VAZ-2108 “Sputnik”
(export name -
Lada Samara
; nicknames - “Eight”, “Chisel”) - Soviet and Russian front-wheel drive car of group II small class with a hatchback body.
Developed and mass-produced at the Volzhsky Automobile Plant in 1984-2003. It was the base model in the Lada Sputnik family of models. Since 2004, the car has been replaced on the assembly line by the VAZ-2113 model.
Story
In 1984, a car rolled off the AvtoVAZ assembly lines that was completely different from all previous models. It received the factory designation VAZ-2108.
VAZ-2108
This model can be considered a new era for AvtoVAZ, since the 2108 was different in every way from the classic cars of this manufacturer. This car was initially given the name “Sputnik” (export models had a different name – “Samara”). Subsequently, the domestic name did not really catch on, but at the same time it became the name of a whole family of cars (consisting of only three models), the base for which was the VAZ-2108. Among the people, this car received its own nicknames - “Eight” and “Chisel”. This model lasted on the assembly line until 2004, after which it was replaced by one of the models of the 10-series family.
In general, the “Eight” can be considered the ancestor of all VAZ cars currently produced, since they use the concept of this model.
The VAZ-2108 differed from any classic model in absolutely everything - the body, the power plant and its location, the transmission. Moreover, this car was created practically from scratch, and no components from its predecessors were used in the design. Of course, a lot of things were borrowed from foreign automakers, and designers from other automobile companies, including Porsche, took part in the development of this car, but still the main merit in the creation of domestic designers.
Therefore, it is worth considering this car in more detail, including the design features of the VAZ-2108, technical characteristics, types of power plants, transmissions, body features and weight and dimensions.
Main competitors
It’s surprising that the G8 was given the green light, because a similar project, Moskvich 2141, was being developed in parallel. Everything was decided by the General Secretary of the CPSU Central Committee L.I. Brezhnev, who adored cars and knew a lot about them, so he could not refuse the new project. If nothing prevented the Volga hatchback from gaining popularity in the domestic market, then abroad it faced serious competition.
Mercedes W124
The brand name already inspires respect. The sedan was produced from 1984 to 1996, equipped with seven types of power units. The model included innovative developments, had perfect aerodynamic performance, and a more comfortable interior.
The windshield was equipped with one wiper covering the maximum surface area of the triplex. To improve rear visibility, all you had to do was press a button on the front console and the rear headrests would immediately recline. The German car looked much more attractive than the Russian one, but the Mercedes had one significant drawback - it was expensive.
Seat Ronda
The B-class hatchback with an elegant appearance and front-wheel drive was produced in Spain from 1982 to 1986 based on the Fiat Ritmo. Assembled on a conveyor belt by robots. 5 doors increased its comfort. High-quality plastic and velor were used to decorate the spacious interior.
The line of power plants included diesel and gasoline engines with a capacity of 55–85 hp. pp., working in tandem with the “mechanics”. The motors were economical, reliable, had good dynamics and a long service life, unlike the “chisel”. But the Russian engine could be overhauled right in the garage.
Skoda Favorite
For this brand, this is also the first car equipped with front-wheel drive. It was produced by the Czechs from 1987 to 1994. The Germans and Italians helped develop the project, so the Skoda Favorite car took its rightful place in European markets.
Thanks to this model, Skoda Auto was accepted into the Volkswagen AG concern in 1991. At first they planned to produce 336 thousand cars, but demand suddenly began to grow, and the assembly line worked 2 times longer. In total, more than 783 thousand Skoda Favorit were sold.
Engines and their characteristics
Let's start with the power units. For this car, several main engines with different volumes and technical specifications were provided. characteristics. But the VAZ-2108 engine diagram is the same for everyone.
Related link:
How to start a VAZ engine in winter
These were 4-cylinder engines with an upper timing belt (8-valve) and camshaft. A distinctive feature from the installations of previous models was the belt drive of the gas distribution mechanism. The method of regulating the thermal clearance of the valves has also changed - rockers were abandoned in favor of shims.
The power system was initially carburetor, but later it was replaced with an injector. Cooling is liquid type with forced circulation of coolant (its volume was 7.8 liters for all types of engines).
Eight engine
The lubrication system is of a combined type (some components were lubricated under pressure, while others were lubricated by splashing). The engine oil required was 3.5 liters.
Initially, the engines used a non-contact ignition system, but after that it was replaced with a microprocessor one (it was used on both carburetor and injection versions).
Finally, perhaps one of the most remarkable features - the engine was located transversely in the engine compartment, which made it possible to increase the space in the cabin, reduce the size of the hood and position it at an angle.
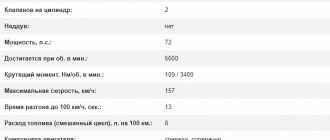
Now about what technical characteristics the VAZ-2108 had. The main powerplants available were: 1.1-litre, 1.3-litre and 1.5-litre. The markings of VAZ-2108 engines were taken according to the brand designation (except for the injection model). So, the base model was considered to be with a 1.3-liter engine, and it was designated as VAZ-2108. And for other versions, to indicate the installed motor, a number was added to the index. As a result, the 1.1-liter version was labeled as VAZ-21081, and the 1.5-liter - 21083.
They did not use such a designation for the injection engine, and it was designated as VAZ-2111.
Next, let's look at what characteristics each VAZ-2108 engine had. So, the basic version was without additional indexes. The VAZ-2108 engine capacity was 1.3 liters, which allowed it to develop a power of 63.7 hp. s., and the maximum torque was 94 Nm at 3600 rpm. crankshaft.
Related link:
How to insulate a VAZ-2108 car
The VAZ-2108 with a 1.1-liter engine was obtained after some processing of the base engine (the piston stroke was reduced), thereby affecting the volume. This engine produced only 53.9 liters. s., and the torque was 79 Nm at the same engine speeds as indicated above.
The characteristics of the VAZ-2108 with 1.5 liters of volume and a carburetor power system were: power - 70 liters. s., torque – 106 Nm at 3400 rpm.
The VAZ-2111 engine installed on the G8 was practically no different in performance from the carburetor version. Their power was the same, but the torque of the injection model was slightly higher than 115 Nm.
These were the main versions of power plants described. But the plant also produced a model equipped with a VAZ-415 rotary piston engine (Wankel engine). This installation had the best performance; it developed 140 hp. With. With a torque of 186 Nm. It was a two-chamber unit with a carburetor power system. But since the service life of the VAZ-415 engines was not very long, this version of the Eight was not particularly popular.
Motorsport
In the mid-1980s, the plant built several mid-engine and front-engine prototypes of rally cars based on the VAZ-2108, with the goal of further homologating them for Group B. These are the VAZ-29084 with all-wheel drive, the VAZ-29081 with rear-wheel drive. But they remained in single copies due to the cancellation of Group B at the end of 1986[12].
The car participated in all-Union races of the USSR, after its collapse it participated in the Russian circuit championships in the “Tourism” (“Tourism - 1600”) and “Supertourism” classes. From 1998 to 2002 - participant in the National Racing Series "Lada Cup".
Transmission
Next, let's look at the technical characteristics of the VAZ-2108 transmission. This car used a three-shaft type gearbox (4 or 5-speed) and with a differential installed in the crankcase. It was controlled by a lever installed in the cabin. But since both the power plant and the gearbox were located transversely, gear shifting was carried out not directly (as in classic models), but through remote traction. The amount of oil in the VAZ-2108 gearbox was: 4-speed version - 3.0 liters, 5- fast - 3.3 liters. Transmission oil was poured into the VAZ-2108 gearbox. The clutch was single-plate, dry type and cable driven.
New transmission
Despite the differential installed in the crankcase, the dimensions of the VAZ-2108 gearbox were smaller than those of the classic versions.
Related link:
Description and installation of the “Lunfey” heater on a VAZ
Both types of gearbox were installed only on the 1.3-liter version. The 1.1-liter engine was not equipped with a 5-speed gearbox, and all 1.5-liter modifications were not equipped with a 4-speed gearbox.
It is noteworthy that the characteristics of both boxes are identical, and the difference comes down only to the presence/absence of 5th speed.
The gear ratios of the VAZ-2108 gearbox of both versions up to 5th gear are the same, and they are all shown in the table:
| Gear ratios of the VAZ-2108 gearbox | |
| Speed | Meaning |
| 1st | 3,636 |
| 2nd | 1,95 |
| 3rd | 1,357 |
| 4th | 0,941 |
| 5th | 0,784 |
| Rear | 3,53 |
The drive from the box to the drive wheels was carried out using two drive shafts, each of which in its design had two ball-type equal angular velocity joints.
Next is the dynamic and speed characteristics of the VAZ-2108 car with different technical equipment. Naturally, the weakest according to these data is the 1.1-liter version. Its maximum speed is only 140 km/h, and it accelerates to 100 km/h in 22 seconds. Its average gasoline consumption is 7.9 liters.
The speed characteristics of the VAZ-2108 with a 1.3-liter unit and both versions of the gearbox have a maximum of 148 km/h, and this version reaches 100 km/h in 19 seconds. But the presence of 5th speed affects gas mileage. The version with a 4-speed gearbox consumes an average of 8.2 liters, and the presence of an additional speed made it possible to reduce this figure to 7.8 liters.
The 1.5-liter version of the V8 with a different power system and 5-speed gearbox has almost identical performance. The maximum speed of these modifications is 156 km/h, but the dynamic performance and fuel consumption vary slightly. The carburetor version accelerates to 100 km/h in 15 seconds, while the injection version does it 0.5 seconds faster.
As for consumption, the carburetor consumes 8.0 liters on average, and the injector consumes 7.7 liters.
Latest prototype models
A sample of the car, which was to be exported to Europe, underwent very stringent tests. In a short period of time, the car traveled about 80,000 km, and this made it possible to find the weak points of the model and correct them.
Towards the end of 1981, a version of the car appeared, the so-called “two hundredth”. It was tested even more seriously, because this car was supposed to be distributed throughout the Union. The tests took place in harsh climatic conditions, sometimes in the Caucasus, sometimes in Turkmenistan, sometimes in the far north.
The “three hundredth” model rolled off the production line in 1983; this car was practically a copy of what you can see on the streets of the country.
Chassis
On the VAZ-2108, the front wheels were not only steered, but also driven. It was possible to organize this thanks to the use of front independent suspension. The main component of the front suspension of the VAZ-2108 are MacPherson struts, which, in addition to their main function, also served as steering knuckles. They consisted of a housing, a shock absorber and a spring, assembled into a single structure. The racks were attached to the body with levers at the bottom and supports at the top. The left and right struts were united by a stabilizer bar.
Related link:
Replacing a CV joint on a VAZ-2108 car
At the rear, a torsion bar suspension was used, the design of which included a beam with mounting brackets, a shock absorber and a spring.
The steering of this car is of the rack-and-pinion type with tie rods for connection to the steering knuckles. No power steering was provided. The brake system was dual-circuit, with diagonal position of the circuits, hydraulic drive and vacuum booster. Disc brakes were installed on the front wheels, and drum brakes were installed on the rear wheels. The hand brake is a mechanical type with a cable drive and acts on the rear mechanisms.
This design of the VAZ-2108 chassis is quite successful and was used not only on models of the Sputnik family, but also on all subsequent VAZ vehicles.
Test
Impudent fellow
This domestic “front-wheel drive” still looks defiant and aggressive. Attention is drawn to the rapid profile of the body with a pointed front part (for this reason, the 2108 received the popular nickname “chisel”), a low roof, a taut rear, and long side doors. The headlight optics are combined into monoblocks, and the bumpers are made of impact-resistant plastic.
The advantage is simplicity
Compared to the classic Zhiguli family, the G8's interior is less luxurious and more ascetic. However, the ergonomics of the 2108 are an order of magnitude higher - the main controls are located in close proximity to the driver, and the small steering wheel with a plump rim has a comfortable grip.
The instrument panel with a minimum of information is easy to read. Its backlight is regulated by a rotating toggle switch, which is located on the left, on the body of the “toolbox”. As for the center console, there is a socket for installing a radio at the top, while the air conditioning unit is located under the cigarette lighter.
Weight and dimensions
Finally, about the load-bearing part. The Eight had a three-door hatchback body. Afterwards, the 5-door hatchback VAZ-2109 and the sedan VAZ-21099 were released on its basis.
The dimensions of the VAZ-2108 were: length - 4.006 m, width -1.75 (including one side mirror), height - 1.402 m. Ground clearance - 170 mm.
The curb weight of the car is 920 kg, and when fully loaded, the Eight weighs more - 1370 kg.
Despite the fact that the model has not been produced for a long time, it still remains popular and is in demand. Moreover, this car is an excellent field for experiments to improve its appearance and technical characteristics.
Appearance
The VAZ 2108 attracted people primarily with its appearance. The angularity contrasted favorably with the straightforwardness of the classics. Even while parked, one could sense the speed and agility of the hatchback, which was more economical, had good energy-intensive bumpers, which were not immediately made, just like the glass.
For the silhouette it is worth saying a special thank you to the designers of the Volzhsky Automobile Plant. They fought literally for every line, defending the installation point of the side mirrors or the width of the door, which they proposed to reduce by 200 mm. But this would make the car lose some of its sporty appearance.
At first, samples with the so-called short front wing rolled off the assembly line. But the plastic cover came off over time and was warped by frost and sunlight. Over time, the wing was replaced with a long, more practical one; it looked advantageous, creating a feeling of completeness in the body work.
Without a doubt, the new model was of a higher level than the classic one. Someone joked that the domestic auto industry “finally got around to making a tracksuit instead of a double-breasted jacket, which is “always fashionable.” Athletes and tuning enthusiasts are still partial to the G8. Unlike five-door cars, it has a stiffer body, it often participates in various competitions, and, as time has shown, the hatchback can be improved endlessly.
In the morning in the newspaper...
The serial Sputnik was launched only six months later than expected. “Every 22 seconds a new car rolls off the assembly line!” - the press proudly reported. VAZ-2108 became the first car of the Volzhsky plant, on the trunk lid of which “Lada” was written in Russian. So “Lada” became the third trade name of AVTOVAZ on the domestic market after “Zhiguli” and “Niva”.
The five-door modification of the VAZ-2109 entered the production line in 1987.
The five-door modification of the VAZ-2109 entered the production line in 1987.
However, Soviet citizens continued to languish in queues. The priority remained the export of Lads for hard currency (for those who don’t remember, this abbreviation meant freely convertible currency). With the entry of the G8 into Western markets, there was a sharp jump in interest in the Lada brand: from 76.5 thousand in 1985 to 137 thousand exported cars in 1986. Exports reached their peak in 1988 - Avtoexport sold 157 thousand Samaras. The investments were justified: up to 90% of the proceeds from the export of mechanical engineering products came from Volga machines.
A plasticine model of a sedan based on the VAZ-2108 was designated VAZ-2110. It was completed back in 1981, the author of the design is V. Pashko. During the work, the sedan was renamed VAZ-21099. The thing is that, according to the system that existed at that time, a new number in a four-digit index designated a new model, and the ministry did not allocate funds for its development. But for the modernization of an existing one, please. So another digit appeared in the digital designation - it was he who said that this was simply another version of an existing car.
A plasticine model of a sedan based on the VAZ-2108 was designated VAZ-2110. It was completed back in 1981, the author of the design is V. Pashko. During the work, the sedan was renamed VAZ-21099. The thing is that, according to the system that existed at that time, a new number in a four-digit index designated a new model, and the ministry did not allocate funds for its development. But for the modernization of an existing one, please. So another digit appeared in the digital designation - it was he who said that this was simply another version of an existing car.
Cars delivered abroad were subject to serious modifications by Autoexport’s partners. There were quite a few of them: the Belgian Scaldia-Volga, the German Deutsche-Lada, the Finnish Konela, the French Sepma... The cars were repainted, the seats were reupholstered, Western electrical equipment and tires were installed. Otherwise, it was difficult to sell Ladas even for the meager money that was asked for them (in Europe, in terms of price, the Lada Samara was at the level of cars of a lower class, for example, the Citroen AX, Fiat Panda or Ford Fiesta).
The sports prototype Lada Samara T3, created on the basis of the all-wheel drive Porsche 911 Carrera S4, has proven itself quite well on rally-raid tracks, but has not won championship laurels.
The sports prototype Lada Samara T3, created on the basis of the all-wheel drive Porsche 911 Carrera S4, has proven itself quite well on rally-raid tracks, but has not won championship laurels.
The foreign buyer needed variety. Only “eights” and “nines” with a 1.1 liter engine were exported (it was developed by Volga engineers simultaneously with 1.3 and 1.5 liter engines and also refined by Porsche specialists). The choice was quite representative: three- and five-door hatchbacks, a four-door sedan, and a Natacha convertible.
We expanded the range by selecting wheels, sunroofs, optics, steering wheels, and even installing a Hitachi air conditioner in the base heater housing. The most exotic version, perhaps, was the Samara Enterprise (or Samara Van and Samara Bizivan) - a van in a standard three-door hatchback body with blind side windows. Imagine, this “format” is very common in Europe! By removing the rear seat and installing a demarcation grid, we got a cargo compartment with a volume of a cubic meter. The carrying capacity was 415 kg, and the car cost, for example, in France (1.3 l, 65 hp) 44,300 francs - 18.6% more expensive than a standard hatchback.
At the 1989 Frankfurt Motor Show, Deutsche-Lada presented the Lada Samara Night version. Spectacular alloy wheels, a sunroof, red trim on a black body - this was the only way to sell a product of the domestic automobile industry in the West. The Belgian company Scaldia-Volga also actively fought for the market.
At the 1989 Frankfurt Motor Show, Deutsche-Lada presented the Lada Samara Night version. Spectacular alloy wheels, a sunroof, red trim on a black body - this was the only way to sell a product of the domestic automobile industry in the West. The Belgian company Scaldia-Volga also actively fought for the market.
With the help of Russian designer V. Yartsev, a version of “Samara” was created with a powerful plastic body kit, which bore the name Carlota.
With the help of Russian designer V. Yartsev, a version of “Samara” was created with a powerful plastic body kit, which bore the name Carlota.
The Lada Samara Natacha convertible was created by Scaldia-Volga with the help of one of the oldest Belgian coachbuilders, Garage Meeus. From November 1990 to December 1995, 456 of these convertibles were produced.
The Lada Samara Natacha convertible was created by Scaldia-Volga with the help of one of the oldest Belgian coachbuilders, Garage Meeus. From November 1990 to December 1995, 456 of these convertibles were produced.
The Natacha convertible received the most radical design changes. The project was carried out by the Brussels company Scaldia-Volga. On the Soviet side, VAZ designer Vladimir Yartsev participated - the one thanks to whom the only President of the USSR M.S. Gorbachev, during his historic visit to AVTOVAZ on April 8, 1986, learned about the existence of the designer profession and short-sightedly wished the plant to become a trendsetter in world fashion...
Cargo modification of Samara Van (aka Enterprise). This cargo-passenger version of the Samara had a luggage compartment with a volume of more than a cubic meter and was in good demand in Europe.
Cargo modification of Samara Van (aka Enterprise). This cargo-passenger version of the Samara had a luggage compartment with a volume of more than a cubic meter and was in good demand in Europe.
from 2002 to 2004 it produced light commercial vehicles VIS-2347. According to some reports, about four thousand were built.
from 2002 to 2004 it produced light commercial vehicles VIS-2347. According to some reports, about four thousand were built.