One of the significant omissions of the Russian automotive industry is the lack of mass-produced passenger diesel. In view of this, local manufacturers have to use foreign analogues. The development of such motors began only in the second half of the last century, and a mass version has not yet appeared. Next, we consider diesel engines on VAZ cars.
Prerequisites
The first experimental diesel passenger cars appeared in Europe in the 1930s. of the past century. In the USSR this happened much later for several reasons.
Firstly, such power units are more difficult to produce compared to their gasoline counterparts.
Secondly, diesel engines of that time were significantly behind them in performance.
Thirdly, diesel engines had pronounced negative performance characteristics: high noise levels, cold start problems, low environmental friendliness.
Fourthly, in those days gasoline was very cheap, so even some heavy equipment was equipped with gasoline engines. For these reasons, diesel engines were mainly used in heavy vehicles, where they were more relevant than gasoline engines due to their high torque.
One of the first Soviet passenger cars to receive a diesel engine was the GAZ-21, and then its export analogue: in the 60s. in Belgium, the car was equipped with several variants of foreign-made naturally-aspirated engines.
In the 70s The active distribution of diesel engines in small and middle class cars began. The main reason for this was the energy crisis of 1973. Passenger diesel engines had developed significantly by that time. They were 1.5-2 times superior to their gasoline counterparts in terms of efficiency and durability, thanks to the greater strength of the parts. Productivity was also increased through the use of turbines.
The first VAZ diesel
At the Volzhsky Automobile Plant, the development of diesel engines for passenger cars began in the 80s. The designers decided to build the engine using parts produced using gasoline technology, tested on Project 2108. They were faced with the problem of the lack of fuel equipment for passenger diesel engines.
As a result, based on block 2103, a VAZ-341 naturally-aspirated power unit with a volume of 1.45 liters and a power of 55 hp was created. With. It is distinguished by a pre-chamber design, which implies mixture formation not in the piston area, but in a separate chamber. Electronics were missing. The distribution of fuel among the cylinders was carried out by a high-pressure fuel pump. The design of the VAZ diesel engine is similar to Ford and Volkswagen engines of the early 80s. It is mentioned that the latter’s engine was taken as a model during development.
Based on the test results, it was confirmed that it is unacceptable to use standard “gasoline” spare parts. The VAZ diesel engine, like other engines of this type, is characterized by increased loads due to a higher compression ratio. Because of this, many elements lacked strength, especially the crank mechanism and the piston group. The situation was aggravated by low manufacturing accuracy.
Based on this, in 1984 it was decided to create a 1.7 liter diesel engine based on the VAZ-2106 using 21083 elements.
In 1986, a turbocharged version of the 3411 with a capacity of 65 hp was created. With. and 114 Nm and produced two Nivas equipped with it with index 21215. However, they soon failed.
And yet, the VAZ-2105 with the 341st engine, which received the index 21055, passed state tests in 1986-1988. However, despite the unification of the engine with a gasoline one, the car was not put into production. This was due to many reasons. One of the main ones is the lack of government financial support.
Differences from gasoline colleagues in the workshop
Changes have been introduced to the modification of the VAZ 2104 with a diesel engine.
- Additional sound insulation of the engine compartment.
- Strengthening the front springs of the suspension struts.
- The gear ratio of the main pair is reduced to 3.9.
- The exhaust duct is wrapped in a loop so as not to pollute the right rear light with soot (after all, the Euro 2 standard).
- The instrument panel is equipped with two elements: a fuel injection pump heating button and a glow plug temperature indicator.
The main difference lies in the technology itself for igniting the combustible mixture in the cylinder. Unlike the VAZ gasoline engine, the VAZ diesel engine does not mix air with fuel at the intake stage. At first, only air is started. Then, when it heats up to about 600 degrees and the piston rushes up, diesel fuel is injected.
The mixture ignites without the help of a spark from the spark plugs. VAZ diesel engines also have glow plugs. They help heat the air in the cylinder during the cold season so that it quickly reaches the optimal temperature and fuel is injected.
Under the hood of the VAZ 21045D there is a new device - a high-pressure fuel pump (HPF). This device is designed to resemble the engine itself. The drive is mechanical, not electric, like a gasoline pump. Using plungers, it pumps enormous pressure into the nozzles. A very important part of a diesel engine, it serves to maintain a pressure of about 100 kg/cm2 (almost 100 atm) in the engine power supply system.
The injector of the VAZ 2104 generation engine is also mechanical. Its main element is a needle, which rises under the pressure of diesel fuel and injects diesel fuel into the cylinder through thin channels. Since ignition in this case must occur without a spark, the dispersion of the fuel aerosol is significantly less than that of a VAZ 2104 injector or carburetor.
The engine layout is also different from gasoline cars. Under the hood, the unit is installed along the movement of the car. The compression ratio in the cylinder is 23, which is unattainable numbers for an injector and carburetor.
Diesel series
The next time VAZ took on the development of diesel engines in 1996 together with BarnaulTransMash. The terms of cooperation assumed that the second enterprise would produce power units developed by VAZ. A family of three engines was created.
The initial one was the 341st engine, increased to 1.52 liters in volume. The more productive 343 engine had a displacement of 1.8 liters. The most powerful option is the same VAZ diesel, equipped with an IHI turbine, with index 3431. The engines received Bosch fuel equipment.
In accordance with this, a range of diesel modifications of standard models has been developed. Such engines were planned to be used on utilitarian machines. Thus, it was planned to equip station wagons 21045 and 21048 with naturally aspirated versions 341 and 343, respectively. On Niva 21215-50 and 21215-70 it was planned to install 1.8 liter naturally aspirated and turbocharged engines, respectively, on VAZ-21315 - only 3431.
By 2000, the Barnaul plant mastered the production of these diesel engines, and as part of pilot production, the installation of diesel engines began on VAZ-2104 and 2105. Such cars were produced in small batches.
Despite the low performance, the engine suited the cars. Given the modest performance of the gasoline power unit, the decrease in dynamics was not particularly significant for such models, but efficiency increased noticeably. At the same time, the engine had the same problems as the first VAZ 341 diesel: due to the low mechanical strength of the piston group, it turned out to be very short-lived. The engine life was 30-40 thousand km. Upon reaching such a mileage, a major overhaul of the VAZ diesel engine was required, which consisted of replacing the cylinder block along with the piston group.
Over time, many technological problems were solved, as a result of which the durability of the engines increased. However, in 2003, the VAZ-21045 was discontinued. The remaining 500 VAZ-341 engines were installed on sedans, which received the index 21055. In just 3 years, about 6,000 diesel cars were produced.
Service
Servicing VAZ engines, which are classified as “classics”, is quite simple, since the structure is the same, only the volume changes. According to the technical documentation, the service standard is 10,000 km. After this mileage, the engine needs to replace the lubricant and filter element.
In addition to standard maintenance procedures, other elements also change depending on the mileage. So, every 20,000 km the air filter is changed. Upon expiration. 40,000 km it is necessary to replace the gas distribution mechanism kit.
If the replacement is not done in a timely manner, the belt (or chain) may break, which will cause bent valves, and even worse, bending of the cylinder head or other consequences that will lead to premature overhaul.
Reasons for failure
Mass production of diesel passenger cars could not be established for several reasons. The main one is the unprofitability of producing such motors due to the significantly outdated design. The engines had the same pre-chamber design as the first 341st prototype, and were significantly behind modern analogues in terms of performance and environmental friendliness. To achieve acceptable performance, it was necessary to create a motor of a different design. Independent development was considered unprofitable, and there were no technical partners for this. In addition, VAZ products sold well even without diesel.
Borrowed engines
Since it did not have its own mass-produced passenger diesel, VAZ repeatedly borrowed third-party engines.
Thus, in 1981, the possibility of converting the VAZ-2121 gasoline engine into a diesel engine was considered with the participation of Porche.
From 1987 to 1990, the manufacturer, together with the German importer Deutsche Lada, developed a plan to create an export version of the Niva with a Volkswagen power unit. However, this company refused to adapt its 1.9 liter engine to the Niva platform.
In 1993, we managed to establish cooperation along the same lines with Peugeot. By order of the French importer Jean Poka, the manufacturer adapted the 1.9 liter XUD-9L engine for installation on the VAZ-2121. The production of the cars was carried out by Lada-Export. Regular Nivas were delivered there, and the standard engine was replaced with a French one. In total, about 6,000 of these cars were produced for France, Spain, Italy and other European markets.
In addition, in Italy, Martorelli equipped Nivas with VM and FNM engines.
However, with the introduction of Euro-2 environmental standards, small-scale production of diesel Nivas was completed.
In 1998, together with Peugeot and Martorelli, VAZ tried to establish production of Nivs with the Peugeot XUD-9SD engine. However, work also had to be stopped due to the introduction of Euro-3 standards.
In addition, from 1995 to 1997, Samara was equipped with a PSA TDU5 engine from Peugeot 106 and Citroen Saxo with third-party attachments and original mounting for the French and Benelux markets.
Latest experiments
In 2007, Tema Plus installed an FNM engine on Chevrolet Niva for individual orders.
In 2014, on Lada 4x4 they experimented with 1.3 l 75 l. With. Fiat Multijet engine. However, it was not compatible with either the transmission due to torque limitations, or with the analog wiring diagram due to the CAN bus.
Super-auto explored the possibility of installing a 4x4 1.5 liter diesel engine from Renault Duster on the Lada 4x4 by 2015. In addition, an experimental car was created with a 100-horsepower 1.8 liter engine.
Change of oil
Perhaps the most common and frequently performed repair operation is changing the oil and oil filter. Consider the sequence of actions:
- Before starting repair and restoration operations, you should remove the negative terminal from the battery.
- If there is engine protection, it must be removed. To do this, you need to unscrew the mounting bolts.
- Next, unscrew the drain plug, which is located on the pan, and wait for the lubricant to drain.
- We tighten the drain plug, while not forgetting to change the copper sealing gasket.
- Using a special puller, remove the oil filter. Before installing a new one, you need to pour 100 grams of new oil into it.
- Unscrew the filler neck and pour in the oil.
- After tightening the filler plug, start the engine and let it run for a few minutes.
- If necessary, add a little to the required level, which can be seen on the dipstick.
Thus, the oil change is considered complete. If the type of lubricant changes, the engine must be flushed.
Diesel design
The initial power unit of the series was created by modernizing the first VAZ 341 engine: the diesel received a piston stroke increased by 4 mm (84 mm). Thanks to this, the volume increased from 1.45 to 1.52 liters. The cylinder head is made of aluminum, guide bushings, valve seats are made of alloy cast iron, combustion chamber inserts are made of heat-resistant alloy. The gas distribution mechanism was borrowed from the VAZ-2108. The working surface of the valves was strengthened by electric melting. Crankshaft - from 2103 with increased tolerance tolerances for stroke variation. We increased the structural rigidity of casting 2103. We installed glow plugs. The engine was equipped with a starter with a power of 1.7 kW (1.9 for the VAZ-21055). This required a high-capacity battery (60 or 65 Ah). In addition, a Bosch fuel pump and a vacuum pump are installed to create vacuum in the brake booster.
There was a derated modification 3413, intended for a small-sized tractor and electric generator drive. It differs from the usual 341 engine by limiting the maximum speed to 3000 instead of 4800.
1.8 liter engines were created by increasing the cylinder diameter from 76 to 82 mm.
There are turbocharged versions of the 1.45 liter 341 engine (3411) and VAZ-343 (3431 with an IHI turbine)
Conclusion
The VAZ 2104 engine, or rather the modifications of AvtoVAZ power units that were installed on this car, are similar in technical characteristics, only during the development process the type of injection, volume and power changed.
As for service, it is typical and typical for all classic models. You can repair the engine with your own hands, without resorting to the services of a car service, which, in principle, is what most motorists do.
The domestic automobile industry is represented by many different models. However, in the history of AvtoVAZ there is one modification that even today causes the most controversial reviews. This is a VAZ 2104 equipped with a diesel power plant. Why was such an engineering move needed? Was it possible to create a car with clearer characteristics and power? What do the owners themselves think about the diesel version of the Four?
Specifications
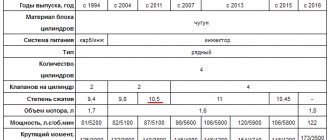
As noted above, due to its outdated design, the VAZ-341 has low performance compared to analogues of those times. Its power is 54 hp. With. at 4600 rpm, torque - 92 Nm at 2300 rpm. That is, even in terms of the second indicator it is inferior to a gasoline engine (103 Nm for the VAZ-21043). Greater torque at low speeds is ensured by a different performance graph and a reduced gear ratio.
Version 3413 is derated to 32 hp. With. at 3000 rpm.
Naturally, the 1.8 liter VAZ diesel is more productive: the technical characteristics are 65 liters. With. at 4600 rpm and 114 Nm at 2500 rpm.
The turbocharged version develops 80 hp. With. at 4600 rpm and 147 Nm at 2500 rpm.
Diesel cars
The diesel engine was installed on the VAZ-2104 by the VAZ Vehicle Operation and Repair Department. Pilot production began in 1998, producing a batch of 50 cars with 341 diesel engines (21045).
Later they began testing the car with the 343rd engine (21048) and its modification (they tried to increase the service life to 150 thousand km). It was planned to establish production by 2005, but this failed.
VAZ-21315 was prepared for release in 2002, but was also not launched.
Model review: VAZ 2104 without embellishment
Few people know that the VAZ 2104 (“four”) also bears the foreign name Lada Nova Break. This is a five-seater station wagon, which belongs to the second generation of AvtoVAZ “classics”.
The first models left the factory in September 1984 and thereby replaced the first generation station wagon - VAZ 2102. Although for another year (until 1985) the Volzhsky Automobile Plant produced both models simultaneously.
"Four" - the first station wagon in the VAZ line
VAZ 2104 cars were created on the basis of the VAZ 2105, only they had significant differences:
- extended rear part;
- folding rear bench;
- increased gas tank up to 45 liters;
- rear wipers with washer.
It must be said that the “four” were actively exported to other countries. In total, 1,142,000 VAZ 2104 units were produced.
Export model for the Spanish car market
Along with the VAZ 2104, its modification was also produced - the VAZ 21043. This is a more powerful car with a 1.5 liter carburetor engine and a five-speed gearbox.
Video: review of the Quartet
Peculiarities
The diesel station wagon differs in some design features from the gasoline VAZ-2104. Due to the greater mass, the diesel engine required the installation of reinforced front suspension springs. The main pair was replaced from 4.1 to 3.9. To compensate for the increased noise level from the diesel engine, additional sound insulation was installed in the engine compartment (on the hood and crankcase protection). The exhaust pipe was wrapped in a loop to prevent soot from contaminating the right canopy. An indicator for heating the glow plugs and a button for heating the fuel filter appeared on the dashboard (but there is no indicator for its activation).
Replacing the water pump
Another operation that motorists perform on classic engines is replacing the water pump. It is carried out mainly due to a faulty drive shaft bearing or when the gap increases and the water pump begins to leak. So, let's consider the sequence of actions aimed at troubleshooting:
- We dismantle the minus terminal of the battery.
- In order to dismantle the water pump, the drive belt must be removed. Depending on the design features, it can be connected to a common system or driven separately.
- The next step is to drain the coolant. To do this, you need to unscrew the radiator drain plug, first replacing the container. You can also drain the coolant using the drain hole on the block.
When replacing the pump, it is recommended to replace the coolant in the engine. It also has its own resource of use, and also gets dirty.
- Once all the coolant has been drained, you can begin replacing the water pump. Depending on the configuration, this unit can be secured with 3 or 5 bolts, which must be unscrewed, and then gently pull the product towards you.
- Installation is carried out in reverse order. At the same time, do not forget that it is necessary to change the gasket, which should come with the new pump.
- Pour coolant into the engine and start the car. Since there is air in the system, it must be removed from there. First, you should bleed the upper pipe and try to remove the maximum amount of air. The remaining amount will come out when the engine runs a little and circulation takes place. After the engine has been running, it is worth adding the coolant to the required level.
Reviews
Shortly after its appearance, “Behind the Wheel” journalists tested a VAZ diesel station wagon. Reviews indicate more confident engine operation at low speeds. So, you can even start from 5th gear, and from 30 km/h smooth traction begins. When driving fast, on the contrary, you will have to shift much more often than in a gasoline car due to the shortened main gear. In any case, in terms of dynamics, a diesel car lags significantly behind. Only at low speeds is there a slight advantage.
When accelerating to 100 km/h, the petrol VAZ-2104 is 8 seconds faster. In addition, a diesel car is inferior in maximum speed by 13 km/h. When accelerating from 20 to 90 km/h, the gap is smaller (about 3 s). In addition, according to reviews from Autoreview, diesel engines have slower reactions to the gas pedal.
As for the increased noise level that usually characterizes such an engine, the VAZ diesel is noticeably louder at idle (by 6-8 dB(A)). As the speed increases, the difference decreases by 1-3 dB(A), then disappears.
As a result of the tests, journalists received a 10% difference in average fuel consumption in mixed conditions. However, the financial benefit from using a diesel engine, taking into account the prices of automobile fuel at the time of testing, was 36%. Journalists calculated that the $1,300 higher cost of the car paid for itself in 180 thousand km.
According to reviews from those who tested the VAZ-21048, it turned out to be much more balanced and, thanks to its higher torque, allowed it to switch much less frequently.
With the same engine, the Niva performed well, especially off-road.
The VAZ-3411 turned out to be similar in character to the 2121 engine. Like a gasoline engine, it performs better at high speeds. At the same time, at low speeds the thrust is lower, even than that of the VAZ-21213, that is, turbo lag is pronounced.
Carburetor engines Injection modification
| VAZ 2104 diesel: technical characteristics, advantages, reviews from owners When the roof was lengthened, stamping appeared that increased rigidity, which made it possible to place a long trunk on the roof, although it was naturally not recommended to overload it, since the calculated rigidity of the station wagon body was significantly lower than that of the sedan . The domestically produced diesel engine could not cope with difficult sections of the road route and the manufacturer decided to increase the engine displacement. |
| Fuel consumption per 100 km VAZ-2104 (injector, carburetor): characteristics - Website about the famous domestic car Grant In order to establish the reasons for the increased consumption and reduce the appetite of the car, you need to contact specialized service stations. , their production continued until 2012, during which time the engine was modernized several times, the body concept remained unchanged, this is a station wagon with five doors, with a spacious luggage compartment. |
- Difficulty in repairing the fuel system. Indeed, the use of low-quality fuel or neglect of the required level of maintenance quickly leads to the fact that the fuel injection pump fails. Its repair is possible only in specialized auto repair shops and is not cheap.
- When the timing belt breaks, the valves bend. That is, in case of an ordinary breakdown, you also have to spend money on buying new valves and adjusting them.
- High price. For all their efficiency in operation, VAZ 2104 diesel models are much more expensive than gasoline ones.
Borrowed engines • Using plungers, pumps enormous pressure into the injectors.
Performance
Due to the heavier engine, the curb weight of the VAZ-21045 increased to 1.06 tons (40 kg compared to 21043), and the total weight increased to 1.515. According to the manufacturer, acceleration to 100 km/h takes 23 seconds (6 seconds more), maximum speed is 125 km/h (18 km/h less). Fuel consumption is 5.2 liters at 90 km/h, 7.5 liters at 120 km/h and 6.2 liters in urban conditions (7, 9.9, 9.8 liters for 21043, respectively).
A car with a 343 engine is closer in dynamics to a VAZ petrol station wagon. The 1.8 liter diesel engine provides acceleration to 100 km/h in 19 seconds and a top speed of 133 km/h.
Acceleration of the VAZ-21215-50 to 100 km/h takes 25 seconds, the maximum speed is 127 km/h versus 19 seconds and 137 km/h for the 21213.
In terms of acceleration dynamics, the VAZ-21215-70 is equal to the gasoline Niva and lags behind in maximum speed by 7 km/h.