trapped air also prevents the creation of operating pressure in the system, as a result of which the fuel pump is forced to operate at higher speeds all the time.
The main causes of fuel injection pump malfunction
The following are the causes of high pressure pump failure. Typically, the following structural elements fail:
- Plungers . Most often they are to blame, since the plunger pairs quickly become dirty. This is due to two reasons. The first is design features that provide a small gap that ensures high pressure in the system. The second is the low quality of diesel fuel, in particular, the presence of sulfur and paraffins in it, which, in fact, pollute the device. Dirt can also come from the engine (carbon deposits, dirt). Wear of the plungers leads to unstable engine operation at idle, increased fuel consumption, and decreased compression. Due to damage to the plunger pair, the bearings can significantly overheat.
- Water in diesel fuel . Also, domestic diesel fuel often has a high water content. Moisture washes away the fuel (at the same time protective) film from the surfaces of fuel injection pump parts, which causes the service life of precision parts to be significantly reduced. This may even cause the pump to jam.
- Dirty fuel filter . Due to a clogged fuel filter, the high-pressure pump, firstly, can become dirty (plunger pairs), and secondly, it wears out, which reduces its overall service life.
- Uneven supply and distribution of injected diesel fuel . This problem can also be caused by a malfunction of the plunger pairs, in particular, wear of the drivers, rack teeth, discharge valves, as well as dirty nozzles.
- Manufacturing defect . This situation is quite rare, but sometimes occurs on cheap pumps. Defects include cracks on the fuel injection pump housing, damage to its bearings, as well as jamming of the plunger bushing.
- Bearing wear . They usually wear out due to a critical decrease in service life (aging). Another option is a manufacturing defect. All this leads to the fact that the operating characteristics of the pump deteriorate, and the bearings and adjacent parts overheat, thereby reducing their service life.
- Piston and bushing jamming . This is a critical failure that can lead to breakage of the rack, cam shaft, gear, governor, keys. Often the cause of jamming is water getting into the cavity between the piston and the bushing.
- Wear of pump parts . This can occur both for natural reasons (with an increase in the mileage of the car) and when water gets inside it. It washes away the protective (working) lubricant from the elements, which significantly reduces both the service life of the pump as a whole and its individual parts.
- Corrosion of the plunger pair . Rusting spots may appear due to the increased water content in diesel fuel.
- Incorrect operation of the cooling system . That is, under prolonged and/or heavy loads, the high-pressure pump may simply overheat. The cooling system can be faulty for various reasons - low level of antifreeze or antifreeze, system clogging, breakdown of individual elements (pump, pipes, radiator, etc.).
If there is a suspicion that the fuel pump rack or associated parts are faulty, then you need to check for the presence/absence of the following defects:
- disconnecting the rack from the regulator parts;
- jamming or loosening of the clamps of the plunger leads;
- jamming of the coupling screws of the gear rims.
One of the most dangerous causes of a malfunction is a violation of the mobility of the fuel rail. In particular, if it jams at the moment of maximum fuel supply, and accordingly, the regulator does not have enough force to shift it to its original position, then an emergency increase in the number of crankshaft revolutions occurs in the engine, due to which the engine “goes into overdrive” all the ensuing consequences. If the rack is “bitten” while the gear is off, then in this case it will be impossible to start the engine at all. Partial jamming of the rack leads to unstable operation of the engine and an increase in its sound output (it begins to “growl”).
When using the machine in severe frost conditions, freezing of individual parts of the pump is sometimes observed, and its partial failure. To prevent this, it is necessary to use oils and diesel fuel with appropriate temperature ratings.
On common rail diesel systems, the control valve (or SCV flow valve) can fail. Usually it is replaced with a new one. Less often, they perform an audit and replace individual parts with new ones. In particular, the valve stem and core are often replaced.
Malfunctions in mechanisms, assemblies of fuel pumps and regulators manifest themselves in violation of the original adjustments due to wear of parts, the occurrence of extraneous noise, overheating of moving joints and fuel leakage.The main cause of pump failure is wear of its parts. In this case, the tension in the fixed fits weakens and the gap in the moving joints increases, the correct relative position of the parts is disrupted, the surface hardness of the parts changes, and foreign deposits accumulate in the form of dirt, soot, etc.
One of the most common pump malfunctions is a decrease in fuel supply and an increase in its unevenness. Fuel supply disruption is caused by wear of plunger pairs, injection valves, plunger drivers and associated rack clamps, rack teeth and bushing gear (pumps such as UTN-5, YaMZ-238 NB), changes in the throughput of injectors and other factors. These violations reduce engine power and efficiency.
Uneven supply of fuel to the engine cylinders leads to unstable operation at low speeds, interruptions in the operation of individual cylinders, and significant vibration of the engine block.
Another malfunction of the fuel pump is manifested in a delay in the injection timing and unevenness in the start of injection at a multi-section pump.
A delay in injection timing is a consequence of wear of a number of parts. Simple parts include: the plane of the pusher adjusting bolt; the roller axis and the pusher body and roller mating with it; ball bearings and mating sockets of the pump housing; camshaft.
The change in the fuel injection advance angle is significantly influenced by wear of the plunger pairs and injection valves.
Let's consider the main operational malfunctions of parts and assemblies of the pump and regulators.
The following malfunctions most often occur with the cam shaft and its mating parts
— cut of the key of the spline bushing of the pump drive;
— cutting the key of the spline gear of the regulator drive;
- cam shaft failure;
— failure of the cam shaft bearings;
— breakage of the key and shaft of the pump cam shaft (ND-21, ND-22).
As a rule, the listed malfunctions cause complete failure of the pump or a significant deviation in its functional characteristics.
If the tightening torque of the cam shaft nut is insufficient, the fit of the spline bushing for the drive of pumps of the UTN-5, TsTN-8,5, -10 types and the automatic injection advance clutch for pumps of the YaMZ type may weaken and cause the key to shear off .
Another reason for shearing the key is increased resistance to turning the cam shaft of the pump due to jamming of the plunger pushers, which is caused by foreign particles and water getting into the pump and regulator, as well as improper assembly and installation of high-pressure sections. The pump drive is disrupted, the fuel supply stops, and the engine does not start.
If the cut of the key is not determined in time, then during further attempts to start the engine, friction may cause welding of the splined bushing or automatic injection advance clutch with the cam shaft. In this case, the fuel supply to the pump is restored, but the setting of the fuel supply advance angle will be disrupted. There is smoke from the exhaust gases and, in some cases, certain flashes in the cylinders. The latter depends on the position in which the engagement of the spline bushing and cam shaft occurred.
It is possible to detect a broken key without disassembling this interface. To do this, remove the hatch from the engine (pumps UTN-5, ND-21) on the cover of the timing gears, through which the fuel supply advance angle is adjusted. Having turned the cam shaft of the pump to the position where the first section begins to feed, pay attention to the position of the blind spline in the spline sleeve. If the key is intact, the missing spline should be in the middle of the lower left quarter of the circle (as viewed from the drive side).
For the same reasons, the key of the regulator drive gear breaks, which leads to regulator failure. If the lever is in the position of maximum crankshaft speed, and the load on the engine is not significant, then the engine will go into overdrive. An increase in engine speed can be prevented by moving the governor lever or rocker arm to the feed off position. Cam shaft failure most often occurs in YaMZ-240B pumps. Breakdown occurs in the most loaded areas of the automatic fuel injection advance clutch, much less often in the middle part.
Failure of camshaft bearings most often occurs due to increased oil contamination. Metal shavings, sawdust, silica and aluminum oxide particles, as well as water accumulate in the high-pressure pump crankcase. If there is no oil in the crankcase, the wear rate of bearings, pushers and other parts increases.
If the bearings are significantly worn, the alternation of fuel supply and injection in individual sections is disrupted. The fuel injection advance angle in all sections is delayed. Engine power decreases and exhaust smoke occurs. The engine runs unsteadily (growls) at low crankshaft speeds. Smoke may come out of the breather and drain pipe of the pump, and the pump housing will become very hot in the areas where the bearings are located.
Wear and destruction of bearings is observed in the following way:
- remove the low pressure booster pump;
- through a window in the housing, a small hard rod is inserted under the cam shaft;
- by shaking the shaft up and down, the technical condition of the bearings is assessed. There should be no noticeable movement of the shaft.
For LP type pumps, the booster pump is driven by a separate eccentric shaft, which is coaxial with the cam shaft and connected to it through a key and a bevel gear. Since the fuel pressure supplied to the head of the distribution pumps can reach 0.35 MPa, there are cases of cutting off the eccentric shaft drive key, as well as its breakage.
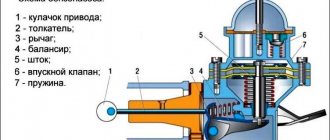
In addition to wear on the working surface, the pusher has the following faults:
— jamming of rollers, bushings, axles;
— breakage of the thread of the adjusting bolt;
- unscrewing the nut and adjusting bolt.
Jamming of rollers, bushings, and pusher axes occurs, as a rule, in the absence of lubrication and contamination of the oil. Large loads on these parts and friction cause them to heat up and seize. The rollers stop rotating, and flats form on their surface. In this case, the pump shaft cams wear out intensively.
Roller jamming can be detected when disassembling the fuel pump; an indirect sign of this malfunction is local heating of the pump housing. Flats on the roller may occur when the pusher rotates relative to the body. The formation of flats on the rollers leads to a delay in the fuel injection advance angle of the faulty section. If partial seizure occurs between the axle, roller and pusher bushing, then with rotation several flats are formed on the surface of the roller. With each new stroke of the pusher, the roller rotates and the fuel injection advance angle changes. The engine begins to run unstably and there is increased vibration. The appearance of flats can be determined by the height of the protrusion of the pusher relative to the pump housing.
Sometimes the pusher jams (seizes) in the guide hole of the pump housing, often resulting in parts breaking. Jamming of the pusher in the upper position leads to failure of the section, i.e., stopping the fuel supply.
Breaking the thread of the pusher adjusting bolt and unscrewing it leads to the fact that the height of the pusher assembly changes.
Screwing in the bolt causes a delay in the fuel injection advance angle. When the pusher bolt nut is loosened, it may spontaneously turn out. When the critical height of the pusher is reached, the plunger hits the discharge valve body. If this malfunction is not corrected, other malfunctions and breakdowns may occur. In particular, a breakdown of the cam shaft bearing, plunger drive, etc. may occur. The tightening state of the adjusting bolt, its position relative to the pusher can be checked by inspection, trying to turn it with an open-end wrench, as well as turning the pump cam shaft.
One of the reasons for pump malfunction is jamming of the plunger pairs.
Hanging of the plunger relative to the bushing causes the rack to jam. The engine will not start . With partial setting, an unstable crankshaft rotation speed is observed.
There are cases of failures of the plungers of the 240B pump due to an increase in the size of the pin or shank of the locking screw or greater tightening forces.
The most common cause of jamming and impaired mobility of plunger pairs is water getting into the gap of precision parts . In this case, the lubricating fuel film on the rubbing surfaces is disrupted, and the plunger begins to work without lubrication. Friction causes scuffing of precision surfaces, their heating and jamming. The presence of water in the fuel causes corrosion of the plunger and liner.
For the same reasons, the dispenser becomes jammed in the plunger pair of ND type distribution pumps. When the plunger jams in ND type pumps, the intermediate gear, shaft, regulator, and key connections break down
A stuck plunger can be detected by partially disassembling the pump. To do this, remove the pump cover and, observing the position of the plungers, rotate the cam shaft several times. It is more difficult to determine partial freezing of plunger pairs. For pumps of the TN type, a violation of the mobility of the plunger can be detected by unscrewing the clamps of the leads one by one. By rotating the cam shaft of the pump, control the ease of rotation of the plunger relative to the sleeve. Partial jamming of the plunger in the bushing is expressed in the form of interruptions in the fuel supply to individual sections and unstable operation of the regulator.
The main malfunction of the plunger return springs is their breakage, which leads to partial, and if the breakage occurs in several places, to complete failure of the pump section.
Seizing of a discharge valve is quite rare. Loss of mobility of valves, as well as plunger pairs, occurs from large mechanical particles entering the gap; deformation of the valve body from increased installation forces, fuel temperature, dynamic loads arising during operation of the valve, corrosion of its parts, misalignment of the valve relative to the seat.
If the valve gets stuck in the seat when it is in its upper position, it leads to failure of the fuel section, and when the valve gets stuck in the lower position, hydraulic shocks are heard. Sometimes large mechanical particles get into the gap between the shut-off cone and the housing seat. A broken valve shank causes the fuel supply to stop.
The reasons for the failure of the injection valve can also be a decrease in rigidity, breakage of the valve spring, or the absence of a valve travel limiter in the fitting. Valve failure when it is skewed, dirt gets into it, or sticking in the upper position can be easily detected without disassembling the high-pressure fuel pump.
To check valve tightness:
- Unscrew the high pressure pipe from the faulty section.
- The pump rack is moved to the off-feed position.
- A manual booster pump creates excess fuel pressure.
- Fuel leakage through the pressure fitting hole indicates a malfunction of the discharge valve.
The pressure fitting has thread breaks, mainly for high-pressure tubes, as well as wear in the form of collapse and deepening of the seat for the tip of the high-pressure tube.
If the seat is deepened significantly, the reliability of the seal and pressure fitting is not ensured, fuel leaks through this connection, and partial or complete failure of this section is observed.
Defective fittings are replaced or restored by slightly shortening the sealing surface on a lathe or grinder.
When the seat is compressed, the flow area of the hole decreases, the resistance to movement increases and, as a result, the cyclic feed decreases. To eliminate this defect, drill a hole in the pressure fitting.
Malfunctions of the fuel pump rack and parts associated with it include the following: jamming, self-unscrewing of the clamps of the plunger arms, tightening screws of the gear rims, disconnection of the rack from the regulator parts.
The most dangerous malfunction of a high-pressure pump occurs due to impaired rack mobility.
When the rack jams in the maximum feed position, if the regulator effort is not enough to move it, an emergency increase in crankshaft speed occurs and the engine goes into overdrive. If sticking occurs in the feed off position, the engine cannot be started.
There are cases of partial jamming of the rack in certain operating modes or increased resistance to its movement. In these cases, the rack moves sharply in the form of a jump, and the fuel supply changes accordingly. The engine runs unsteadily and growls. Jamming of the rack occurs due to high contamination of the crankcase oil (in UTN-5, YaMZ pumps). Abrasive particles, falling into the gap between the rack and the gear rim, cause a disruption in its mobility.
Another reason for the rack to jam is water ingress , especially in winter. When the engine is running, water, along with air, enters the pump and is deposited in the form of dew on its walls, rack, and crowns during parking. At low temperatures, water freezes, the rack becomes frozen together with the gear rims. The engine does not start or goes into overdrive. This malfunction is most common in multi-cylinder engines YaMZ-238NB, YaMZ-240B.
Moisture may enter the pump when the engine is heated with hot water in winter. The presence of water causes corrosion of the rack teeth and rims, which leads to increased resistance, movement of the rack and, in unfavorable cases, jamming.
Sticking of the rack in TN type pumps can occur due to the plunger arms biting in the clamps in their extreme positions . To eliminate this defect, it is necessary to limit the movement of the rack. To do this, a split ring is placed on the rack of a TN type pump between the clamp and the housing, which after installation is bent to its normal position. Usually installing one or two old sealing washers is enough to eliminate sticking of the rack.
If dirt gets into the rack-crown interface, it is enough to rinse the pump to eliminate the binding.
For pumps of the UTN-5 and YaMZ types, the coupling of the rotary sleeve-plunger sleeve may become jammed, which also results in failure of the rack and the pump as a whole.
Indirect reasons for the loss of rack mobility are also jamming of plunger pairs, the dispenser, its drive (for LP pumps), malfunction of the regulator, 15% of LP pump failures are due to jamming and breakdown of the dispenser drive.
In order to detect rack seizure , the rods are disconnected from the regulator lever and the stop bracket. Then, using the pump control levers, move the rack to its extreme position. The movement of the rack is determined by characteristic clicks in its extreme positions. It is advisable to rotate the cam shaft several times. There should be no jamming or increased resistance to movement of parts.
The movement of the pump rack can be seen directly if you unscrew the YaMZ limiter housing or plug. For other brands of pumps, you need to remove the cover to do this. To eliminate rack jamming, you need to find the sticking point. You can determine the seizing section by pumping up the ring gear relative to the rack. If the connection is working properly, you should feel a small gap.
When freezing, remove the pump from the engine, bring it into a warm room, and remove the covers. After thawing and restoration of mobility of the slats, drain the oil and flush the pump with diesel fuel. After pouring fresh oil into the crankcase, the pump is installed on the engine.
In more complex cases, sequential disassembly of the pump is required.
Self-loosening of clamps, coupling screws, and toothed rims leads to section failure, expressed in irregular fuel supply. The cyclic feed in the failed section changes randomly, the cylinder operates unstable. When the fuel supply is turned off, the engine can continue to operate on one of the cylinders. Screws are loosened due to insufficient screws.
determine whether the tightening screws have been loosened by removing the pump covers. In exceptional cases, it is possible to restore the adjustment approximately. To do this, fix the position of the plunger relative to the sleeve identical to other, properly working pairs. If there are matching marks on the ring gear and the rotary sleeve, troubleshooting is simplified. Fine adjustments can only be made on a fuel stand.
Disconnecting the pump rack from the regulator can lead to emergency situations. In case of significant wear of the thrust cam and the rack hole (in an LP type pump), it is possible that these mating parts can be disconnected, then the running engine sharply increases the crankshaft speed, which also leads to engine runaway. Disconnection of the rack in pumps UTN-5 and YaMZ occurs when the cotter pins fall out and break. This malfunction can be detected in the same way as a stuck rack.
One of the vulnerable components of fuel equipment of the TN8.5+10 type is the regulator . The presence in the kinematic chain of the regulator of a large number of movable joints, which have small supporting surfaces and perceive significant pressures of variable magnitude, leads to rapid wear of parts and, consequently, to an increase in gaps in their joints. One-sided and increased gaps in all matings contribute to the occurrence of axial play (rack backlash), reaching 3....5 mm.
Due to uneven wear of parts, for example, the guide grooves of the movable coupling and the pins of the regulator fork, the rack and its guides, bushings and others, the mating parts sometimes jam. Moreover, if the engine is running with a high fuel supply and the load is suddenly removed, the crankshaft develops a high rotation speed, which can lead to engine failure.
Increased noise and uncharacteristic knocking occur when regulator parts break down. In cases of a significant increase in the moving parts and a weakening of the tension in the stationary joints in the regulator, vibration and movement of moving parts increases, overheating of the rubbing surfaces occurs, which causes even greater wear. Externally, these malfunctions are expressed by the appearance of smoke from the regulator and pump. Rack oscillation leads to unstable engine operation both at constant speed and when the load changes. Overheating of parts is caused by heavily contaminated oil or its absence.
“Driving” of the rack and increased noise, as a result of unstable operation of the diesel engine, are possible in case of incorrect adjustment of the regulator, for example, with an excessively turned out rocker screw (YMZ pump), or a small range between the revolutions of the beginning and end of the regulator’s operation.
The following parts may be damaged or deformed in the regulators::
— teeth of the drive gears and the regulator shaft;
— bevel gear teeth of the booster pump and regulator drive (LP pumps);
— idler gear teeth (LP pumps);
— regulator shaft, key, teeth (LP pumps);
— dispenser drive;
— roller bearings (thrust, etc.);
- spiral and cylindrical springs.
Breakage of gear teeth causes increased noise, knocking, beating, and vibration of the pump rack. In most cases, further operation is not possible.
If the governor drive breaks down on in-line pumps, the mutual connection maintained by the governor is broken: flow rate and rotation speed. If you do not reduce the maximum supply of the nominal or starting mode manually, an emergency increase in engine speed will occur.
The entry of water or large abrasive particles into the pump causes jamming of the precision pairs and, as a result, breakdown of the regulator parts.
Breakage of the teeth of the bevel and intermediate gears in the LP pump regulator, as well as deformation of the regulator shaft, shearing of the keys, and breakdown of the metering drive lead to the cessation of fuel supply by the high pressure section . The engine stalls and does not start.
Failure of the regulator roller bearings (TN type pump) causes the rack to run out, and the basic characteristics of the regulator are disrupted. When the spring stiffness decreases, the rotational purity of the start of the regulator's action to turn off the feed decreases, and the feed correction coefficient also changes.
Serious malfunctions of the regulator are caused by wear of the weight legs and the release bearing. With these malfunctions, the gaps in the kinematic chain of the regulator increase, and the “backlash” of the rack increases. The loads are rotated to a larger angle, their centrifugal force increases, as a result of which the fuel supply is turned off faster.
The degree of regulator unevenness for the nominal mode can be determined by the formula:
(Pm. Xx - Pp)*2 Q= ———————- * 100% (Pm. Xx + Pp)
Where:
Q - degree of regulator unevenness;
PM xx - maximum crankshaft rotation speed at idle;
Рп — nominal crankshaft rotation speed;
For a new pump, the degree of regulator unevenness at nominal mode should not exceed 10%. During operation, the degree of governor unevenness increases due to an increase in idle speed while simultaneously reducing the rated engine speed.
Changing the fuel supply is carried out with increased efforts in the regulator. Increased gaps and friction force in the joints lead to the fact that the regulator does not have time to respond to changes in load and crankshaft speed, as a result of which the engine operates unstably, and the range of changes in crankshaft speed increases. When idling, the engine growls.
Another common malfunction of the fuel injection pump is the leakage of the seals, which results in leakage of fuel and oil.
As fuel passes through the front oil seal, the engine oil dilutes. Fuel leakage can cause the pump and regulator crankcase to overflow and, as a result, engine runaway.
Overfilling of the high pressure pump crankcase can occur for the following reasons:
— increased wear of the booster pump;
— destruction of the sealing ring or its inappropriate dimensions (LP pump);
- extreme wear of plunger pairs;
— defective seat of the plunger pair;
- crack in the body.
To determine the cause of fuel leakage , you need to find the location of the leak. To do this, you need to remove the side cover and create excess fuel pressure in the pump head using the booster pump.
For pumps of the TN and UTN-5 types, fuel leakage is most often observed in the seats of the plunger pairs, which is caused by the absence of a copper sealing ring or the ingress of foreign particles between the sleeve and the seat, as well as risks and burrs on the seat.
In distribution-type pumps, the crankcase is overfilled with fuel through the metering drive, and the plunger pair is sealed when the tightness of their fit is broken. In addition to fuel getting into the pump, it can leak outward in places between the high-pressure sections and the housing (LP pump) along the thread of the pressure fitting. The cause of fuel leakage at the LP pump is insufficient tightening of the studs and insufficient thickness of the rubber o-ring.
You can replace both the upper and lower rubber o-rings on the rubber pump without disturbing its adjustments. To do this, remove the dispenser drive, unscrew the four tie rod nuts and carefully press out the section sleeve. The plunger and drive gears remain in place. After replacing the O-rings, carefully press the sleeve into the body. At the same time, special attention is paid to ensuring that the plunger, sleeve and dispenser take the correct working position. Then place the metering drive on the pump, check the ease of its movement and tighten the nuts of the tie rods.
Leaking seals may cause air to leak into the system. The most common places for air leaks are the fuel fittings of the low pressure supply pipe going to the booster pump on the suction side, a bypass valve, or a broken bypass pipeline. In these cases, failures of some pumping elements and interruptions in the fuel supply to individual sections occur. When starting the engine, there are misfires and not all of its cylinders are working.
in the pump head loses its tightness This pump malfunction manifests itself in a decrease in power, difficult starting, and interruptions in engine operation.
A malfunction of the bypass valve occurs when dirt gets into it or the spring breaks.
How to determine fuel injection pump malfunctions
Please note that it is best to test the high pressure pump on professional stands specifically designed for this purpose. They allow you to find out the operating characteristics of the pump and other elements of the vehicle’s fuel system. However, such a check is only possible in a car service center, since such a stand is specialized and expensive equipment. In garage conditions, it is possible to carry out only a partial check of the fuel injection pump and determine only the main fault, while other possible faults will not be noticed!
Checking the presence of water in plunger pairs
To do this, you need to remove the timing belt and carefully twist the pulley. If it rotates with variable force, then everything is fine and there is no water in the pump. If rotation occurs under the influence of significant force and does not occur at all, then moisture is present. This is very harmful for both the pump and the engine as a whole, since the motor will work with increased effort when starting, until it completely jams (failure).
Checking the pressure in the plunger pair
There are special tools for this - testers, for example, KI-4802 or TAD-01A. If you don’t have such a tool at hand, you can use a pressure gauge with a high measurement range. So, it needs to be screwed into the seat of the fuel pipe, or into the central hole of the high pressure pump head. With a normal running engine, pressure readings should be approximately 300 kg/cm² and above (in fact, the corresponding value will vary for different brands of cars, as well as engine operating modes). If the fuel pressure is lower, it means that the plunger pair has worn out significantly and needs to be repaired or replaced (most often).
Control sensors
Modern common rail diesel systems that are controlled by an ECU (electronic control unit) tend to have problems with the sensors and/or their signal wiring. This often activates the Check Engine light on the dashboard. You need to use an error scanner to read their numbers and decipher them. Next, in accordance with the information received, make a decision on repairs.
Disassembly and repair of leaks
The following describes the sequence of actions for self-repair of fuel injection pump. With the engine running, disconnect the rod connecting the gas pedal to the lever that regulates the fuel supply. Then manually swing the lever in the radial direction, trying to stretch the return spring.
If no diesel leakage is observed through the annular gap, it means that the seal is not worn out. Otherwise, restoration repair of the interface is required.
While the pump has not yet been removed from the engine, make sure that the fuel shutoff solenoid valve is working properly. If the engine starts and stops when you turn the key, the valve is working. What to do in a situation where this component fails while driving will be discussed below.
Now all that remains is to move on to disassembling the pump. Before disconnecting the fuel lines and electrical connections from the unit, it is necessary to wipe its body and connections with a rag soaked in diesel fuel, and then wipe dry to prevent dirt from entering the fuel system. Rinse the removed pump again, then remove the cover and drain the fuel from it.
First of all, you need to disassemble the fuel supply control drive and inspect the seals, as well as assess the degree of wear of the associated parts. O-rings must be replaced. For this purpose, you need to buy a repair kit for the device being repaired.
As for worn parts, there are two ways to restore them: restore the worn axle using chrome plating, or grind and install a repair bronze bushing in the body. The body will have to be bored before this.
Injection pump repair
Troubleshooting methods for a high-pressure fuel pump depend on the type of device, as well as the cause of the breakdown. We list the most common repair measures.
Replacing the plunger pair with your own hands
Before performing an independent check (without using a special stand), you must have handyman tools and a new plunger pair on hand, as well as have experience in performing repair work. We will describe the description of checking the condition of the high-pressure fuel pump using the example of a common Bosch injection pump.
It is necessary to understand that dismantling the pump depends on the specific model and even the car engine, so the procedure will be described in general terms. So, to replace a plunger pair (the most common type of repair) you need to:
- remove the terminals from the car battery;
- disconnect all wires and hoses suitable for it from the high-pressure pump;
- dismantle parts that prevent its removal from the car;
- unscrew the fasteners and dismantle the pump;
- carefully disassemble the pump, it is important not to lose small parts, and also remember the disassembly sequence (you can photograph this process step by step on your phone);
- unscrew and remove the plunger from the pump;
- clean all pump parts from dirt (you can use special carb cleaners or similar cleaners for this);
- check the rollers, bearings and racks on the pump; they should not show significant wear;
- remove the valves and the so-called “silencer” from the old plunger pair, and then install them on the new pair;
- Carry out installation work in reverse order.
Rack jamming
If you find that the rack is sticking, then the first thing to do is to find the place where it is “sticking”. This can be done by pumping up the ring gear relative to the rack in the corresponding section. If the rack does not jam, then there will be a small gap.
In this case, independent repair is hardly possible. However, in any case, it is necessary to dismantle the pump and show it to a specialist!
Preventive measures
As you know, prevention is the best repair, therefore, to save money and ensure normal engine operation, it is advisable to carry out simple preventive measures that will help extend the life of the high-pressure fuel pump. In particular:
- flushing the fuel system should be performed approximately once or twice a year;
- be sure to change the fuel filter on time (it is not advisable to clean it, because small particles of dirt will most likely remain on the filter);
- use high-quality fuel (at any gas station there is documentation indicating how long ago the fuel was delivered, as well as information about its composition, tolerances and seasonality );
- in winter, it is important to use winter diesel fuel, or to lower the freezing point (increase fluidity) of diesel fuel, you can use special compounds - antigels;
- it is advisable to leave the car for long periods of time (especially in cold weather) with a full tank, since moisture condensation forms on the inner walls of the tank overnight, which flows down and mixes with the fuel; instead, you can use the moisture removers mentioned above;
- do not allow the fuel level in the tank to drop critically;
- in winter, it is imperative to warm up the engine for several minutes before driving, taking into account the coolant temperature and oil pressure gauge readings;
- use special lubricating additives for diesel fuel if there is a suspicion of low quality diesel fuel.
The measures listed above will contribute to the normal operation of not only the high-pressure pump, but also the entire fuel system of the car as a whole.
Source of the article: https://etlib.ru/blog/1161-neispravnosti-tnvd
External manifestations of fuel deficiency
What are the signs of a faulty fuel pump? As was said at the beginning of the article, the main reasons for the loss of fuel injection pump performance are wear of rubbing surfaces and low fuel quality. Here we can clarify that low quality diesel fuel also means water getting into the fuel. The following are external symptoms of a malfunctioning fuel pump:
- It is difficult to start the engine - most likely, the plunger pair (or pairs) have worn out, and the pump does not develop the required pressure. Checked in a simple way. You need to put a rag on the injection pump, pour cold water on it and wait a few minutes. Then try again. If the engine starts, then the reason is indeed wear. When cooled, the mating gaps decrease and the viscosity of the fuel increases, as a result of which the pump provides the required pressure.
- Loss of power. Due to the increased gaps, the injection pressure decreases and the operation of the all-mode speed controller deteriorates.
- Engine overheating. The reasons may be incorrect operation of the injection advance machine. In this case, you can’t put off repairing the fuel injection pump “for later.”
- Growing “appetite” for the power unit. Caused by fuel leaks, wear of plunger joints, and incorrect injection timing.
- Rough operation of the engine, which may be a consequence of too early injection and uneven supply of diesel fuel to different cylinders. True, the latter is practically impossible on distribution injection pumps, so most likely the problem is in the injectors.
- Black exhaust from the exhaust pipe. The reason may be that the fuel injection angle is too late.
Assembly and speed adjustment
When the unit is assembled, you need to fill it with diesel fuel by manually turning the drive roller, after which you can install it in place and connect the fuel lines, hoses and electrical wiring of the control system.
After the engine is started, you should make sure that the fuel injection advance machine is operating correctly, depending on the pressure in the cavity of the low-pressure vane pump. This unit has its own idle speed regulator. If necessary, adjust this parameter by screwing or unscrewing the adjusting screw.
Before performing this procedure, it is recommended to remember the position of the screw by counting the number of threads protruding from the locknut so that, in extreme cases, you can return to the original setting. The engine manual indicates the required number of engine idle speeds. Usually they drop from 1100 rpm after starting to 750 - after warming up a diesel engine with a manual transmission, and to 850 - on an engine with an automatic transmission.
My dear diesel: why fuel injection pumps break and how they are repaired
Since the final registration of diesel engines in passenger cars, not only owners, but also craftsmen have looked at this “miracle of technology” with a little caution. Yes, the gain on fuel and traction is obvious - but what happens if the engine breaks down? A feature of all heavy fuel engines without exception is the precision of assembly of the most critical parts, as well as the amount of operating pressure - of course, if we are talking about modern engines. Looking at the standard service hours regarding the repair and maintenance of fuel equipment, everyone involuntarily asks the question: “Is the game worth the candle?” Yes and no.
On the one hand, you get an incredibly productive internal combustion engine with locomotive traction and reduced consumption, on the other hand, you need increased attention to fuel quality, more frequent replacement of the fuel filter and quite high costs if repairs or replacement of system elements are necessary. But if the first scale has tipped the scales, and you have become the owner of a diesel car with a Common Rail system, then it’s worth looking at how the elements of this system are repaired. Today we will find out how fuel injection pump repair is carried out.
Briefly about the device
Common Rail: this phrase is on everyone’s lips, and many even know what it is. In simple terms, this is nothing more than a system for injecting diesel fuel from a common rail directly into the engine cylinder under very high pressure (1,600 - 1,800 bar). Some will say: but diesel fuel has been injected directly for a long time, what’s so special? The answer lies on the surface, in the name itself: it is a “single highway”.
Pressure check
Finally, the pressure in the pressure line is checked, which is an indirect check of the condition of the plunger pair. For this purpose, you will need a pressure gauge rated for pressures up to 350 bar, a connecting hose for connecting to the pump and an adapter that includes a bleed valve.
The TAD-01A pressure gauge or the older KI-4802 pressure gauge is suitable as a measuring device. If the adapter is not available for sale, you will have to make it yourself.
Of course, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of the connecting thread and where you plan to screw the connecting hose. To measure, the device is connected to the central hole of the distribution block or to one of the pressure fittings.
After connecting the pressure gauge to the injection pump, rotate the pump shaft using the starter and record the reading of the dial indicator. If the device shows more than 250 atmospheres, this is normal (the pressure will be higher when the engine is running).
Emergency repair of solenoid valve
As promised above, a few words about what to do if the fuel shutoff solenoid valve fails along the way. In this case, the engine will suddenly stop. True, there may be several reasons for this. To discard the version of the malfunction of the solenoid valve, it must be excluded from operation, since in normal mode it is always open.
To do this, you need to remove the supply wire, isolate it from ground, then unscrew the valve, remove the tip with the spring from it and put the device back. If the engine still won't start, the reason is obviously something else. If the engine starts, you need to look for a fault in the valve.
To do this while not on the road, you must first get home. True, you will then have to turn off the engine roughly, but simply: put the car on the handbrake, engage a higher gear and release the clutch pedal.
And then start repairing. First you should check whether the electromagnet winding has burned out. To do this, connect the valve to the battery positive using a piece of good wire, and then try to start the engine. If it starts, it means the winding has burned out. Otherwise, look for a voltage leak from the supply wire.
The main working unit of the injection pump
This pair consists of two parts - a piston (aka plunger) and a sleeve (bushing). Since high pressure is created in the assembly, leaks between the components are not allowed. Therefore, the working surfaces of the piston and liner have a high degree of processing, which is why the pair is often called precision.
The essence of the pair’s work is based on the reciprocating movement of the plunger inside the sleeve. In this case, through channels or valves, fuel enters the cavity above the plunger and is removed after compression.
It all works like this: when the piston moves down, a channel or supply valve opens (depending on the injection pump device), and fuel is pumped into the cavity. When moving up, the supply stops (the channel or valve closes) and the plunger begins to compress the diesel fuel. When a certain pressure value is reached, the discharge valve opens and diesel fuel (already in a compressed state) enters the line leading to the injectors.
In general, the operation of the plunger pair itself is very simple, but there are many nuances and features, including design ones, that affect the functioning of this unit. Therefore, the operating principle of fuel injection pumps should be considered separately for each of these types.